matlab的FIR滤波器设计
1.matlab设计fir滤波器的方法
matlab可以使用fir1函数设计低通、高通、低通、带通等具有严格线性相位特性的滤波器。
fir1函数的几种语法如下:
b=fir1(n,wn);
b=fir1(n,wn,'ftype');
b=fir1(n,wn,'ftype',window)
b=fir1(...,'noscale')
各个参数的含义:
- b:返回fir滤波器的单位脉冲相应,偶对称,长度为n+1;
- n:滤波器的阶数,设计出的滤波器长度为n+1;
- wn:滤波器的截止频率,取值范围0
- window:指定使用的窗函数,默认是汉明窗(Hamming),最常用的还有汉宁窗(Hanning)、布莱克曼窗(Blackman)、凯赛窗(Kaiser);
- noscale:指定归一化滤波器的幅度‘
2.fir1函数设计滤波器
设计滤波器,采用汉明窗,长度41(阶数40),采样频率2000hz:
- 1.低通,截至频率200hz;
- 2.高通,截至频率200hz;
- 3.带通,通带200-400hz;
- 4.带阻,阻带200-400h’z
clear all; close all; clc;
% 滤波器长度
N=41;
%采样频率
fs=2000;
%各种滤波器的特征频率
fc_lpf=200;
fc_hpf=200;
fp_bandpass=[200 400];
fc_stop=[200 400];
%以采样频率的一般,对频率归一化
wn_lpf=fc_lpf*2/fs;
wn_hpf=fc_hpf*2/fs;
wn_bandpass=fp_bandpass*2/fs;
wn_stop=fc_stop*2/fs;
%采用fir1函数设计FIR滤波器
b_lpf=fir1(N-1,wn_lpf);
b_hpf=fir1(N-1,wn_hpf,'high');
b_bandpass=fir1(N-1,wn_bandpass,'bandpass');
b_stop=fir1(N-1,wn_stop,'stop');
%求幅频响应
m_lpf=20*log(abs(fft(b_lpf)))/log(10);
m_hpf=20*log(abs(fft(b_hpf)))/log(10);
m_bandpass=20*log(abs(fft(b_bandpass)))/log(10);
m_stop=20*log(abs(fft(b_stop)))/log(10);
% 设置频率响应的横坐标单位为hz
x_f=0:(fs/length(m_lpf)):fs/2;
% 单位脉冲响应
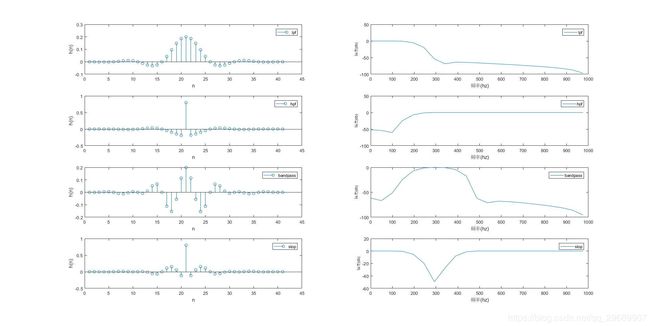
subplot(4,2,1);stem(b_lpf);xlabel('n');ylabel('h(n)');legend('lpf');
subplot(4,2,3);stem(b_hpf);xlabel('n');ylabel('h(n)');legend('hpf');
subplot(4,2,5);stem(b_bandpass);xlabel('n');ylabel('h(n)');legend('bandpass');
subplot(4,2,7);stem(b_stop);xlabel('n');ylabel('h(n)');legend('stop');
% 幅频响应
subplot(4,2,2);plot(x_f,m_lpf(1:length(x_f)));xlabel('频率(hz)');ylabel('幅度(db)','fontsize',8);legend('lpf')
subplot(4,2,4);plot(x_f,m_hpf(1:length(x_f)));xlabel('频率(hz)');ylabel('幅度(db)','fontsize',8);legend('hpf')
subplot(4,2,6);plot(x_f,m_bandpass(1:length(x_f)));xlabel('频率(hz)');ylabel('幅度(db)','fontsize',8);legend('bandpass')
subplot(4,2,8);plot(x_f,m_stop(1:length(x_f)));xlabel('频率(hz)');ylabel('幅度(db)','fontsize',8);legend('stop');
3.滤波
前面已经设计了低通,带通,高通的滤波器,根据参数设置得到了滤波器系数:
b_lpf、b_hpf、b_bandpass、b_stop
假设我们现在由原始数据xx,要对xx进行滤波,得到数据yy,在matlab应该怎么操作呢
就一句:
yy=filter(b_lpf,1,xx);