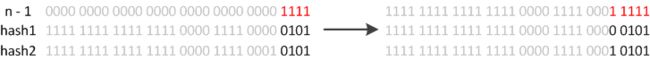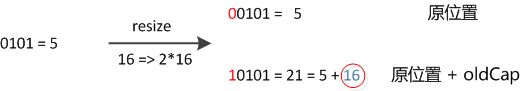jdk1.8对hashmap的简单介绍
基于哈希表实现的Map接口。此实现提供了所有可选映射操作,并允许空值(value)和空键(key)。(HashMap类大致相当于Hashtable,只是它是线程不安全的,并且允许空值)这个类不能保证映射的顺序;特别是,它不能保证顺序随时间保持不变。
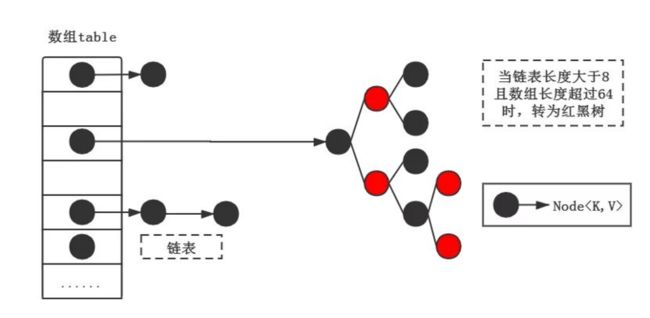
hashmap底层结构
hashmap底层由数组和链表实现(jdk1.8中当链表的长度大于8时,链表会转换成红黑树)
hashmap的初始容量和最多容量
初始容量16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16最大容量 1 << 30
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 为什么不是1 << 31,因为最左侧的一位表示符号位,容量不能为负数为什么规定容量必须是2的n次幂
- 加快hash计算速度
- 均匀分布,减少hash冲突
//计算索引算法
i=(len - 1) & hashlen为数组的长度,由于len是2的n次方,(n-1)转换成2进制后全部为1.2的n次方,可以通过位移操作来实现,可以加快hash计算速度,结合按位与计算加快数组下标的计算。例如在HashMap做扩容时,满足2的幂就是相当于每次扩容都是翻倍(就是<<1右移一位),这样扩容时在重新计算下标位置时,只有两种情况,一种是下标不变,另一种是下标变为:原下标位置+扩容前容量,这样扩容后节点移动相对较少,也可以提高性能。。
可以改善数据的均匀分布,减少hash冲突,毕竟hash冲突越大,代表数组中一个链的长度越大,这样的话会降低hashmap的性能。
其中关键代码为HashMap中的数组下标计算:i = (n - 1) & hash,该计算方法可以实现一个均匀分布。
hashmap怎么计算hash值,为什么
高16位和低16位进行异或
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}主要还是为了解决hash碰撞问题。让高位和低位都参与hash值的计算
怎么指定hashmap的初始值,怎么保证输入的值是2的n次方
new HashMap<>(n);保证输入的值是2的n次方,该算法让最高位的1后面的位全变为1
//返回大于输入参数且最近的2的整数次幂的数。比如10,则返回16
// Returns a power of two size for the given target capacity.
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}hashmap在什么情况下进行扩容
加载因子0.75. 如果默认容量是16,那么当元素达到16 x 0.75=12时,就会发生扩容.
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;为什么加载因子是0.75
在HashMap的源码中有这么一段注释
* Ideally, under random hashCodes, the frequency of
* nodes in bins follows a Poisson distribution
* (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Poisson_distribution) with a
* parameter of about 0.5 on average for the default resizing
* threshold of 0.75, although with a large variance because of
* resizing granularity. Ignoring variance, the expected
* occurrences of list size k are (exp(-0.5) * pow(0.5, k) /
* factorial(k)). The first values are:
* 0: 0.60653066
* 1: 0.30326533
* 2: 0.07581633
* 3: 0.01263606
* 4: 0.00157952
* 5: 0.00015795
* 6: 0.00001316
* 7: 0.00000094
* 8: 0.00000006
* more: less than 1 in ten million大概意思是:
在理想情况下,使用随机哈希码,在扩容阈值(加载因子)为0.75的情况下,节点出现在频率在Hash桶(表)中遵循参数平均为0.5的泊松分布。忽略方差,即X = λt,P(λt = k),其中λt = 0.5的情况,按公式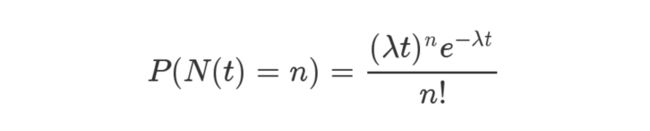
选择0.75作为默认的加载因子,完全是时间和空间成本上寻求的一种折衷选择。
在jdk1.8中在什么情况下链表会转换成红黑树
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;jdk1.8 resize的过程
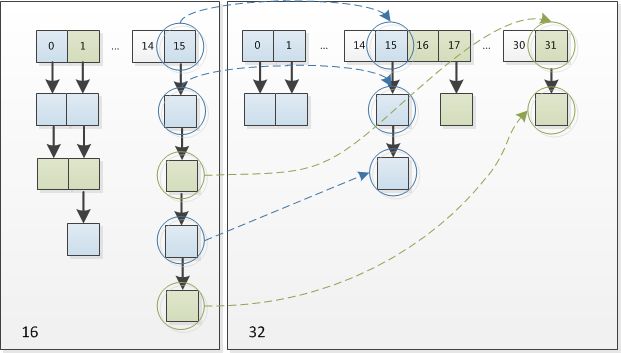
当put时,如果发现目前的bucket占用程度已经超过了Load Factor所希望的比例,那么就会发生resize。在resize的过程,简单的说就是把bucket扩充为2倍,之后重新计算index,把节点再放到新的bucket中。resize的注释是这样描述的:当超过限制的时候会resize,然而又因为我们使用的是2次幂的扩展(指长度扩为原来2倍),所以,元素的位置要么是在原位置,要么是在原位置再移动2次幂的位置。
例如我们从16扩展为32时,具体的变化如下所示:
因此元素在重新计算hash之后,因为n变为2倍,那么n-1的mask范围在高位多1bit(红色),因此新的index就会发生这样的变化:
因此,我们在扩充HashMap的时候,不需要重新计算hash,只需要看看原来的hash值新增的那个bit是1还是0就好了,是0的话索引没变,是1的话索引变成“原索引+oldCap”。可以看看下图为16扩充为32的resize示意图:
这个设计确实非常的巧妙,既省去了重新计算hash值的时间,而且同时,由于新增的1bit是0还是1可以认为是随机的,因此resize的过程,均匀的把之前的冲突的节点分散到新的bucket了。
final Node[] resize() {
Node[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node[] newTab = (Node[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
Node loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
} 你知道get和put的原理吗?equals()和hashCode()的都有什么作用?
通过对key的hashCode()进行hashing,并计算下标( n-1 & hash),从而获得buckets的位置。如果产生碰撞,则利用key.equals()方法去链表或树中去查找对应的节点
头插法与尾插法
jdk1.7插入元素到单链表中采用头插法,jdk1.8采用的是尾插法。
- jdk1.7 插入链表的头部,有一种看法是新插入的数据被查询的概率比较大,插入到头部查询相对比较快. 但是在多线程环境中扩容可能会造成循环链表,导致CPU100%
- jdk1.8 改进:采用尾插法,在扩容时不用重新计算hash值,元素索引值的变换是有规律的.
Entry与Node
- jdk1.7 一对key,value叫做Entry
- jdk1.8 一对key,value叫做Node
为什么要重写equals和hashCode
- hashCode决定了Node/Entry在数组中的位置
- equals 在元素发生碰撞时比较使用
hashmap默认使用java.lang.Object#equals 对比的是对象的地址,hashmap对象存储堆中,地址肯定不一样,所以要根据业务实现自己的equals,然而equals判断需要,然而hashmap在判断是先判断hashCode相等后才会去执行equals.
if (p.hash == hash &&((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
....案例
public class Name {
private String first; //first name
private String last; //last name
public String getFirst() {
return first;
}
public void setFirst(String first) {
this.first = first;
}
public String getLast() {
return last;
}
public void setLast(String last) {
this.last = last;
}
public Name(String first, String last) {
this.first = first;
this.last = last;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object object) {
System.out.println("equals is running...");
Name name = (Name) object;
return first.equals(name.getFirst()) && last.equals(name.getLast());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
Name n1 = new Name("mali", "sb");
System.out.println("the hashCode of n1 : " + n1.hashCode());
map.put(n1, "yes");
Name n2 = new Name("mali", "sb");
System.out.println("the hashCode of n2 : " + n2.hashCode());
System.out.println("is the key existed? ture or false? -> "
+ map.containsKey(n2));
}
} ![]()
原文: https://rumenz.com/rumenbiji/java-hashmap-interview.html