使用hadoop对一组数据排序,求平均值。
1,求平均值
输入文档如下: 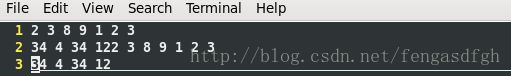
基本思路是利用map来产生<1,num>这样的数据,这样reduce处理的数据形式是<1,num1 nmu2 …..>.
代码:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
public class Count {
public static class TokenizerMapper
extends Mapper{
private final static Text one = new Text("1");
private final static IntWritable two = new IntWritable(1);
//map函数
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString());
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
String val = itr.nextToken();
int va = Integer.parseInt(val);
two.set(va);
context.write(one, two);
}
}
}
public static class IntSumReducer
extends Reducer {
private IntWritable result = new IntWritable();
//reduce函数
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable values,
Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
int k = 0;
for (IntWritable val : values) {
sum += val.get();
k++;
}
result.set(sum/k);
context.write(key, result);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: wordcount ");
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = new Job(conf, "Count");
job.setJarByClass(Count.class);
job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
然后对源程序编译打包成jar文件,并且把输入文件上传到hdfs系统中。运行 ![]()
![]()
![]()
成功后显示: 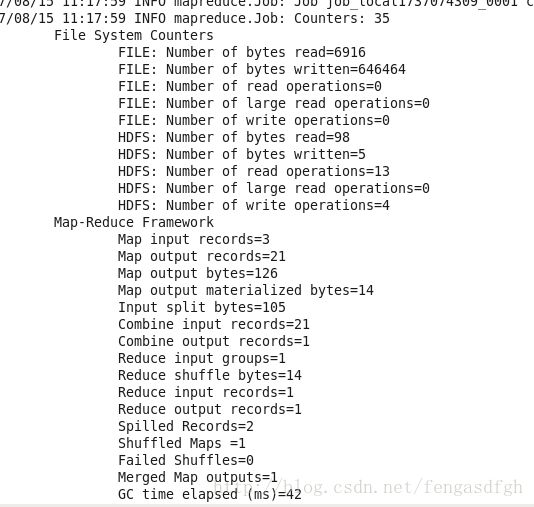
我们查看结果; 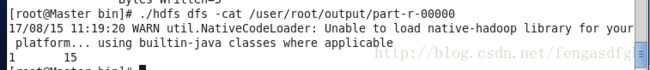
1 15就是结果,这里的15就是平均值。
这里我们只用到了了一个reduce,所以只有一个输出文件。
2,对数据排序
我们这里说的是全局排序,因为数据在map完成后会根据partition分区,再根据key排序,所以如果我们能把某一个区间的值都给一个reduce,那么所有的reduce输出的文件连起来就是有序的。
代码:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JobClient;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JobConf;
public class Count {
//比较器
public static class IntKeyComparator extends WritableComparator{
protected IntKeyComparator(){
super(IntWritable.class, true);
}
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b){
return -super.compare(b,a);
}
}
//分区
public static class EdgePartitioner
extends Partitioner<IntWritable, Text>{
public int getPartition(IntWritable key, Text value, int numPartitions){
//为了方便,我这里使用了简单的分区
int va = Integer.parseInt(key.toString());
if (va > 25)
return 1;
else return 0;
}
}
public static class TokenizerMapper
extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, IntWritable, Text>{
private final static Text one = new Text("1");
private final static IntWritable two = new IntWritable(1);
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString());
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
String val = itr.nextToken();
int va = Integer.parseInt(val);
context.write(new IntWritable(va), one);
}
}
}
public static class IntSumReducer
extends Reducer<IntWritable,Text, IntWritable, Text> {
private IntWritable result = new IntWritable();
public void reduce(IntWritable key, Iterable values,
Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(key ,new Text(""));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: wordcount " );
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = new Job(conf, "Count");
job.setJarByClass(Count.class); job.setPartitionerClass(EdgePartitioner.class);
job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(2);
job.setSortComparatorClass(IntKeyComparator.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
} 在这里,区间的划分我们可以使用采样来保证均匀。在采样时,我们可以使用hadoop的几种采样工具,RandomSampler,InputSampler,IntervalSampler。这些可以自己了解。
输入文件: 
将源程序打包,运行。在文件系统里可以看到成功输出的2个文件 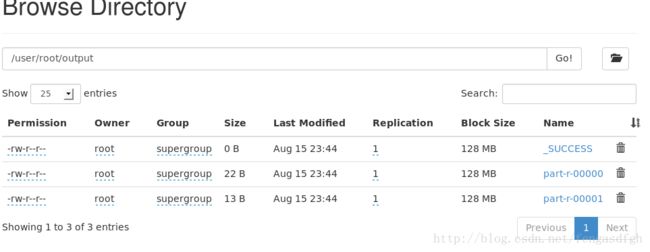
第一个文件的结果: 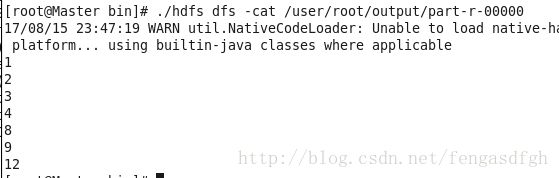
第二个文件: ![]()
在以后我还会补充其他的问题。