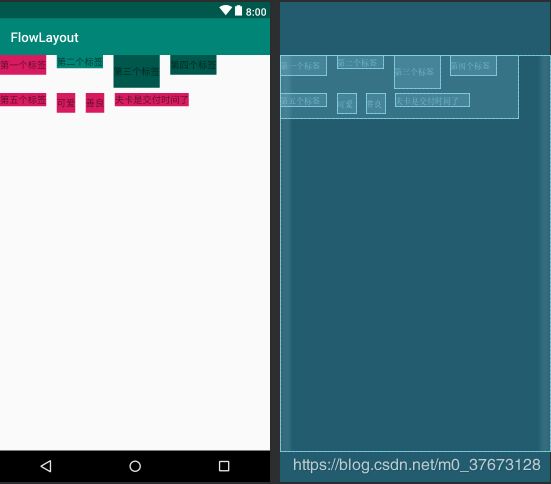
Android自定义流布局实现
Android自定义流布局实现
刚入职不久,从事汽车界的Android开发工作,虽然大部分开发工作都是供应商完成,但想来还是有必要提升一下自己的Android开发技术,不然被供应商忽悠了都不知道,先从Android自定义View开始提升吧。本文所涉及的自定义View的开发是根据技术博客和视频教程所学,并自己动手实现的可运行实例,由于技术有限,文中可能还是会出现很多的错误观点,日后加深理解后会及时纠正,现在记录下来方便后期查看。
自定义View主要分为View和ViewGroup的重写,他们各自重写的方法又各自有着重点,继承View着重与重写onMeasure和onDraw方法,继承ViewGroup着重于重写onMeasure和onLayout方法。这是因为子View一般只存在自己本身,没有更多的子View在其内部需要layout,更多的在于绘制本身;而ViewGroup则不同,在它内部存在各种子View需要他去布局,onDraw方法反而是子View自己的事务,无需ViewGroup多加关注。本文所涉及的自定义流布局则属于继承ViewGroup的布局实现,主要介绍重写的onMeasure和onLayout方法。
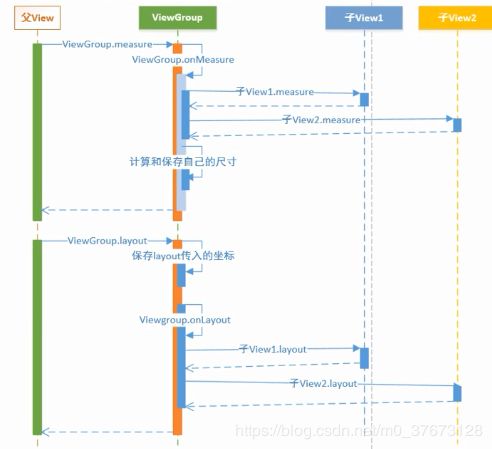
自定义View的开发流程如上图所示,主要包括以下几个步骤:
(1)调用父View.onMeasure方法
(2)对ViewGroup中的每个子View进行测量。
对子View的测量主要是确定子View的measureSpec参数,measureSpec由32位int值构成,其中前两位代表view的measure mode,后三十位代表view的measure size,这样通过一个参数就可以将view测量完成。子View的尺寸受父View的MeasureSpec限制,根据父View的MeasureSpec可以得到子View在不同的MeasureSpec下的尺寸,具体规则体现为下图:

(3)计算和保存自己的尺寸
在子View都测量完成后就可以根据子View的测量大小确认自己的布局大小了,确认父View的尺寸后测量流程就完成了。下面就可以根据测量的尺寸进行布局子View了。
(4)保存layout传入的坐标,调用ViewGroup.onLayout
(5)确认各子View的坐标值并布局
至此,自定义流布局搭建完成,其中还涉及很多细节注意问题,比如数据初始化,子View保存,尺寸保存等,这些在代码细节中均有体现,并在代码中做了一定的注释,下面是流布局的主要代码:
public class FlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
private List<List<View>> allLines;//把每一行的View保存下来,便于在layout中计算每一行的View的left值
private List<Integer> allHeights;//把每一行的行高保存下来,便于在layout中计算每一行View的top值
private int mHorizontalSpacing = dp2px(16);//自定义横向间隙
private int mVerticalSpacing = dp2px(8);//自定义纵向间隙
public FlowLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
private void initMeasureParams() {
allLines = new ArrayList<>();
allHeights = new ArrayList<>();
}
/**
* onMeasure方法负责自身以及子View的测量
* 包括测量模式和尺寸的确定
* */
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
/*-------------------------------------------------------先ViewGroup.measure>>ViewGroup.onMeasure----------------------------------------------------*/
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
/*----------------------------------------------------------------------一些参数的定义与初始化--------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
//初始化参数,必须在这里初始化,因为有可能因为异常导致重新测量绘制,重新测量绘制时参数得重新初始化
initMeasureParams();
int count = getChildCount();
List<View> childViews = new ArrayList<>();
int lineWidthUsed = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
int parentNeedWidth = 0;
int parentNeedHeight = 0;
//父容器本身的宽高度
int selfWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int selfHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
//为了计算出子View在父View中真正占用的空间
int paddingleft = getPaddingLeft();
int paddingright = getPaddingRight();
int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom();
/*--------------------------------------------------------------------子View的measure--------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/**
* 进行子View的测量,根据父View的MeasureSpec确定子View的MeasureSpec
* 注意子ViewMeasureSpec的确认过程,可以进入getChildMeasureSpec查看,三个参数分别为父View的MeasureSpec,父View的padding,子View的尺寸参数值
* 根据这三个参数,可以得到子View的测量模式和对应测量模式下的尺寸值,从而也就确定了子View的MeasureSpec,这样就完成了子View的测量
* MeasureSpec由32位int值构成,前两位为mode,后30位为size
* */
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
LayoutParams childLP = childView.getLayoutParams();
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec, paddingleft + paddingright,
childLP.width);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec, paddingTop + paddingBottom,
childLP.height);
childView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
/*-------------------------------------------------------子View测量完成,下面计算和度量自己的尺寸--------------------------------------------------------*/
/**
* 需要注意的是,在onMeasure函数执行完成之后才有view.getWidth,getHeight等方法,在onMeasure执行完之前只能调用getMeasuredWidth
* 因此想知道childView的占用空间,这里只能调用getMeasuredWidth
* */
int childMeasuredWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
int childMeasuredHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
if(childMeasuredWidth + lineWidthUsed + mHorizontalSpacing > selfWidth) {// 换行
parentNeedWidth = Math.max(parentNeedWidth, lineWidthUsed + mHorizontalSpacing);
parentNeedHeight = parentNeedHeight + lineHeight + mVerticalSpacing;
allLines.add(childViews);
allHeights.add(lineHeight);
lineWidthUsed = 0;
lineHeight = 0;
childViews = new ArrayList<>();
}
childViews.add(childView);
lineWidthUsed = lineWidthUsed + childMeasuredWidth + mHorizontalSpacing;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight,childMeasuredHeight);
}
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int realWidth = widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY?selfWidth:parentNeedWidth;
int realHeight = heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY?selfHeight:parentNeedHeight;
setMeasuredDimension(realWidth,realHeight);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int viewCount = 0;
int curT = getPaddingTop();//初始化顶部坐标
int curL = getPaddingLeft();//初始化靠左坐标
for(int i = 0; i < allLines.size(); i++) {
//得到一行的View
List<View> viewLine = allLines.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < viewLine.size(); j++){
//第i行的第j个子View
View childView = getChildAt(viewCount+j);
/** 第i行的第j个View的坐标*/
int left = curL;
int right = curL + childView.getMeasuredWidth();
int top = curT;
int bottom = curT + childView.getMeasuredHeight();
childView.layout(left, top, right, bottom);
/** 第i行的第j+1个View的坐标left值更新*/
curL = right + mHorizontalSpacing;
}
viewCount = viewCount +viewLine.size();//第i行的第1个子View
/** 换行之后View的坐标top值更新*/
curT = curT + allHeights.get(i) + mVerticalSpacing;
/** 换行之后第一个View的坐标left值重置为初始化边界值*/
curL = getPaddingLeft();
}
}
public static int dp2px(int dp) {
return (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP,dp, Resources.getSystem().getDisplayMetrics());
}
}