必须了解的SpringBoot知识:自动装配原理和自定义starter
SpringBoot自动装配原理 & 自定义starter
Springboot自动装配的原理
学了Springboot后,秉承着不能只做框架的搬运工,最好是了解一下框架是如何运行的,方便自己成为更好的搬运工……
在主程序入口我们可以看到一个注解 @SpringBootApplication,这个注解的核心三个注解为:
- @ComponentScan — 扫描组件&自动装配
- @SpringBootConfiguration — 继承@Configuration注解,加载配置文件
- @EnableAutoConfiguration — 这个就是自动装配的核心注解
自动装配的过程
先看一下@EnableAutoConfiguration注解里面的内容,idea通过按住Ctrl+鼠标点击该注解即可进入。
进入后可以看到有一个注解–>@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})

这个注解会import AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class,我们继续进入可以看到selectImports()方法

为了便于理解,我总结一下这个方法的功能,具体代码可以在有大概印象后去理解:它具有扫描META-INF/spring.factories文件的功能,这个spring.factories文件里面是采用键值对的方式存储的。
而其中有个key=org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration可以设置使与value值同名的自动配置类生效。我们随便点开一个autoconfigure的jar包就可以看到相同结构的META-INF/spring.factories。
key=org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration对应的value的配置类命名规则是:xxxAutoConfiguration,这些AutoConfiguration有多个注解,有些注解是设置生效的时机,其中有一个 @EnableConfigurationProperties({DataSourceProperties.class}) 可以装配一些xxxProperties类,这些xxxProperties类有注解 @ConfigurationProperties,功能是:获取主配置文件的属性,绑定对应元素,封装成bean用于导入到spring容器中
总结
下面总结一下自动装配的原理(过程):
- 通过@EnableAutoConfiguration注解寻找META-INF目录下的spring.factories
- 加载spring.factories中设定好的自动配置类(xxxAutoConfiguration)
- 自动装配类中有==@ConditionalOnXXX==来设置生效的情况,还有一些starter通过@EnableConfigurationPropertie去自动装配xxxProperties

- xxxProperties类拥有注解 @ConfigurationProperties,它可以读取全局配置文件,并自动绑定到对应属性中
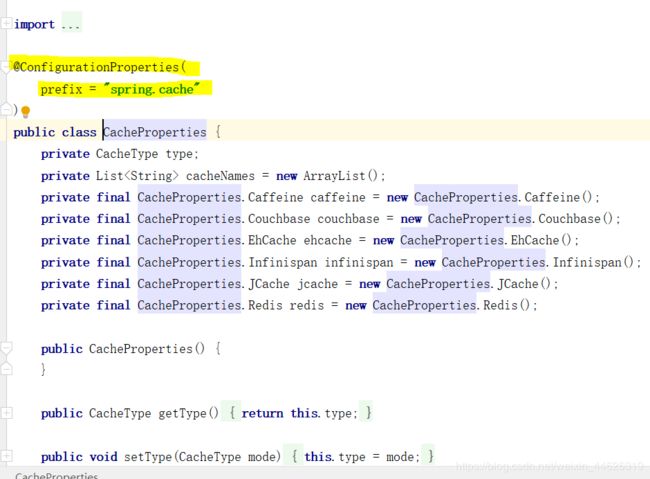
图片中@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “spring.cache”)的意思是,读取全局配置文件中前缀为spring.cache的属性,到时候在全局配置文件中设置 spring.cache.type=xxx,就会绑定到type中。 - 最终完成自动装配!
手动撸一个starter
看懂了是如何实现starter的自动装配,那么我们自己动手写一个starter吧!
跟着我走一遍,过程中可能会遇到问题,但是遇到了问题,才会更好的理解底层的实现。
初始步骤
在这里要注意命名规则,我们命名artifac的时候是:xxx-spring-boot-starter -->(Maven模块的名字),xxx-spring-boot-autoconfigure -->(SpringBoot模块的名字) ,我后面的实例名字有点问题,虽然影响不打,可是不符合约定的操作,建议按照约定来!
xxx是指你自己的命名,比如mybatis就是:mybatis-spring-boot-starter
xxx-spring-boot-starter 编写
这个启动器我们很简单,只需要直接在pom.xml加入我们xxx-spring-boot-configure的依赖就行了。
pom.xml:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>com.zzt.startergroupId>
<artifactId>zzt001-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.zzt.startergroupId>
<artifactId>zzt001-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigurerartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
如果你不知道怎么填写该依赖,那么你只要进入到xxx-spring-boot-configure的pom.xml,寻找复制黏贴过去即可:

xxx-spring-boot-configurater 编写
步骤如下:
- 删除主程序XXXSpringBootApplication和pox.xml的build配置还有test目录,++只保留最基础的starter++
pom.xml:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.2.7.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<groupId>com.zzt.startergroupId>
<artifactId>zzt001-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigurerartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<name>zzt001-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigurername>
<description>Demo project for Spring Bootdescription>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starterartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processorartifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
我们在后面使用 @ConfigurationProperties 的时候可能会提示提示
Spring Boot Configuration Annotation Proessor not found in classpath
那么添加多一个依赖,见上面,其实不加也可以但是看着心烦……
- 编写 xxxAutoConfiguration & xxxService & xxxProperties
在这里我的xxx是Person
首先编写PersonProperties:
package com.zzt.starter;/*
* @author: G_night
* 转载请申明作者
* Reprint please state the author
*/
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
//下面注解的用处是以后使用我们这个starter的时候
//可以在application.properties设置zzt.first.info=你要写的值
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "zzt.first")
public class PersonProperties {
private String info;//info对应zzt.first.info
public String getInfo() {
return info;
}
public void setInfo(String info) {
this.info = info;
}
}
接下来编写PersonService类:
package com.zzt.starter;/*
* @author: G_night
* 转载请申明作者
* Reprint please state the author
*/
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
public class PersonService {
PersonProperties personProperties;
public PersonProperties getPersonProperties() {
return personProperties;
}
public void setPersonProperties(PersonProperties personProperties) {
this.personProperties = personProperties;
}
public void say(String info){
System.out.println("自己做的Starter----配置信息-----info:"+personProperties.getInfo());
System.out.println("传递的info:"+info);
}
}
最后编写PersonAutoConfiguration类:
package com.zzt.starter;/*
* @author: G_night
* 转载请申明作者
* Reprint please state the author
*/
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnWebApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication //设置在web应用生效
@EnableConfigurationProperties(PersonProperties.class)
public class PersonAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
PersonProperties personProperties;
@Bean
public PersonService personService(){
PersonService personService=new PersonService();
personService.setPersonProperties(personProperties);
return personService;
}
}
- 在resources下创建META-INF目录,再创建spring.factories,千万别打错了,本人一开始就打错了……如果你发现后面使用的时候无法自动注入,那么考虑这里是否出错~
在spring.factories设置要加载的对象:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.zzt.starter.PersonAutoConfiguration
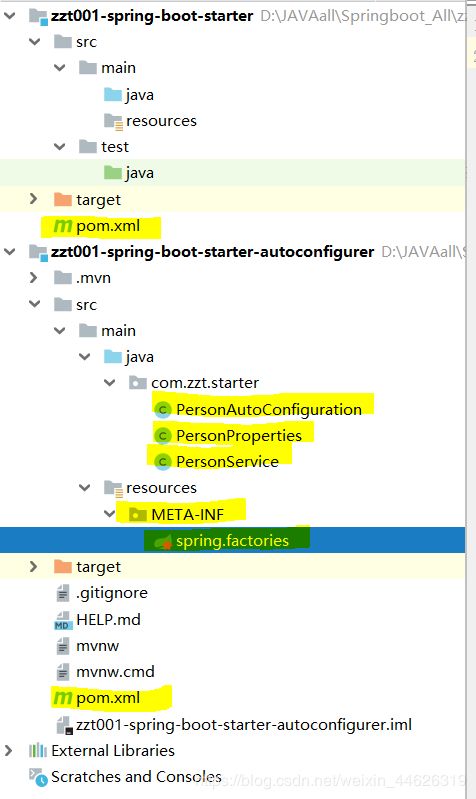
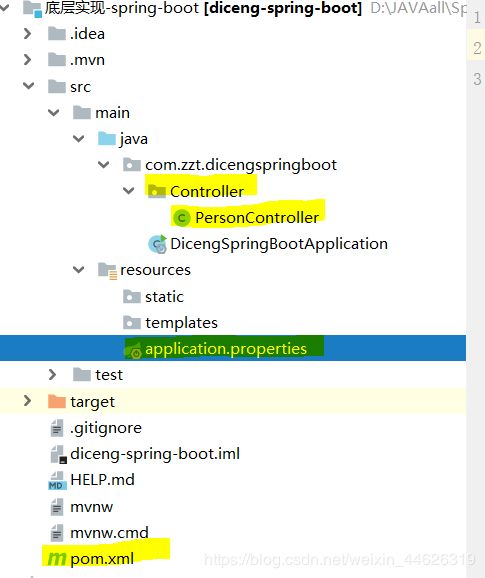
上面两个Module写完以后,目录大概是这样的
黄色的地方就是创建or修改的!
打包项目
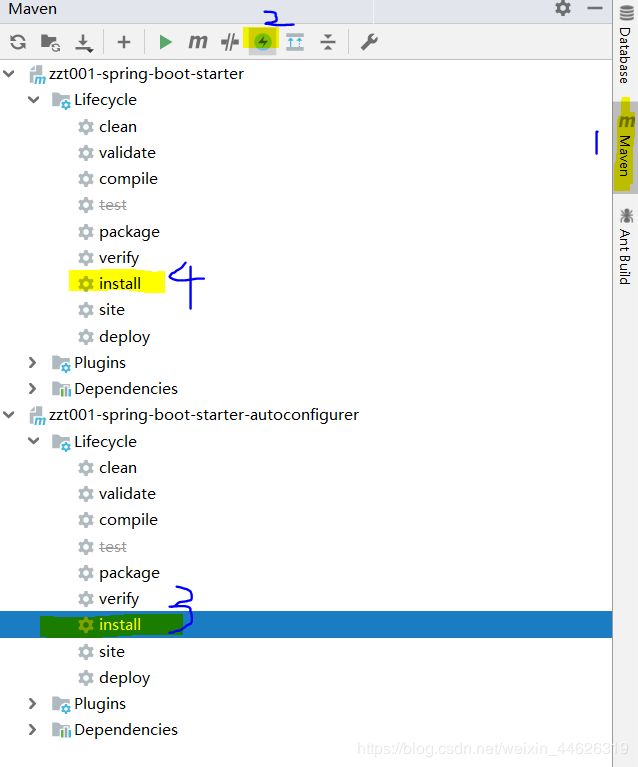
编写完以后要打包到maven仓库,要注意打包顺序!先打包xxx-spring-boot-configure 再打包 xxx-spring-boot-starter
打包方式和普通打包maven项目一样
实战使用
创建一个Springboot,选择web,其实也可以不选但是我在自动配置类写了==@ConditionalOnWebApplication==,所以要选择web,主要是觉得这样好观察使用
- 自己编写一个controller
package com.zzt.dicengspringboot.Controller;/*
* @author: G_night
* 转载请申明作者
* Reprint please state the author
*/
import com.zzt.starter.PersonService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class PersonController {
@Autowired
private PersonService personService;
@RequestMapping("/person")
public String person(){
System.out.println("访问了person");
this.personService.say("ok!");
return "返回看以下你的IDE看一下输出是否正常把!";
}
}
- 在application.properties设置info值
# 配置自己的starter的设置
zzt.first.info=success
- 启动项目,输入localhost:8080/person访问
一些可能会遇到的错误
- Controller的位置不对,导致我们无法访问localhost:8080/person
- 扫描不到PersonService,无法@Autowired
解决方法是添加扫描,看注释的示例:
package com.zzt.dicengspringboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
@SpringBootApplication
//@ComponentScan({"com.zzt.starter"}) 一开始spring.factories写错了,淦
//@ComponentScan({"com.zzt.dicengspringboot.Controller"})
//如果层级目录设置不对可能会扫描不到,这时候加上这句扫描就可以了,建议看一下扫描的层级规则
public class DicengSpringBootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DicengSpringBootApplication.class, args);
}
}
好了这就是自己编写的很简单的starter!
有问题欢迎交流,可能有些书写有点小错误,见谅。