Java初学者之数组
数组
1、数组元素的默认初始化值
public class TestArray1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//对于基于基本数据类型的变量创建的数,byte,short,int,long,float
//1.对于byte short int long 而言:创建数组以后,默认值为0
int[] scores=new int[4];
scores[0] =89;
scores[3]=90;
for(int i=0;i结果如下:
89
0
0
90
89
0
0
90
0.0
1.2
0.0
a
false
false
false
A A
B B
null
D D
+
2.一维数组
一、数组通过引用操作。
二、定义一个数组变量只是给出一个内存中存放数组的地址,对数组的操作是通过引用其地址来实现的。
三、一维数组的使用
public class TestArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.如何定义一个数组
//1.1数组的声明
String[] names;//数据类型[] 数组名
int scores[];//数据类型 数组名[]
String[] title;
//1.2初始化
//第一种:静态初始化
names=new String[] {"li","liu”,"hh"};//数组名=new String[]{数据};
title=new String[] {"学渣","学霸","学神"};
//第二种:动态初始化
scores =new int[3];//数组名 = new 数据类型[数据长度]
//2.如何调用相应的数组元素:通过数组元素的下标的方式来调用
//下角标从0开始,到n-1结束。其中n表示的数组的长度
scores[0]=0;
scores[1]=99;
scores[2]=100;
//3.数组的长度:通过数组的length属性
System.out.println(names.length);//3
System.out.println(scores.length);//4
//4.如何遍历数组元素
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) {11
System.out.println("姓名:"+names[i]+" "+"成绩:"+scores[i]+" "+"称号:"+title[i]);
}
}
}
四、一维数组的内存结构

五、一维数组使用的注意点
1.声明的表示方法
int[] myInt={12,13,14};
或者
Int[] myInt;
myInt=new int[]{12,13,14};
2.数组一旦初始化,其长度不可改变。
public class TestArray2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] i=new int[] {12,13,14};
int[] j=new int[10];
for(int k=0;k结果:
12
13
14
15
16
0
0
0
0
0
六、一维数组练习题
- (1)定义类Pritimive,在类中定义一个有3个元素的boolean类型的数组t作为其成员变量。
数组元素未赋值。
定义类Array1,在Array1的main( )方法中创建Pritimive对象d,输出其成员变量t的三个元素值。练习目的:检验基本数据类型数组创建时的自动赋值。
(2)给对象d的成员变量t赋值为{true, true , true},并输出t的三个元素值。
public class TestPritimive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Pritimive的对象d
Pritimive d=new Pritimive();
//遍历d的数组元素
for(int i=0;i结果为
false
false
false
true
true
true
2. 从键盘读入学生成绩,找出最高分,并输出学生成绩等级。
成绩>=最高分-10
等级为’A’
成绩>=最高分-20
等级为’B’
成绩>=最高分-30
等级为’C’
其余
等级为’D’
提示:先读入学生人数,根据人数创建int数组,存放学生成绩。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestStudentScore {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建Scanner的对象,并从键盘获取学生的个数n
Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入学生的个数为:");
int count=s.nextInt();//count用量记录学生的个数
//2.根据输入的学生的个数n,创建一个长度为n的int型的数组
int[] scores=new int[count];
int maxScore=0;
//3.依次从键盘获取n个学生的成绩,并赋给相应的数组元素,并获取n个学生中的最高分
System.out.println("请依次输入"+count+"个学生成绩");
for(int i=0;imaxScore) {
maxScore=scores[i];
}
}
System.out.println("最高数为:"+maxScore);
//4.遍历学生成绩的数组,并根据学生成绩与最高分的差值,赋予相应的等级,并输出
for(int i=0;i=maxScore-10) {
level='A';
}
else if(scores[i]>=maxScore-20) {
level='B';
}
else if(scores[i]>=maxScore-30) {
level='C';
}
else if(scores[i]>=maxScore-40) {
level='D';
}
else {
level='E';
}
System.out.println("student"+i+" "+"score is"+" "+scores[i]+" "+"grade is"+" "+level);
}
}
}
结果为:
请输入学生的个数:
5
请输入5个成绩:
99
89
79
69
59
最高数为:99
student0 score is 99 grade is A
student1 score is 89 grade is A
student2 score is 79 grade is B
student3 score is 69 grade is C
student4 score is 59 grade is D
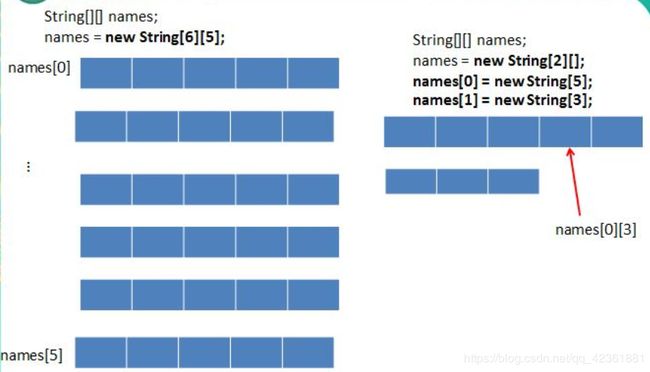
3、二维数组(多维数组)
一、二维数组的使用
public class TestArray3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] scores1=new int[10];
int[][] scores2;
String[][] names;
//1.二维数组的初始化
scores2=new int[][] {{1,2,3},{3,4,5},{6}};//静态初始化
names=new String[3][2];//动态初始化的方式一
names=new String[3][];//动态初始化的方式二
names[0]=new String[1];
names[1]=new String[2];
names[2]=new String[3];
//错误的初始化方式
//names=new String[][];
//names=new String[][5];
//2.如何来引用具体的某个元素
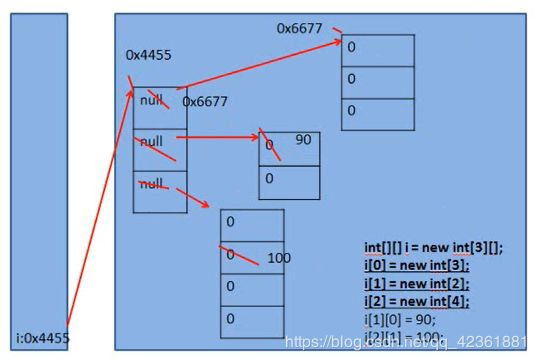
int[][] i=new int[3][2];//int[] i[]=new int[3][2];
i[1][0]=90;
i[2][1]=100;
//3.数组的长度
//二维数组的长度:length属性
System.out.println(i.length);//3
System.out.println(i[0].length);//2
System.out.println(names.length);//3
System.out.println(names[1].length);//2
//4.如何遍历二维数组
for(int m=0;m2、二维数组的内存结构
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.数组下标越界异常:java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
/* int[] i=new int[10];
i[0]=90;
i[10]=99;
*/
/* for(int m=0;m<=i.length;m++) {
System.out.println(i[m]);
}
*/
//2.空指针异常:java.lang.NullPointerException
//第一种
/* boolean[] b=new boolean[3];
b=null;//错误
System.out.println(b[0]);
*/
//第二种:
/* String[] str=new String[4];
str[3]=new String("AA");//str="AA";//要加这一行才不会出错
System.out.println(str[3].toString());
*/
//第三种:
int[][] j=new int[3][];
j[2][0]=12;//错误,不能赋值,因为行中列不确定为null
}
}
四、二维数组的练习
1、(静态初始化) : int[][]arr = new int[][]{{3,8,2},{2,7}{9,01,6}};定义一个名称为arr的二维数组,二维数组中有三个一维数组,每一个一维数组中具体元素也都已初始化,第一个一维数组ar[(0]= {3,8,2};第二个一维数组arr[1]={2,7};第三个一维数组arr[2]= {9,0,1,6};
第三个一维数组的长度表示方式: arr[2].length;
public class TestGetSum {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] m=new int[][] {{3,8,2},{2,7},{9,0,1,6}};
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i结果:
3 8 2
2 7
9 0 1 6
总和为38
2、输出杨辉三角
使用二维数组打印一个10行杨辉三角.
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
1 5 10 10 5 1
[提示1
1.第一行有1个元素,第n行有n个元素
2.每一行的第一个元素和最后一个元素都是1
3.从第三行开始,对于非第一个元素和最后一个元素的元素.
yanghui[i][j] = yanghui[i-1][j-1] + yanghui[i-1][j];
public class TestYangHui {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] yangHui=new int[10][];
//1.初始化二维数组
for(int i=0;i1&&j>0&&j 结果为:
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
1 5 10 10 5 1
1 6 15 20 15 6 1
1 7 21 35 35 21 7 1
1 8 28 56 70 56 28 8 1
1 9 36 84 126 126 84 36 9 1
五、数组的常见算法
1.数组的基本算法
/*
1.求数组元素的最大值、最小值、平均数、总和等
2.数组的复制、反转
3.数组元素的排序
*/
public class TestArray4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr=new int[] {12,43,9,0,-65,-99,100,9};
//最大值
int max=arr[0];
for(int i=1;iarr[i]) {
min=arr[i];
}
}
System.out.println("数组的最小值为:"+min);
//总和
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;iarr[j+1]) {
int temp=arr[j];
arr[j]=arr[j+1];
arr[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println("冒泡排序:");
//遍历
for(int i=0;iarr[j]) {
t=j;
}
}
if(t!=i) {
int temp=arr[t];
arr[t]=arr[i];
arr[i]=temp;
}
}
System.out.println("直接选择排序:");
//遍历
for(int i=0;i 结果为:
数组的最大值为:100
数组的最小值为:-99
总和为:9
平均数:1
数组复制:
12 43 9 0 -65 -99 100 9
数组反转:
9 100 -99 -65 0 9 43 12
直接选择排序:
-99 -65 0 9 9 12 43 100