28-Spring源码解析之事务(1)——事务初始化源码
Spring版本:
5.2.1.RELEASE
目录
- 一、JDBC方式下的事务使用示例
- 1. 创建数据表`city`结构
- 2. 创建`Dao`层
- 3. 创建`Service`层
- 4. 创建`Controller`层
- 5.创建`Spring`配置文件(`applicationContext.xml`)
- 6. `web.xml` 文件
- 二、事务自定义标签
- 2.1 `AopAutoProxyConfigurer`类的`configureAutoProxyCreator`方法
- 2.2.1 注册`InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator`
- 三、创建与事务有关的代理类
- 3.1 获取对应`method`或`class`的增强器
- 3.1.1 获取所有增强器
- 3.1.2 候选增强器中寻找到匹配项
- 总结
- 参考
Spring中声明式事务让我们从复杂的事务处理中得到解脱,使我们再也不需要去处理获得连接、关闭连接、事务提交和事务回滚等操作,再也不需要在与事务相关的方法中处理大量的try...catch...finally代码。Spring中事务的使用虽然已经相对简单很多,但是,还是有很多的使用及配置规则,这里只列举出最常用的使用方法。
同样,我们还是以最简单的示例进行直观的介绍。
一、JDBC方式下的事务使用示例
1. 创建数据表city结构
CREATE TABLE `city` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`Name` varchar(128) DEFAULT NULL,
`CountryCode` varchar(128) DEFAULT NULL,
`District` varchar(128) DEFAULT NULL,
`Population` int DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=72 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
2. 创建Dao层
@Repository
public class CityDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void insert() {
String sql = "INSERT INTO `city` (`Name`, `CountryCode`, `District`, `Population`) VALUES (?,?,?,?)";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,"aaa","IDN","hc",12);
}
}
3. 创建Service层
@Service
public class CityService {
@Autowired
private CityDao cityDao;
@Transactional
public void insertCity() throws Exception {
cityDao.insert();
int i = 10 / 0;
}
}
4. 创建Controller层
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/city")
public class CityController {
@Autowired
CityService cityService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@Transactional
public String test() {
try {
cityService.insertCity();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "world";
}
}
5.创建Spring配置文件(applicationContext.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="dao" />
<context:component-scan base-package="service" />
<!--配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="user" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value=""/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT"/>
</bean>
<!--配置JDBC-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" >
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
</beans>
6. web.xml 文件
因为本例子是在SpringMVC下进行的,因此,需要配置web.xml。
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>spring4-mybatis3-demo</display-name>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<filter>
<filter-name>SpringEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>SpringEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*
虽然上述例子是在SpringMVC下进行的,但是为了更简洁的表达例子,没有增加实体类而是直接将要插入的信息放到了Dao层。
测试时只需要在浏览器上输入:localhost:8080/项目名/city/test就可以出来结果。 由于在Service层的insertCity方法中加入了int i = 10 / 0这个运行时异常和@Transactional注解,因此数据不会被保存到数据库中。
注意:默认情况下Spring中的事务处理只对RuntimeException方法进行回滚,所以,如果此处将RuntimeException替换成普通的Exception不会产生回滚效果。
二、事务自定义标签
对于Spring中每个功能的分析我们都要从以下几点进行:
- 该功能的开关在哪
- 该功能注册在
Spring中的类有哪些 - 这些类在哪些地方发挥作用,发挥什么样的作用
那么,首先我们就要找一下事务功能的开关在哪里。我们首先从Spring的配置文件(applicationContext.xml)入手,在配置文件(applicationContext.xml)中有这样一个配置:
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
这个配置就是事务的开关,如果没有这个配置,那么Spring中就不会存在事务功能。
我们从这个配置开始分析。首先我们知道Spring的默认标签,而是一个自定义标签,自定义标签解析的过程一定做了很多事情。因此我们先从自定义标签解析开始分析。
通过搜索关键字annotation-driven,最终锁定在TxNamespaceHandler类的init()方法中。
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("advice", new TxAdviceBeanDefinitionParser());
// -------------------注册解析annotation-driven的解析器AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser---------------
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-driven", new AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("jta-transaction-manager", new JtaTransactionManagerBeanDefinitionParser());
}
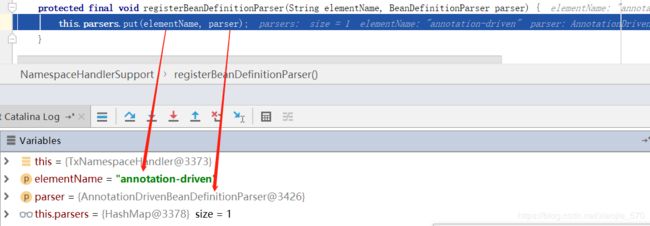
上述代码的作用就是为AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser类型的解析器。
根据自定义标签的规则和上述代码,我们可以知道,在遇到Spring会使用AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser类的内部类AopAutoProxyConfigurer的parse方法进行解析。
我们直接进入AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser类的parse方法。
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
// 注册事务的事件监听器工厂
registerTransactionalEventListenerFactory(parserContext);
String mode = element.getAttribute("mode");
if ("aspectj".equals(mode)) {
// mode="aspectj"
registerTransactionAspect(element, parserContext);
}
else {
// Spring中的事务是以AOP为基础
AopAutoProxyConfigurer.configureAutoProxyCreator(element, parserContext);
}
return null;
}
上述代码要开始解析AopAutoProxyConfigurer类的configureAutoProxyCreator方法。
2.1 AopAutoProxyConfigurer类的configureAutoProxyCreator方法
我们以默认配置为例子进行分析,进入AopAutoProxyConfigurer类的configureAutoProxyCreator方法。
首先我们要知道AopAutoProxyConfigurer类是AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser类的内部类,这个类只有一个方法:configureAutoProxyCreator。
private static class AopAutoProxyConfigurer {
public static void configureAutoProxyCreator(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
// ----------------------------------【功能一】-2.1.1详细介绍---------------------------------------------
// 注册InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
AopNamespaceUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(parserContext, element);
// TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME = "internalTransactionAdvisor"
String txAdvisorBeanName = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME;
if (!parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(txAdvisorBeanName)) {
Object eleSource = parserContext.extractSource(element);
// ----------------------------------【功能二】-TransactionAttributeSource---------------------------------------------
// Create the 【TransactionAttributeSource】 definition.
RootBeanDefinition sourceDef = new RootBeanDefinition(
"org.springframework.transaction.annotation.AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource");
sourceDef.setSource(eleSource);
sourceDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
String sourceName = parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(sourceDef);
// ----------------------------------【功能三】-TransactionInterceptor---------------------------------------------
// Create the 【TransactionInterceptor】 definition.
RootBeanDefinition interceptorDef = new RootBeanDefinition(TransactionInterceptor.class);
interceptorDef.setSource(eleSource);
interceptorDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registerTransactionManager(element, interceptorDef);
interceptorDef.getPropertyValues().add("transactionAttributeSource", new RuntimeBeanReference(sourceName));
String interceptorName = parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(interceptorDef);
// ----------------------------------【功能四】-TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor---------------------------------------------
// Create the 【TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor】 definition.
RootBeanDefinition advisorDef = new RootBeanDefinition(BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor.class);
advisorDef.setSource(eleSource);
advisorDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
// 将sourceName的Bean注入到advisorDef的transactionAttributeSource属性中
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("transactionAttributeSource", new RuntimeBeanReference(sourceName));
// 将interceptorName的Bean注入到advisorDef的adviceBeanName属性中
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("adviceBeanName", interceptorName);
// 如果配置了order属性,则将其加入到advisorDef的order属性中
if (element.hasAttribute("order")) {
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("order", element.getAttribute("order"));
}
// 将advisorDef对象的BeanDefinition注册到Spring容器中
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(txAdvisorBeanName, advisorDef);
CompositeComponentDefinition compositeDef = new CompositeComponentDefinition(element.getTagName(), eleSource);
compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(sourceDef, sourceName));
compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(interceptorDef, interceptorName));
compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(advisorDef, txAdvisorBeanName));
parserContext.registerComponent(compositeDef);
}
}
}
该方法做了2件事情
- 将
InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类、TransactionAttributeSource类、TransactionInterceptor类和BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor类的beanDefinition注册到Spring容器中。 - 将
TransactionAttributeSource和TransactionInterceptor放到了BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor中。
2.2.1 注册InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
上面2.2节的configureAutoProxyCreator方法中的第一句是一个非常重要的代码:
AopNamespaceUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(parserContext, element);
我们进入AopNamespaceUtils类的registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary方法。
public static void registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
ParserContext parserContext, Element sourceElement) {
// ----------------------------------------核心--------------------------------------------------
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = AopConfigUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
parserContext.getRegistry(), parserContext.extractSource(sourceElement));
useClassProxyingIfNecessary(parserContext.getRegistry(), sourceElement);
registerComponentIfNecessary(beanDefinition, parserContext);
}
继续进入AopConfigUtils类的registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary方法。
public static BeanDefinition registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source);
}
到这里我们知道了,上面2.2节的configureAutoProxyCreator方法的主要目的就是注册一个InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类型的BeanDefinition。
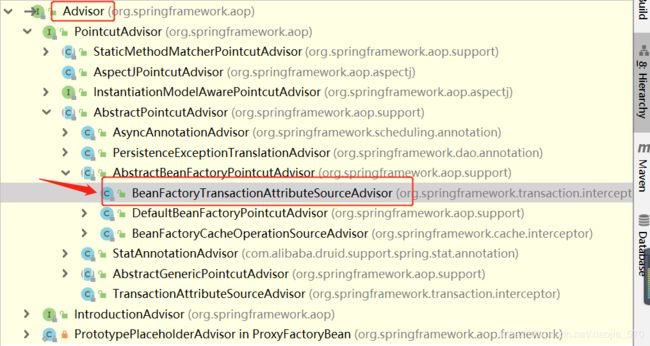
那么注册这个InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的目的是什么呢?我们看一下这个类的类图。

从上面图可以看出来,InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类就是一个BeanPostProcessor,就是说在Spring中,所有的Bean实例化的时候,Spring都会保证调用InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的postProcessorAfterInitialization方法。
我们以前面的示例为例,当实例化CityService的Bean的时候,会调用InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类的postProcessorAfterInitialization方法。
三、创建与事务有关的代理类
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
result = beanProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (result == null) {
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
进入InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类的postProcessorAfterInitialization方法。但是由于InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类没有重写postProcessorAfterInitialization方法,所以只能调用其父类AbstractAutoProxyCreator的postProcessorAfterInitialization方法。
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
// 是否是由于避免循环依赖而创建的Bean代理
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
// ---------------------------------核心方法--------------------------------------
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
这里实现的主要目的是对指定的Bean进行封装。
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// 已经处理过了
// 说明:包装过的Bean会放到targetSourcedBeans中。
if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
// ---------------------------------【功能一】 3.1 详细介绍--------------------------------------
// 找出指定Bean对于的增强器
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
// 该Bean有增强器,将当前bean和标志需要增强true放到advisedBeans中
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// ---------------------------------【功能二】 3.2 详细介绍--------------------------------------
// 根据找到的增强器创建代理
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
实际上上面的方法我们在AOP系列文章中有提过。
在wrapIfNecessary方法中做了两件事情:
- 找出指定
Bean对应的增强器 - 根据找出的增强器创建代理
3.1 获取对应method或class的增强器
在wrapIfNecessary方法中做的第一件事情就是找出指定Bean对应的增强器,实际上这是两件事情:找到所有增强器,看增强器是否匹配当前Bean。
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, TargetSource targetSource) {
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}
我们继续进入findEligibleAdvisors方法
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// ---------------------------------【功能一】 3.1.1 详细介绍--------------------------------------
// 找到所有增强器
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
// ---------------------------------【功能二】 3.1.2 详细介绍--------------------------------------
// 找到匹配当前Bean的增强器
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
3.1.1 获取所有增强器
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
return this.advisorRetrievalHelper.findAdvisorBeans();
}
继续进入BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper类的findAdvisorBeans方法
public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans() {
// Determine list of advisor bean names, if not cached already.
String[] advisorNames = null;
synchronized (this) {
advisorNames = this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames;
if (advisorNames == null) {
// ---------------------------------------------核心方法--------------------------------------
// 通过BeanFactoryUtils类将beanFactory中所有Advisor类型的BeanName都找到,就是从beanDefinition中找
advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false);
// 将找到的Advisor类型的BeanName缓存起来
this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames;
}
}
if (advisorNames.length == 0) {
return new LinkedList<Advisor>();
}
List<Advisor> advisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>();
for (String name : advisorNames) {
if (isEligibleBean(name)) {
if (this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(name)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping currently created advisor '" + name + "'");
}
}
else {
try {
// ---------------------------------------------核心方法--------------------------------------
advisors.add(this.beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class));
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
Throwable rootCause = ex.getMostSpecificCause();
if (rootCause instanceof BeanCurrentlyInCreationException) {
BeanCreationException bce = (BeanCreationException) rootCause;
if (this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(bce.getBeanName())) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping advisor '" + name +
"' with dependency on currently created bean: " + ex.getMessage());
}
// Ignore: indicates a reference back to the bean we're trying to advise.
// We want to find advisors other than the currently created bean itself.
continue;
}
}
throw ex;
}
}
}
}
return advisors;
}
以上方法做了三件事情:
- 从
beanFactory中的BeanDefintion中找到Advisor类型的beanName - 将找到的
Advisor类型的beanName存储到缓存(cachedAdvisorBeanNames)中。 - 实例化找到的
Advisor类型的Bean,然后将找到的所有的Advisor类型的Bean放到advisors中返回
我们还记得在本篇文章的2.1节注册了一个BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor类型的beanDefinition嘛。实际上这个BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor类就是实现了Advisor接口的类。因此这里面实例化的正是:BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor类
3.1.2 候选增强器中寻找到匹配项
当找出对应的呃增强之后,我们接下来的任务就是看这些增强是否与对应的class或者method匹配了。
protected List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(beanName);
try {
return AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass);
}
finally {
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(null);
}
}
我们进入AopUtils类的findAdvisorsThatCanApply方法
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {
if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
return candidateAdvisors;
}
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>();
// 首先处理引介增强
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
// 引介增强已经处理
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// already processed
continue;
}
// 处理普通Bean的增强
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
我们进入canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)方法
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass);
}
else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
// It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies.
return true;
}
}
当前的advisor为BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor类型的。而BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor类间接实现了PointcutAdvisor接口,因此会在canApply方法的第二个if判断时通过判断,将pca.getPointcut()的返回值作为参数继续调用canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);。
pca.getPointcut()会返回TransactionAttributeSource类型
public class BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor extends AbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor {
private TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource;
private final TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut pointcut = new TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut() {
@Override
protected TransactionAttributeSource getTransactionAttributeSource() {
return transactionAttributeSource;
}
};
public Pointcut getPointcut() {
return this.pointcut;
}
....省略
}
下面我们就使用TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut类型的实例作为方法canApply的参数继续跟踪canApply。
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
// 此时pci表示:BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {
// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...
return true;
}
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<Class<?>>(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
classes.add(targetClass);
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) {
if ((introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null &&
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) ||
// ---------------------------------------------核心方法--------------------------------------
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
上面方法就是为了查找当前类是否有增强器。
我们继续看调用的TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut类的matches方法
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
if (TransactionalProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
// 这个时在自定义标签解析的时候注入给BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor类的
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null);
}
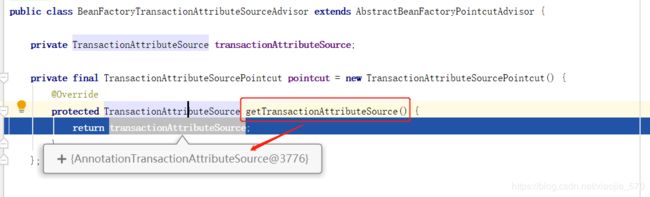
上面的tas是AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource类型的。
我们继续进入AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource类的getTransactionAttribute方法。但是该类没有该方法,因此调用类AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource的父类AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource的getTransactionAttribute方法
public TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return null;
}
// First, see if we have a cached value.
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(method, targetClass);
Object cached = this.attributeCache.get(cacheKey);
if (cached != null) {
// Value will either be canonical value indicating there is no transaction attribute,
// or an actual transaction attribute.
if (cached == NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE) {
return null;
}
else {
return (TransactionAttribute) cached;
}
}
else {
// ---------------------------------------------核心方法--------------------------------------
TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
// Put it in the cache.
if (txAttr == null) {
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE);
}
else {
String methodIdentification = ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(method, targetClass);
if (txAttr instanceof DefaultTransactionAttribute) {
((DefaultTransactionAttribute) txAttr).setDescriptor(methodIdentification);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Adding transactional method '" + methodIdentification + "' with attribute: " + txAttr);
}
// ---------------------------------------------重要语句:加入缓存--------------------------------------
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, txAttr);
}
return txAttr;
}
}
我们看到getTransactionAttribute方法也没有真正提供匹配的代码,而是进行一些Spring经常用的套路。即
首先从缓存中加载,如果缓存中没有的话,再去匹配,但是匹配的工作委托给了computeTransactionAttribute方法。最后将匹配的结果放入this.attributeCache中。下面我们进入computeTransactionAttribute方法。
protected TransactionAttribute computeTransactionAttribute(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
// Don't allow no-public methods as required.
if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
return null;
}
// Ignore CGLIB subclasses - introspect the actual user class.
Class<?> userClass = ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass);
// The method may be on an interface, but we need attributes from the target class.
// If the target class is null, the method will be unchanged.
// method代表接口中的方法
// specificMethod代表实现类中的方法
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, userClass);
// If we are dealing with method with generic parameters, find the original method.
specificMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
// -------------------------------------首先查看方法中是否存在事务声明-----------------------------------------------
// First try is the method in the target class.
TransactionAttribute txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod);
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// -------------------------------------首先查看方法所在类中是否存在事务声明-----------------------------------------------
// Second try is the transaction attribute on the target class.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
if (specificMethod != method) {
// 查找接口方法
// Fallback is to look at the original method.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method);
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// 到接口中的类中去寻找
// Last fallback is the class of the original method.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
}
return null;
}
对于事务属性的获取规则是这样的顺序
- 首先如果方法中存在事务属性,则使用方法上的属性
- 其次使用方法所在类上的属性,
- 如果方法所在类的属性上还是没有搜索到对应的事务属性,再搜索接口中的方法
- 如果接口中的方法没有最后尝试使用接口的类上的声明
上面的几种情况不论进入了哪个匹配,最后都会调用findTransactionAttribute方法。
那么接下来我们进入findTransactionAttribute方法
protected TransactionAttribute findTransactionAttribute(Method method) {
return determineTransactionAttribute(method);
}
进入AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource类的determineTransactionAttribute方法
protected TransactionAttribute determineTransactionAttribute(AnnotatedElement ae) {
if (ae.getAnnotations().length > 0) {
for (TransactionAnnotationParser annotationParser : this.annotationParsers) {
TransactionAttribute attr = annotationParser.parseTransactionAnnotation(ae);
if (attr != null) {
return attr;
}
}
}
return null;
}
上面方法中的this.annotationParsers是在当前类AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource创建实例调用构造方法的时候初始化的,其中的值被加入了SpringTransactionAnnotationParser,因此当进行属性获取的时候使用的是SpringTransactionAnnotationParser类的parseTransactionAnnotation方法进行解析的。
public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotatedElement ae) {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotationAttributes(ae, Transactional.class);
if (attributes != null) {
// ----------------------------------------------------核心--------------------------------------------------------
return parseTransactionAnnotation(attributes);
}
else {
return null;
}
}
至此,我们终于看到了获取注解标记的代码。上述代码包含两个功能
- 首先会判断当前类是否含有
@Transacation注解 - 其次如果有的话调用
parseTransactionAnnotation来解析含有@Transacation注解的方法的详细属性
接着我们进入parseTransactionAnnoattion方法
protected TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
RuleBasedTransactionAttribute rbta = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute();
// 解析 propagation
Propagation propagation = attributes.getEnum("propagation");
rbta.setPropagationBehavior(propagation.value());
// 解析 isolation
Isolation isolation = attributes.getEnum("isolation");
rbta.setIsolationLevel(isolation.value());
// 解析 timeout
rbta.setTimeout(attributes.getNumber("timeout").intValue());
// 解析 readOnly
rbta.setReadOnly(attributes.getBoolean("readOnly"));
// 解析 value
rbta.setQualifier(attributes.getString("value"));
ArrayList<RollbackRuleAttribute> rollBackRules = new ArrayList<RollbackRuleAttribute>();
// 解析 rollbackFor
Class<?>[] rbf = attributes.getClassArray("rollbackFor");
for (Class<?> rbRule : rbf) {
RollbackRuleAttribute rule = new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule);
rollBackRules.add(rule);
}
// 解析 rollbackForClassName
String[] rbfc = attributes.getStringArray("rollbackForClassName");
for (String rbRule : rbfc) {
RollbackRuleAttribute rule = new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule);
rollBackRules.add(rule);
}
// 解析 noRollbackFor
Class<?>[] nrbf = attributes.getClassArray("noRollbackFor");
for (Class<?> rbRule : nrbf) {
NoRollbackRuleAttribute rule = new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule);
rollBackRules.add(rule);
}
// 解析 noRollbackForClassName
String[] nrbfc = attributes.getStringArray("noRollbackForClassName");
for (String rbRule : nrbfc) {
NoRollbackRuleAttribute rule = new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule);
rollBackRules.add(rule);
}
rbta.getRollbackRules().addAll(rollBackRules);
return rbta;
}
上面方法就实现了对对应类或者方法的事务属性的提取操作,最后将提取的结果返回,一直返回到getTransactionAttribute中。
至此,事务功能的初始化工作便结束了,当判断某个Bean适用于增强时(findAdvisorsThatCanApply),也就是适用于增强器:BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor。
总结
本篇文章主要做了两件事情:
- 通过调用
findCandidateAdvisors方法来获取所有增强器。 - 通过调用
findAdvisorsThatCanApply方法判断当前类或者方法是否有匹配的增强器,将匹配到的类或者方法加入到缓存AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource.attributeCache属性中。
下面给出整体的调用流程图。因为事务的功能是在创建每个Bean时,调用initializeBean时进行的,因此我们从initializeBean开始给出

红色框的两条语句是用来加入缓存的,在后面进行事务增强时使用。
下一篇我们介绍当调用被@Transalnal注解标注的方法时,Spring所做的事情。
参考
[1] 《Spring源码深度解析》