PCL学习:点云分割-欧式聚类分割
http://www.pointclouds.org/documentation/tutorials/cluster_extraction.php#cluster-extraction
基于欧式距离的分割和基于区域生长的分割本质上都是用区分邻里关系远近来完成的。由于点云数据提供了更高维度的数据,故有很多信息可以提取获得。欧几里得算法使用邻居之间距离作为判定标准,而区域生长算法则利用了法线,曲率,颜色等信息来判断点云是否应该聚成一类。
(1)欧几里德算法
具体的实现方法大致是:
- 找到空间中某点p10,有kdTree找到离他最近的n个点,判断这n个点到p的距离。将距离小于阈值r的点p12,p13,p14....放在类Q里
- 在 Q\p10 里找到一点p12,重复1
- 在 Q\p10,p12 找到一点,重复1,找到p22,p23,p24....全部放进Q里
- 当 Q 再也不能有新点加入了,则完成搜索了
因为点云总是连成片的,很少有什么东西会浮在空中来区分。但是如果结合此算法可以应用很多东东。比如
- 半径滤波删除离群点
- 采样一致找到桌面或者除去滤波
当然,一旦桌面被剔除,桌上的物体就自然成了一个个的浮空点云团。就能够直接用欧几里德算法进行分割了,这样就可以提取出我们想要识别的东西;在这里我们就可以使用提取平面,平面去掉,利用聚类的方法再显示剩下的所有聚类的结果。
测试示例:
1. 加载点云,滤波;
2. 分割平面模型;
3. 去除所有平面点云,对余下的点进行聚类分割;
4. 显示聚类分割结果。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int color_bar[][3]=
{
{ 255,0,0},
{ 0,255,0 },
{ 0,0,255 },
{ 0,255,255 },
{ 255,255,0 },
{ 255,255,255 },
{ 255,0,255 }
};
int
main (int argc, char** argv)
{
// Read in the cloud data
pcl::PCDReader reader;
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud), cloud_f (new pcl::PointCloud);
reader.read ("..\\..\\source\\table_scene_lms400.pcd", *cloud);
std::cout << "PointCloud before filtering has: " << cloud->points.size () << " data points." << std::endl; //*
// Create the filtering object: downsample the dataset using a leaf size of 1cm
pcl::VoxelGrid vg;
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered (new pcl::PointCloud);
vg.setInputCloud (cloud);
vg.setLeafSize (0.01f, 0.01f, 0.01f);
vg.filter (*cloud_filtered);
std::cout << "PointCloud after filtering has: " << cloud_filtered->points.size () << " data points." << std::endl; //*
// Create the segmentation object for the planar model and set all the parameters
pcl::SACSegmentation seg;
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers (new pcl::PointIndices);
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients (new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_plane (new pcl::PointCloud ());
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients (true);
seg.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);
seg.setMethodType (pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setMaxIterations (100);
seg.setDistanceThreshold (0.02);
int i=0, nr_points = (int) cloud_filtered->points.size ();
while (cloud_filtered->points.size () > 0.3 * nr_points)
{
// Segment the largest planar component from the remaining cloud
seg.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);
seg.segment (*inliers, *coefficients);
if (inliers->indices.size () == 0)
{
std::cout << "Could not estimate a planar model for the given dataset." << std::endl;
break;
}
// Extract the planar inliers from the input cloud
pcl::ExtractIndices extract;
extract.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);
extract.setIndices (inliers);
extract.setNegative (false);
// Write the planar inliers to disk
extract.filter (*cloud_plane);
std::cout << "PointCloud representing the planar component: " << cloud_plane->points.size () << " data points." << std::endl;
// Remove the planar inliers, extract the rest
extract.setNegative (true);
extract.filter (*cloud_f);
cloud_filtered = cloud_f;
}
// Creating the KdTree object for the search method of the extraction
pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree);
tree->setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);
std::vector cluster_indices;
pcl::EuclideanClusterExtraction ec;
ec.setClusterTolerance (0.02); //设置近邻搜索的搜索半径为2cm
ec.setMinClusterSize (100); //设置一个聚类需要的最少点数目为100
ec.setMaxClusterSize (25000); //设置一个聚类需要的最大点数目为25000
ec.setSearchMethod (tree); //设置点云的搜索机制
ec.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered); //设置原始点云
ec.extract (cluster_indices); //从点云中提取聚类
// 可视化部分
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("segmention");
// 我们将要使用的颜色
float bckgr_gray_level = 0.0; // 黑色
float txt_gray_lvl = 1.0 - bckgr_gray_level;
int num = cluster_indices.size();
int j = 0;
for (std::vector::const_iterator it = cluster_indices.begin (); it != cluster_indices.end (); ++it)
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_cluster (new pcl::PointCloud);
for (std::vector::const_iterator pit = it->indices.begin (); pit != it->indices.end (); pit++)
cloud_cluster->points.push_back (cloud_filtered->points[*pit]); //*
cloud_cluster->width = cloud_cluster->points.size ();
cloud_cluster->height = 1;
cloud_cluster->is_dense = true;
std::cout << "PointCloud representing the Cluster: " << cloud_cluster->points.size () << " data points." << std::endl;
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "cloud_cluster_" << j << ".pcd";
writer.write (ss.str (), *cloud_cluster, false); //*
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom cloud_in_color_h(cloud,
color_bar[j][0],
color_bar[j][1],
color_bar[j][2]);//赋予显示点云的颜色
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_cluster, cloud_in_color_h, std::to_string(j));
j++;
}
//等待直到可视化窗口关闭。
while (!viewer.wasStopped())
{
viewer.spinOnce(100);
boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::microseconds(100000));
}
return (0);
} cmd命令: .\cluster_extraction.exe
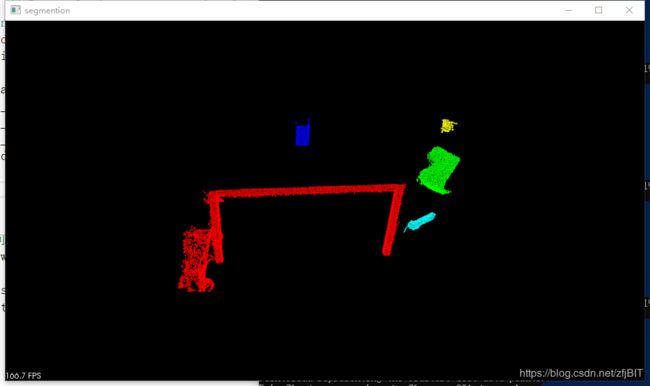
打印信息:分为了5类;
PointCloud before filtering has: 460400 data points.
PointCloud after filtering has: 41049 data points.
PointCloud representing the planar component: 20536 data points.
PointCloud representing the planar component: 12442 data points.
PointCloud representing the Cluster: 4857 data points.
PointCloud representing the Cluster: 1386 data points.
PointCloud representing the Cluster: 321 data points.
PointCloud representing the Cluster: 291 data points.
PointCloud representing the Cluster: 123 data points.可视化聚类结果:
5类,不同的聚类使用不同的颜色表示,同一聚类中的点集使用同一种颜色;