第一部分 设计模式概述
企业开发中,除了功能性需求(Functional Requirement)之外,非功能性需求(Non Functional Requirement)也同样重要。在非功能性需求中描述了项目的诸多系统性质量(Systemic Quality)。这些质量包括了灵活性、可维护性、可扩展性。大师编写的代码,质量往往比较高。很多新手在编写项目的同时,bug定位难、经常返工,归根结底在于:不注重设计。
如果新手与大师之间必然要有一道分水岭,那么这一道分水岭,唯系统设计这一个能力,就足以说明问题了。然而 系统设计能力,又应该怎样去提升呢?实际上不论任何行业,学习技能的诀窍不外乎三点: 守、破、离,也就是: 模仿、突破、开拓。那么首先要做的,就是模仿。
所谓设计,我们要模仿的,是前辈们在系统设计时,为我们总结好的经验;以及前辈们在系统设计时,遇到问题后,如何利用模式解决这些问题的。也就是——设计模式。
什么叫设计呢?设计的英文——Design。
在旅游之前,需要规划好出行路线;需要准备好常用药;需要打包好换洗衣服、洗漱化妆用品。
开始一天的工作之前,列好今日工作任务清单
演讲之前,写好草稿
...
以上的这些,都叫做设计。
那么程序员们所说的设计,又是什么呢?这里的设计,即OOD(Object-Oriented Design)——面向对象设计。也就是在实际地编写代码之前,先要规划好思路,不管你的思路到底有没有落到图纸上,哪怕只是打一个腹稿,这也叫做设计!
注: OOD与之对应的又有OOA(Object-Oriented Analysis)——面向对象分析,以及OOP(Object-Oriented Programming)——面向对象编程。它们之间的顺序是: 先分析;再设计;最后编码
什么又叫模式呢?模式的英文——Pattern
- 当篮球运动员带着篮球,到达了三分线的位置时,为了能够让篮球投到篮框里,手指、手臂将使用多大的力量——这已经形成了他自己的模式
- 厨师在在做菜时,要先煮米饭,再炒菜;要先把菜、肉、各类食材调料准备好,再热锅放油
- ...
这些都是生活以及工作、学习中,你去解决某些问题时,所形成的模式。
那么如何一句话概括:什么是模式?模式就是: 通用问题的通用解决方案。
RESTful接口,想必大部分的Java程序员都接触过。当我们使用大篇幅的if - else解决问题时、当我们大段大段地复制粘贴我们的代码时,我们有没有思考过,是否可以更优雅地解决这些问题呢?
本篇文章,将籍由常见的RESTful接口,为大家讲解三个设计模式:
- 装饰器模式
- 策略模式
- 简单工厂模式
第二部分 搭建开发环境
本篇使用的项目,将采用Maven + Spring Boot来搭建,其中maven配置文件及Spring Boot启动类如下
- pom.xml
4.0.0
com.itheima
sample
1.0-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.1.5.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-aop
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
- Application.java
package com.itheima;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
第三部分 装饰器模式
1 version 0.1
需求
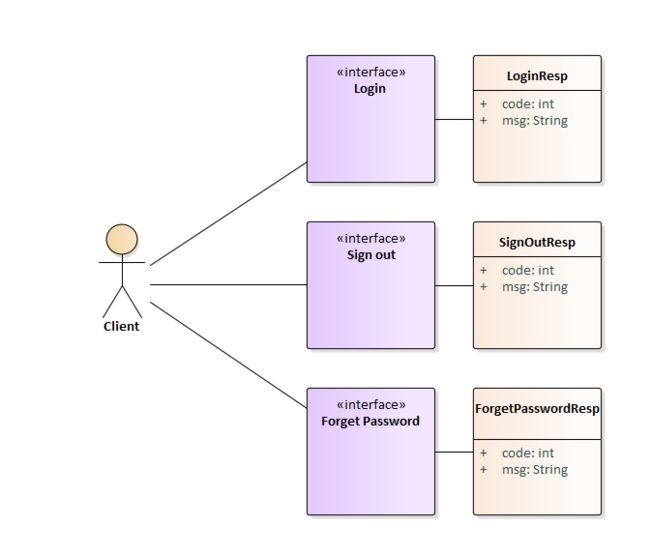
比如一个系统里有三个接口:
-
/user/login
登录
-
/user/signout
注册
-
/user/forget
忘记密码
对客户端调用后的响应信息来说,不论调用的是哪个方法,系统中都会有两个通用的字段:
-
code
响应码。
方法执行正确,即为0
方法执行如果出错,即非0值。
客户端在接收到响应码之后,如果是0,走常规流程;如果非0,走异常流程。
-
msg
响应信息
每个响应码对应一条响应信息。一般情况下是英文。
客户端可以利用国际化技术,将英文转换成中文
响应信息便于客户端调试
设计
基于以上的信息,大部分程序员们的设计将会是这样的:
- 在每个ResponseBody里面,都写上两条属性:
code、msg - 在每个接口方法里面,手动填充code,及msg
类图
代码
- UserController.java
package com.itheima.controller;
import com.itheima.response.ForgetPasswordResp;
import com.itheima.response.LoginResp;
import com.itheima.response.SignoutResp;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path = "/user")
public class UserController {
// 忘记密码接口
@RequestMapping(path = "/forget_password", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public ForgetPasswordResp forgetPassword() {
ForgetPasswordResp result = new ForgetPasswordResp();
// 业务处理
// if (用户名不存在) {
// result.code = 2230;
// result.msg = "user not found";
// return result;
// } else if (...) {
// ...
// return result;
// }
// ...
result.code = 0;
result.msg = "success";
return result;
}
// 登录接口
@RequestMapping(path = "/login", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public LoginResp login() {
LoginResp result = new LoginResp();
// 业务处理
// if (用户名不存在) {
// result.code = 2230;
// result.msg = "user not found";
// return result;
// } else if (...) {
// ...
// return result;
// }
// ...
result.code = 0;
result.msg = "success";
return result;
}
// 注册接口
@RequestMapping(path = "/signout", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public SignoutResp signout() {
SignoutResp result = new SignoutResp();
// 业务处理
// if (用户名不存在) {
// result.code = 2230;
// result.msg = "user not found";
// return result;
// } else if (...) {
// ...
// return result;
// }
// ...
result.code = 0;
result.msg = "success";
return result;
}
}
- ForgetPasswordResp.java
package com.itheima.response;
// 除了msg和code之外,无需向客户端响应任何信息
// 客户端如果接收到了code=0,则默认为接收到了重置密码的邮件
public class ForgetPasswordResp {
public String msg;
public int code;
public ForgetPasswordResp() {
}
public ForgetPasswordResp(String msg, int code) {
this.msg = msg;
this.code = code;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ForgetPasswordResp{" +
"msg='" + msg + '\'' +
", code=" + code +
'}';
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
}
- LoginResp.java
package com.itheima.response;
public class LoginResp {
public String token;
public String msg;
public int code;
public LoginResp() {
}
public LoginResp(String token, String msg, int code) {
this.token = token;
this.msg = msg;
this.code = code;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "LoginResp{" +
"token='" + token + '\'' +
", msg='" + msg + '\'' +
", code=" + code +
'}';
}
public String getToken() {
return token;
}
public void setToken(String token) {
this.token = token;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
}
- SignoutResp.java
package com.itheima.response;
public class SignoutResp {
public String token;
public String msg;
public int code;
public SignoutResp() {
}
public SignoutResp(String token, String msg, int code) {
this.token = token;
this.msg = msg;
this.code = code;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SignoutResp{" +
"token='" + token + '\'' +
", msg='" + msg + '\'' +
", code=" + code +
'}';
}
public String getToken() {
return token;
}
public void setToken(String token) {
this.token = token;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
}
问题
接口约束如果想换成:
- code为200是正常值
- msg所对应的信息换成了"operate success"
所有的接口函数都得重新改一遍
2 version 0.2
解决方案
- 当接口函数没有任何的异常抛出时,即默认为成功。利用
Spring切面,对所有的正常返回施加干预 - 将
code及msg抽离出来,封装成ResponseCommon。 - 所有的
Response,复用ResponseCommon。在组合复用与继承复用两个选项中,选择组合复用 - 使用了组合复用后,会破坏数据结构,利用
jackson中的JsonUnwrapped缓解
类图
代码
- UserController.java
package com.itheima.controller;
import com.itheima.response.ForgetPasswordResp;
import com.itheima.response.LoginResp;
import com.itheima.response.SignoutResp;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path = "/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping(path = "/forget_password", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public ForgetPasswordResp forgetPassword() {
ForgetPasswordResp result = new ForgetPasswordResp();
// 业务处理
// 将以下代码删除
// result.code = 0;
// result.msg = "success";
return result;
}
@RequestMapping(path = "/login", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public LoginResp login() {
LoginResp result = new LoginResp();
// 业务处理
// 将以下代码删除
// result.code = 0;
// result.msg = "success";
return result;
}
@RequestMapping(path = "/signout", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public SignoutResp signout() {
SignoutResp result = new SignoutResp();
// 业务处理
// 将以下代码删除
// result.code = 0;
// result.msg = "success";
return result;
}
}
- ForgetPasswordResp.java
package com.itheima.response;
// 除了msg和code之外,无需向客户端响应任何信息
// 客户端如果接收到了code=0,则默认为接收到了重置密码的邮件
public class ForgetPasswordResp {
public ResponseCommon responseCommon;
public ForgetPasswordResp() {
}
public ForgetPasswordResp(ResponseCommon responseCommon) {
this.responseCommon = responseCommon;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ForgetPasswordResp{" +
"responseCommon=" + responseCommon +
'}';
}
public ResponseCommon getResponseCommon() {
return responseCommon;
}
public void setResponseCommon(ResponseCommon responseCommon) {
this.responseCommon = responseCommon;
}
}
- LoginResp.java
package com.itheima.response;
public class LoginResp {
public String token;
public ResponseCommon responseCommon;
public LoginResp() {
}
public LoginResp(String token, ResponseCommon responseCommon) {
this.token = token;
this.responseCommon = responseCommon;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "LoginResp{" +
"token='" + token + '\'' +
", responseCommon=" + responseCommon +
'}';
}
public String getToken() {
return token;
}
public void setToken(String token) {
this.token = token;
}
public ResponseCommon getResponseCommon() {
return responseCommon;
}
public void setResponseCommon(ResponseCommon responseCommon) {
this.responseCommon = responseCommon;
}
}
- SignoutResp.java
package com.itheima.response;
public class SignoutResp {
public String token;
public ResponseCommon respnoseCommon;
public SignoutResp() {
}
public SignoutResp(String token, ResponseCommon respnoseCommon) {
this.token = token;
this.respnoseCommon = respnoseCommon;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SignoutResp{" +
"token='" + token + '\'' +
", respnoseCommon=" + respnoseCommon +
'}';
}
public String getToken() {
return token;
}
public void setToken(String token) {
this.token = token;
}
public ResponseCommon getRespnoseCommon() {
return respnoseCommon;
}
public void setRespnoseCommon(ResponseCommon respnoseCommon) {
this.respnoseCommon = respnoseCommon;
}
}
- ResponseCommon.java
package com.itheima.response;
public class ResponseCommon {
private String msg;
private int code;
public ResponseCommon() {
}
public ResponseCommon(String msg, int code) {
this.msg = msg;
this.code = code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
}
- ResponseCommoneAssembler.java
package com.itheima.config;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import com.itheima.response.ResponseCommon;
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpRequest;
import org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpResponse;
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseBodyAdvice;
@ControllerAdvice
public class ResponseCommonAssembler implements ResponseBodyAdvice问题
回过头再查看一下ForgetPasswordResp.java,除了一个responseCommon属性之外,再无其它;对于UserController.java中的forgetPassword接口方法,也无需处理其他的业务。非要给它安排一个ForgetPasswordResp响应体,是不是多此一举?
3 version 0.3
按正常的套路,把方法的返回值改成void就可以了。但是在ResponseCommonAssembler中,我们响应体所有的属性,找到ResponseCommon字段,再将0和success填充进去。把响应体改成了void之后,就没有ResponseCommon字段了,怎么玩?
解决方案
在ResponseCommonAssembler中,添加"函数返回类型是否为void"的条件判断,直接创建一个新的ResponseCommon对象,将code填充为0,将msg填充为"success",并将这个对象直接返回。
代码
- UserController.java
package com.itheima.controller;
import com.itheima.response.ForgetPasswordResp;
import com.itheima.response.LoginResp;
import com.itheima.response.SignoutResp;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path = "/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping(path = "/forget_password", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public void forgetPassword() {
// 业务处理
// 将以下代码删除
// result.code = 0;
// result.msg = "success";
}
@RequestMapping(path = "/login", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public LoginResp login() {
LoginResp result = new LoginResp();
// 业务处理
// 将以下代码删除
// result.code = 0;
// result.msg = "success";
return result;
}
@RequestMapping(path = "/signout", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public SignoutResp signout() {
SignoutResp result = new SignoutResp();
// 业务处理
// 将以下代码删除
// result.code = 0;
// result.msg = "success";
return result;
}
}
- ResponseCommonAssembler.java
package com.itheima.config;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import com.itheima.response.ResponseCommon;
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpRequest;
import org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpResponse;
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseBodyAdvice;
@ControllerAdvice
public class ResponseCommonAssembler implements ResponseBodyAdvice4 version 1.0
现在的问题是,我们并不能保证,客户端的每一次请求,都会得到一个成功的响应。那么当用户请求出问题时,又该如何解决呢?
解决方案
异常,并不是系统或者框架才能够使用的。当用户请求后,
参数填写错误、用户名不存在等错误亦可使用异常机制处理。依然利用
Spring切面,对所有的异常返回施加干预
代码
- GlobalExceptionHandler.java
package com.itheima.config;
import com.itheima.exception.ExceptionCommon;
import com.itheima.response.ResponseCommon;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
/**
* 异常拦截器
*
*/
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
private final static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GlobalExceptionHandler.class);
/**
* 自定义异常
*
* @see com.itheima.exception.*
* @param req
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = ExceptionCommon.class)
@ResponseBody
public ResponseCommon commonExceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest req, ExceptionCommon e) {
return e.getResponseCommon();
}
}
- ExceptionCommon.java
package com.itheima.exception;
import com.itheima.response.ResponseCommon;
public class ExceptionCommon extends Exception {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3867913775058901502L;
private ResponseCommon responseCommon;
public ExceptionCommon() {
super();
}
public ExceptionCommon(ResponseCommon responseCommon) {
super();
this.responseCommon = responseCommon;
}
public ExceptionCommon(Integer respCode, String respMsg) {
super();
responseCommon = new ResponseCommon();
responseCommon.setCode(respCode);
responseCommon.setMsg(respMsg);
}
public ResponseCommon getResponseCommon() {
return responseCommon;
}
public void setResponseCommon(ResponseCommon responseCommon) {
this.responseCommon = responseCommon;
}
}
- UserController.java
package com.itheima.controller;
import com.itheima.response.ForgetPasswordResp;
import com.itheima.response.LoginResp;
import com.itheima.response.SignoutResp;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path = "/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping(path = "/forget_password", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public void forgetPassword() throws ExceptionCommon {
// 异常校验,如果校验失败,则抛出异常
// 业务处理
}
@RequestMapping(path = "/login", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public LoginResp login() throws ExceptionCommon {
LoginResp result = new LoginResp();
// 异常校验,如果校验失败,则抛出异常
// 业务处理
return result;
}
@RequestMapping(path = "/signout", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public SignoutResp signout() throws ExceptionCommon {
SignoutResp result = new SignoutResp();
// 异常校验,如果校验失败,则抛出异常
// 业务处理
return result;
}
}
5 装饰器模式
科普一下装饰器模式吧
动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责。——《设计模式 - 可复用面向对象软件的基础》
第四部分 策略模式 & 简单工厂
1 version 0.1
需求
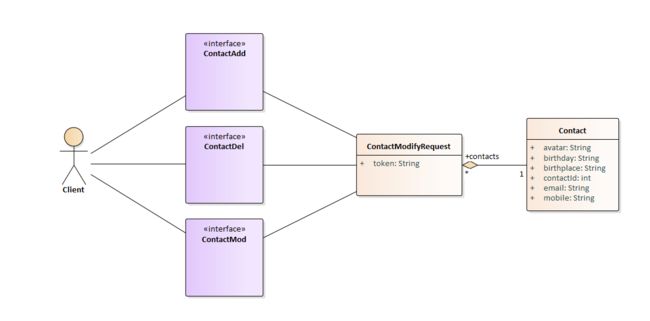
- 制作一个企业通讯录,用户可以对通讯录信息进行增删改查
设计
想必大部分的程序员在设计功能的时候,直接把增删改查做成四个接口方法了。设计得再稍微复杂一点,可以批量增、批量删、批量改。
查询功能,用户提交的请求数据,只需要带一个token过来就可以了。所以暂只考虑增、删、改功能
类图
代码
- ManageController.java
package com.itheima.controller;
import com.itheima.exception.ExceptionCommon;
import com.itheima.request.Contact;
import com.itheima.request.ContactModifyRequest;
import com.itheima.validation.LogicValidation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path = "/manage")
public class ManageController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private ContactMapper contactMapper;
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(path = "/contact_add", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public void contactAdd(@RequestBody ContactModifyRequest model) throws ExceptionCommon {
User user = userMapper.queryByToken(model.getUserToken());
// 判断用户已存在,若不存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateUserNotNull(user);
// 判断用户是管理员,若不是管理员,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateUserIsManager(user);
for (Contact contact : model.getContacts()) {
// 判断被添加的用户不存在,若已存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateContactContactIsNull(contact);
contactMapper.addContact(contact);
}
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(path = "/contact_del", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public void contactDel(@RequestBody ContactModifyRequest model) throws ExceptionCommon {
User user = userMapper.queryByToken(model.getUserToken());
// 判断用户已存在,若不存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateUserNotNull(user);
// 判断用户是管理员,若不是管理员,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateUserIsManager(user);
for (Contact contact : model.getContacts()) {
// 判断被添加的用户已存在,若不存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateContactContactNotNull(contact);
contactMapper.delContact(contact);
}
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(path = "/contact_mod", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public void contactMod(@RequestBody ContactModifyRequest model) throws ExceptionCommon {
User user = userMapper.queryByToken(model.getUserToken());
// 判断用户已存在,若不存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateUserNotNull(user);
// 判断用户是管理员,若不是管理员,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateUserIsManager(user);
for (Contact contact : model.getContacts()) {
// 判断被添加的用户已存在,若不存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateContactContactNotNull(contact);
contactMapper.modContact(contact);
}
}
}
- Contact.java
package com.itheima.request;
public class Contact {
private String contactId;
private String mobile;
private String email;
private String avatar;
private String birthday;
private String birthplace;
public Contact() {
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Contact{" +
"userId='" + contactId + '\'' +
", mobile='" + mobile + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", avatar='" + avatar + '\'' +
", birthday='" + birthday + '\'' +
", birthplace='" + birthplace + '\'' +
'}';
}
public String getContactId() {
return contactId;
}
public void setContactId(String contactId) {
this.contactId = contactId;
}
public String getMobile() {
return mobile;
}
public void setMobile(String mobile) {
this.mobile = mobile;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getAvatar() {
return avatar;
}
public void setAvatar(String avatar) {
this.avatar = avatar;
}
public String getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(String birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getBirthplace() {
return birthplace;
}
public void setBirthplace(String birthplace) {
this.birthplace = birthplace;
}
}
- ContactModifyRequest.java
package com.itheima.request;
import java.util.List;
public class ContactModifyRequest {
private String token;
private List contacts;
public ContactModifyRequest() {
}
public ContactModifyRequest(String token, List contacts) {
this.token = token;
this.contacts = contacts;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ContactModifyRequest{" +
"token='" + token + '\'' +
", contacts=" + contacts +
'}';
}
public String getToken() {
return token;
}
public void setToken(String token) {
this.token = token;
}
public List getContacts() {
return contacts;
}
public void setContacts(List contacts) {
this.contacts = contacts;
}
}
2 version 0.2
问题
- 对于客户端,通讯录信息的增删改,完全可以调用同一个接口。目前让客户端调用了多个接口
- 对于服务端,增删改接口的大部分业务代码是重合的。完全可以合并到一起
解决方案
- 在Contact类中,添加一个枚举值,由客户端决定:此条Contact是添加、还是修改、或者删除
- 在ManageController中,合并增、删、改的接口方法为一个
- 在ManageController中,遍历Contact,判断枚举是什么,进入增删改流程
设计
代码
- Contact.java
package com.itheima.request;
public class Contact {
private String contactId;
private String mobile;
private String email;
private String avatar;
private String birthday;
private String birthplace;
private String operationType;
public Contact() {
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Contact{" +
"userId='" + contactId + '\'' +
", mobile='" + mobile + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", avatar='" + avatar + '\'' +
", birthday='" + birthday + '\'' +
", birthplace='" + birthplace + '\'' +
", operationType='" + operationType + '\'' +
'}';
}
public String getContactId() {
return contactId;
}
public void setContactId(String contactId) {
this.contactId = contactId;
}
public String getMobile() {
return mobile;
}
public void setMobile(String mobile) {
this.mobile = mobile;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getAvatar() {
return avatar;
}
public void setAvatar(String avatar) {
this.avatar = avatar;
}
public String getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(String birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getBirthplace() {
return birthplace;
}
public void setBirthplace(String birthplace) {
this.birthplace = birthplace;
}
public String getOperationType() {
return operationType;
}
public void setOperationType(String operationType) {
this.operationType = operationType;
}
}
- ManageController.java
package com.itheima.controller;
import com.itheima.exception.ExceptionCommon;
import com.itheima.request.Contact;
import com.itheima.request.ContactModifyRequest;
import com.itheima.validation.LogicValidation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path = "/manage")
public class ManageController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private ContactMapper contactMapper;
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(path = "/contact_mod", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public void contactMod(@RequestBody ContactModifyRequest model) throws ExceptionCommon {
User user = userMapper.queryByToken(model.getUserToken());
// 判断用户已存在,若不存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateUserNotNull(user);
// 判断用户是管理员,若不是管理员,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateUserIsManager(user);
for (Contact contact : model.getContacts()) {
if (contact.getOperationType().equals("add")) {
// 判断被添加的用户不存在,若已存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateContactContactIsNull(contact);
contactMapper.addContact(contact);
} else if (contact.getOperationType().equals("del")) {
// 判断被添加的用户已存在,若不存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateContactContactNotNull(contact);
contactMapper.delContact(contact);
} else /* if (contact.getOperationType().equals("mod")) */ {
// 判断被添加的用户已存在,若不存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateContactContactNotNull(contact);
contactMapper.modContact(contact);
}
}
}
}
3 version 0.3
问题
-
if - else搞得这么多,菜鸟们总是很愿意这么搞,经常会一个方法写得很长。可维护性、可读性都会很差。
解决方案
利用
策略模式,将每一个条件分支封装成策略。利用
简单工厂模式,由所有策略类的父类,根据操作类别,创建具体策略。
类图
代码
- ManageController.java
package com.itheima.controller;
import com.itheima.controller.strategy.AbstractContactModifyStrategy;
import com.itheima.exception.ExceptionCommon;
import com.itheima.request.Contact;
import com.itheima.request.ContactModifyRequest;
import com.itheima.validation.LogicValidation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path = "/manage")
public class ManageController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private ContactMapper contactMapper;
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(path = "/contact_mod", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public void contactMod(@RequestBody ContactModifyRequest model) throws ExceptionCommon {
User user = userMapper.queryByToken(model.getUserToken());
// 判断用户已存在,若不存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateUserNotNull(user);
// 判断用户是管理员,若不是管理员,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateUserIsManager(user);
for (Contact contact : model.getContacts()) {
AbstractContactModifyStrategy strategy = AbstractContactModifyStrategy.strategyWithOperationType(contact.getOperationType());
strategy.operate(contact);
}
}
}
- AbstractContactModifyStrategy.java
package com.itheima.controller.strategy;
import com.itheima.request.Contact;
public abstract class AbstractContactModifyStrategy {
public final static AbstractContactModifyStrategy strategyWithOperationType(String operationType) throws ExceptionCommon {
if (operationType.equals("add")) {
return new AbstractContactAddStrategy();
} else if (operationType.equals("del")) {
return new AbstractContactDelStrategy();
} else /* if (operationType.equals("mod")) */ {
return new AbstractContactModStrategy();
}
}
public abstract void operate(Contact contact);
}
- ContactAddStrategy.java
package com.itheima.controller.strategy;
import com.itheima.request.Contact;
import com.itheima.validation.LogicValidation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class ContactAddStrategy extends AbstractContactModifyStrategy {
@Autowired
private ContactMapper contactMapper;
@Override
public void operate(Contact contact) throws ExceptionCommon {
// 判断被添加的用户不存在,若已存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateContactContactIsNull(contact);
contactMapper.addContact(contact);
}
}
- ContactDelStrategy.java
package com.itheima.controller.strategy;
import com.itheima.request.Contact;
import com.itheima.validation.LogicValidation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class ContactDelStrategy extends AbstractContactModifyStrategy {
@Autowired
private ContactMapper contactMapper;
@Override
public void operate(Contact contact) throws ExceptionCommon {
// 判断被添加的用户已存在,若不存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateContactContactNotNull(contact);
contactMapper.delContact(contact);
}
}
- ContactModStrategy.java
package com.itheima.controller.strategy;
import com.itheima.request.Contact;
import com.itheima.validation.LogicValidation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class ContactModStrategy extends AbstractContactModifyStrategy {
@Autowired
private ContactMapper contactMapper;
@Override
public void operate(Contact contact) throws ExceptionCommon {
// 判断被添加的用户已存在,若不存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateContactContactNotNull(contact);
contactMapper.modContact(contact);
}
}
4 version 1.0
问题
- 虽然在ManageController当中,不需要写长段的
if - else条件判断了。但是依然把if - else延迟到了AbstractContactModifyStrategy当中。即: 每添加一个策略,都需要对AbstractContactModifyStrategy进行修改
解决方案
- 在AbstractContactModifyStrategy当中,添加一个注册方法,每个AbstractContactModifyStrategy的子类,都需要调用这一个注册方法。将具体的实现类注册到AbstractContactModifyStrategy当中。
- 对于每个具体的策略类,添加static静态方法。在static静态方法中,调用父类的注册方法,将自己注册进父类中
- static静态方法只在类加载的时候才会被调用,因为本次项目使用的是Spring-Boot,直接添加类注解
@Component,当Spring扫描到此组件时,会自动加载这个类。这个类的static就会被执行了
代码
- AbstractContactModifyStrategy.java
package com.itheima.controller.strategy;
import com.itheima.request.Contact;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
public abstract class AbstractContactModifyStrategy {
private static Map> map = new HashMap<>();
public final static AbstractContactModifyStrategy strategyWithOperationType(String operationType) throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
return map.get(operationType).newInstance();
}
public final static void registerClass(String operateType, Class clz) {
map.put(operateType, clz);
}
public abstract void operate(Contact contact);
}
- ContactAddStrategy.java
package com.itheima.controller.strategy;
import com.itheima.request.Contact;
import com.itheima.validation.LogicValidation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class ContactAddStrategy extends AbstractContactModifyStrategy {
@Autowired
private ContactMapper contactMapper;
@Override
public void operate(Contact contact) {
// 判断被添加的用户不存在,若已存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateContactContactIsNull(contact);
contactMapper.addContact(contact);
}
static {
AbstractContactModifyStrategy.registerClass("add", ContactAddStrategy.class);
}
}
- ContactDelStrategy.java
package com.itheima.controller.strategy;
import com.itheima.request.Contact;
import com.itheima.validation.LogicValidation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class ContactDelStrategy extends AbstractContactModifyStrategy {
@Autowired
private ContactMapper contactMapper;
@Override
public void operate(Contact contact) {
// 判断被添加的用户已存在,若不存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateContactContactNotNull(contact);
contactMapper.delContact(contact);
}
static {
AbstractContactModifyStrategy.registerClass("del", ContactDelStrategy.class);
}
}
- ContactModStrategy.java
package com.itheima.controller.strategy;
import com.itheima.request.Contact;
import com.itheima.validation.LogicValidation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class ContactModStrategy extends AbstractContactModifyStrategy {
@Autowired
private ContactMapper contactMapper;
@Override
public void operate(Contact contact) {
// 判断被添加的用户已存在,若不存在,则抛异常(由LogicValidation负责抛异常)
LogicValidation.validateContactContactNotNull(contact);
contactMapper.modContact(contact);
}
static {
AbstractContactModifyStrategy.registerClass("mod", ContactModStrategy.class);
}
}
5 策略模式 & 工厂模式模式
- 策略模式
定义一系列的算法,把它们一个个封装起来,并且使它们可相互替换。——《设计模式 - 可复用面向对象软件的基础》
- 简单工厂模式
将“类实例化的操作”与“使用对象的操作”分开,让使用者不用知道具体参数就可以实例化出所需要的“产品”类,从而避免了在客户端代码中显式指定,实现了解耦。
本文中,第二部分 version 0.3,多条
if - else,即使用了简单工厂,用于创建策略类。
第五部分 总结
本篇介绍了三个模式: 装饰器模式、策略模式、简单工厂模式
- 利用装饰器模式,动态地为每一个响应体,添加了code及msg。
- 当无异常时,响应体填充code为0; msg为"success"
- 当有异常时,为每一个程序内部的异常,取出填充到响应体中
- 利用策略模式,为通讯录的增、删、改,分别封装了算法。
- 利用简单工厂模式,根据请求体中的枚举,生产了相应的策略。