dpdk_lcore_note_DPDK_lcore_学习笔记
DPDK 16.07 lcore学习笔记
- 文档保留了 markdown 格式。可以转为纯文本格式,方便在其他编辑器中使用语法高亮阅读代码。
- 文档行文主要是提纲式的。如果阅读过程发现缺少了方向。请立刻回到章节的开首处,查询总体的函数调用图。
1. DPDK核绑定的全局概览
DPDK核绑定的相关函数,都集中在rte_eal_init()函数中调用:
其中主要分为六部分:
- 检测所有的
cpu。 - 解释核绑定相关参数。
主线程的核绑定。中断处理线程的创建副线程的创建。线程启动和等待。
注意:
本文中,cpu所指的是机器上的逻辑核(也被称为logical processor,简称为processor)。
以下的是rte_eal_init()函数的调用图:
main
+-> rte_eal_init
+-> rte_eal_log_early_init
+-> eal_log_level_parse
+-> rte_set_log_level
|
| /* <-- 检测所有的`cpu` -->*/
+=> rte_eal_cpu_init
| +=> rte_eal_get_configuration /* 取得 全局变量`rte_config`的指针。 */
| +=> lcore_config[].detected = eal_cpu_detected(lcore_id); /* 检测`cpu`是否存在 */
| +=> config->lcore_role[lcore_id] = ROLE_RTE; /* 'ROLE_RTE`表示`cpu`存在 */
| +=> lcore_config[].core_id = eal_cpu_core_id(lcore_id); /* 取得`cpu`的`lcore_id`。 */
| +=> lcore_config[].socket_id = eal_cpu_socket_id(lcore_id); /* 取得`NUMA node id`。 */
|
| /* <-- 解释核绑定相关参数 --> */
+=> eal_parse_args
| +-> eal_parse_common_option
| |
| | /* option: -c */
| +=> eal_parse_coremask
| |
| | /* option: -l */
| +=> eal_parse_corelist
| |
| | /* option: --proc-type */
| +=> eal_parse_proc_type
| |
| | /* option: --master-lcore */
| +=> eal_parse_master_lcore
| |
| | /* option: --lcores */
| +=> eal_parse_lcores
|
+-> rte_srand(rte_rdtsc());
+-> rte_config_init
+-> rte_eal_pci_init
+-> rte_eal_vfio_setup
+-> rte_eal_ivshmem_init
+-> rte_eal_memory_init
+-> eal_hugedirs_unlock
+-> rte_eal_memzone_init
+-> rte_eal_tailqs_init
+-> rte_eal_ivshmem_obj_init
+-> rte_eal_log_init
+-> rte_eal_alarm_init
+-> rte_eal_timer_init
+-> eal_check_mem_on_local_socket
+-> eal_plugins_init
|
| /* <--- `主线程`的核绑定 ---> */
+=> eal_thread_init_master(rte_config.master_lcore) /* 主线程绑核 */
| +=> RTE_PER_LCORE(_lcore_id) = lcore_id; /* 使用`线程变量`记录`lcore`下标 */
| +=> eal_thread_set_affinity() /* 线程绑定`cpu` */
| +=> rte_gettid /* 使用`线程变量`记录`线程号` */
| | +=> static RTE_DEFINE_PER_LCORE(int, _thread_id); /* 声明静态的`线程变量`记录`线程号` */
| | +=> RTE_PER_LCORE(_thread_id) = rte_sys_gettid(); /* 取得`线程号` */
| | +=> syscall(SYS_gettid); /* 系统函数取得`线程号` */
| +=> rte_thread_set_affinity(&lcore_config[lcore_id].cpuset); /* 线程核绑定 */
| +=> pthread_setaffinity_np /* pthread库的线程核绑定 */
| | /* 使用实际核绑定后的`cpusetp`,更新到相关线程变量`RTE_PER_LCORE`和全局变量`lcore_config` */
| +=> RTE_PER_LCORE(_socket_id) = eal_cpuset_socket_id(cpusetp);
| +=> memmove(&RTE_PER_LCORE(_cpuset), cpusetp,...);
| +=> lcore_config[lcore_id].socket_id = RTE_PER_LCORE(_socket_id);
| +=> memmove(&lcore_config[lcore_id].cpuset, cpusetp, sizeof(rte_cpuset_t));
|
+-> eal_thread_dump_affinity /* 打印核绑定设置 */
|
+-> rte_eal_dev_init /* init pmd devices */
|
| /* <--- `中断处理线程`的创建 ---> */
+-> rte_eal_intr_init /* init interrupt-handling */
| +-> pthread_create(&intr_thread, NULL, eal_intr_thread_main, NULL);
| | +~> eal_intr_thread_main /* 这个处理中断的线程是没有绑核的 */
| +-> rte_thread_setname ("eal-intr-thread")
|
| /* <--- `副线程`的创建 ---> */
| /* 遍历所有的`副线程`*/
+=> RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(i)
| /* 创建`主线程`和`副线程`间的沟通管道 */
+=> pipe(lcore_config[i].pipe_master2slave);
+=> pipe(lcore_config[i].pipe_slave2master);
| /* 创建`副线程` */
+=> pthread_create(&lcore_config[i].thread_id, NULL, eal_thread_loop, NULL);
| +~> eal_thread_loop
| +=> eal_thread_set_affinity /*`副线程`核绑定*/
| +=> read(m2s, &c, 1); /* 等待`主线程`发送到`副线程`的消息 */
| +=> write(s2m, &c, 1); /* `副线程`确认收到`主线程`的消息 */
| +=> lcore_config[lcore_id].f(fct_arg); /* 执行`业务处理回调函数` */
|
+-> rte_thread_setname /*`副线程`重命名*/
|
| /* <--- `线程`启动和等待 ---> */
+=> rte_eal_mp_remote_launch(sync_func, NULL, SKIP_MASTER); /* 设置每一个`副线程`的回调函数为`sync_func()` */
| +=> RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id) /* 遍历所有的`副线程`来执行回调函数 */
| +=> rte_eal_remote_launch(f, arg, lcore_id); /* `副线程`来执行回调函数 */
| +=> lcore_config[slave_id].f = f; /* 设置`副线程`的`业务函数f` */
| +=> lcore_config[slave_id].arg = arg; /* 设置`副线程`的`参数arg` */
| +=> write(m2s, &c, 1); /* 发送消息到`副线程`,通知`副线程`执行`业务函数`。 */
| +=> read(s2m, &c, 1); /* 等待`副线程`的确认。并判断`副线程`启动是否有异常。 */
+=> rte_eal_mp_wait_lcore(); /* 等待所有线程返回 */
| +=> RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id); /* 遍历所有的`副线程` */
| +=> rte_eal_wait_lcore(lcore_id); /* 等待某一`副线程`返回 */
|
+-> rte_eal_pci_probe
+-> rte_eal_mcfg_complete
说明:
- 以下的例子采用的是同一物理构造的机器。
- 机器有 2 路物理
cpu插槽。单颗cpu插槽有 12 个核。 - 没有开启
超线程。所以单颗cpu插槽的cpu数也是 12 个。 - 2 路合计
cpu数为 24 个。
2. 数据结构和全局变量
2.1. rte_cpuset_t类型
rte_cpuset_t类型在 linux 中其实就是系统的cpu_set_t类。
其中 __bits[] 上的每一位代表了一个cpu。
typedef unsigned long __cpu_mask
typedef struct {
__cpu_mask __bits[16];
} cpu_set_t;
typedef cpu_set_t rte_cpuset_t;
注意:
- 使用
CPU_ZERO(),CPU_SET()等宏函数来操作rte_cpuset_t类型。
2.2. struct lcore_config结构体
struct lcore_config结构体,用于表示一个lcore的用户设置。其中可以将成员变量分为三类:
- 核绑定相关成员变量。
- 主副线程通信相关成员变量。
- 业务处理相关成员变量。
注意:
lcore实际上是使用线程来实现。两者在后续的描述中可能会混用。请根据上下文理解。
详细的描述如下:
- 核绑定相关成员变量:
detected:cpu是否存在。0:不存在。非0:存在。
socket_id:cpu所在的NUMA node id。(这里没有任何错误,请看下面详细的说明!)- 这里的
socket_id字段的名字容易误导。通过分析代码发现: - 由于在 OS 层中可以自由开启或关闭
NUMA功能。从而在不同的情况下,NUMA node_id会有所不同。- 最简单的例子就是,关闭
NUMA功能后,所有的cpu都会属于node0。但是cpu的总数是没有改变的。
- 最简单的例子就是,关闭
- 而物理
cpu插槽的标识号,是由主板电路决定的。- 物理
cpu插槽的标识号,是不会随NUMA功能的开关而影响的。 - 物理
cpu插槽的标识号,可以通过cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu${cpu_index}/topology/physical_package_id指令得出。 - 其中
${cpu_index}是cpu序号。
- 物理
DPDK中的socket_id字段在分析代码后,其实所指的是cpu所在的NUMA node id。NUMA node id的数值为/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu${cpu_index}/node${node_id}的${node_id}。- 其中
${cpu_index}是cpu序号。
- 在后续的描述中。代码上会保留使用
socket_id;但是在解释中会使用NUMA node_id来表达。
- 这里的
core_id:cpu的标识号。数值与硬件相关。cpu的标识号不一定连续。cpu的标识号数值为/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu${cpu_index}/topology/core_id。其中${cpu_index}是cpu序号。
core_index:lcore的序号。- 有效的序号从零开始,且是连续的。
-1:无效数据。- 只有
core_index可以唯一的区分lcore。
cpusetlcore所绑定的cpuset。lcore只可以绑定到一个cpu上。当使用-l或者-c命令行参数。lcore可以绑定到多个cpu上。当使用--lcores命令行参数。
- 主副线程通信相关成员变量:
pipe_master2slave[2]:主线程到副线程的通信管道。pipe_master2slave[0],表示的是主线程到副线程管道的读端。pipe_master2slave[1],表示的是主线程到副线程管道的写端。
pipe_slave2master[2]:副线程到主线程的通信管道。pipe_slave2master[0],表示的是副线程到主线程`管道的读端。pipe_slave2master[1],表示的是主线程到副线程管道的写端。
- 业务处理相关成员变量:
thread_id:线程号。f:用户业务函数。arg:输入到用户业务函数的参数。ret:用户业务函数的返回值。state:线程的状态。WAIT:等待命令。RUNNING:线程正在运行业务函数。FINISHED:线程运行完业务函数。
注意:
struct lcore_config结构体中,成员变量core_id,socket_id,无法可靠区分lcore。- 因为当
NUMA关闭的时候。socket_id的数值会全部变为0,而core_id却有可能会重复。 - 详细的例子请看后续的
rte_eal_cpu_init()函数。
- 因为当
socket_id的主要作用是识别NUMA node,用于内存的分配。struct lcore_config结构体中,成员变量core_index和thread_id,无论NUMA是否开启,都可以正确区分lcore。
结构体源码如下:
/**
* Structure storing internal configuration (per-lcore)
*/
struct lcore_config {
unsigned detected; /**< true if lcore was detected */
pthread_t thread_id; /**< pthread identifier */
int pipe_master2slave[2]; /**< communication pipe with master */
int pipe_slave2master[2]; /**< communication pipe with master */
lcore_function_t * volatile f; /**< function to call */
void * volatile arg; /**< argument of function */
volatile int ret; /**< return value of function */
volatile enum rte_lcore_state_t state; /**< lcore state */
unsigned socket_id; /**< physical socket id for this lcore */
unsigned core_id; /**< core number on socket for this lcore */
int core_index; /**< relative index, starting from 0 */
rte_cpuset_t cpuset; /**< cpu set which the lcore affinity to */
};
2.2.1. 全局变量 lcore_config
全局变量lcore_config[]数组,表示lcore的用户设置。
全局变量lcore_config[]的定义如下:
/* internal configuration (per-core) */
struct lcore_config lcore_config[RTE_MAX_LCORE];
注意:
全局变量lcore_config[n]的下标比struct lcore_config结构体中的core_id,core_index的作用还要大。具体请看RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE()宏函数的实现。
2.3. struct rte_config结构体
struct rte_config结构体,用于记录lcore和内存在DPDK应用程序中的设置。
成员变量描述如下:
master_lcore:主线程所在的lcore的序号(序号从零开始,并且是连续的)。lcore_count:机器上所有lcore的个数。lcore_role:每一个lcore的状态。ROLE_OFF:lcore没有在DPDK中使用。ROLE_RTE:lcore在DPDK中使用。
process_type:进程是主进程还是副进程。RTE_PROC_AUTO:自动检测。RTE_PROC_PRIMARY:默认值。主进程。RTE_PROC_SECONDARY:副进程。RTE_PROC_INVALID:无效进程。
mem_config:内存设置。
源代码如下:
/**
* The global RTE configuration structure.
*/
struct rte_config {
/* master lcore 的 id */
uint32_t master_lcore; /**< Id of the master lcore */
uint32_t lcore_count; /**< Number of available logical cores. */
enum rte_lcore_role_t lcore_role[RTE_MAX_LCORE]; /**< State of cores. */
/** Primary or secondary configuration */
enum rte_proc_type_t process_type;
/**
* Pointer to memory configuration, which may be shared across multiple
* DPDK instances
*/
struct rte_mem_config *mem_config;
} __attribute__((__packed__));
2.3.1. 全局变量rte_config
全局变量rte_config,表示DPDK的用户配置。
全局变量rte_config的定义如下:
/* Address of global and public configuration */
static struct rte_config rte_config = {
.mem_config = &early_mem_config,
};
3. 检测所有的cpu
rte_eal_cpu_init()函数用于检测所有的cpu。并用来初始化全局变量rte_config和lcore_config[]。
函数流程如下:
- 使用
eal_cpu_detected函数,遍历所有的路径/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu${cpu_index}。其中${cpu_index}从0到RTE_MAX_LCORE - 1。
1.1. 如果路径/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu${cpu_index}不存在:
1.2.1.lcore_config[lcore_id].cpuset设置为0。
1.1.2.rte_config.lcore_role[${cpu_index}]设置为ROLE_OFF。
1.1.3.lcore_config[${cpu_index}].core_index设置为-1。
1.1.4.lcore_config[${cpu_index}].core_id设置为0。
1.1.5.lcore_config[${cpu_index}].socket_id设置为0。
1.2. 如果路径/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu${cpu_index}存在:
1.2.1.lcore_config[lcore_id].cpuset设置为0x1U << lcore_id。
1.2.2.rte_config.lcore_role[${cpu_index}]设置为ROLE_RTE。
1.2.3.lcore_config[${cpu_index}].core_index设置为core index。
1.2.4.lcore_config[${cpu_index}].core_id设置为eal_cpu_core_id(${cpu_index})。
1.2.5.lcore_config[${cpu_index}].socket_id设置为eal_cpu_socket_id(${cpu_index})。 rte_config.lcore_count设置为 机器上所有cpu的个数。
函数调用图如下:
rte_eal_init
+-> rte_eal_cpu_init
+-> rte_eal_get_configuration /* 取得 全局变量`rte_config`的指针。 */
+-> lcore_config[].detected = eal_cpu_detected(lcore_id); /* 检测`cpu`是否存在 */
+-> config->lcore_role[lcore_id] = ROLE_RTE; /* 'ROLE_RTE`表示`cpu`存在 */
+-> lcore_config[].core_id = eal_cpu_core_id(lcore_id); /* 取得`cpu`的`lcore_id`。 */
+-> lcore_config[].socket_id = eal_cpu_socket_id(lcore_id); /* 取得`NUMA node id`。 */
rte_eal_cpu_init简化后的代码;
int
rte_eal_cpu_init(void)
{
/* pointer to global configuration */
struct rte_config *config = rte_eal_get_configuration();
unsigned lcore_id;
unsigned count = 0;
/*
* Parse the maximum set of logical cores, detect the subset of running
* ones and enable them by default.
*/
for (lcore_id = 0; lcore_id < RTE_MAX_LCORE; lcore_id++) {
lcore_config[lcore_id].core_index = count;
/* init cpuset for per lcore config */
CPU_ZERO(&lcore_config[lcore_id].cpuset);
/* in 1:1 mapping, record related cpu detected state */
lcore_config[lcore_id].detected = eal_cpu_detected(lcore_id);
if (lcore_config[lcore_id].detected == 0) {
config->lcore_role[lcore_id] = ROLE_OFF;
lcore_config[lcore_id].core_index = -1;
continue;
}
/* By default, lcore 1:1 map to cpu id */
CPU_SET(lcore_id, &lcore_config[lcore_id].cpuset);
/* By default, each detected core is enabled */
config->lcore_role[lcore_id] = ROLE_RTE;
lcore_config[lcore_id].core_id = eal_cpu_core_id(lcore_id);
lcore_config[lcore_id].socket_id = eal_cpu_socket_id(lcore_id);
count++;
}
/* Set the count of enabled logical cores of the EAL configuration */
config->lcore_count = count;
return 0;
}
例子:
不论是否开启NUMA功能。rte_eal_cpu_init函数运行完后rte_config.lcore_count都为 24。
但是rte_config.lcore_count在后面,经过解释核绑定相关参数后,会有可能修改。
NUMA关闭时:
使用lscpu查看到的系统配置为:
lscpu
> Architecture: x86_64
> CPU(s): 24 # 总`cpu`数
> On-line CPU(s) list: 0-23 # `cpu序号`
> Thread(s) per core: 1 # 每个`核`的`线程`个数(没有开启`超线程`)
> Core(s) per socket: 12 # 每个`cpu插槽`的`核`数
> Socket(s): 2 # `cpu插槽`个数
> NUMA node(s): 1 # `NUMA node`个数
> NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-23 # `node 0`上`cpu`序号
当eal_cpu_detected运行完后,lcore_config[n]和rte_config.lcore_role[n] 的数值如下表所示:
| n | lcore_config[n] | lcore_config[n] | lcore_config[n] | lcore_config[n] | lcore_config[n] | rte_config |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| .detected | .core_index | .core_id | .socket_id | .cpuset | .lcore_role[n] | |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0x1U << 0 | ROLE_RTE |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0x1U << 1 | ROLE_RTE |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0x1U << 2 | ROLE_RTE |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0x1U << 3 | ROLE_RTE |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0x1U << 4 | ROLE_RTE |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0x1U << 5 | ROLE_RTE |
| 6 | 1 | 6 | 8 | 0 | 0x1U << 6 | ROLE_RTE |
| 7 | 1 | 7 | 9 | 0 | 0x1U << 7 | ROLE_RTE |
| 8 | 1 | 8 | 10 | 0 | 0x1U << 8 | ROLE_RTE |
| 9 | 1 | 9 | 11 | 0 | 0x1U << 9 | ROLE_RTE |
| 10 | 1 | 10 | 12 | 0 | 0x1U << 10 | ROLE_RTE |
| 11 | 1 | 11 | 13 | 0 | 0x1U << 11 | ROLE_RTE |
| 12 | 1 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0x1U << 12 | ROLE_RTE |
| 13 | 1 | 13 | 1 | 0 | 0x1U << 13 | ROLE_RTE |
| 14 | 1 | 14 | 2 | 0 | 0x1U << 14 | ROLE_RTE |
| 15 | 1 | 15 | 3 | 0 | 0x1U << 15 | ROLE_RTE |
| 16 | 1 | 16 | 4 | 0 | 0x1U << 16 | ROLE_RTE |
| 17 | 1 | 17 | 5 | 0 | 0x1U << 17 | ROLE_RTE |
| 18 | 1 | 18 | 8 | 0 | 0x1U << 18 | ROLE_RTE |
| 19 | 1 | 19 | 9 | 0 | 0x1U << 19 | ROLE_RTE |
| 20 | 1 | 20 | 10 | 0 | 0x1U << 20 | ROLE_RTE |
| 21 | 1 | 21 | 11 | 0 | 0x1U << 21 | ROLE_RTE |
| 22 | 1 | 22 | 12 | 0 | 0x1U << 22 | ROLE_RTE |
| 23 | 1 | 23 | 13 | 0 | 0x1U << 23 | ROLE_RTE |
| … | 0 | -1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ROLE_OFF |
注意:
core_id不一定是连续的。这个数值与硬件相关。- 由于关闭了
NUMA,所以只有一个的NUMA node。所有cpu都属于NUMA node0。 rte_config.lcore_role[n]的数据在后面,经过解释核绑定相关参数后,会有可能修改。
NUMA开启时:
使用lscpu查看到的系统配置为:
lscpu
> Architecture: x86_64
> CPU(s): 24 # 总`cpu`数
> On-line CPU(s) list: 0-23 # `cpu序号`
> Thread(s) per core: 1 # 每个`核`的`线程`个数(没有开启`超线程`)
> Core(s) per socket: 12 # 每个`cpu插槽`的`核`数
> Socket(s): 2 # `cpu插槽`个数
> NUMA node(s): 2 # `NUMA node`个数
> NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-11 # `node 0`上`cpu`序号
> NUMA node1 CPU(s): 12-23 # `node 1`上`cpu`序号
当eal_cpu_detected运行完后,lcore_config[n]的数值如下表所示:
| n | lcore_config[n] | lcore_config[n] | lcore_config[n] | lcore_config[n] | lcore_config[n] | rte_config |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| .detected | .core_index | .core_id | .socket_id | .cpuset | .lcore_role[n] | |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0x1U << 0 | ROLE_RTE |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0x1U << 1 | ROLE_RTE |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0x1U << 2 | ROLE_RTE |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0x1U << 3 | ROLE_RTE |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0x1U << 4 | ROLE_RTE |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0x1U << 5 | ROLE_RTE |
| 6 | 1 | 6 | 8 | 0 | 0x1U << 6 | ROLE_RTE |
| 7 | 1 | 7 | 9 | 0 | 0x1U << 7 | ROLE_RTE |
| 8 | 1 | 8 | 10 | 0 | 0x1U << 8 | ROLE_RTE |
| 9 | 1 | 9 | 11 | 0 | 0x1U << 9 | ROLE_RTE |
| 10 | 1 | 10 | 12 | 0 | 0x1U << 10 | ROLE_RTE |
| 11 | 1 | 11 | 13 | 0 | 0x1U << 11 | ROLE_RTE |
| 12 | 1 | 12 | 0 | 1 | 0x1U << 12 | ROLE_RTE |
| 13 | 1 | 13 | 1 | 1 | 0x1U << 13 | ROLE_RTE |
| 14 | 1 | 14 | 2 | 1 | 0x1U << 14 | ROLE_RTE |
| 15 | 1 | 15 | 3 | 1 | 0x1U << 15 | ROLE_RTE |
| 16 | 1 | 16 | 4 | 1 | 0x1U << 16 | ROLE_RTE |
| 17 | 1 | 17 | 5 | 1 | 0x1U << 17 | ROLE_RTE |
| 18 | 1 | 18 | 8 | 1 | 0x1U << 18 | ROLE_RTE |
| 19 | 1 | 19 | 9 | 1 | 0x1U << 19 | ROLE_RTE |
| 20 | 1 | 20 | 10 | 1 | 0x1U << 20 | ROLE_RTE |
| 21 | 1 | 21 | 11 | 1 | 0x1U << 21 | ROLE_RTE |
| 22 | 1 | 22 | 12 | 1 | 0x1U << 22 | ROLE_RTE |
| 23 | 1 | 23 | 13 | 1 | 0x1U << 23 | ROLE_RTE |
| … | 0 | -1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ROLE_OFF |
注意:
core_id不一定是连续的。这个数值与硬件相关。- 由于启用了
NUMA,所以有两个的NUMA node。所以cpu分别属于不同的NUMA node。 rte_config.lcore_role[n]的数据在后面,经过解释核绑定相关参数后,会有可能修改。
3.1. rte_eal_get_configuration函数和全局变量rte_config
rte_eal_get_configuration返回全局变量rte_config的指针。
由于全局变量rte_config是一个静态的全局变量。
所以需要rte_eal_get_configuration返回其指针。
函数调用图如下:
rte_eal_init
+-> rte_eal_cpu_init
+-> rte_eal_get_configuration /* <== 取得 全局变量`rte_config`的指针。 */
+-> lcore_config[].detected = eal_cpu_detected(lcore_id); /* 检测`cpu`是否存在 */
+-> config->lcore_role[lcore_id] = ROLE_RTE; /* 'ROLE_RTE`表示`cpu`存在 */
+-> lcore_config[].core_id = eal_cpu_core_id(lcore_id); /* 取得`cpu`的`lcore_id`。 */
+-> lcore_config[].socket_id = eal_cpu_socket_id(lcore_id); /* 取得`NUMA node id`。 */
函数源码如下:
/* Return a pointer to the configuration structure */
struct rte_config *
rte_eal_get_configuration(void)
{
return &rte_config;
}
3.2. eal_cpu_detected() 函数
eal_cpu_detected会检测路径/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu${cpu_index}/topology/core_id来得出cpu是否存在。
函数调用图如下:
rte_eal_init
+-> rte_eal_cpu_init
+-> rte_eal_get_configuration /* 取得 全局变量`rte_config`的指针。 */
+-> lcore_config[].detected = eal_cpu_detected(lcore_id); /* <== 检测`cpu`是否存在 */
+-> config->lcore_role[lcore_id] = ROLE_RTE; /* 'ROLE_RTE`表示`cpu`存在 */
+-> lcore_config[].core_id = eal_cpu_core_id(lcore_id); /* 取得`cpu`的`lcore_id`。 */
+-> lcore_config[].socket_id = eal_cpu_socket_id(lcore_id); /* 取得`NUMA node id`。 */
函数源码如下:
/* Check if a cpu is present by the presence of the cpu information for it */
int
eal_cpu_detected(unsigned lcore_id)
{
char path[PATH_MAX];
int len = snprintf(path, sizeof(path), SYS_CPU_DIR
"/"CORE_ID_FILE, lcore_id);
if (len <= 0 || (unsigned)len >= sizeof(path))
return 0;
if (access(path, F_OK) != 0)
return 0;
return 1;
}
其中的实现类似于调用以下的bash指令。
# 查看所有的`cpu`:
ls /sys/devices/system/cpu/ | grep cpu
> cpu0
> ...
> cpu23
# 测试`cpu0`的`core_id`是否存在。成功返回的例子:
stat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/topology/core_id
> File: ‘/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/topology/core_id’
# 测试`cpu24`的`core_id`是否存在。失败返回的例子:
stat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu23/topology/core_id
> stat: cannot stat ‘/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu24/topology/core_id’: No such file or directory
3.3. eal_cpu_core_id() 函数
eal_cpu_core_id会读取/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu${cpu_index}/topology/core_id的数值。
最后用调用eal_parse_sysfs_value解释出core_id。
函数调用图如下:
rte_eal_init
+-> rte_eal_cpu_init
+-> rte_eal_get_configuration /* 取得 全局变量`rte_config`的指针。 */
+-> lcore_config[].detected = eal_cpu_detected(lcore_id); /* 检测`cpu`是否存在 */
+-> config->lcore_role[lcore_id] = ROLE_RTE; /* 'ROLE_RTE`表示`cpu`存在 */
+-> lcore_config[].core_id = eal_cpu_core_id(lcore_id); /* <== 取得 cpu 的 lcore_id。 */
| +-> eal_parse_sysfs_value
+-> lcore_config[].socket_id = eal_cpu_socket_id(lcore_id); /* 取得`NUMA node id`。 */
```c
函数源码如下:
```c
/* Get the cpu core id value from the /sys/.../cpuX core_id value */
unsigned
eal_cpu_core_id(unsigned lcore_id)
{
char path[PATH_MAX];
unsigned long id;
int len = snprintf(path, sizeof(path), SYS_CPU_DIR "/%s", lcore_id, CORE_ID_FILE);
if (len <= 0 || (unsigned)len >= sizeof(path))
goto err;
if (eal_parse_sysfs_value(path, &id) != 0)
goto err;
return (unsigned)id;
err:
RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, "Error reading core id value from %s "
"for lcore %u - assuming core 0\n", SYS_CPU_DIR, lcore_id);
return 0;
}
其中的实现类似于调用以下的 bash 指令。
# 打印`cpu`的`core_id`:
cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/topology/core_id
> 0
cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu23/topology/core_id
> 13
3.4. eal_cpu_socket_id()函数
eal_cpu_socket_id()函数会检测路径/sys/devices/system/node/node${node_id}/cpu${cpu_index}来得出cpu所在的NUMA node_id。
eal_cpu_socket_id()函数只能以试错的方法来发现NUMA node_id。
注意:
eal_cpu_socket_id函数的名字容易误导。eal_cpu_socket_id函数其实返回的是NUMA node_id,而不是物理cpu插槽的标识号。
- 由于在 OS 层中可以自由开启或关闭
NUMA功能。从而在不同的情况下,NUMA node_id会有所不同。- 最简单的例子就是,关闭
NUMA功能后,所有的cpu都会属于node0。但是cpu的总数是没有改变的。 - 关闭
NUMA功能后,所有的内存都会是一致处理。所以容易出现冲突。
- 最简单的例子就是,关闭
- 而物理
cpu插槽的标识号,是由主板电路决定的。- 物理
cpu插槽的标识号,是不会随NUMA功能的开关而影响的。 - 物理
cpu插槽的标识号,可以通过cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu${cpu_index}/topology/physical_package_id指令得出。 - 其中
${cpu_index}是cpu序号。
- 物理
函数调用图如下:
rte_eal_init
+-> rte_eal_cpu_init
+-> rte_eal_get_configuration /* 取得 全局变量`rte_config`的指针。 */
+-> lcore_config[].detected = eal_cpu_detected(lcore_id); /* 检测`cpu`是否存在 */
+-> config->lcore_role[lcore_id] = ROLE_RTE; /* 'ROLE_RTE`表示`cpu`存在 */
+-> lcore_config[].core_id = eal_cpu_core_id(lcore_id); /* 取得`cpu`的`lcore_id`。 */
+-> lcore_config[].socket_id = eal_cpu_socket_id(lcore_id); /* <== 取得 NUMA node id。 */
函数源码如下:
/*
* Get CPU socket id (NUMA node) for a logical core.
*
* This searches each nodeX directories in /sys for the symlink for the given
* lcore_id and returns the numa node where the lcore is found. If lcore is not
* found on any numa node, returns zero.
*/
unsigned
eal_cpu_socket_id(unsigned lcore_id)
{
unsigned socket;
for (socket = 0; socket < RTE_MAX_NUMA_NODES; socket++) {
char path[PATH_MAX];
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/node%u/cpu%u", NUMA_NODE_PATH,
socket, lcore_id);
if (access(path, F_OK) == 0)
return socket;
}
return 0;
}
其中的实现类似于调用以下的 bash 指令:
# 检测路径是否存在
# 路径存在例子。证明`cpu0`属于`node0`
stat /sys/devices/system/node/node0/cpu0
> File: ‘/sys/devices/system/node/node0/cpu0’ -> ‘../../cpu/cpu0’
# 路径不存在例子。证明`cpu0`不属于`node1`
stat /sys/devices/system/node/node1/cpu0
> stat: cannot stat ‘/sys/devices/system/node/node1/cpu0’: No such file or directory
4. 解释核绑定相关参数
eal_parse_args()函数用于解释程序命令行的参数。
eal_parse_args()函数最后,会调用到以下的解释函数来,解释核绑定相关参数:
| 命令行参数 | 解释函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| -c | eal_parse_coremask | 用掩码来表示lcore绑定,一个lcore只可以绑定到一个cpu上。 |
| -l | eal_parse_corelist | 用数列来表示lcore绑定,一个lcore只可以绑定到一个cpu上。 |
| –proc-type | eal_parse_proc_type | 进程的类型 |
| –master-lcore | eal_parse_master_lcore | 主线程所在的lcore序号 |
| –lcores | eal_parse_lcores | 用lcores@cpus来表示lcore绑定,一个lcore可以绑定到多个cpu上。 |
与解释核绑定相关参数的函数调用图如下:
rte_eal_init
+-> eal_parse_args
+-> eal_parse_common_option
|
| /* option: -c */
+-> eal_parse_coremask
|
| /* option: -l */
+-> eal_parse_corelist
|
| /* option: --proc-type */
+-> eal_parse_proc_type
|
| /* option: --master-lcore */
+-> eal_parse_master_lcore
|
| /* option: --lcores */
+-> eal_parse_lcores
4.1. eal_parse_coremask()函数
eal_parse_coremask()函数,用于解释命令行参数-c。用掩码来表示lcore的核绑定。
命令行参数-c,以十六进制字符串来表示lcore的掩码。
如:-c0xfa5,-c0xfa5,-c0Xfa5,-cfa5,-c0fa5,都是正确的输入值。
eal_parse_coremask()函数完成后,会修改全局变量lcore_config[n]和rte_config.lcore_role[n]:
- 掩码比特位为
1:rte_config.lcore_role[lcore] = ROLE_RTE;lcore_config[lcore].core_index设置为掩码所指定的序号。
- 掩码比特位为
0:rte_config.lcore_role[lcore] = ROLE_OFF;lcore_config[lcore].core_index = -1;
最后重新设置rte_config.lcore_role的数值为掩码中比特位为1的个数。
如:-c0x0fa5,则线程数为8,线程的lcore绑定设置如下:
- lcore 0 绑定到 cpu 0;
- lcore 2 绑定到 cpu 2;
- lcore 5 绑定到 cpu 5;
- lcore 7 绑定到 cpu 7;
- lcore 8 绑定到 cpu 8;
- lcore 9 绑定到 cpu 9;
- lcore 10 绑定到 cpu 10;
- lcore 11 绑定到 cpu 11;
函数源码如下:
int
eal_parse_coremask(const char *coremask)
{
struct rte_config *cfg = rte_eal_get_configuration();
int i, j, idx = 0;
unsigned count = 0;
char c;
int val;
if (coremask == NULL)
return -1;
/* Remove all blank characters ahead and after .
* Remove 0x/0X if exists.
*/
/* 去除所有前导的空白字符 */
while (isblank(*coremask))
coremask++;
/* 去除前导的`0x`或`0X`字符 */
if (coremask[0] == `0` && ((coremask[1] == `x`)
|| (coremask[1] == `X`)))
coremask += 2;
i = strlen(coremask);
/* 去除后续的空白字符 */
while ((i > 0) && isblank(coremask[i - 1]))
i--;
if (i == 0)
return -1;
/* 从低到高位,取出十六进制字符 */
for (i = i - 1; i >= 0 && idx < RTE_MAX_LCORE; i--) {
c = coremask[i];
if (isxdigit(c) == 0) {
/* invalid characters */
return -1;
}
val = xdigit2val(c);
/* 从低到高位,解释字符所对应的掩码
* 掩码比特位为`1`:
* rte_config.lcore_role[idx] = ROLE_RTE;
* lcore_config[idx].core_index 设置为掩码所指定的序号。
* 掩码比特位为`0`:
* rte_config.lcore_role[idx] = ROLE_OFF;
* lcore_config[idx].core_index = -1;
*/
for (j = 0; j < BITS_PER_HEX && idx < RTE_MAX_LCORE; j++, idx++)
{
if ((1 << j) & val) {
if (!lcore_config[idx].detected) {
RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, "lcore %u "
"unavailable\n", idx);
return -1;
}
cfg->lcore_role[idx] = ROLE_RTE;
lcore_config[idx].core_index = count;
count++;
} else {
cfg->lcore_role[idx] = ROLE_OFF;
lcore_config[idx].core_index = -1;
}
}
}
/* 检查是否有前导字符`0` */
for (; i >= 0; i--)
if (coremask[i] != `0`)
return -1;
/* 将其余没有置位的`lcore`设置为无效 */
for (; idx < RTE_MAX_LCORE; idx++) {
cfg->lcore_role[idx] = ROLE_OFF;
lcore_config[idx].core_index = -1;
}
if (count == 0)
return -1;
/* 更新`rte_config.lcore_role`为掩码所指定的`lcore`的个数。*/
/* Update the count of enabled logical cores of the EAL configuration */
cfg->lcore_count = count;
return 0;
}
例子:
假设输入命令行参数有-c 0x0fa5。可以得出以下lcore掩码图例:
全局变量lcore_config[n]和rte_config.lcore_role[n]经过修改后的数值如下:
| n | lcore_config[n] | lcore_config[n] | lcore_config[n] | lcore_config[n] | lcore_config[n] | rte_config |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| .detected | .core_index | .core_id | .socket_id | .cpuset | .lcore_role[n] | |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
0 | 0 | 0x1U << 0 | ROLE_RTE |
| 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 0 | 0x1U << 1 | ROLE_OFF |
| 2 | 1 | 1 |
2 | 0 | 0x1U << 2 | ROLE_RTE |
| 3 | 1 | -1 | 3 | 0 | 0x1U << 3 | ROLE_OFF |
| 4 | 1 | -1 | 4 | 0 | 0x1U << 4 | ROLE_OFF |
| 5 | 1 | 2 |
5 | 0 | 0x1U << 5 | ROLE_RTE |
| 6 | 1 | -1 | 8 | 0 | 0x1U << 6 | ROLE_OFF |
| 7 | 1 | 3 |
9 | 0 | 0x1U << 7 | ROLE_RTE |
| 8 | 1 | 4 |
10 | 0 | 0x1U << 8 | ROLE_RTE |
| 9 | 1 | 5 |
11 | 0 | 0x1U << 9 | ROLE_RTE |
| 10 | 1 | 6 |
12 | 0 | 0x1U << 10 | ROLE_RTE |
| 11 | 1 | 7 |
13 | 0 | 0x1U << 11 | ROLE_RTE |
| 12 | 1 | -1 | 0 | 0 | 0x1U << 12 | ROLE_OFF |
| 13 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 0 | 0x1U << 13 | ROLE_OFF |
| 14 | 1 | -1 | 2 | 0 | 0x1U << 14 | ROLE_OFF |
| 15 | 1 | -1 | 3 | 0 | 0x1U << 15 | ROLE_OFF |
| 16 | 1 | -1 | 4 | 0 | 0x1U << 16 | ROLE_OFF |
| 17 | 1 | -1 | 5 | 0 | 0x1U << 17 | ROLE_OFF |
| 18 | 1 | -1 | 8 | 0 | 0x1U << 18 | ROLE_OFF |
| 19 | 1 | -1 | 9 | 0 | 0x1U << 19 | ROLE_OFF |
| 20 | 1 | -1 | 10 | 0 | 0x1U << 20 | ROLE_OFF |
| 21 | 1 | -1 | 11 | 0 | 0x1U << 21 | ROLE_OFF |
| 22 | 1 | -1 | 12 | 0 | 0x1U << 22 | ROLE_OFF |
| 23 | 1 | -1 | 13 | 0 | 0x1U << 23 | ROLE_OFF |
| … | 0 | -1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ROLE_OFF |
最后的 rte_config.lcore_role 为8。因为掩码0x0fa5中共有8个比特位设置为1。
4.2. eal_parse_corelist()函数
eal_parse_corelist()函数,用于解释命令行参数-l。用数列来表示lcore的核绑定。
命令行参数-l,以十进制数列来表示lcore的序号。
lcore以’,‘来分隔。连续的lcore范围可以使用’-'来表示。
如:-l0,1,3-5,则线程数为5,lcore绑定设置如下:
- lcore 0 绑定到 cpu 0;
- lcore 1 绑定到 cpu 1;
- lcore 3 绑定到 cpu 3;
- lcore 4 绑定到 cpu 4;
- lcore 5 绑定到 cpu 5;
函数代码如下:
static int
eal_parse_corelist(const char *corelist)
{
struct rte_config *cfg = rte_eal_get_configuration();
int i, idx = 0;
unsigned count = 0;
char *end = NULL;
int min, max;
if (corelist == NULL)
return -1;
/* 去除所有前导的空白字符 */
/* Remove all blank characters ahead and after */
while (isblank(*corelist))
corelist++;
i = strlen(corelist);
/* 去除所有后续的空白字符 */
while ((i > 0) && isblank(corelist[i - 1]))
i--;
/* 重置全局变量`lcore_config[n]`和`rte_config.lcore_role[n]` */
/* Reset config */
for (idx = 0; idx < RTE_MAX_LCORE; idx++) {
cfg->lcore_role[idx] = ROLE_OFF;
lcore_config[idx].core_index = -1;
}
/* Get list of cores */
min = RTE_MAX_LCORE;
do {
while (isblank(*corelist))
corelist++;
if (*corelist == '\0')
return -1;
/* 以十进制解释数列的字符 */
errno = 0;
idx = strtoul(corelist, &end, 10);
if (errno || end == NULL)
return -1;
while (isblank(*end))
end++;
/* 如果后续的字符为`-`,则使用`min`记录下的下标的最小值 */
if (*end == '-') {
min = idx;
} else if ((*end == ',') || (*end == '\0')) {
/* 如果后续的字符为`,`或者`0`,则使用`max`记录下的下标的最大值 */
max = idx;
if (min == RTE_MAX_LCORE)
min = idx;
/* 重新设置`min`到`max`,所包含的`核绑定`设置。
* rte_config.lcore_role[idx] = ROLE_RTE;
* lcore_config[idx].core_index 设置为数列所指定的序号。
*/
for (idx = min; idx <= max; idx++) {
if (cfg->lcore_role[idx] != ROLE_RTE) {
cfg->lcore_role[idx] = ROLE_RTE;
lcore_config[idx].core_index = count;
count++;
}
}
min = RTE_MAX_LCORE;
} else
return -1;
corelist = end + 1;
} while (*end != '\0');
if (count == 0)
return -1;
/* Update the count of enabled logical cores of the EAL configuration */
cfg->lcore_count = count;
return 0;
}
4.3. eal_parse_proc_type()函数
eal_parse_proc_type()函数,用于解释命令行参数--proc-type。来表示进程的类型。
命令行参数--proc-type的输入范围如下:
| 输入参数字符串 | 返回值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| “auto” | RTE_PROC_AUTO | 自动检测 |
| “primary” | RTE_PROC_PRIMARY | 默认值。主进程 |
| “secondary” | RTE_PROC_SECONDARY | 副进程 |
| 其他 | RTE_PROC_INVALID | 无效进程 |
函数源码如下:
static enum rte_proc_type_t
eal_parse_proc_type(const char *arg)
{
if (strncasecmp(arg, "primary", sizeof("primary")) == 0)
return RTE_PROC_PRIMARY;
if (strncasecmp(arg, "secondary", sizeof("secondary")) == 0)
return RTE_PROC_SECONDARY;
if (strncasecmp(arg, "auto", sizeof("auto")) == 0)
return RTE_PROC_AUTO;
return RTE_PROC_INVALID;
}
4.4. eal_parse_master_lcore()函数
eal_parse_master_lcore()函数,用于解释命令行参数--master-lcore所指定的主线程所在的lcore序号。
最后赋值到rte_config.master_lcore。
函数源码如下:
/* Changes the lcore id of the master thread */
static int
eal_parse_master_lcore(const char *arg)
{
char *parsing_end;
struct rte_config *cfg = rte_eal_get_configuration();
errno = 0;
/* 设置 rte_config.master_lcore */
cfg->master_lcore = (uint32_t) strtol(arg, &parsing_end, 0);
if (errno || parsing_end[0] != 0)
return -1;
if (cfg->master_lcore >= RTE_MAX_LCORE)
return -1;
master_lcore_parsed = 1;
return 0;
}
4.5. eal_parse_lcores()函数
eal_parse_coremask()函数,用于解释命令行参数-lcore。用lcore的核绑定。
其中的lcores和cpus都可以使用数列来表示。
也可以使用(和)来括起来组成一组。
如果@cpus没有提供。则绑定的cpu对应于lcore。
如:1,2@(5-7),(3-5)@(0,2),(0,6),7-8,则线程数为9,线程的lcore绑定设置如下:
- lcore 0 绑定到 cpuset 0x41 (cpu 0,6);
- lcore 1 绑定到 cpuset 0x2 (cpu 1);
- lcore 2 绑定到 cpuset 0xe0 (cpu 5,6,7);
- lcore 3,4,5 绑定到 cpuset 0x5 (cpu 0,2);
- lcore 6 绑定到 cpuset 0x41 (cpu 0,6);
- lcore 7 绑定到 cpuset 0x80 (cpu 7);
- lcore 8 绑定到 cpuset 0x100 (cpu 8);
注意:
命令行参数-lcore,并不常用。
函数代码如下:
/*
* The format pattern: --lcores='[<,lcores[@cpus]>...]'
* lcores, cpus could be a single digit/range or a group.
* '(' and ')' are necessary if it's a group.
* If not supply '@cpus', the value of cpus uses the same as lcores.
* e.g. '1,2@(5-7),(3-5)@(0,2),(0,6),7-8' means start 9 EAL thread as below
* lcore 0 runs on cpuset 0x41 (cpu 0,6)
* lcore 1 runs on cpuset 0x2 (cpu 1)
* lcore 2 runs on cpuset 0xe0 (cpu 5,6,7)
* lcore 3,4,5 runs on cpuset 0x5 (cpu 0,2)
* lcore 6 runs on cpuset 0x41 (cpu 0,6)
* lcore 7 runs on cpuset 0x80 (cpu 7)
* lcore 8 runs on cpuset 0x100 (cpu 8)
*/
static int
eal_parse_lcores(const char *lcores)
{
struct rte_config *cfg = rte_eal_get_configuration();
static uint16_t set[RTE_MAX_LCORE];
unsigned idx = 0;
unsigned count = 0;
const char *lcore_start = NULL;
const char *end = NULL;
int offset;
rte_cpuset_t cpuset;
int lflags;
int ret = -1;
if (lcores == NULL)
return -1;
/* 去除所有前导的空白字符 */
/* Remove all blank characters ahead and after */
while (isblank(*lcores))
lcores++;
CPU_ZERO(&cpuset);
/* 重置全局变量`lcore_config[n]`和`rte_config.lcore_role[n]`
* 注意连`lcore_config[n].cpuset`也清零了。
*/
/* Reset lcore config */
for (idx = 0; idx < RTE_MAX_LCORE; idx++) {
cfg->lcore_role[idx] = ROLE_OFF;
lcore_config[idx].core_index = -1;
CPU_ZERO(&lcore_config[idx].cpuset);
}
/* Get list of cores */
do {
while (isblank(*lcores))
lcores++;
if (*lcores == '\0')
goto err;
lflags = 0;
/* record lcore_set start point */
lcore_start = lcores;
/* go across a complete bracket */
if (*lcore_start == '(') {
lcores += strcspn(lcores, ")");
if (*lcores++ == '\0')
goto err;
}
/* scan the separator '@', ','(next) or '\0'(finish) */
lcores += strcspn(lcores, "@,");
if (*lcores == '@') {
/* 解释 set 集合 */
/* explicit assign cpu_set */
offset = eal_parse_set(lcores + 1, set, RTE_DIM(set));
if (offset < 0)
goto err;
/* 将 set 集合 转换为 cpuset */
/* prepare cpu_set and update the end cursor */
if (0 > convert_to_cpuset(&cpuset,
set, RTE_DIM(set)))
goto err;
end = lcores + 1 + offset;
} else { /* ',' or '\0' */
/* haven't given cpu_set, current loop done */
end = lcores;
/* go back to check - */
offset = strcspn(lcore_start, "(-");
if (offset < (end - lcore_start) &&
*(lcore_start + offset) != '(')
lflags = 1;
}
if (*end != ',' && *end != '\0')
goto err;
/* 解释 lcore_set */
/* parse lcore_set from start point */
if (0 > eal_parse_set(lcore_start, set, RTE_DIM(set)))
goto err;
/* 如果没有使用'@',则使用`lcore_set`,来表示`cpu_set` */
/* without '@', by default using lcore_set as cpu_set */
if (*lcores != '@' &&
0 > convert_to_cpuset(&cpuset, set, RTE_DIM(set)))
goto err;
/* start to update lcore_set */
for (idx = 0; idx < RTE_MAX_LCORE; idx++) {
if (!set[idx])
continue;
if (cfg->lcore_role[idx] != ROLE_RTE) {
lcore_config[idx].core_index = count;
cfg->lcore_role[idx] = ROLE_RTE;
count++;
}
if (lflags) {
CPU_ZERO(&cpuset);
CPU_SET(idx, &cpuset);
}
rte_memcpy(&lcore_config[idx].cpuset, &cpuset,
sizeof(rte_cpuset_t));
}
lcores = end + 1;
} while (*end != '\0');
if (count == 0)
goto err;
cfg->lcore_count = count;
ret = 0;
err:
return ret;
}
/*
* Parse elem, the elem could be single number/range or '(' ')' group
* 1) A single number elem, it's just a simple digit. e.g. 9
* 2) A single range elem, two digits with a '-' between. e.g. 2-6
* 3) A group elem, combines multiple 1) or 2) with '( )'. e.g (0,2-4,6)
* Within group elem, '-' used for a range separator;
* ',' used for a single number.
*/
static int
eal_parse_set(const char *input, uint16_t set[], unsigned num)
{
unsigned idx;
const char *str = input;
char *end = NULL;
unsigned min, max;
memset(set, 0, num * sizeof(uint16_t));
while (isblank(*str))
str++;
/* only digit or left bracket is qualify for start point */
if ((!isdigit(*str) && *str != '(') || *str == '\0')
return -1;
/* process single number or single range of number */
if (*str != '(') {
errno = 0;
idx = strtoul(str, &end, 10);
if (errno || end == NULL || idx >= num)
return -1;
else {
while (isblank(*end))
end++;
min = idx;
max = idx;
if (*end == '-') {
/* process single - */
end++;
while (isblank(*end))
end++;
if (!isdigit(*end))
return -1;
errno = 0;
idx = strtoul(end, &end, 10);
if (errno || end == NULL || idx >= num)
return -1;
max = idx;
while (isblank(*end))
end++;
if (*end != ',' && *end != '\0')
return -1;
}
if (*end != ',' && *end != '\0' &&
*end != '@')
return -1;
for (idx = RTE_MIN(min, max);
idx <= RTE_MAX(min, max); idx++)
set[idx] = 1;
return end - input;
}
}
/* process set within bracket */
str++;
while (isblank(*str))
str++;
if (*str == '\0')
return -1;
min = RTE_MAX_LCORE;
do {
/* go ahead to the first digit */
while (isblank(*str))
str++;
if (!isdigit(*str))
return -1;
/* get the digit value */
errno = 0;
idx = strtoul(str, &end, 10);
if (errno || end == NULL || idx >= num)
return -1;
/* go ahead to separator '-',',' and ')' */
while (isblank(*end))
end++;
if (*end == '-') {
if (min == RTE_MAX_LCORE)
min = idx;
else /* avoid continuous '-' */
return -1;
} else if ((*end == ',') || (*end == ')')) {
max = idx;
if (min == RTE_MAX_LCORE)
min = idx;
for (idx = RTE_MIN(min, max);
idx <= RTE_MAX(min, max); idx++)
set[idx] = 1;
min = RTE_MAX_LCORE;
} else
return -1;
str = end + 1;
} while (*end != '\0' && *end != ')');
/*
* to avoid failure that tail blank makes end character check fail
* in eal_parse_lcores( )
*/
while (isblank(*str))
str++;
return str - input;
}
/* convert from set array to cpuset bitmap */
static int
convert_to_cpuset(rte_cpuset_t *cpusetp,
uint16_t *set, unsigned num)
{
unsigned idx;
CPU_ZERO(cpusetp);
for (idx = 0; idx < num; idx++) {
if (!set[idx])
continue;
if (!lcore_config[idx].detected) {
RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, "core %u "
"unavailable\n", idx);
return -1;
}
CPU_SET(idx, cpusetp);
}
return 0;
}
/** Number of elements in the array. */
#define RTE_DIM(a) (sizeof (a) / sizeof ((a)[0]))
5. 主线程的核绑定
全局的函数调用图:
rte_eal_init
+-> eal_thread_init_master(rte_config.master_lcore) /* `主线程`绑核 */
+-> RTE_PER_LCORE(_lcore_id) = lcore_id; /* 使用`线程变量`记录`lcore`下标 */
+-> eal_thread_set_affinity() /* 线程绑定`cpu` */
+-> rte_gettid /* 使用`线程变量`记录`线程号` */
| +-> static RTE_DEFINE_PER_LCORE(int, _thread_id); /* 声明静态的`线程变量`记录`线程号` */
| +-> RTE_PER_LCORE(_thread_id) = rte_sys_gettid(); /* 取得`线程号` */
| +-> syscall(SYS_gettid); /* 系统函数取得`线程号` */
+-> rte_thread_set_affinity(&lcore_config[lcore_id].cpuset); /* 线程核绑定 */
+-> pthread_setaffinity_np /* pthread库的线程核绑定 */
| /* 使用实际核绑定后的`cpusetp`,更新到相关线程变量`RTE_PER_LCORE`和全局变量`lcore_config` */
+-> RTE_PER_LCORE(_socket_id) = eal_cpuset_socket_id(cpusetp);
+-> memmove(&RTE_PER_LCORE(_cpuset), cpusetp,...);
+-> lcore_config[lcore_id].socket_id = RTE_PER_LCORE(_socket_id);
+-> memmove(&lcore_config[lcore_id].cpuset, cpusetp, sizeof(rte_cpuset_t));
后续会分拆讲解线程变量和各个相关函数。
5.1. 线程变量及其宏函数
DPDK定义了三个宏函数来为了给每一个线程,用于管理自己的线程变量。
其中定义和声明的时候,使用了__thread关键字来实现线程变量。
| 宏 | 描述 |
|---|---|
RTE_DEFINE_PER_LCORE() |
定义线程变量 |
RTE_DECLARE_PER_LCORE() |
声明线程变量 |
RTE_PER_LCORE() |
读写线程变量 |
三个宏函数的源码如下:
/**
* Macro to define a per lcore variable "var" of type "type", don`t
* use keywords like "static" or "volatile" in type, just prefix the
* whole macro.
*/
#define RTE_DEFINE_PER_LCORE(type, name) \
__thread __typeof__(type) per_lcore_##name
/**
* Macro to declare an extern per lcore variable "var" of type "type"
*/
#define RTE_DECLARE_PER_LCORE(type, name) \
extern __thread __typeof__(type) per_lcore_##name
/**
* Read/write the per-lcore variable value
*/
#define RTE_PER_LCORE(name) (per_lcore_##name)
DPDK为每一个线程都定义以下三个全局变量:
分别用于记录逻辑核,NUMA node,cpu set。
/* `lcore`下标 */
RTE_DEFINE_PER_LCORE(unsigned, _lcore_id) = LCORE_ID_ANY;
/* `lcore`所绑定的`cpuset`的`NUMA node` */
RTE_DEFINE_PER_LCORE(unsigned, _socket_id) = (unsigned)SOCKET_ID_ANY;
/* `lcore`所绑定的`cpuset` */
RTE_DEFINE_PER_LCORE(rte_cpuset_t, _cpuset);
__thread关键字作用:
__thread修饰的变量,在线程中地址都不一样,__thread变量每一个线程有一份独立实体,各个线程的值互不干扰。__thread是GCC内置的线程局部存储设施,存取效率可以和全局变量相比。__thread变量每一个线程有一份独立实体,各个线程的值互不干扰。- 可以用来修饰那些带有全局性且值可能变,但是又不值得用全局变量保护的变量。
__thread使用规则:
- 只能修饰
POD类型(类似整型指针的标量,不带自定义的构造、拷贝、赋值、析构的类型,二进制内容可以任意复制 memset,memcpy,且内容可以复原)。- 不能修饰
class类型,因为无法自动调用构造函数和析构函数。- 可以用于修饰全局变量,函数内的静态变量。
- 不能修饰函数的局部变量或者class的普通成员变量。
__thread变量值只能初始化为编译器常量(值在编译器就可以确定)。参考:
__thread关键字
Thread-Local Storage
5.2. eal_thread_init_master函数
eal_thread_init_master函数用为给主线程绑核。
传入的参数为进程命令行参数--master-lcore所指定的lcore下标。
- 线程变量
RTE_PER_LCORE(_lcore_id)设置为主线程的lcore下标。 - 调用
eal_thread_set_affinity函数绑定cpu。
函数调用图如下:
rte_eal_init
+-> eal_thread_init_master(rte_config.master_lcore) /* <== `主线程`绑核 */
+-> RTE_PER_LCORE(_lcore_id) = lcore_id; /* 使用`线程变量`记录`lcore`下标 */
+-> eal_thread_set_affinity() /* 线程绑定`cpu` */
eal_thread_init_master() 函数源码如下:
void eal_thread_init_master(unsigned lcore_id)
{
/* set the lcore ID in per-lcore memory area */
RTE_PER_LCORE(_lcore_id) = lcore_id;
/* set CPU affinity */
if (eal_thread_set_affinity() < 0)
rte_panic("cannot set affinity\n");
}
5.2.1. eal_thread_set_affinity()函数
eal_thread_set_affinity()函数是EAL层的核绑定。
- 使用
rte_lcore_id()函数取得当前线程所在的lcore下标。 - 使用
rte_gettid()函数,来取得当前线程的线程号。 - 调用
rte_thread_set_affinity()函数,来绑定到lcore_config[lcore_id].cpuset所指定的cpuset。
函数调用图如下:
rte_eal_init
+-> eal_thread_init_master(rte_config.master_lcore) /* `主线程`绑核 */
+-> eal_thread_set_affinity() /* <== 线程绑定`cpu` */
+-> rte_gettid /* 使用`线程变量`记录`线程号` */
+-> rte_thread_set_affinity(&lcore_config[lcore_id].cpuset); /* 线程核绑定 */
函数源码如下:
/* set affinity for current EAL thread */
static int
eal_thread_set_affinity(void)
{
unsigned lcore_id = rte_lcore_id();
/* acquire system unique id */
rte_gettid();
/* update EAL thread core affinity */
return rte_thread_set_affinity(&lcore_config[lcore_id].cpuset);
}
5.2.1.1. rte_gettid()函数
rte_gettid()函数使用线程变量记录线程号。
rte_gettid()函数,来取得当前线程的线程号。rte_gettid()函数定义了一个静态的线程变量RTE_PER_LCORE(_thread_id)。rte_gettid()函数通过rte_sys_gettid()函数来读取线程号。
3.1.rte_sys_gettid()函数,最后调用系统函数syscall()来取得线程号。
函数调用图如下:
rte_eal_init
+-> eal_thread_init_master(rte_config.master_lcore) /* `主线程`绑核 */
+-> eal_thread_set_affinity() /* 线程绑定`cpu` */
+-> rte_gettid /* <== 使用`线程变量`记录`线程号` */
+-> static RTE_DEFINE_PER_LCORE(int, _thread_id); /* 声明静态的`线程变量`记录`线程号` */
+-> RTE_PER_LCORE(_thread_id) = rte_sys_gettid(); /* 取得`线程号` */
+-> syscall(SYS_gettid); /* 系统函数取得`线程号` */
函数源码如下:
static inline int rte_gettid(void)
{
static RTE_DEFINE_PER_LCORE(int, _thread_id) = -1;
if (RTE_PER_LCORE(_thread_id) == -1)
RTE_PER_LCORE(_thread_id) = rte_sys_gettid();
return RTE_PER_LCORE(_thread_id);
}
/* require calling thread tid by gettid() */
int rte_sys_gettid(void)
{
return (int)syscall(SYS_gettid);
}
5.2.1.2. rte_thread_set_affinity()函数
·rte_thread_set_affinity()设置核绑定的关键函数。
函数会完成核绑定,并且将实际的核绑定数据更新回关线程变量RTE_PER_LCORE和全局变量lcore_config。
其中的流程如下:
- 使用
pthread_setaffinity_np进行核绑定。这个是系统的核绑定函数。 - 使用实际核绑定后的
cpusetp,更新到相关线程变量RTE_PER_LCORE和全局变量lcore_config。
2.1. 使用eal_cpuset_socket_id()函数得出实际cpusetp所在的NUMA node id,并更新到RTE_PER_LCORE(_socket_id)。
2.2. 更新RTE_PER_LCORE(_cpuset)。
2.3. 更新lcore_config[lcore_id].socket_id.
2.4. 更新lcore_config[lcore_id].cpuset。
注意:
由于cpusetp所指向的数据,在经过pthread_setaffinity_np()后有可能修改,所以需要将实际核绑定后的cpusetp更新到全局变量lcore_config和RTE_PER_LCORE(_socket_id)。
使用memmove()函数拷贝,是因为源和目的地址有可能相同。
更新线程变量RTE_PER_LCORE,则有利于加速后续的读取。
rte_eal_init
+-> eal_thread_init_master(rte_config.master_lcore) /* `主线程`绑核 */
+-> eal_thread_set_affinity /* 线程绑定`cpu` */
+-> rte_thread_set_affinity(&lcore_config[lcore_id].cpuset); /* <== 线程核绑定 */
+-> pthread_setaffinity_np /* pthread库的线程核绑定 */
| /* 使用实际核绑定后的`cpusetp`,更新到相关线程变量`RTE_PER_LCORE`和全局变量`lcore_config` */
+-> RTE_PER_LCORE(_socket_id) = eal_cpuset_socket_id(cpusetp);
+-> memmove(&RTE_PER_LCORE(_cpuset), cpusetp,...);
+-> lcore_config[lcore_id].socket_id = RTE_PER_LCORE(_socket_id);
+-> memmove(&lcore_config[lcore_id].cpuset, cpusetp, sizeof(rte_cpuset_t));
函数源码如下:
int
rte_thread_set_affinity(rte_cpuset_t *cpusetp)
{
int s;
unsigned lcore_id;
pthread_t tid;
tid = pthread_self();
/* 核绑定 */
s = pthread_setaffinity_np(tid, sizeof(rte_cpuset_t), cpusetp);
if (s != 0) {
RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, "pthread_setaffinity_np failed\n");
return -1;
}
/* 更新实际核绑定后的`cpusetp`到相关全局变量`RTE_PER_LCORE`*/
/* store socket_id in TLS for quick access */
RTE_PER_LCORE(_socket_id) =
eal_cpuset_socket_id(cpusetp);
/* store cpuset in TLS for quick access */
memmove(&RTE_PER_LCORE(_cpuset), cpusetp,
sizeof(rte_cpuset_t));
/* 更新实际核绑定后的`cpusetp`到相关全局变量`lcore_config`*/
lcore_id = rte_lcore_id();
if (lcore_id != (unsigned)LCORE_ID_ANY) {
/* EAL thread will update lcore_config */
lcore_config[lcore_id].socket_id = RTE_PER_LCORE(_socket_id);
memmove(&lcore_config[lcore_id].cpuset, cpusetp,
sizeof(rte_cpuset_t));
}
return 0;
}
5.2.1.2.1. eal_cpuset_socket_id()函数
eal_cpuset_socket_id()返回cpusetp所在的NUMA node_id。
注意:
如果cpusetp所指向的cpu分别属于不同的NUMA node_id,则函数会返回SOCKET_ID_ANY。
函数源码如下:
int eal_cpuset_socket_id(rte_cpuset_t *cpusetp)
{
unsigned cpu = 0;
int socket_id = SOCKET_ID_ANY;
int sid;
if (cpusetp == NULL)
return SOCKET_ID_ANY;
do {
if (!CPU_ISSET(cpu, cpusetp))
continue;
if (socket_id == SOCKET_ID_ANY)
socket_id = eal_cpu_socket_id(cpu);
/* 如果`cpusetp`所指向的`cpu`分别属于不同的`NUMA node_id`,
* 函数会返回`SOCKET_ID_ANY`。 */
sid = eal_cpu_socket_id(cpu);
if (socket_id != sid) {
socket_id = SOCKET_ID_ANY;
break;
}
} while (++cpu < RTE_MAX_LCORE);
return socket_id;
}
6. DPDK中断处理线程
在DPDK中。会新建一个线程用于中断的处理。线程的名称为"eal-intr-thread"。
该线程是没有核绑定的。这里不详细展开。
函数调用图:
rte_eal_init
+-> rte_eal_intr_init /* init interrupt-handling */
+-> pthread_create(&intr_thread, NULL, eal_intr_thread_main, NULL);
| +~> eal_intr_thread_main /* 这个处理中断的线程是没有绑核的 */
+-> rte_thread_setname ("eal-intr-thread")
7. rte_eal_init()函数中副线程的创建
在rte_eal_init()中,会通过pthread_create()来创建各个的副线程。
- 使用
RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE()宏函数来遍历所有业务lcore
1.1. 创建主线程和副线程间的沟通管道。
1.2. 使用pthread_create()创建副线程。副线程的处理函数是eal_thread_loop()。
1.3. 使用rte_thread_setname()函数修改副线程的名称。
注意:
lcore_config[i].thread_id的地址会传入到pthread_create()函数,从而纪录下新建的副线程的线程号。
lcore_config[i].thread_id的数组会在eal_thread_loop()业务处理函数中使用到。
全局函数调用图如下:
rte_eal_init
| /* 遍历所有的`副线程`*/
+-> RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(i)
| /* 创建`主线程`和`副线程`间的沟通管道 */
+-> pipe(lcore_config[i].pipe_master2slave);
+-> pipe(lcore_config[i].pipe_slave2master);
| /* 创建`副线程` */
+-> pthread_create(&lcore_config[i].thread_id, NULL, eal_thread_loop, NULL);
| +~> eal_thread_loop
| +-> eal_thread_set_affinity /*`副线程`核绑定*/
| +-> read(m2s, &c, 1); /* 等待`主线程`发送到`副线程`的消息 */
| +-> write(s2m, &c, 1); /* `副线程`确认收到`主线程`的消息 */
| +-> lcore_config[lcore_id].f(fct_arg); /* 执行`业务处理回调函数` */
+-> rte_thread_setname /*`副线程`重命名*/
函数源码如下:
int
rte_eal_init(int argc, char **argv)
{
/* ... */
RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(i) {
/* 创建`主线程`和`副线程`间的沟通管道 */
/*
* create communication pipes between master thread
* and children
*/
if (pipe(lcore_config[i].pipe_master2slave) < 0)
rte_panic("Cannot create pipe\n");
if (pipe(lcore_config[i].pipe_slave2master) < 0)
rte_panic("Cannot create pipe\n");
lcore_config[i].state = WAIT;
/* 创建`副线程` */
/* create a thread for each lcore */
ret = pthread_create(&lcore_config[i].thread_id, NULL,
eal_thread_loop, NULL);
if (ret != 0)
rte_panic("Cannot create thread\n");
/* Set thread_name for aid in debugging. */
snprintf(thread_name, RTE_MAX_THREAD_NAME_LEN,
"lcore-slave-%d", i);
ret = rte_thread_setname(lcore_config[i].thread_id,
thread_name);
if (ret != 0)
RTE_LOG(DEBUG, EAL,
"Cannot set name for lcore thread\n");
}
/* ... */
}
7.1. RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE()宏函数
RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE()宏函数用于遍历所有的副线程。这里不深入探讨。
注意:
参数i,有做出参的作用。数值为循环中当前lcore的下标。在eal_thread_loop()函数中会使用到。
/**
* Macro to browse all running lcores except the master lcore.
*/
#define RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(i) \
for (i = rte_get_next_lcore(-1, 1, 0); \
i
/**
* Get the next enabled lcore ID.
*
* @param i
* The current lcore (reference).
* @param skip_master
* If true, do not return the ID of the master lcore.
* @param wrap
* If true, go back to 0 when RTE_MAX_LCORE is reached; otherwise,
* return RTE_MAX_LCORE.
* @return
* The next lcore_id or RTE_MAX_LCORE if not found.
*/
static inline unsigned
rte_get_next_lcore(unsigned i, int skip_master, int wrap)
{
i++;
if (wrap)
i %= RTE_MAX_LCORE;
while (i < RTE_MAX_LCORE) {
if (!rte_lcore_is_enabled(i) ||
(skip_master && (i == rte_get_master_lcore()))) {
i++;
if (wrap)
i %= RTE_MAX_LCORE;
continue;
}
break;
}
return i;
}
/**
* Test if an lcore is enabled.
*
* @param lcore_id
* The identifier of the lcore, which MUST be between 0 and
* RTE_MAX_LCORE-1.
* @return
* True if the given lcore is enabled; false otherwise.
*/
static inline int
rte_lcore_is_enabled(unsigned lcore_id)
{
struct rte_config *cfg = rte_eal_get_configuration();
if (lcore_id >= RTE_MAX_LCORE)
return 0;
return cfg->lcore_role[lcore_id] != ROLE_OFF;
}
/**
* Get the id of the master lcore
*
* @return
* the id of the master lcore
*/
static inline unsigned
rte_get_master_lcore(void)
{
return rte_eal_get_configuration()->master_lcore;
}
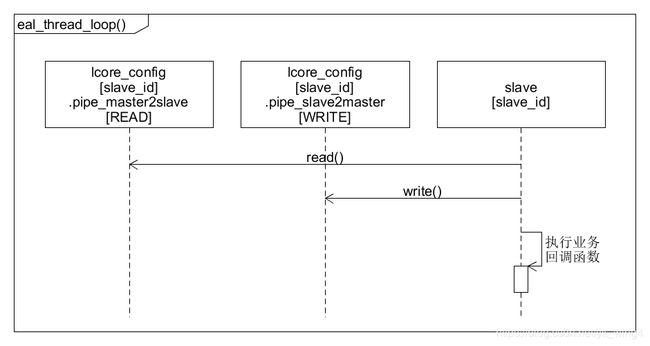
7.2. eal_thread_loop()函数: 副线程循环
eal_thread_loop()函数是副线程循环,函数步骤如下:
- 取得
副线程的线程号。 副线程核绑定。副线程的死循环。
3.1. 等待主线程发送到副线程的消息。
3.2.副线程确认收到主线程的消息。
3.3. 执行业务处理回调函数。
3.4. 将业务处理回调函数的结果,放置到lcore_config[lcore_id].ret中。
3.5. 设置副线程状态为FINISHED。
3.6. 跳回到3.1,继续等待主线程的消息。
函数调用图:
rte_eal_init
| /* 遍历所有的`副线程`*/
+-> RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(i)
| /* 创建`主线程`和`副线程`间的沟通管道 */
+-> pipe(lcore_config[i].pipe_master2slave);
+-> pipe(lcore_config[i].pipe_slave2master);
| /* 创建`副线程` */
+-> pthread_create(&lcore_config[i].thread_id, NULL, eal_thread_loop, NULL);
+~> eal_thread_loop
+-> eal_thread_set_affinity /*`副线程`核绑定*/
+-> read(m2s, &c, 1); /* 等待`主线程`发送到`副线程`的消息 */
+-> write(s2m, &c, 1); /* `副线程`确认收到`主线程`的消息 */
+-> lcore_config[lcore_id].f(fct_arg); /* 执行`业务处理回调函数` */
函数源码如下:
/* main loop of threads */
__attribute__((noreturn)) void *
eal_thread_loop(__attribute__((unused)) void *arg)
{
char c;
int n, ret;
unsigned lcore_id;
pthread_t thread_id;
int m2s, s2m;
char cpuset[RTE_CPU_AFFINITY_STR_LEN];
/* 取得`副线程`的线程号 */
thread_id = pthread_self();
/* retrieve our lcore_id from the configuration structure */
RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id) {
if (thread_id == lcore_config[lcore_id].thread_id)
break;
}
if (lcore_id == RTE_MAX_LCORE)
rte_panic("cannot retrieve lcore id\n");
m2s = lcore_config[lcore_id].pipe_master2slave[0]; /* read end of master to slave pipe */
s2m = lcore_config[lcore_id].pipe_slave2master[1]; /* write end of master to slave pipe */
/* set the lcore ID in per-lcore memory area */
RTE_PER_LCORE(_lcore_id) = lcore_id;
/* `副线程`核绑定 */
/* set CPU affinity */
if (eal_thread_set_affinity() < 0)
rte_panic("cannot set affinity\n");
ret = eal_thread_dump_affinity(cpuset, RTE_CPU_AFFINITY_STR_LEN);
/* read on our pipe to get commands */
while (1) {
void *fct_arg;
/* 等待`主线程`发送到`副线程`的消息 */
/* wait command */
do {
n = read(m2s, &c, 1);
} while (n < 0 && errno == EINTR);
if (n <= 0)
rte_panic("cannot read on configuration pipe\n");
lcore_config[lcore_id].state = RUNNING;
/* `副线程`确认收到`主线程`的消息 */
/* send ack */
n = 0;
while (n == 0 || (n < 0 && errno == EINTR))
n = write(s2m, &c, 1);
if (n < 0)
rte_panic("cannot write on configuration pipe\n");
if (lcore_config[lcore_id].f == NULL)
rte_panic("NULL function pointer\n");
/*执行`业务处理回调函数`*/
/* call the function and store the return value */
fct_arg = lcore_config[lcore_id].arg;
ret = lcore_config[lcore_id].f(fct_arg); /* 执行`业务处理回调函数` */
lcore_config[lcore_id].ret = ret;
rte_wmb();
lcore_config[lcore_id].state = FINISHED; /* 设置副线程状态为`FINISHED` */
}
/* never reached */
/* pthread_exit(NULL); */
/* return NULL; */
}
eal_thread_loop()函数的交互图如下:
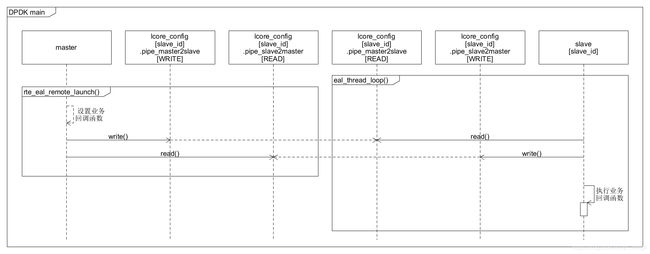
8. 线程启动和等待
在rte_eal_init()函数中,通过rte_eal_mp_remote_launch()先传入一个哑元函数sync_func(),来确保所有的副线程都已经就绪。
- 调用
rte_eal_mp_remote_launch()函数,传入一个哑元函数sync_func(),给每一个副线程来执行。 - 调用
rte_eal_mp_wait_lcore()函数,等待所以线程返回。
全局函数调用图:
rte_eal_init()
+-> rte_eal_mp_remote_launch(sync_func, NULL, SKIP_MASTER); /* 设置每一个`副线程`的回调函数为`sync_func()` */
| +-> RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id) /* 遍历所有的`副线程`来执行回调函数 */
| +-> rte_eal_remote_launch(f, arg, lcore_id); /* `副线程`来执行回调函数 */
| +-> lcore_config[slave_id].f = f; /* 设置`副线程`的`业务函数f` */
| +-> lcore_config[slave_id].arg = arg; /* 设置`副线程`的`参数arg` */
| +-> write(m2s, &c, 1); /* 发送消息到`副线程`,通知`副线程`执行`业务函数`。 */
| +-> read(s2m, &c, 1); /* 等待`副线程`的确认。并判断`副线程`启动是否有异常。 */
+-> rte_eal_mp_wait_lcore(); /* 等待所有线程返回 */
+-> RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id); /* 遍历所有的`副线程` */
+-> rte_eal_wait_lcore(lcore_id); /* 等待某一`副线程`返回 */
rte_eal_init()函数中,有关源主线程启动的源码片段如下:
/* Launch threads, called at application init(). */
int
rte_eal_init(int argc, char **argv)
{
/* ... */
/*
* Launch a dummy function on all slave lcores, so that master lcore
* knows they are all ready when this function returns.
*/
rte_eal_mp_remote_launch(sync_func, NULL, SKIP_MASTER);
rte_eal_mp_wait_lcore();
/* ... */
}
哑元函数sync_func()什么都没有处理。直接返回0,表示正确的返回。
哑元函数sync_func()源码如下:
static int
sync_func(__attribute__((unused)) void *arg)
{
return 0;
}
8.1. rte_eal_mp_remote_launch()函数:线程启动函数
rte_eal_mp_remote_launch()函数用于载入业务函数。函数流程如下:
- 检查所有的
副线程,是否都在WAIT状态。
1.1 如果不是所有的副线程都在WAIT状态,则返回-EBUSY,跳出程序。
1.2 如果所有的副线程都在WAIT状态,进行后续的步骤。 - 遍历所有的
副线程。
2.1. 调用rte_eal_remote_launch(),为各个副线程载入业务函数f,并通知副线程执行。 主线程按需执行业务函数f。
3.1. 如果参数call_master设置为CALL_MASTER,则主线程需要执行业务函数f。
3.2. 如果参数call_master设置为SKIP_MASTER,则主线程不用执行业务函数f。
注意:
rte_eal_mp_remote_launch()函数,只能用于主线程中执行。
函数调用图如下:
rte_eal_init()
+-> rte_eal_mp_remote_launch(sync_func, NULL, SKIP_MASTER); /* <== 设置每一个`副线程`的回调函数为`sync_func()` */
| +-> RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id) /* 遍历所有的`副线程`来执行回调函数 */
| +-> rte_eal_remote_launch(f, arg, lcore_id); /* `副线程`来执行回调函数 */
+-> rte_eal_mp_wait_lcore(); /* 等待所有线程返回 */
函数源码如下:
/*
* Check that every SLAVE lcores are in WAIT state, then call
* rte_eal_remote_launch() for all of them. If call_master is true
* (set to CALL_MASTER), also call the function on the master lcore.
*/
int
rte_eal_mp_remote_launch(int (*f)(void *), void *arg,
enum rte_rmt_call_master_t call_master)
{
int lcore_id;
int master = rte_get_master_lcore();
/* 检查所有的`副线程`,是否都在`WAIT`状态。 */
/* check state of lcores */
RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id) {
if (lcore_config[lcore_id].state != WAIT)
return -EBUSY;
}
/* 遍历所有的`副线程`。 */
/* 调用`rte_eal_remote_launch()`,为各个`副线程`载入`业务函数f`,并通知`副线程`执行。 */
/* send messages to cores */
RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id) {
rte_eal_remote_launch(f, arg, lcore_id);
}
/* `主线程`按`call_master`参数,来执行`业务函数f`。 */
if (call_master == CALL_MASTER) {
lcore_config[master].ret = f(arg);
lcore_config[master].state = FINISHED;
}
return 0;
}
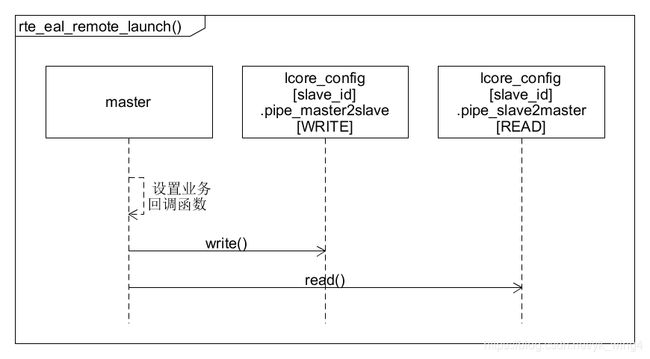
8.1.1. rte_eal_remote_launch()函数:副线程`启动函数
rte_eal_remote_launch()函数,用于设置副线程的业务函数,并通知该副线程执行业务函数`。
- 设置
副线程的业务函数f及其参数arg到副线程对应的lcore_config。 - 发送消息到
副线程,通知副线程执行业务函数。 - 等待
副线程的确认。 - 判断
副线程启动是否有异常。一旦有异常则抛出rte_panic。
注意:
一旦副线程返回。副线程状态会切换到FINISHED。
为下一次调用rte_eal_mp_remote_launch()或rte_eal_remote_launch()作准备。
函数调用图如下:
rte_eal_init()
+-> rte_eal_mp_remote_launch(sync_func, NULL, SKIP_MASTER); /* 设置每一个`副线程`的回调函数为`sync_func()` */
| +-> RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id) /* 遍历所有的`副线程`来执行回调函数 */
| +-> rte_eal_remote_launch(f, arg, lcore_id); /* <== `副线程`来执行回调函数 */
| +-> lcore_config[slave_id].f = f; /* 设置`副线程`的`业务函数f` */
| +-> lcore_config[slave_id].arg = arg; /* 设置`副线程`的`参数arg` */
| +-> write(m2s, &c, 1); /* 发送消息到`副线程`,通知`副线程`执行`业务函数`。 */
| +-> read(s2m, &c, 1); /* 等待`副线程`的确认。并判断`副线程`启动是否有异常。 */
+-> rte_eal_mp_wait_lcore(); /* 等待所有线程返回 */
函数源码如下:
/*
* Send a message to a slave lcore identified by slave_id to call a
* function f with argument arg. Once the execution is done, the
* remote lcore switch in FINISHED state.
*/
int
rte_eal_remote_launch(int (*f)(void *), void *arg, unsigned slave_id)
{
int n;
char c = 0;
int m2s = lcore_config[slave_id].pipe_master2slave[1]; /* write end of master to slave pipe */
int s2m = lcore_config[slave_id].pipe_slave2master[0]; /* read end of slave to master pipe */
if (lcore_config[slave_id].state != WAIT)
return -EBUSY;
/* 设置`副线程`的`业务函数f`及其`参数arg`到副线程对应的`lcore_config`。 */
lcore_config[slave_id].f = f;
lcore_config[slave_id].arg = arg;
/* 发送消息到`副线程`,通知`副线程`执行`业务函数`。 */
/* send message */
n = 0;
while (n == 0 || (n < 0 && errno == EINTR))
n = write(m2s, &c, 1);
if (n < 0)
rte_panic("cannot write on configuration pipe\n");
/* 等待`副线程`的确认。并判断`副线程`启动是否有异常。 */
/* wait ack */
do {
n = read(s2m, &c, 1);
} while (n < 0 && errno == EINTR);
if (n <= 0)
rte_panic("cannot read on configuration pipe\n");
return 0;
}
rte_eal_remote_launch()函数的交互图如下:
以下是 DPDK 主副线程交互图。
其中合并了主线程rte_eal_remote_launch()函数,和副线程eal_thread_loop()函数。
8.2. rte_eal_mp_wait_lcore()函数
rte_eal_mp_wait_lcore()函数,用于等待所有副线程返回。
- 遍历所有的
副线程。
1.1. 使用rte_eal_wait_lcore()函数,来等待某一副线程返回。
函数调用图如下:
rte_eal_init
+-> rte_eal_mp_remote_launch(sync_func, NULL, SKIP_MASTER); /* 设置每一个`副线程`的回调函数为`sync_func()` */
+-> rte_eal_mp_wait_lcore(); /* <== 等待所有线程返回 */
+-> RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id); /* 遍历所有的`副线程` */
+-> rte_eal_wait_lcore(lcore_id); /* 等待某一`副线程`返回 */
rte_eal_mp_wait_lcore()函数源码如下:
void
rte_eal_mp_wait_lcore(void)
{
unsigned lcore_id;
RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id) {
rte_eal_wait_lcore(lcore_id);
}
}
8.2.1. rte_eal_wait_lcore()函数
rte_eal_wait_lcore()函数,用于等待某一副线程返回。
- 如果
副线程状态为WAIT,直接返回0。 - 使用死循环等待,直到
副线程状态为WAIT或者FINISHED。 - 切换
副线程状态为WAIT。 - 返回
副线程的返回值。
注意:
rte_eal_wait_lcore()函数执行完后。副线程状态为WAIT。
函数调用图如下:
rte_eal_init
+-> rte_eal_mp_remote_launch(sync_func, NULL, SKIP_MASTER); /* 设置每一个`副线程`的回调函数为`sync_func()` */
+-> rte_eal_mp_wait_lcore(); /* 等待所有线程返回 */
+-> RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id); /* 遍历所有的`副线程` */
+-> rte_eal_wait_lcore(lcore_id); /* <== 等待某一`副线程`返回 */
函数源码如下:
/*
* Wait until a lcore finished its job.
*/
int
rte_eal_wait_lcore(unsigned slave_id)
{
if (lcore_config[slave_id].state == WAIT)
return 0;
/* 使用死循环等待,直到`副线程`状态为`WAIT`或者`FINISHED`。*/
while (lcore_config[slave_id].state != WAIT &&
lcore_config[slave_id].state != FINISHED);
rte_rmb();
/* we are in finished state, go to wait state */
lcore_config[slave_id].state = WAIT;
return lcore_config[slave_id].ret;
}