学习记录之三维重建1:sfm稀疏点云重建的实现
- 重建结果
- 多目三维重建
- 重建流程
- 各函数接口
- Bundle Adjustment
- 代码片段
本文讲述 多目重建及其 BA优化的实现,原理就不赘述了,可移步大佬博客学习( 传送门1)。对于新人小白来说需要提前学习的知识为相机小孔成像模型,几种常用的特征点提取算法、几种常用的特征点匹配算法、Lowe’s Ratio Test 、RANSAC的作用等,关于三维重建的相关知识大佬博客里都有很清晰的讲解。
本文先展示重建结果,再对多目重建的流程进行介绍,并分别简述了各个重要接口,最后介绍了点云优化过程。
重建结果
这里使用的是手机拍摄的图片进行重建,共拍摄所得8张图片(注意在拍摄时图片间必须要有视角重叠,旋转角度不能太大,拍摄张数根据自己的需求决定,如果要重建结果比较完整,拍摄图片的张数越多越好,当然了这样消耗的时间也会变多),如图为我使用的数据集。
下面分别为SFM和PMVS的重建结果。

多目三维重建
重建流程
多目三维重建可从一系列图片(可有序,可无序,本文为无序)重建出场景的三维结构,其分别需要经历特征提取、特征匹配、点云初始化、点云融合这四个步骤,程序以python-opencv为基础进行编写,其流程如图2所示。
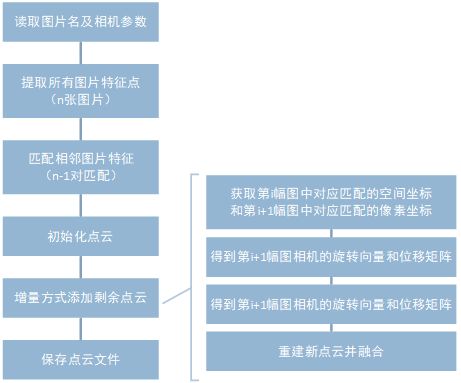
- 在重建最开始,毫无疑问需要读取待重建图片,这里读取其文件路径;同时还需要读取在相机标定过程中生成的相机内参,用于后续重建过程。
- 接下来对所有图片进行特征提取,这里提取的是AKAZE特征点(之较SIFT速度更快,效果也不错),保存所有图片的特征点及对应的描述子和颜色信息,这里通过三个numpy数组保存。
- 特征提取之后需要进行特征匹配,本文新点云生成时使用了solvePnPRANSAC方法,因此这里对相邻图像进行匹配,共N-1个匹配对。
- 在三维重建中,使用增量法添加后续点云。以第一个相机为基准,后续所有相机都是相对于相机1来说的。首先根据相机1和相机2初始化点云。
- 如何增量式添加后续点云是多目三维重建的关键,本文使用opencv的triangulatePoints函数进行点云的重建,该函数需要两个相机的旋转矩阵和位移矩阵,因此问题的关键就转变为获取哪两个相机的旋转矩阵和位移矩阵。有两个选择,1) 既然以第一个相机为基准,那后续所有相机都与第一个相机匹配,从而获得R,T 。2) 相邻两个相机匹配,获得相机i+1相对于i的R和T,由递推关系可知道第i个相机相对于相机1的位置,那么第i+1个相机相对于相机1的位置也可以知道。但是这两个选择都不可靠,对于选择1)来说,相机1与相机2,相机1与相机3…相机1与相机n,由于相机1与相机n其图片差异可能非常法,他们之间几乎没有匹配,因此选择1)不可行;对于选择2)来说,根据他itui关系,其旋转矩阵是可以求出的,但是因为比例放缩问题,其平移矩阵无法求出。本文使用solvePnPRANSAC函数,利用相机i和相机i+1匹配对中相机i对应点已经求出的空间坐标和相机i+1对应点的像素坐标,可以求出相机i+1相对于相机1的R和T,从而可以求出相机i和相机i+1匹配对中生成的新点云,再进行点云融合。
- 点云计算后,需要保存相关文件用于后续操作,这里保存其空间结构和对应颜色信息的numpy文件。同时还编写了ply文件保存程序,用于生成相应的三维文件,可使用三维显示软件打开。
各函数接口
- 特征提取extract_feathers():
该部分提取所有图片的SIFT特征点,并保留相应的特征描述子和颜色信息,各信息在列表中的位置与图片序号相对应。 - 特征匹配match_feathers():
这里使用FLANNE算法对两图片关键地进行匹配(FLANNE更适合数据量大时),使用Lowe的错误匹配过滤方法保留可用匹配。 - 对所有相邻图片进行特征匹配match_all_feather():
根据后续增量式添加点云的需要,需要对相邻图片进行特征匹配,循环调用N-1次函数2即可。 - 计算外参 find_transform():
根据极线约束与本征矩阵计算原理,使用cv2.findEssentialMat函数计算本征矩阵,随后使用cv2.recoverPose函数恢复相机外参,即R、T,并保存mask内点标记。 - 三维重建reconstruction():
利用函数4已经可以得到各个相机的R和T,根据R、T计算出相应的投影矩阵P(P=K[R T]),再调用cv2.triangulatePoints函数计算出空间点。注意,该三角化函数第三、四个参数的尺寸为2N,需要各个像素坐标的构成的矩阵转置;该函数需要将输入参数都转化为float型;该函数输出为4维齐次坐标系表示的空间点,尺寸为4N,同样需要提取出各个空间点的三维坐标。 - 获取匹配点坐标/颜色信息get_matched_points():
该函数从所有特征点中选择存在匹配对的特征点,保存其坐标及颜色信息。 - 获取内点坐标/颜色信息maskout_color():
在函数7获取匹配点的基础之上,根据函数4的mask内点标记,保存内点的坐标及颜色信息。 - 初始化点云init_structure():
初始化点云即根据前两幅图片进行双目三维重建得到初始点云,多目重建中从第三张图片开始也都是利用相同的方法进行双目重建生成新的点云再累加到该初始点云上。其流程图如图3所示。
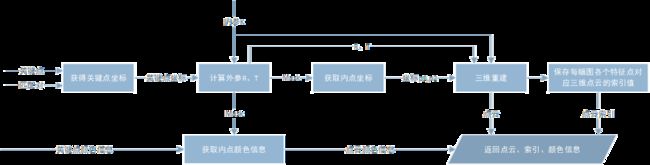
- 获取空间点和像素点用于solvePnPRansac get_objpoints_and_imgpoints():
solvePnPRansac函数需要第i幅图片的空间点及对应匹配的第i+1幅图片的像素点,用于计算第i+1幅图片的相机位置,本函数获取所需空间点和像素点。 - 点云融合fusion_structure():
增量式三维重建需要对新生成的点云进行融合,对于匹配对中的每一个新生成的点:如果该点已经存在于之前点云,则无需加入新点,只需要给第i+1幅图相应的特征点标记索引即可;如果该点不存在于之前的点云,则加入该点,并对第i幅图和第i+1幅图相应的特征点都标记索引。
Bundle Adjustment
在上面一个小结中,已经完成了多目三维重建,实现了从多张照片中恢复场景结构的功能,但是计算结果和实际坐标之间仍然存在一些误差,随着图片数量的增多,这个误差也就越来越大,BA就是用来优化这个误差的。
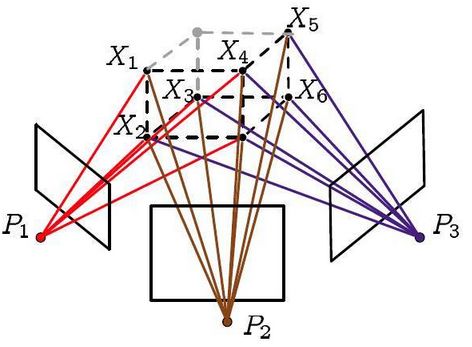
- 名称来源:Bundle Adjustment也叫光束平差法,所谓bundle,来源于bundle of light,其本意就是指的光束,这些光束指的是三维空间中的点投影到像平面上的光束,而重投影误差正是利用这些光束来构建的,因此称为光束法。如图4所示,图中带颜色的线表示的就是光束。
-
重投影误差:上面提到,可利用这些光束计算重投影误差。在重建过程中有两次“投影”过程:第一次投影是拍摄时进行的,其投影结果就是照片本身;第二次投影就是“重投影”,是根据之前计算出的内外参数、空间点坐标计算出的对应点的像素坐标。同一个空间点的两次投影的像素差值就是重投影误差。
-
算法模型:BA其本质是一个非线性优化算法,其目的是最小重投影误差,算法模型如下所示:
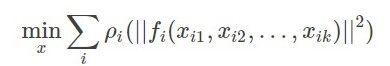
其中xij为需要优化的参数,BA中指的是点云坐标;f(x)为重投影误差;ρ为损失函数。 -
算法流程:之前实现的三维重建过程无需改动,只需要在生成点云之后加入BA过程即可。这里通过两个过程进行点云优化,一是删除重映射误差大的点,二则是BA优化过程,使用的是scipy.optimize库中的least_squares方法。
代码片段
这里为SFM主函数实现代码,完整版代码在我的GitHub中,在我的项目中是通过GUI界面调用相关重建接口的,因此在使用时注意文件所在位置。
def sfm_rec():
image_dir = rec_config.image_dir + '/'
image_names = glob.glob(image_dir+'*.jpg') # 读取图片本身的名字
image_names = sorted(image_names)
with open("../project_name.txt", "r") as f:
project_name = f.read()
K = np.load('../calibration/camera_params/' + project_name + '/K.npy')
# 提取特征点、特征匹配
print('提取所有图片特征点')
keypoints_for_all, descriptors_for_all, colors_for_all = extract_feathers(image_names)
# print(colors_for_all)
print('匹配所有图片特征')
matches_for_all = match_all_feather(keypoints_for_all, descriptors_for_all)
for i in range(len(matches_for_all)):
print(len(matches_for_all[i]),end=' ')
# 初始化点云
print('\n初始化点云')
structure, correspond_struct_idx, colors, rotations, motions, projections = init_structure(K, keypoints_for_all, colors_for_all,
matches_for_all)
print("初始化点云数目:",len(structure))
# 增量方式添加剩余点云
print('增量方式添加剩余点云')
for i in tqdm(range(1, len(matches_for_all))):
# 获取第i幅图中匹配点的空间三维坐标,以及第i+1幅图匹配点的像素坐标
obj_points, img_points = get_objpoints_and_imgpoints(matches_for_all[i], correspond_struct_idx[i], structure,
keypoints_for_all[i + 1])
# solvePnPRansac得到第i+1个相机的旋转和平移
# 在python的opencv中solvePnPRansac函数的第一个参数长度需要大于7,否则会报错
# 这里对小于7的点集做一个重复填充操作,
if len(obj_points) < 7:
while len(img_points) < 7:
obj_points = np.append(obj_points, [obj_points[0]], axis=0)
img_points = np.append(img_points, [img_points[0]], axis=0)
# 得到第i+1幅图相机的旋转向量和位移矩阵
_, r, T, _ = cv2.solvePnPRansac(obj_points, img_points, K, np.array([]))
R, _ = cv2.Rodrigues(r) # 将旋转向量转换为旋转矩阵
rotations.append(R)
motions.append(T)
# 根据R T进行重建
p1, p2 = get_matched_points(keypoints_for_all[i], keypoints_for_all[i + 1], matches_for_all[i])
c1, c2 = get_matched_colors(colors_for_all[i], colors_for_all[i + 1], matches_for_all[i])
new_structure, new_proj = reconstruction(K, rotations[i], motions[i], R, T, p1, p2)
projections.append(new_proj)
# 点云融合
structure, colors, correspond_struct_idx[i], correspond_struct_idx[i + 1] = fusion_structure(matches_for_all[i],
correspond_struct_idx[
i],
correspond_struct_idx[
i + 1],
structure,
new_structure,
colors, c1)
print("新生成点云数" ,len(new_structure) , "第" , i , "次融合后点云数" , len(structure))
print(len(structure))
# BA优化
print('删除误差较大的点')
structure = delete_error_point(rotations, motions, K, correspond_struct_idx, keypoints_for_all, structure)
# 由于经过bundle_adjustment的structure,会产生一些空的点(实际代表的意思是已被删除)
# 修改各图片中关键点的索引
# 修改点云中的None为 -1
for i in range(len(structure)):
if math.isnan(structure[i][0]):
structure[i] = -1
# 修改各图片中的索引
for a in range(len(correspond_struct_idx)):
for b in range(len(correspond_struct_idx[a])):
if correspond_struct_idx[a][b] != -1:
if structure[int(correspond_struct_idx[a][b])][0] == -1:
correspond_struct_idx[a][b] = -1
else:
correspond_struct_idx[a][b] -= (np.sum(structure[:int(correspond_struct_idx[a][b])] == -1)/3)
i = 0
# 删除那些为空的点
while i < len(structure):
if structure[i][0] == -1:
structure = np.delete(structure, i, 0)
colors = np.delete(colors, i, 0)
i -= 1
i += 1
reproject_error(rotations, motions, K, correspond_struct_idx, keypoints_for_all, structure)
print('BA优化')
motions = np.array(motions)
rotations = np.array(rotations)
structure = bundle_adjustment(structure, correspond_struct_idx, motions, rotations, keypoints_for_all, K)
reproject_error(rotations, motions, K, correspond_struct_idx, keypoints_for_all, structure)
#保存Bundle.rd.out
print("点云已生成,正在保存.out文件")
# 旋转向量转化为旋转矩阵
Rotations = np.empty((len(rotations), 3, 3))
for i in range(len(rotations)):
R, _ = cv2.Rodrigues(rotations[i])
Rotations[i] = R
save_bundle_rd_out(structure, K, Rotations, motions, colors, correspond_struct_idx, keypoints_for_all)
np.save(image_dir + 'Structure', structure)
np.save(image_dir + 'Colors', colors)
np.save(image_dir + 'Projections', projections)