Dubbox 基本特性之异步调用
相对比与前一个小节来说,异步调用的功能也是很实用的,现在异步化的操作是越来越多了,异步化的好处也是比较明显的,可以加快后台的处理效率,做到代码直接的解耦,Dubbo就是一个支持异步调用的RPC框架
3.2.1 异步调用的场景
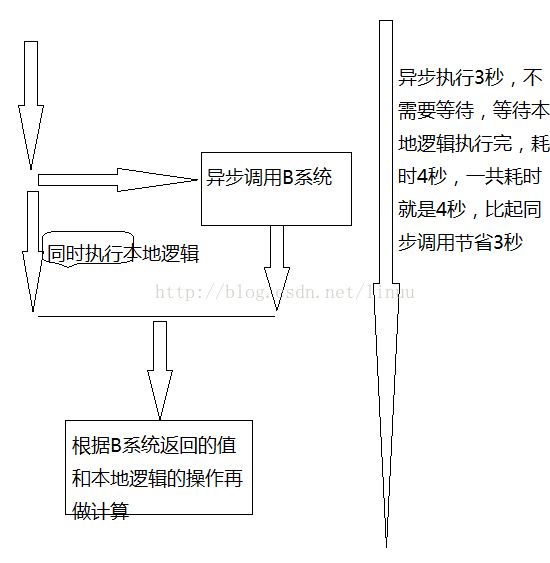
假设系统A,远程调用B系统的某个方法,这个方法与数据库的交互很多,逻辑相对复杂,正常的代码执行的时间是3秒,A系统调用完B系统之后,还需要做一些其他的逻辑操作,这个代码耗时可能需要4秒,等这个3秒的逻辑做完之后,根据B系统返回的结果再做一些其他的操作,那么同步调用的时间是3秒+4秒 = 7秒,那么一次操作的时间就是7秒
异步访问B系统:
3.2.2 同步调用的实现:
接口实现(provider和consumer端都需要)
package org.bazinga.service;
public interface AsyncInvokeService {
public Integer getResult();
}
接口实现,我们默认线程sleep三秒,3秒代表代码复杂的逻辑操作和数据库的交互的时间
package org.bazinga.service.impl;
import org.bazinga.service.AsyncInvokeService;
public class AsyncInvokeServiceImpl implements AsyncInvokeService {
public Integer getResult() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000l); //模拟复杂的逻辑操作时间和数据库交互的时间消耗
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 1;
}
}在不开启异步调用的配置的时候,spring的配置文件和普通配置是一样的spring-dubbo-provider-async.xml,需要注意的是我们线程故意睡了3秒,这边我们配置timeout的时间为4秒,否则就会调用超时:
服务提供者端的测试类:
package org.bazinga.service.test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class DubboxProviderAsyncService {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"spring-dubbo-provider-async.xml");
context.start();
Thread.sleep(2000000l);
}
}
服务消费者端的测试类:
package org.bazinga.service.test;
import org.bazinga.service.AsyncInvokeService;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class DubboConsumerAsyncService {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"spring-dubbo-consumer-async.xml");
context.start();
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int count = 0; count < 10; count++) { // 调用10次
AsyncInvokeService asyncInvokeService =
(AsyncInvokeService)context.getBean("asyncInvokeService");
Integer result = asyncInvokeService.getResult(); //wait 返回结果 等待3秒
Thread.sleep(4000l); //模拟本地复杂的逻辑操作,耗时4秒
Integer localcalcResult = 2;//本地经过4秒处理得到的计算数据是2
System.out.println(result + localcalcResult);//根据远程调用返回的结果和本地操作的值,得到结果集
}
System.out.println("call 10 times,cost time is "
+ (System.currentTimeMillis() - beginTime));
Thread.sleep(2000000l);
}
}先启动DubboxProviderAsyncService,然后再启动DubboConsumerAsyncService的main函数:
消费端的控制台打印信息是:
运行没有问题,但是调用10次,一共耗时71秒,假如改成异步调用,我们不需要等待调用返回的结果,而是在用的时候,再去获取值的话,这样会大大的提高执行的速度
3.2.3异步调用实现
异步调用的实现,很简单,现在我们修改一下配置文件,使其支持异步调用,其实配置相对比较简单,只需要在调用端的spring的配置文件中加上async=”true”,注意一定是在调用端配置该关键字,异步调用,顾名思义,就是需要告之调用者,调用之后不需要等待(Note:修改的是调用的spring配置文件spring-dubbo-consumer-async.xml)
修改消费者的测试代码,配置文件的修改只是告诉Dubbo,调用者会进行异步调用,但如何异步调用,还是需要调用者自己去实现的,实现依赖于RpcContext:
package org.bazinga.service.test;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import org.bazinga.service.AsyncInvokeService;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcContext;
public class DubboConsumerAsyncService {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"spring-dubbo-consumer-async.xml");
context.start();
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int count = 0; count < 10; count++) { // 调用10次
// AsyncInvokeService asyncInvokeService =
// (AsyncInvokeService)context.getBean("asyncInvokeService");
// Integer result = asyncInvokeService.getResult(); //wait 返回结果 等待3秒
//
// Thread.sleep(4000l); //模拟本地复杂的逻辑操作,耗时4秒
//
// Integer localcalcResult = 2;//本地经过4秒处理得到的计算数据是2
//
// System.out.println(result + localcalcResult);//根据远程调用返回的结果和本地操作的值,得到结果集
AsyncInvokeService asyncInvokeService = (AsyncInvokeService) context
.getBean("asyncInvokeService");
Integer remotingResult = asyncInvokeService.getResult(); // 不等待
Thread.sleep(4000l); // 模拟本地复杂的逻辑操作,耗时4秒
Future future = RpcContext.getContext().getFuture();
try {
remotingResult = future.get();
} catch (java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Integer localcalcResult = 2;// 本地经过4秒处理得到的计算数据是2
System.out.println(remotingResult + localcalcResult);// 根据远程调用返回的结果和本地操作的值,得到结果集
}
System.out.println("call 10 times,cost time is "
+ (System.currentTimeMillis() - beginTime));
Thread.sleep(2000000l);
}
}
关键代码就是:
Integer remotingResult = asyncInvokeService.getResult(); // 不等待Future future = RpcContext.getContext().getFuture(); 可以看出结果没有变,仍旧是3,但是调用时间变成了41秒,异步调用的好处就可以显示出来了
3.2.4本章小结
异步调用是一个很实用的功能,在一些特定的开发业务场景下,能发挥很大的作用,Dubbo对异步调用支持的比较完善,并且方便开发人员适用,需要一个简单的标签就可以完成该功能了,方便大家的对该功能的掌握。