C++ STL - List
list 类 (VC++)
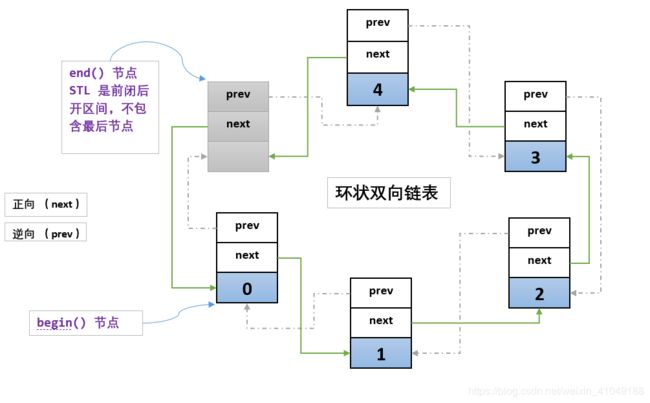
C++标准库列表类是序列容器的类模板,用于在线性排列中维护其元素,并允许在序列中的任何位置进行有效的插入和删除。 序列存储为双向链接的元素列表,每个包含一些 Type 类型的成员。
语法
template <class Type, class Allocator= allocator<Type>>
class list
参数
Type
要存储在列表中的元素数据类型。
Allocator
表示所存储分配器对象的类型,该分配器对象封装有关列表的内存分配和解除分配的详细信息。 此参数是可选的,默认值为allocator。
容器类型选择通常应根据应用程序所需的搜索和插入的类型。 当对任何元素的随机访问超出限制并且仅要求在序列的末尾插入或删除元素时,矢量应作为用于管理序列的首选容器。 当需要随机访问并且在序列起始处和末尾处插入和删除元素已到达极限时,应首选类 deque 容器进行操作。
列表成员函数 merge、reverse、unique、remove 和 remove_if 已针对对列表的操作进行了优化,它们可作为泛型对应函数的高性能替代函数。
当成员函数必须插入或删除列表中的元素时,将发生列表的重新分配。 在所有这类情况下,仅指向受控制序列被消除部分的迭代器或引用将变为无效。
- operator!= 【左侧的列表对象是否不等于右侧的列表对象】
- operator< 【左侧的列表对象是否小于右侧的列表对象】
- operator<= 【左侧的列表对象是否小于或等于右侧的列表对象】
- operator== 【左侧的列表对象是否等于右侧的列表对象】
- operator> 【左侧的列表对象是否大于右侧的列表对象】
- operator>= 【左侧的列表对象是否大于或等于右侧的列表对象】
成员:
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| allocator_type | 表示列表对象的 allocator 类的类型,allocator_type是模板参数分配器的同义词 |
| const_iterator | 提供可读取列表中 const 元素的双向迭代器的类型 |
| const_pointer | 提供指向列表中const元素的指针的类型 |
| const_reference | 提供对存储于列表中供读取和执行 const 操作的 const 元素的引用的类型,const_reference 类型不能用于修改元素的值 |
| const_reverse_iterator | 提供可读取列表中任何 const 元素的双向迭代器的类型 |
| difference_type | 提供引用同一列表中的元素的两个迭代器之间的差异的类型 |
| iterator | 提供可读取或修改列表中任何元素的双向迭代器的类型,类型iterator可用于修改元素的值 |
| pointer | 提供指向列表元素的指针,类型pointer可用于修改元素的值。在大多数情况下,应使用 iterator 访问列表对象中的元素 |
| reference | 提供对存储在列表中的元素的引用的类型 |
| reverse_iterator | 提供可读取或修改反向列表中的元素的双向迭代器的类型 |
| size_type | 计算列表中元素的数目的类型 |
| value_type | 表示列表中存储的数据类型的类型 |
示例:
Typedef.h
#pragma once
#include
#includeTypedef.cpp
#include "Typedef.h"
void typedef_fun_dome()
{
allocator_type_dome();
const_iterator_dome();
const_pointer_dome();
const_reference_dome();
const_reverse_iterator_dome();
difference_type_dome();
iterator_dome();
pointer_dome();
reference_dome();
reverse_iterator_dome();
size_type_dome();
value_type_dome();
}
void allocator_type_dome()
{
cout << "allocator_type : 表示列表对象的分配器类的类型,allocator_type是模板参数分配器的同义词" << endl;
cout << "typedef Allocator allocator_type;" << endl;
list<int> c1; //使用默认分配器
list<int, allocator<int>>c2 = list<int, allocator<int>>(allocator<int>());//使用默认分配器
list<int>c3(c1.get_allocator()); //c3将使用与c1相同的分配器类
c3.push_back(1);
list<int>::allocator_type xlst = c1.get_allocator();//现在可以在c1使用的分配器类上调用函数
cout << "类型:" << typeid(xlst).name() << endl;
cout << xlst.max_size() << endl;
}
void const_iterator_dome()
{
cout << "const_iterator;提供可读取列表中 const 元素的双向迭代器的类型 const_iterator 类型不能用于修改元素的值:" << endl;
list<int> c1{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
list<int>::const_iterator citb = c1.begin();
cout << "list::const_iterator:" << typeid(citb).name() << endl;
cout << "c1= ";
for (; citb != c1.end(); citb++)
{
cout << " " << *citb;
}
cout << endl;
}
void const_pointer_dome()
{
cout << "const_pointer;提供指向列表中const元素的指针,const_pointer 类型不能用于修改元素的值:" << endl;
list<int> c1{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
list<int>::const_pointer cptrb ;
list<int>::iterator it=c1.begin();
cout << "c1= ";
for (size_t i = 0; i < c1.size(); i++)
{
cptrb = &*(it);
cout << " " << *cptrb;
it++; // List 的内存空间不一定是连续的 不能用 cptrb++(指针递增),必须是迭代器递增。
}
cout << endl;
}
void const_reference_dome()
{
cout << "const_reference;提供对存储于列表中供读取和执行 const 操作的 const 元素的引用的类型:" << endl;
list <int> c1;
c1.push_back(10);
c1.push_back(20);
const list <int> c2 = c1;
const int& i = c2.front();
cout << "& i type =" << typeid(i).name() <<" " <<typeid(c2.front()).name()<< endl;
const int& j = c2.back();
cout << "The first element is " << i << endl;
cout << "The second element is " << j << endl;
}
void const_reverse_iterator_dome()
{
cout << "const_reverse_iterator 提供可读取列表中任何 const 元素的双向迭代器的类型,const_reverse_iterator 类型无法修改元素的值,它用于反向循环访问列表:" << endl;
list<int> c1{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
list<int>::const_reverse_iterator critb = c1.crbegin();
cout << typeid(critb).name() << endl;
cout << "c1= ";
for (; critb != c1.crend(); critb++)
{
cout << " " << *critb;
}
cout << endl;
}
void difference_type_dome()
{
cout << "difference_type 可用于表示列表中迭代器所指向元素之间元素数目的有符号整数类型:" << endl;
list <int> c1;
list <int>::iterator c1_Iter, c2_Iter;
c1.push_back(30);
c1.push_back(20);
c1.push_back(30);
c1.push_back(10);
c1.push_back(30);
c1.push_back(20);
cout << "c1=";
for (auto i : c1)
{
cout << " " << i;
}
cout << endl;
c1_Iter = c1.begin();
c2_Iter = c1.end();
list <int>::difference_type df_typ1, df_typ2, df_typ3;
df_typ1 = count(c1_Iter, c2_Iter, 10);
df_typ2 = count(c1_Iter, c2_Iter, 20);
df_typ3 = count(c1_Iter, c2_Iter, 30);
cout << "The number '10' is in c1 collection " << df_typ1 << " times.\n";
cout << "The number '20' is in c1 collection " << df_typ2 << " times.\n";
cout << "The number '30' is in c1 collection " << df_typ3 << " times.\n";
}
void iterator_dome()
{
cout << "iterator 提供可读取或修改列表中任何元素的双向迭代器的类型 类型iterator可用于修改元素的值:" << endl;
list<int> c1{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
list<int>::iterator itb = c1.begin();
list<int>::iterator ite = c1.end();
cout << "修改前:c1= ";
while (itb!=ite)
{
cout << " " << *itb;
itb++;
}
cout << endl;
itb = c1.begin();
for (; itb != ite; itb++)
{
*itb = *itb + 1;
}
itb = c1.begin();
cout << "修改后:c1= ";
while (itb != ite)
{
cout << " " << *itb;
itb++;
}
cout << endl;
}
void pointer_dome()
{
cout << "pointer 提供指向列表元素的指针 类型pointer可用于修改元素的值:" << endl;
list<int> c1{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
list<int>::pointer ptrb = &(*c1.begin()); //取值的地址
list<int>::iterator it = c1.begin(); //迭代器
cout << "before c1=";
for (int i = 0; i < c1.size(); i++)
{
cout << " " << *ptrb;
it++;
if (it == c1.end())
{
break;
}
ptrb = &(*it);
}
cout << endl;
//指针复位
ptrb = &(*c1.begin());
it = c1.begin();
for (int i = 0; i < c1.size(); i++)
{
*ptrb+=10;
it++;
if (it == c1.end())
{
break;
}
ptrb = &(*it);
}
//指针复位
ptrb = &(*c1.begin());
it = c1.begin();
cout << "after c1=";
for (int i = 0; i < c1.size(); i++)
{
cout << " " << *ptrb;
it++;
if (it == c1.end())
{
break;
}
ptrb = &(*it);
}
cout << endl;
}
void reference_dome()
{
cout << "reference 提供对存储在列表中的元素的引用的类型:" << endl;
list <int> c1;
c1.push_back(10);
c1.push_back(20);
int& i = c1.front();
int& j = c1.back();
cout << "The first element is " << i << endl;
cout << "The second element is " << j << endl;
}
void reverse_iterator_dome()
{
cout << "reverse_iterator 提供可读取或修改反向列表中的元素的双向迭代器的类型" << endl;
list <int> c1;
list <int>::iterator c1_Iter;
list <int>::reverse_iterator c1_rIter;
// If the following line replaced the line above, *c1_rIter = 40;
// (below) would be an error
//list ::const_reverse_iterator c1_rIter;
c1.push_back(10);
c1.push_back(20);
c1.push_back(30);
c1_rIter = c1.rbegin();
cout << "The last element in the list is " << *c1_rIter << "." << endl;
cout << "The list is:";
for (c1_Iter = c1.begin(); c1_Iter != c1.end(); c1_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c1_Iter;
cout << endl;
// rbegin can be used to start an iteration through a list in
// reverse order
cout << "The reversed list is:";
for (c1_rIter = c1.rbegin(); c1_rIter != c1.rend(); c1_rIter++)
cout << " " << *c1_rIter;
cout << endl;
c1_rIter = c1.rbegin();
*c1_rIter = 40;
cout << "The last element in the list is now " << *c1_rIter << "." << endl;
}
void size_type_dome()
{
cout << "size_type 计算列表中元素的数目的类型:" << endl;
list <int> c1;
list <int>::size_type i;
c1.push_back(5);
i = c1.size();
cout << "List length is " << i << "." << endl;
c1.push_back(7);
i = c1.size();
cout << "List length is now " << i << "." << endl;
}
void value_type_dome()
{
cout << "value_type ;表示列表中存储的数据类型的类型,value_type 是模板参数 Type 的同义词 : " << endl;
list<int>::value_type AnInt;
AnInt = 44;
cout << AnInt << endl;
}
#include"Typedef.h"
int main(void)
{
//list list1{};
//cout << sizeof(list1) << endl; //12
typedef_fun_dome();
return 0;
}
| assign | 将元素从列表中擦除并将一组新的元素复制到目标列表 |
| front | 返回对列表中第一个元素的引用 , 如果列表为空,返回的结果则不确定;如果将 front 的返回值分配给 const_reference,则无法修改列表对象。 如果将 front 的返回值分配给 reference,则可修改列表对象。 |
| back | 返回对列表中最后一个元素的引用, 列表的最后一个元素。 如果列表为空,则返回值不确定;如果将 back 的返回值分配给 const_reference,则无法修改列表对象。 如果将 back 的返回值分配给 reference,则可修改列表对象。 |
| cbegin | 返回发现列表中第一个元素的位置的常量迭代器 ;指向范围的第一个元素或略高于空范围末尾的位置(对于空范围)cbegin() == cend()的const双向访问迭代器;由于使用 cbegin 的返回值,因此不能修改范围中的元素。 |
| cend | 返回发现一个列表中最后一个元素之后的位置的常量迭代器;指向刚超出范围末尾的位置的 const 双向访问迭代器。cend 用于测试迭代器是否超过了其范围的末尾。 |
| clear | 消除列表中的全部元素 |
| crbegin | 返回发现反向列表中第一个元素的位置的常量迭代器 |
| crend | 返回用于发现反向列表中最后一个元素之后的位置的常量迭代器 |
| emplace | 将构造的元素插入到列表中的指定位置 ;如果引发了异常,list 将保持不变,该异常将被重新引发 |
| emplace_back | 在列表的结尾处添加一个就地构造的元素 |
| emplace_front | 在列表的起始位置添加一个就地构造的元素 |
| empty | 测试列表是否为空; 如果列表为空,则为 true;如果列表不为空,则为 false。 |
| end | 返回用于发现列表中最后一个元素之后的位置的迭代器; 用于发现列表中最后一个元素之后的位置的双向迭代器。 如果列表为空,则 list::end == list::begin ;end用于测试迭代器是否已到达其列表的末尾 |
| erase | 从列表中的指定位置移除一个或一系列元素 |
| get_allocator | 返回用于构造列表的 allocator 对象的一个副本 |
| insert | 将一个、几个或一系列元素插入列表中的指定位置 |
| max_size | 列表的最大可取长度。 |
| merge | 将元素从参数列表移除,将它们插入目标列表,将新的组合元素集以升序或其他指定顺序排序; 参数列表和目标列表必须用相同的比较关系进行排序,生成的序列将以这种关系进行排序。 第一个成员函数的默认排列顺序是升序。 第二个成员函数强制类Traits的用户指定的比较操作复合 |
| pop_back | 删除列表末尾的元素 |
| pop_front | 删除列表起始处的一个元素。 |
| push_back | 在列表的末尾添加元素。 |
| push_front | 在列表的开头添加元素。 |
| rbegin | 返回发现反向列表中第一个元素的位置的迭代器。 |
| rend | 返回发现反向列表中最后一个元素之后的位置的迭代器。 |
| remove | 清除列表中与指定值匹配的元素。剩余元素的排序不受影响。 |
| remove_if | 将满足指定谓词的元素从列表中消除。 |
| resize | 为列表指定新的大小 |
| reverse | 反转列表中元素的顺序 |
| sort | 按升序或用户指定的其他顺序排列列表元素 |
| splice | 从源列表中删除元素并将其插入到目标列表中。 |
| swap | 交换两个列表的元素 |
| unique | 从列表中删除满足某些其他二元谓词的相邻重复元素或相邻元素 |
assign:函数参数列表
void assign(size_type Count, const Type& Val);
void assign initializer_list<Type> IList);
template <class InputIterator>
void assign( InputIterator First,InputIterator Last);
清除目标列表中的任何现有元素后,将原始列表或其他列表中的一系列指定的元素插入目标列表中,或将指定值的新元素的副本插入目标列表中
insert :函数参数列表
iterator insert(iterator Where, const Type& Val);
iterator insert(iterator Where, Type&& Val);
void insert(iterator Where, size_type Count, const Type& Val);
iterator insert(iterator Where, initializer_list<Type> IList);
template <class InputIterator>
void insert(iterator Where, InputIterator First, InputIterator Last);
第一对成员函数将源列表中的所有元素插入到目标列表中,然后将 Where引用的位置插入目标列表,并从源列表中删除所有元素。 (&Source不能等于this.
第二对成员函数将Iter引用的元素插入Where引用的目标列表中的位置之前,并从源列表中删除Iter。 (如果 Where == Iter || Where == ++Iter,则不会发生更改。)
第三对成员函数在Where引用的目标列表中的元素First之前Last插入 * 指定的范围,并从源列表中删除该范围的元素。 (如果&Source == this,范围[First, Last)不能包括Where. 指向的元素。
如果范围接合插入 N 个元素和 &Source != this,则类 iterator 的对象会递增 N 次。
在所有情况下,迭代器、指针或引用接合的元素的引用都会保持有效状态且会转换为目标容器。
merge :函数参数:
void merge(list<Type, Allocator>& right);
template <class Traits>
void merge(list<Type, Allocator>& right, Traits comp);
参数列表右侧与目标列表合并。
参数列表和目标列表必须用相同的比较关系进行排序,生成的序列将以这种关系进行排序。 第一个成员函数的默认排列顺序是升序。 第二个成员函数强制类Traits的用户指定的比较操作复合。
splice:函数参数列表
// insert the entire source list
void splice(const_iterator Where, list<Type, Allocator>& Source);
void splice(const_iterator Where, list<Type, Allocator>&& Source);
// insert one element of the source list
void splice(const_iterator Where, list<Type, Allocator>& Source, const_iterator Iter);
void splice(const_iterator Where, list<Type, Allocator>&& Source, const_iterator Iter);
// insert a range of elements from the source list
void splice(const_iterator Where, list<Type, Allocator>& Source, const_iterator First, const_iterator Last);
void splice(const_iterator Where, list<Type, Allocator>&& Source, const_iterator First, const_iterator Last);
第一对成员函数将源列表中的所有元素插入到目标列表中,然后将 Where引用的位置插入目标列表,并从源列表中删除所有元素。 (&Source不能等于this.
第二对成员函数将Iter引用的元素插入Where引用的目标列表中的位置之前,并从源列表中删除Iter。 (如果 Where == Iter || Where == ++Iter,则不会发生更改。)
第三对成员函数在Where引用的目标列表中的元素First之前Last插入 * 指定的范围,并从源列表中删除该范围的元素。 (如果&Source == this,范围[First, Last)不能包括Where. 指向的元素。
如果范围接合插入 N 个元素和 &Source != this,则类 iterator 的对象会递增 N 次。
在所有情况下,迭代器、指针或引用接合的元素的引用都会保持有效状态且会转换为目标容器。
unique:函数参数列表
void unique();
template <class BinaryPredicate>
void unique(BinaryPredicate pred);
此函数假设列表是经过排序的,因此所有重复元素都是相邻的。 不相邻的重复元素将不被删除。
第一个成员函数删除比较等于其前一个元素的每个元素。
第二个成员函数删除与其前面的元素相比,满足预置谓词函数的每个元素。 可以使用<函数>标头中声明的任何二进制函数对象进行参数预置,也可以创建自己的函数对象。
测试dome:
Member_function.h
#pragma once
#include
#includeMember_function.cpp
#include "Member_function.h"
template <class T>
class is_odd : public std::unary_function<T, bool>
{
public:
bool operator( ) (T& val)
{
return (val % 2) == 1;
}
};
template <typename S> void print(const S& s) {
cout << s.size() << " elements: ";
for (const auto& p : s) {
cout << "(" << p << ") ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void Member_function_dome()
{
assign_dome();
back_front_dome();
cbegin_cend_dome();
clear_dome();
crbegin_crend_dome();
emplace_dome();
emplace_back_dome();
emplace_front_dome();
empty_dome();
erase_dome();
front_back_dome();
insert_dome();
max_size_size_dome();
merge_dome();
pop_back_and_pop_front_dome();
remove_dome();
remove_if_dome();
resize_dome();
reverse_dome();
sort_dome();
splice_dome();
swap_dome();
unique_dome();
}
void assign_dome()
{
cout << "assign 清除列表中的元素,并将一组新元素复制到目标列表:" << endl;
list<int> c1, c2;
list<int>::const_iterator cIter;
c1.push_back(10);
c1.push_back(20);
c1.push_back(30);
c2.push_back(40);
c2.push_back(50);
c2.push_back(60);
cout << "c1 =";
for (auto c : c1)
cout << " " << c;
cout << endl;
c1.assign(++c2.begin(), c2.end());
cout << "c1 =";
for (auto c : c1)
cout << " " << c;
cout << endl;
c1.assign(7, 4);
cout << "c1 =";
for (auto c : c1)
cout << " " << c;
cout << endl;
c1.assign({ 10, 20, 30, 40 });
cout << "c1 =";
for (auto c : c1)
cout << " " << c;
cout << endl;
}
void back_front_dome()
{
cout << "back() 返回列表最后一个元素;front() 返回列表第一个元素:" << endl;
list <int> c1;
c1.push_back(10);
c1.push_back(11);
int& i = c1.back();
const int& ii = c1.front();
cout << "The last integer of c1 is " << i << endl;
i--;
cout << "The next-to-last integer of c1 is " << ii << endl;
}
void cbegin_cend_dome()
{
cout << "cbegin() ; cend() :返回常量迭代器:" << endl;
list<int> c1{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
auto i1 = c1.cbegin();
auto i2 = c1.cend();
cout << "c1 = ";
for (auto i : c1)
{
cout << " " << i;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "c1.cbegin() =" << *i1 << " " << typeid(i1).name() << endl;
cout << " -- c1.cend() =" << *(--i2) << " " << typeid(i2).name() << endl;
}
void clear_dome()
{
cout << "clear() 消除列表中的全部元素:" << endl;
list <int> c1;
c1.push_back(10);
c1.push_back(20);
c1.push_back(30);
cout << "The size of the list is initially " << c1.size() << endl;
c1.clear();
cout << "The size of list after clearing is " << c1.size() << endl;
}
void crbegin_crend_dome()
{
cout << "crbegin() ; crend() :返回反向常量迭代器: " << endl;
list<int> c1{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
cout << "c1 = ";
for (auto crib = c1.crbegin(); crib != c1.crend(); crib++)
{
cout << " " << *crib;
}
cout << endl;
}
void emplace_dome()
{
cout << "emplace() 将构造的元素插入到列表中的指定位置 :" << endl;
list <string> c2;
string str("a");
c2.emplace(c2.begin(), move(str));
cout << "Moved first element: " << c2.back() << endl;
}
void emplace_back_dome()
{
cout << "emplace_back() 在列表的结尾处添加一个就地构造的元素" << endl;
list <string> c2;
string str("a");
c2.emplace_back(move(str));
cout << "Moved first element: " << c2.back() << endl;
}
void emplace_front_dome()
{
cout << "emplace_front() 在列表的起始位置添加一个就地构造的元素" << endl;
list <string> c2;
string str("a");
c2.emplace_front(move(str));
cout << "Moved first element: " << c2.front() << endl;
}
void empty_dome()
{
cout << "empty() 判断链表是否为空;如果列表为空,则为 true;如果列表不为空,则为 false。" << endl;
list <int> c1;
c1.push_back(10);
if (c1.empty())
cout << "The list is empty." << endl;
else
cout << "The list is not empty." << endl;
}
void erase_dome()
{
cout << " erase() 从列表中的指定位置移除一个或一系列元素:" << endl;
list <int> c1;
list <int>::iterator Iter;
c1.push_back(10);
c1.push_back(20);
c1.push_back(30);
c1.push_back(40);
c1.push_back(50);
cout << "The initial list is:";
for (Iter = c1.begin(); Iter != c1.end(); Iter++)
cout << " " << *Iter;
cout << endl;
c1.erase(c1.begin());
cout << "在擦除第一个元素之后,列表变成:";
for (Iter = c1.begin(); Iter != c1.end(); Iter++)
cout << " " << *Iter;
cout << endl;
Iter = c1.begin();
Iter++;
c1.erase(Iter, c1.end());
cout << "在擦除除第一个元素之外的所有元素之后,列表变成: ";
for (Iter = c1.begin(); Iter != c1.end(); Iter++)
cout << " " << *Iter;
cout << endl;
}
void front_back_dome()
{
cout << "front() ; back() 返回列表中第一个元素和 最后一个元素 :" << endl;
list <int> c1;
c1.push_back(10);
c1.push_back(11);
int& i = c1.back();
int& j = c1.front();
cout << "The frist integer of c1 is " << j << endl;
cout << "The last integer of c1 is " << i << endl;
}
void insert_dome()
{
cout << "insert() 将一个、几个或一系列元素插入列表中的指定位置:" << endl;
list <int> c1, c2;
list <int>::iterator Iter;
c1.push_back(10);
c1.push_back(20);
c1.push_back(30);
c2.push_back(40);
c2.push_back(50);
c2.push_back(60);
cout << "c1 =";
for (auto c : c1)
cout << " " << c;
cout << endl;
Iter = c1.begin();
Iter++;
c1.insert(Iter, 100);
cout << "c1 =";
for (auto c : c1)
cout << " " << c;
cout << endl;
Iter = c1.begin();
Iter++;
Iter++;
c1.insert(Iter, 2, 200);
cout << "c1 =";
for (auto c : c1)
cout << " " << c;
cout << endl;
c1.insert(++c1.begin(), c2.begin(), --c2.end());
cout << "c1 =";
for (auto c : c1)
cout << " " << c;
cout << endl;
// initialize a list of strings by moving
list < string > c3;
string str("a");
c3.insert(c3.begin(), move(str));
cout << "Moved first element: " << c3.front() << endl;
// Assign with an initializer_list
list <int> c4{ {1, 2, 3, 4} };
c4.insert(c4.begin(), { 5, 6, 7, 8 });
cout << "c4 =";
for (auto c : c4)
cout << " " << c;
cout << endl;
}
void max_size_size_dome()
{
cout << "max_size() ; size() ;返回列表的最大长度,返回列表中元素的数目:" << endl;
list<int> c1{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
cout << "max_size()=" << c1.max_size() << endl;
cout << "size()= " << c1.size() << endl;
}
void merge_dome()
{
cout << "merge() ;将元素从参数列表移除,将它们插入目标列表,将新的组合元素集以升序或其他指定顺序排序:" << endl;
list <int> c1, c2, c3;
list <int>::iterator c1_Iter, c2_Iter, c3_Iter;
c1.push_back(3);
c1.push_back(6);
c2.push_back(2);
c2.push_back(4);
c3.push_back(5);
c3.push_back(1);
cout << "c1 =";
for (c1_Iter = c1.begin(); c1_Iter != c1.end(); c1_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c1_Iter;
cout << endl;
cout << "c2 =";
for (c2_Iter = c2.begin(); c2_Iter != c2.end(); c2_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c2_Iter;
cout << endl;
c2.merge(c1); // Merge c1 into c2 in (default) ascending order
c2.sort(greater<int>());
cout << "After merging c1 with c2 and sorting with >: c2 =";
for (c2_Iter = c2.begin(); c2_Iter != c2.end(); c2_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c2_Iter;
cout << endl;
cout << "c3 =";
for (c3_Iter = c3.begin(); c3_Iter != c3.end(); c3_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c3_Iter;
cout << endl;
c2.merge(c3, greater<int>());
cout << "After merging c3 with c2 according to the '>' comparison relation: c2 =";
for (c2_Iter = c2.begin(); c2_Iter != c2.end(); c2_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c2_Iter;
cout << endl;
}
void pop_back_and_pop_front_dome()
{
cout << "pop_back();删除列表末尾的元素 . pop_front(); 删除列表起始处的一个元素:" << endl;
list<int> c1{ 1,2 };
cout << "c1.size()= " << c1.size() << endl;
c1.pop_back();
c1.pop_front();
cout << "c1.size()= " << c1.size() << endl;
}
void remove_dome()
{
cout << "remove() 清除列表中与指定值匹配的元素:" << endl;
list <int> c1;
list <int>::iterator c1_Iter, c2_Iter;
c1.push_back(5);
c1.push_back(100);
c1.push_back(5);
c1.push_back(200);
c1.push_back(5);
c1.push_back(300);
cout << "The initial list is c1 =";
for (c1_Iter = c1.begin(); c1_Iter != c1.end(); c1_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c1_Iter;
cout << endl;
list <int> c2 = c1;
c2.remove(5);
cout << "After removing elements with value 5, the list becomes c2 =";
for (c2_Iter = c2.begin(); c2_Iter != c2.end(); c2_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c2_Iter;
cout << endl;
}
void remove_if_dome()
{
cout << "remove_if() 将满足指定谓词的元素从列表中消除:" << endl;
list <int> c1;
list <int>::iterator c1_Iter, c2_Iter;
c1.push_back(3);
c1.push_back(4);
c1.push_back(5);
c1.push_back(6);
c1.push_back(7);
c1.push_back(8);
cout << "The initial list is c1 =";
for (c1_Iter = c1.begin(); c1_Iter != c1.end(); c1_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c1_Iter;
cout << endl;
list <int> c2 = c1;
c2.remove_if(is_odd<int>());
cout << "After removing the odd elements, "
<< "the list becomes c2 =";
for (c2_Iter = c2.begin(); c2_Iter != c2.end(); c2_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c2_Iter;
cout << endl;
}
void resize_dome()
{
cout << "resize() 为列表指定新的大小:" << endl;
list <int> c1;
c1.push_back(10);
c1.push_back(20);
c1.push_back(30);
c1.resize(4, 40);
cout << "The size of c1 is " << c1.size() << endl;
cout << "The value of the last element is " << c1.back() << endl;
c1.resize(5);
cout << "The size of c1 is now " << c1.size() << endl;
cout << "The value of the last element is now " << c1.back() << endl;
c1.resize(2);
cout << "The reduced size of c1 is: " << c1.size() << endl;
cout << "The value of the last element is now " << c1.back() << endl;
}
void reverse_dome()
{
cout << "reverse() 反转列表中元素的顺序:" << endl;
list <int> c1;
list <int>::iterator c1_Iter;
c1.push_back(10);
c1.push_back(20);
c1.push_back(30);
cout << "c1 =";
for (c1_Iter = c1.begin(); c1_Iter != c1.end(); c1_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c1_Iter;
cout << endl;
c1.reverse();
cout << "Reversed c1 =";
for (c1_Iter = c1.begin(); c1_Iter != c1.end(); c1_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c1_Iter;
cout << endl;
}
void sort_dome()
{
cout << "sort() 按升序或用户指定的其他顺序排列列表元素:" << endl;
list <int> c1;
list <int>::iterator c1_Iter;
c1.push_back(20);
c1.push_back(10);
c1.push_back(30);
cout << "Before sorting: c1 =";
for (c1_Iter = c1.begin(); c1_Iter != c1.end(); c1_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c1_Iter;
cout << endl;
c1.sort();
cout << "After sorting c1 =";
for (c1_Iter = c1.begin(); c1_Iter != c1.end(); c1_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c1_Iter;
cout << endl;
c1.sort(greater<int>());
cout << "After sorting with 'greater than' operation, c1 =";
for (c1_Iter = c1.begin(); c1_Iter != c1.end(); c1_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c1_Iter;
cout << endl;
}
void splice_dome()
{
cout << "splice() 拼接, 从源列表中删除元素并将其插入到目标列表中:" << endl;
list<int> c1{ 10,11 };
list<int> c2{ 20,21,22 };
list<int> c3{ 30,31 };
list<int> c4{ 40,41,42,43 };
list<int>::iterator where_iter;
list<int>::iterator first_iter;
list<int>::iterator last_iter;
cout << "Beginning state of lists:" << endl;
cout << "c1 = ";
print(c1);
cout << "c2 = ";
print(c2);
cout << "c3 = ";
print(c3);
cout << "c4 = ";
print(c4);
where_iter = c2.begin();
++where_iter; // start at second element
c2.splice(where_iter, c1);
cout << "After splicing c1 into c2:" << endl;
cout << "c1 = ";
print(c1);
cout << "c2 = ";
print(c2);
first_iter = c3.begin();
c2.splice(where_iter, c3, first_iter);
cout << "After splicing the first element of c3 into c2:" << endl;
cout << "c3 = ";
print(c3);
cout << "c2 = ";
print(c2);
first_iter = c4.begin();
last_iter = c4.end();
// set up to get the middle elements
++first_iter;
--last_iter;
c2.splice(where_iter, c4, first_iter, last_iter);
cout << "After splicing a range of c4 into c2:" << endl;
cout << "c4 = ";
print(c4);
cout << "c2 = ";
print(c2);
}
void swap_dome()
{
cout << "swap() 交换两个列表的元素:" << endl;
list <int> c1, c2, c3;
list <int>::iterator c1_Iter;
c1.push_back(1);
c1.push_back(2);
c1.push_back(3);
c2.push_back(10);
c2.push_back(20);
c3.push_back(100);
cout << "The original list c1 is:";
for (c1_Iter = c1.begin(); c1_Iter != c1.end(); c1_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c1_Iter;
cout << endl;
c1.swap(c2);
cout << "After swapping with c2, list c1 is:";
for (c1_Iter = c1.begin(); c1_Iter != c1.end(); c1_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c1_Iter;
cout << endl;
swap(c1, c3);
cout << "After swapping with c3, list c1 is:";
for (c1_Iter = c1.begin(); c1_Iter != c1.end(); c1_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c1_Iter;
cout << endl;
}
void unique_dome()
{
cout << "unique() 从列表中删除满足某些其他二元谓词的相邻重复元素或相邻元素:" << endl;
list <int> c1;
list <int>::iterator c1_Iter, c2_Iter, c3_Iter;
not_equal_to<int> mypred;
c1.push_back(-10);
c1.push_back(10);
c1.push_back(10);
c1.push_back(20);
c1.push_back(20);
c1.push_back(-10);
cout << "The initial list is c1 =";
for (c1_Iter = c1.begin(); c1_Iter != c1.end(); c1_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c1_Iter;
cout << endl;
list <int> c2 = c1;
c2.unique();
cout << "After removing successive duplicate elements, c2 =";
for (c2_Iter = c2.begin(); c2_Iter != c2.end(); c2_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c2_Iter;
cout << endl;
list <int> c3 = c2;
c3.unique(mypred);
cout << "After removing successive unequal elements, c3 =";
for (c3_Iter = c3.begin(); c3_Iter != c3.end(); c3_Iter++)
cout << " " << *c3_Iter;
cout << endl;
}
list 测试
#ifndef _LISTTEST_
#define _LISTTEST_
namespace list_test_01
{
void list_test(long& size);
void list_fun_test();
}
#endif // !_LISTTEST_
#include "ListTest.h"
#include"TestFunc.h"
#include
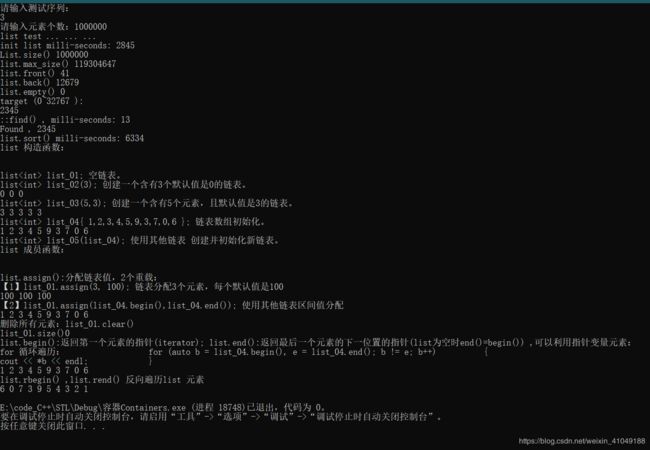
#include list_01; 空链表。" << endl;
list<int> list_02(3);
cout << "list list_02(3); 创建一个含有3个默认值是0的链表。" << endl;
for (auto i : list_02)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
list<int> list_03(5,3);
cout << "list list_03(5,3); 创建一个含有5个元素,且默认值是3的链表。" << endl;
for (auto i : list_03)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
list<int> list_04{ 1,2,3,4,5,9,3,7,0,6 };
cout << "list list_04{ 1,2,3,4,5,9,3,7,0,6 }; 链表数组初始化。" << endl;
for (auto i : list_04)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
list<int> list_05(list_04);
cout << "list list_05(list_04); 使用其他链表 创建并初始化新链表。" << endl;
cout << "list 成员函数:" << endl;
cout << "\n\n";
cout << "list.assign():分配链表值,2个重载:" << endl;
list_01.assign(3, 100);
cout << "【1】list_01.assign(3, 100); 链表分配3个元素,每个默认值是100" << endl;
for (auto i : list_01)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
list_01.assign(list_04.begin(),list_04.end());
cout << "【2】list_01.assign(list_04.begin(),list_04.end()); 使用其他链表区间值分配" << endl;
for (auto i : list_01)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
cout << "删除所有元素:list_01.clear()" << endl;
list_01.clear();
cout << "list_01.size()" << list_01.size() << endl;
cout << "list.begin():返回第一个元素的指针(iterator); list.end():返回最后一个元素的下一位置的指针(list为空时end()=begin()) ,可以利用指针变量元素:" << endl;
cout << "for 循环遍历: "<<"\
for (auto b = list_04.begin(), e = list_04.end(); b != e; b++)\
{\
cout << *b << endl;\
}\
" << endl;
for (auto b = list_04.begin(), e = list_04.end(); b != e; b++)
{
cout << *b <<" ";
}
cout << "\n";
cout << "list.rbegin() ,list.rend() 反向遍历list 元素 " << endl;
for (auto rb = list_04.rbegin(), re = list_04.rend(); rb != re; rb++)
{
cout << *rb << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}