A Generalized Deep Learning Approach for Evaluating Secondary Pulmonary Tuberculosis...论文总结
A Generalized Deep Learning Approach for Evaluating Secondary Pulmonary Tuberculosis on Chest Computed Tomography
要解决的问题:
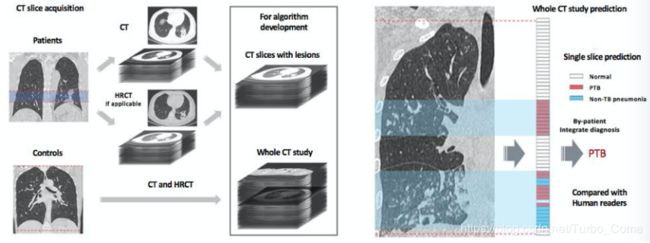
结核型肺炎 Pulmonary Tuberculosis PTB and 非结核型肺炎non-tuberculous(non-TB )的差异是大的,但依靠临床和放射科来判断肺结核的疾病类型仍然很困难,成本高,速度慢。因此,如何应用深度学习技术审核CT图像,协助医生来进行诊断,区别PTB和TB,以及正常的肺部CT图像至关重要。
贡献:
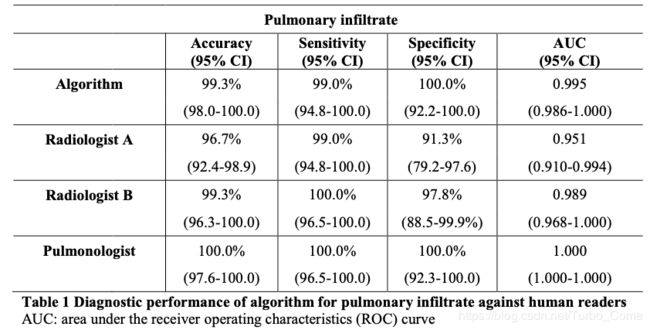
1.提出了一个新颖的算法,可以自动化的发现、预测 secondary PTB从non-TB 和正常病人的CT图像中。并且效果非常显著,和业界专家们的标注基本持平。
2.他们的算法能够被嵌入到移动端的、CT诊断等设备中进行使用
3.他们共享CT数据和训练好的算法,去协助其他医院机构使用、进一步改进,扩展
方法:
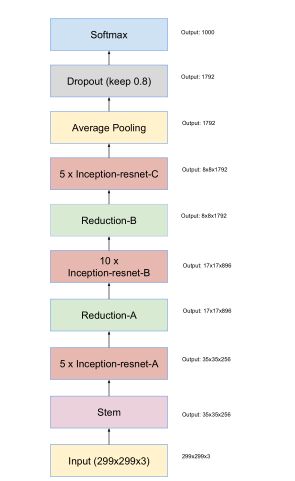
网络:pre-trained Inception-Res-net-v2(训练好的ImageNet迁移过来)
nception-ResNet-v2是Inception V3模型根据ResNet网络变化而来的一种图像分类的算法。
在最后的FC layer之前, 使用了4个平行的FC(4096,2048,1024,512),相同的输入平行放置。
由于PTB和non-TB肺炎的切片数量不均衡,在预测类别时,修改类别权重,以此来平衡每个类别。
采用类别权重增加异常切片的数量,使得算法可以学习到更多的潜在的特征。
之后选择三个具有不同类别权重的 Inception-Res-net-v2模型。 在这三个模型上使用
非加权平均方法对分片级别的概率进行合并。
Imgs: 256*256 thickness:0.625-8 mm
实验:
WCPR Dataset(HRCT 高分辨率CT)
1,124 patients (285,647 total slices including 217,387 HRCT slices)
439 PTB patients (124,680 total slices including 99,217 HRCT slices),
484 non-TB pneumonia patients (116,070 total slices including 83,466 HRCT slices)
201 normal patients (44,897 total slices including 34,704 HRCT slices)