黑马mybatis框架笔记day04
第四天
1 Mybatis 延迟加载策略
通过前面的学习,我们已经掌握了 Mybatis 中一对一,一对多,多对多关系的配置及实现,可以实现对象的关联查询。实际开发过程中很多时候我们并不需要总是在加载用户信息时就一定要加载他的账户信息。此时就是我们所说的延迟加载。
1.1 什么是延迟加载
延迟加载:
就是在需要用到数据时才进行加载,不需要用到数据时就不加载数据。延迟加载也称懒加载.
好处:
先从单表查询,需要时再从关联表去关联查询,大大提高数据库性能,因为查询单表要比关联查询多张表速度要快。
坏处:
因为只有当需要用到数据时,才会进行数据库查询,这样在大批量数据查询时,因为查询工作也要消耗时间,所以可
能造成用户等待时间变长,造成用户体验下降。
1.2 实现需求
需求:
查询账户(Account)信息并且关联查询用户(User)信息。如果先查询账户(Account)信息即可满足要求,当我们需要
查询用户(User)信息时再查询用户(User)信息。把对用户(User)信息的按需去查询就是延迟加载。
mybatis第三天实现多表操作时,我们使用了resultMap来实现一对一,一对多,多对多关系的操作。主要是通过
association、collection 实现一对一及一对多映射。association、collection 具备延迟加载功能。
1.3 使用 assocation 实现延迟加载
需求:
查询账户信息同时查询用户信息。
1.3.1 账户的持久层 DAO 接口
/**
*
* Title: IAccountDao
* Description: 账户的持久层接口
* Company: http://www.itheima.com/
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
* 查询所有账户,同时获取账户的所属用户名称以及它的地址信息
* @return
*/
List<Account> findAll();
}
1.3.2 账户的持久层映射文件
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao">
<resultMap type="account" id="accountMap">
<id column="aid" property="id"/>
<result column="uid" property="uid"/>
<result column="money" property="money"/>
<association property="user" javaType="user" select="com.itheima.dao.IUserDao.findById"
column="uid"/>
resultMap>
<select id="findAll" resultMap="accountMap">
select * from account
select>
mapper>
select: 填写我们要调用的 select 映射的 id
column : 填写我们要传递给 select 映射的参数
1.3.3 用户的持久层接口和映射文件
public interface IUserDao {
/**
* 根据 id 查询
* @param userId
* @return
*/
User findById(Integer userId);
}
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.dao.IUserDao">
<select id="findById" resultType="user" parameterType="int" >
select * from user where id = #{uid}
select>
mapper>
1.3.4 开启 Mybatis 的延迟加载策略
我们需要在 Mybatis 的配置文件 SqlMapConfig.xml 文件中添加延迟加载的配置。
<settings>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
settings>
1.4 使用 Collection 实现延迟加载
同样我们也可以在一对多关系配置的结点中配置延迟加载策略。< collection>结点中也有 select 属性,column 属性。
需求:
完成加载用户对象时,查询该用户所拥有的账户信息
1.4.1 在 User 实体类中加入 List属性
/**
*
* Title: User
* Description: 用户的实体类
* Company: http://www.itheima.com/
*/
public class User implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private Date birthday;
private String sex;
private String address;
private List<Account> accounts;
...
}
1.4.2 编写用户和账户持久层接口的方法
/**
* 查询所有用户,同时获取出每个用户下的所有账户信息
* * @return
*/
List<User> findAll();
/**
* 根据用户 id 查询账户信息
* @param uid
* @return
*/
List<Account> findByUid(Integer uid);
1.4.3 编写用户持久层映射配置
<resultMap type="user" id="userMap">
<id column="id" property="id">id>
<result column="username" property="username"/>
<result column="address" property="address"/>
<result column="sex" property="sex"/>
<result column="birthday" property="birthday"/>
<collection property="accounts" ofType="account"
select="com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao.findByUid"
column="id">
collection>
resultMap>
<select id="findAll" resultMap="userMap">
select * from user
select>
<collection>标签:
主要用于加载关联的集合对象
select 属性:
用于指定查询 account 列表的 sql 语句,所以填写的是该 sql 映射的 id
column 属性:
用于指定 select 属性的 sql 语句的参数来源,上面的参数来自于 user 的 id 列,所以就写成 id 这一个字段名了
1.4.4 编写账户持久层映射配置
<select id="findByUid" resultType="account" parameterType="int">
select * from account where uid = #{uid}
select>
2 Mybatis 缓存
像大多数的持久化框架一样,Mybatis 也提供了缓存策略,通过缓存策略来减少数据库的查询次数,从而提高性能。
Mybatis 中缓存分为一级缓存,二级缓存。

2.1 Mybatis 一级缓存
一级缓存是 SqlSession 级别的缓存,只要 SqlSession 没有 flush 或 close,它就存在。
2.1.1 一级缓存的分析
一级缓存是 SqlSession 范围的缓存,当调用 SqlSession 的修改,添加,删除,commit(),close()等方法时,就会清空一级缓存。
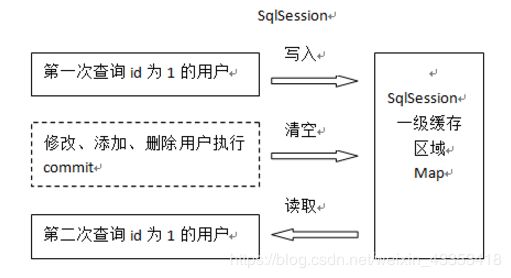
第一次发起查询用户 id 为 1 的用户信息,先去找缓存中是否有 id 为 1 的用户信息,如果没有,从数据库查询用户信息。
得到用户信息,将用户信息存储到一级缓存中。
如果 sqlSession 去执行 commit 操作(执行插入、更新、删除),清空 SqlSession 中的一级缓存,这样做的目的为了让缓存中存储的是最新的信息,避免脏读。
第二次发起查询用户 id 为 1 的用户信息,先去找缓存中是否有 id 为 1 的用户信息,缓存中有,直接从缓存中获取用户信息。
2.2 Mybatis 二级缓存
二级缓存是 mapper 映射级别的缓存,多个 SqlSession 去操作同一个 Mapper 映射的 sql 语句,多个SqlSession 可以共用二级缓存,二级缓存是跨 SqlSession 的。
2.2.1 二级缓存结构图

首先开启 mybatis 的二级缓存。
sqlSession1 去查询用户信息,查询到用户信息会将查询数据存储到二级缓存中。
如果 SqlSession3 去执行相同 mapper 映射下 sql,执行 commit 提交,将会清空该 mapper 映射下的二级缓存区域的数据。
sqlSession2 去查询与 sqlSession1 相同的用户信息,首先会去缓存中找是否存在数据,如果存在直接从缓存中取出数据。
2.2.2 二级缓存的开启与关闭
- 第一步:在 SqlMapConfig.xml 文件开启二级缓存
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
settings>
因为 cacheEnabled 的取值默认就为 true,所以这一步可以省略不配置。为 true 代表开启二级缓存;为false 代表不开启二级缓存。
- 第二步:配置相关的 Mapper 映射文件
<cache>标签表示当前这个 mapper 映射将使用二级缓存,区分的标准就看
mapper 的 namespace 值。
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.dao.IUserDao">
<cache>cache>
mapper>
- 第三步:配置 statement 上面的 useCache 属性
<select id="findById" resultType="user" parameterType="int" useCache="true">
select * from user where id = #{uid}
select>
将 UserDao.xml 映射文件中的<select>标签中设置 useCache=”true”代表当前这个 statement 要使用二级缓存,如果不使用二级缓存可以设置为 false。
注意:针对每次查询都需要最新的数据 sql,要设置成 useCache=false,禁用二级缓存。
【注】当我们在使用二级缓存时,所缓存的类一定要实现 java.io.Serializable 接口,这种就可以使用序列化方式来保存对象。
3 Mybatis 注解开发
这几年来注解开发越来越流行,Mybatis 也可以使用注解开发方式,这样我们就可以减少编写 Mapper 映射文件了。本次我们先围绕一些基本的 CRUD 来学习,再学习复杂映射关系及延迟加载。
3.1 mybatis 的常用注解说明
@Insert:实现新增
@Update:实现更新
@Delete:实现删除
@Select:实现查询
@Result:实现结果集封装
@Results:可以与@Result 一起使用,封装多个结果集
@ResultMap:实现引用@Results 定义的封装
@One:实现一对一结果集封装
@Many:实现一对多结果集封装
@SelectProvider: 实现动态 SQL 映射
@CacheNamespace:实现注解二级缓存的使用
3.2 使用 Mybatis 注解实现基本 CRUD
- 编写实体类
/**
*
* Title: User
* Description: 用户的实体类
* Company: http://www.itheima.com/
*/
public class User implements Serializable {
private Integer userId;
private String userName;
private Date userBirthday;
private String userSex;
private String userAddress;
}
- 使用注解方式开发持久层接口
/**
*
* Title: IUserDao
* Description: 用户的持久层接口
* Company: http://www.itheima.com/
*/
public interface IUserDao {
/**
* 查询所有用户
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from user")
@Results(id="userMap",
value= {
@Result(id=true,column="id",property="userId"),
@Result(column="username",property="userName"),
@Result(column="sex",property="userSex"),
@Result(column="address",property="userAddress"),
@Result(column="birthday",property="userBirthday")
})
List<User> findAll();
/**
* 根据 id 查询一个用户
* @param userId
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from user where id = #{uid} ")
@ResultMap("userMap")
User findById(Integer userId);
/**
* 保存操作
* @param user
* @return
*/
@Insert("insert into user(username,sex,birthday,address)
values(#{username},#{sex},#{birthday},#{address}
)")
@SelectKey(keyColumn="id",keyProperty="id",resultType=Integer.class,before =
false, statement = { "select last_insert_id()" })
int saveUser(User user);
/**
* 更新操作
* @param user
* @return
*/
@Update("update user set username=#{username},address=#{address},
sex=#{sex},birthday=#{birthday} where id =#{id} ")
int updateUser(User user);
/**
* 删除用户
* @param userId
* @return
*/
@Delete("delete from user where id = #{uid} ")
int deleteUser(Integer userId);
/**
* 查询使用聚合函数
* @return
*/
@Select("select count(*) from user ")
int findTotal();
/**
* 模糊查询
* @param name
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from user where username like #{username} ")
List<User> findByName(String name);
}
通过注解方式,我们就不需要再去编写 UserDao.xml 映射文件了。
- 编写 SqlMapConfig 配置文件
<configuration>
<properties resource="jdbcConfig.properties">properties>
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.itheima.domain"/>
typeAliases>
<environments default="mysql">
<environment id="mysql">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
dataSource>
environment>
environments>
<mappers>
<package name="com.itheima.dao"/>
mappers>
configuration>
3.3 使用注解实现复杂关系映射开发
实现复杂关系映射之前我们可以在映射文件中通过配置来实现,在使用注解开发时我们需要借助@Results 注解,@Result 注解,@One 注解,@Many 注解。
3.3.1 复杂关系映射的注解说明
@Results 注解
代替的是标签<resultMap>
该注解中可以使用单个@Result 注解,也可以使用@Result 集合
@Results({@Result(),@Result()})或@Results(@Result())
@Resutl 注解
代替了 <id>标签和<result>标签
@Result 中 属性介绍:
id 是否是主键字段
column 数据库的列名
property 需要装配的属性名
one 需要使用的@One 注解(@Result(one=@One)()))
many 需要使用的@Many 注解(@Result(many=@many)()))
@One 注解(一对一)
代替了<assocation>标签,是多表查询的关键,在注解中用来指定子查询返回单一对象。
@One 注解属性介绍:
select 指定用来多表查询的 sqlmapper
fetchType 会覆盖全局的配置参数 lazyLoadingEnabled。。
使用格式:
@Result(column=" ",property="",one=@One(select=""))
@Many 注解(多对一)
代替了<Collection>标签,是是多表查询的关键,在注解中用来指定子查询返回对象集合。
注意:聚集元素用来处理“一对多”的关系。需要指定映射的 Java 实体类的属性,属性的 javaType
(一般为 ArrayList)但是注解中可以不定义;
使用格式:
@Result(property="",column="",many=@Many(select=""))
3.3.2 使用注解实现一对一复杂关系映射及延迟加载
- 添加 User 实体类及 Account 实体类
/**
*
* Title: User
* Description: 用户的实体类
* Company: http://www.itheima.com/
*/
public class User implements Serializable {
private Integer userId;
private String userName;
private Date userBirthday;
private String userSex;
private String userAddress;
}
/**
*
* Title: Account
* Description: 账户的实体类
* Company: http://www.itheima.com/
*/
public class Account implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private Integer uid;
private Double money;
//多对一关系映射:从表方应该包含一个主表方的对象引用
private User user;
}
- 添加账户的持久层接口并使用注解配置
/**
*
* Title: IAccountDao
* Description: 账户的持久层接口
* Company: http://www.itheima.com/
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
* 查询所有账户,采用延迟加载的方式查询账户的所属用户
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from account")
@Results(id="accountMap",
value= {
@Result(id=true,column="id",property="id"),
@Result(column="uid",property="uid"),
@Result(column="money",property="money"),
@Result(column="uid",
property="user",
one=@One(select="com.itheima.dao.IUserDao.findById",
fetchType=FetchType.LAZY) )
})
List<Account> findAll();
}
- 添加用户的持久层接口并使用注解配置
/**
*
* Title: IUserDao
* Description: 用户的持久层接口
* Company: http://www.itheima.com/
*/
public interface IUserDao {
/**
* 查询所有用户
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from user")
@Results(id="userMap",
value= {
@Result(id=true,column="id",property="userId"),
@Result(column="username",property="userName"),
@Result(column="sex",property="userSex"),
@Result(column="address",property="userAddress"),
@Result(column="birthday",property="userBirthday")
})
List<User> findAll();
/**
* 根据 id 查询一个用户
* @param userId
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from user where id = #{uid} ")
@ResultMap("userMap")
User findById(Integer userId);
}
3.3.3 使用注解实现一对多复杂关系映射
需求:
查询用户信息时,也要查询他的账户列表。使用注解方式实现。
分析:
一个用户具有多个账户信息,所以形成了用户(User)与账户(Account)之间的一对多关系
- User 实体类加入 List
/**
*
* Title: User
* Description: 用户的实体类
* Company: http://www.itheima.com/
*/
public class User implements Serializable {
private Integer userId;
private String userName;
private Date userBirthday;
private String userSex;
private String userAddress;
//一对多关系映射:主表方法应该包含一个从表方的集合引用
private List<Account> accounts;
}
- 编写用户的持久层接口并使用注解配置
* <p>Title: IUserDao</p>
* <p>Description: 用户的持久层接口</p>
* <p>Company: http://www.itheima.com/ </p>
*/
public interface IUserDao {
/**
* 查询所有用户
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from user")
@Results(id="userMap",
value= {
@Result(id=true,column="id",property="userId"),
@Result(column="username",property="userName"),
@Result(column="sex",property="userSex"),
@Result(column="address",property="userAddress"),
@Result(column="birthday",property="userBirthday"),
@Result(column="id",property="accounts",
many=@Many(
select="com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao.findByUid",
fetchType=FetchType.LAZY
) )
})
List<User> findAll();
}
@Many:
相当于<collection>的配置
select 属性:代表将要执行的 sql 语句
fetchType 属性:代表加载方式,一般如果要延迟加载都设置为 LAZY 的值
- 编写账户的持久层接口并使用注解配置
/**
*
* Title: IAccountDao
* Description: 账户的持久层接口
* Company: http://www.itheima.com/
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
* 根据用户 id 查询用户下的所有账户
* * @param userId
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from account where uid = #{uid} ")
List<Account> findByUid(Integer userId);
}
3.4 mybatis 基于注解的二级缓存
- 在 SqlMapConfig 中开启二级缓存支持
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
settings>
- 在持久层接口中使用注解配置二级缓存
/**
*
* Title: IUserDao
* Description: 用户的持久层接口
* Company: http://www.itheima.com/
*/
@CacheNamespace(blocking=true)//mybatis 基于注解方式实现配置二级缓存
public interface IUserDao {}