leetcode高频题笔记之贪心算法
文章目录
- 860.柠檬水找零
- 455.分发饼干
- 121.买卖股票的最佳时机
- 122.买卖股票的最佳时机II
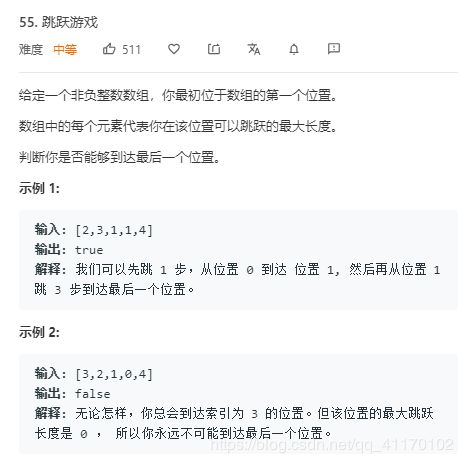
- 55.跳跃游戏
- 45.跳跃游戏II
- 435.无重叠区间
- 452.用最少数量的箭引爆气球
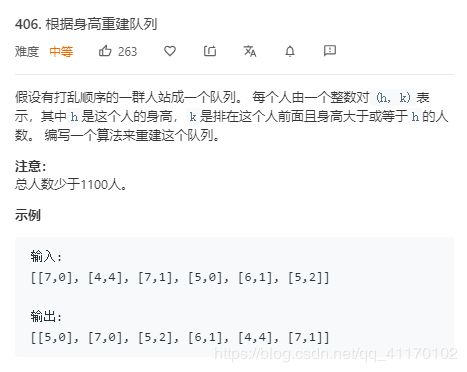
- 406.根据身高重建队列
- 605.种花问题
- 392.判断子序列
- 665.非递减数列
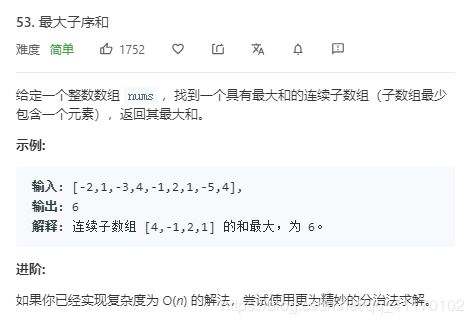
- 53.最大子序和
- 763.划分字母区间
860.柠檬水找零
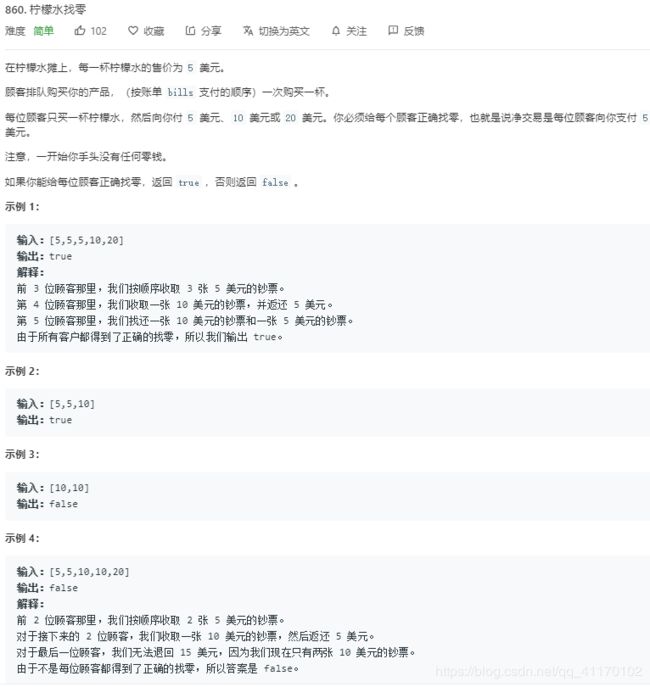
在20元找零处用到了贪心,贪10元的个数,如果有就先找10元+5元,没有再找三个5元
public class Solution {
public boolean lemonadeChange(int[] bills) {
int five = 0;
int ten = 0;
for (int bill : bills) {
if (bill == 5) five++;//支付5元
else if (bill == 10) {//支付10元
if (five > 0) {//如果有5元的,找5元
five--;
ten++;
} else {//如果没有5元的就无法找零退出
return false;
}
} else {//支付20元
if (ten > 0 && five > 0) {//如果有10元和5元的,找10元+5元
ten--;
five--;
} else if (ten == 0 && five >= 3) {//如果没有10元的有3张及以上5元的
five -= 3;
} else//如果零钱不够,退出
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
455.分发饼干
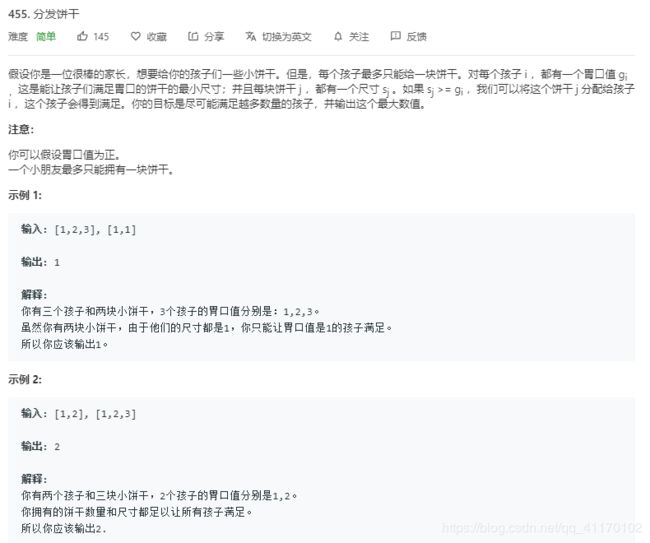
将两个数组进行排序
从最小胃口的孩子和最小的饼干开始比较,如果不满足饼干后移一位,如果满足计数加一,饼干和小孩都后移一位
public class Solution {
public int findContentChildren(int[] g, int[] s) {
Arrays.sort(g);
Arrays.sort(s);
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int count = 0;
while (i < g.length && j < s.length) {
if (g[i] <= s[j]) {
count++;
i++;
j++;
} else {
j++;
}
}
return count;
}
}
121.买卖股票的最佳时机
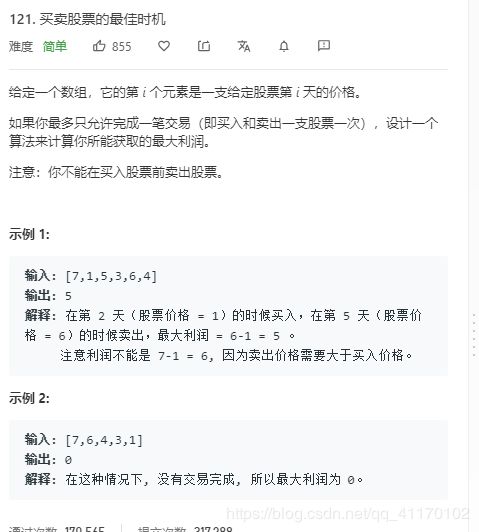
遍历数组,如果值小于当前最小值更换当前最小值,如果值大于当前最小值和最小值做差更新最大差
public class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if (prices.length == 0) return 0;
int max = 0;
int minPrice = prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
if (prices[i] < minPrice) minPrice = prices[i];
else max = Math.max(prices[i] - minPrice, max);
}
return max;
}
}
122.买卖股票的最佳时机II
public class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prices.length - 1; i++) {
if (prices[i] < prices[i + 1]) res += prices[i + 1] - prices[i];
}
return res;
}
}
55.跳跃游戏
采用从后往前的贪心算法
设置一个变量为endReachable初始化为最后位置
从后往前遍历数组,如果nums[i] + i >= endReachable
说明从i位置可以到达endReachable,于是将endReachable设置为i
遍历完数组,如果endReachable == 0,说明从第一个位置可以到达endReachable,而通过各个endReachable能到达最后位置,所以就能到达
public class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null) return false;
int endReachable = nums.length - 1;
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (nums[i] + i >= endReachable) {
endReachable = i;
}
}
return endReachable == 0;
}
}
从前往后的贪心算法
如下图,开始的位置是 2,可跳的范围是橙色的。然后因为 3 可以跳的更远,所以跳到 3 的位置。
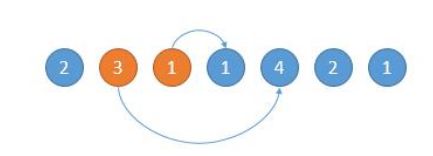
如下图,然后现在的位置就是 3 了,能跳的范围是橙色的,然后因为 4 可以跳的更远,所以下次跳到 4 的位置。
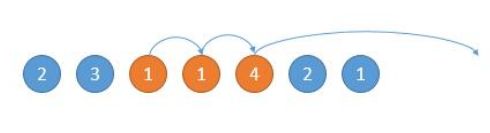
如果发生endReachable < i,即出现了0,且0无法跳过,则不能到达最后位置,返回
我们令
- endReachable 为当前能跳的边界值
- maxPosition能跳的这几个点能跳到的最远位置
public class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
int endReachable = 0;//一步到达的边界值
int maxPosition = 0;//在范围内可以到达的最远你的值
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
//出现0了,且还跳不过的那种,不能到达最后
if (endReachable < i) return false;
maxPosition = Math.max(maxPosition, nums[i] + i);
if (i == endReachable) {
endReachable = maxPosition;
}
}
return maxPosition >= nums.length - 1;
}
}
45.跳跃游戏II
正向的进行贪心
如下图,开始的位置是 2,可跳的范围是橙色的。然后因为 3 可以跳的更远,所以跳到 3 的位置。

如下图,然后现在的位置就是 3 了,能跳的范围是橙色的,然后因为 4 可以跳的更远,所以下次跳到 4 的位置。

循环为什么到nums.length - 1就停止了,因为
if (i == endReachable) {
endReachable = maxPosition;
steps++;
}
这一步的判断,如果最远步数刚好跳到了最后一个点,setps会多加一次,如案例[2,3,1,1,4]的第二步可以到最后位置,如果遍历到nums.length - 1,则上述代码会执行三次,结果为3
我们令
- endReachable 为当前能跳的边界值
- maxPosition能跳的这几个点能跳到的最远位置
- steps跳了的步数
public class Solution {
public int jump(int[] nums) {
int endReachable = 0;//一步到达的边界值
int maxPosition = 0;//在范围内可以到达的最远你的值
int steps = 0;//步数
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
maxPosition = Math.max(maxPosition, nums[i] + i);
if (i == endReachable) {
endReachable = maxPosition;
steps++;
}
}
return steps;
}
}
435.无重叠区间
- 将数组按结尾升序排列
- 找出共有多少个没有重叠的区域,记为count
- 用
总数-count得到需要移除的数目
public class Solution {
public int eraseOverlapIntervals(int[][] intervals) {
if (intervals == null || intervals.length == 0) return 0;
//将数组按区间结尾升序排列
Arrays.sort(intervals, new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return o1[1] - o2[1];
}
});
//第一段的结尾
int x_end = intervals[0][1];
//至少有1段
int count = 1;
for (int[] cur : intervals) {
if (cur[0] >= x_end) {
x_end = cur[1];
count++;
}
}
return intervals.length - count;
}
}
452.用最少数量的箭引爆气球
问题读起来听绕口的,仔细分析后其实就是求:不重叠区间的个数
与无重叠区间问题中的求不重叠区间 个数有一点点不同,边界值可以取等号,如[1,2]和[2,3]是存在重叠的
所以cur[0] >= x_end的条件需要改成cur[0] > x_end
public class Solution {
//问题转化为:求独立区间的个数
public int findMinArrowShots(int[][] points) {
if (points.length == 0) return 0;
Arrays.sort(points, new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return o1[1] - o2[1];
}
});
//独立区间个数,至少有一个
int count = 1;
//第一个气球的x_end
int x_end = points[0][1];
for (int[] cur : points) {
if (cur[0] > x_end) {
count++;
x_end = cur[1];
}
}
return count;
}
}
406.根据身高重建队列
首先,将数组按身高降序排列,如果身高相同的按k大小升序排列
然后,按照k的大小进行插入
下插入的最大的数字是符合k的定义的,再插入次大的数字,最大的数字后移,因为小的数在大的数面前是看不见的,所以不影响大的数的k的定义,因为是由大到小排列的,所以可以直接插入
public class Solution {
public int[][] reconstructQueue(int[][] people) {
if (people == null || people.length == 0 || people[0].length == 0) return people;
///身高按降序,身高相同时,次数按升序
Arrays.sort(people, new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return o1[0] == o2[0] ? o1[1] - o2[1] : o2[0] - o1[0];
}
});
//插入
List<int[]> queue = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] p : people) {
queue.add(p[1], p);
}
return queue.toArray(new int[queue.size()][]);
}
}
605.种花问题
贪心+常数优化
依次遍历数组,如果不为1,判断求一个数和后一个数是否都为0,如果是将值改为1,并计数+1,当计数等于n时就退出不再继续
public class Solution {
public boolean canPlaceFlowers(int[] flowerbed, int n) {
int len = flowerbed.length;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len && count < n; i++) {
if (flowerbed[i] == 1) continue;
int pre = i == 0 ? 0 : flowerbed[i - 1];
int next = i == len - 1 ? 0 : flowerbed[i + 1];
if (pre == 0 && next == 0) {
flowerbed[i] = 1;
count++;
}
}
return count == n;
}
}
392.判断子序列

遍历s,将s的字符在t中进行匹配,每次匹配从上一个匹配到的数的后一位开始,如果出现没有匹配到,则不是子串
public class Solution {
public boolean isSubsequence(String s, String t) {
int index = -1;
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
index = t.indexOf(c, index + 1);
if (index == -1) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
665.非递减数列

依次遍历数组,如果nums[i] < nums[i - 1],则需要进行修改,修改的情况有两种
- 修改nums[i]的值,判断一下nums[i-2]是否大于nums[i],如果大于,说明nums[i]才是错误的,将值改为nums[i-1]的值
- 修改nums[i-1]的值,将nums[i]赋值给nums[i-1]
public class Solution {
public boolean checkPossibility(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length < 2) return true;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length && count < 2; i++) {
if (nums[i] >= nums[i - 1]) continue;
count++;
if (i - 2 >= 0 && nums[i] < nums[i - 2]) {
nums[i] = nums[i - 1];
} else {
nums[i - 1] = nums[i];
}
}
return count <= 1;
}
}
53.最大子序和
public class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int curMax = nums[0];
int trueMax = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
curMax = Math.max(nums[i], curMax + nums[i]);
trueMax = Math.max(curMax, trueMax);
}
return trueMax;
}
}
763.划分字母区间
将每个字母的最后一次出现下标存放在last数组中
依次遍历字符串,并更新访问过的字符的最大last值
当遍历到i==last时,说明一个区域划分完了,记录位置并存储
public class Solution {
public List<Integer> partitionLabels(String S) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
int[] last = new int[26];
//记录每个字母最后出现的位置
for (int i = 0; i < S.length(); i++) {
last[S.charAt(i) - 'a'] = i;
}
int curend = 0;
int newfirst = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < S.length(); i++) {
curend = Math.max(curend, last[S.charAt(i) - 'a']);
if (i == curend) {
res.add(i - newfirst + 1);
newfirst = i + 1;
}
}
return res;
}
}