【前端】【html5/css3】前端学习之路(四)(CSS3动画/CSS3伸缩布局/CSS3背景)
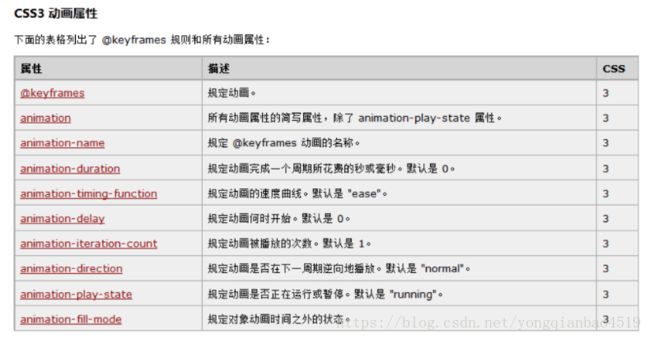
一、动画【 animation 】
动画是CSS3中具有颠覆性的特征之一,可通过设置多个节点来精确控制一个或一组动画,常用来实现复杂的动画效果。
语法格式:
| animation:动画名称 花费时间 运动曲线 何时开始 播放次数 是否反方向; |
以上的几项,除了 名字,动画时间,延时 有严格顺序要求之外,其他顺序随意。
直接用案例理解吧。
案例一(基本理解)
.animationtest {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: pink;
float: left;
/*animation:动画名称 花费时间 运动曲线 何时开始 播放次数 是否反方向;*/
/*动画名称:要和keyframe的动画名称相同,才可以对应上*/
/*播放次数:可以任意写数字次数,如果想要无限次播放则使用infinite*/
/*是否反方向:不回放可以不填也可以填normal,如果想要回放则可以用alternate*/
animation: move 4s ease 0s infinite normal;
}
.animationtest2 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
float: left;
background-color: skyblue;
animation: move2 4s infinite alternate;
}
/*keyframes有两种设置方式,一种是简单分为两步,也就是 form>to 两步,也可以利用 0%>100% 为区间进行详细的动画区分*/
@keyframes move {
from {
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
}
to {
width: 700px;
height: 500px;
background-color: blue;
}
}
@keyframes move2 {
20% {
width: 250px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
}
50% {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: greenyellow;
}
70% {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: pink;
}
100% {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: deeppink;
}
}
以上能够理解animation的主要作用,接下来做两个案例。
案例二(心脏跳动案例)
效果:
图片:
代码:
div {
width: 400px;
margin: 100px auto;
}
img {
width: 400px;
height: 100%;
/*animation:动画名称 花费时间 运动曲线 何时开始 播放次数 是否反方向;*/
animation: heartbeat 1s ease-out infinite;
}
@keyframes heartbeat {
30% {
transform: scale(1);
}
60% {
transform: scale(1.1);
}
100% {
transform: scale(1);
}
}

案例三(大海波涛)
效果:
图片:
代码:
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background-color: lightseagreen;
/*删除掉多余部分,使得左下两条滚动条不显示*/
overflow: hidden;
}
.sun {
width: 80px;
height: 80px;
margin: 60px 60px;
position: relative;
}
.sun::before, .sun::after {
content: '';
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
background-color: #ffffff;
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
border-radius: 50%;
animation: sun 2s linear infinite;
}
.sun::after {
width: 80px;
height: 80px;
background: rgba(255, 255, 255, .7);
border-radius: 50%;
animation: sun 2s linear 0.5s infinite;
}
img {
width: 100%;
height: auto;
position: absolute;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
}
.img1 {
animation: move linear 2s infinite alternate;
}
.img2 {
animation: move linear 2s infinite 1s alternate;
}
@keyframes move {
0% {
bottom: 0;
}
50% {
bottom: -50px;
}
100% {
bottom: 0;
}
}
@keyframes sun {
0% {
transform: translate(-50%, -50%) scale(1);
box-shadow: 0 0 16px rgba(255,255,255,0.7);
}
50% {
transform: translate(-50%, -50%) scale(1.1);
box-shadow: 0 0 30px rgba(255,255,255,0.7);
}
100% {
transform: translate(-50%, -50%) scale(1);
box-shadow: 0 0 16px rgba(255,255,255,0.7);
}
}


二、CSS3伸缩布局
CSS3在布局方面做了非常大的改进,使得我们对块级元素的布局排列变得十分灵活,适应性非常强,其强大的伸缩性,在响应式开中可以发挥极大的作用。
1.基本使用方式
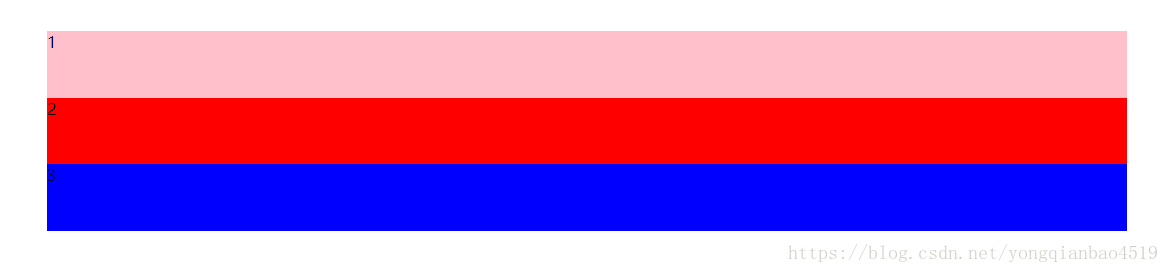
在原先的CSS中,如果我们要将一个盒子均分成三等份,那么我们会这么分:
section {
/*注意,伸缩布局父盒子也要用百分比来设定宽度*/
width: 80%;
height: 200px;
margin: 100px auto;
}
div {
/*如果是CSS3要将三个盒子分成三等份,一般是用以下方式:*/
width: 33.33%;
height: 100%;
float: left;
}
1
2
3
这样虽然可以均分三个盒子,但是三个盒子的伸缩性非常差,如果页面产生变化,比如缩小或者扩大,盒子是无法跟随页面的大小进行伸缩的,此时我们就可以用伸缩布局了。
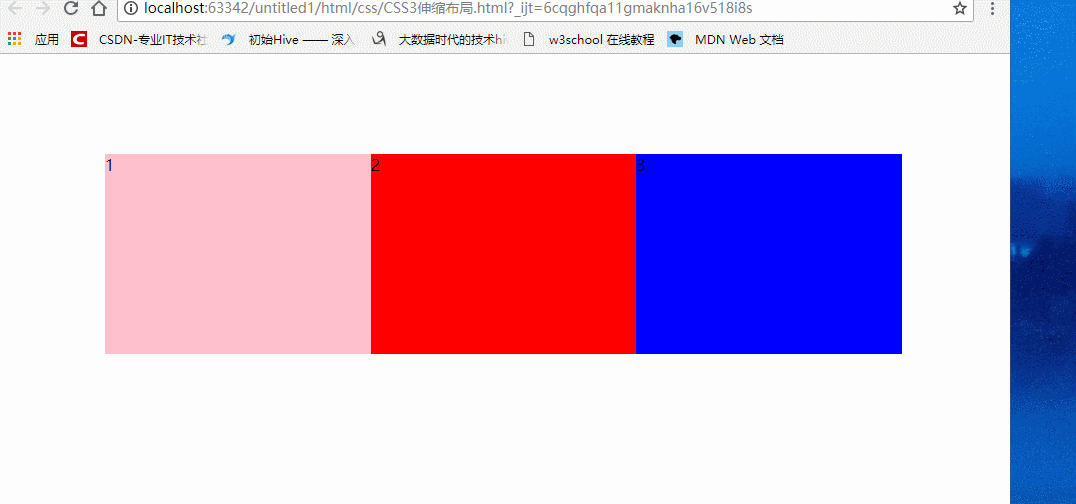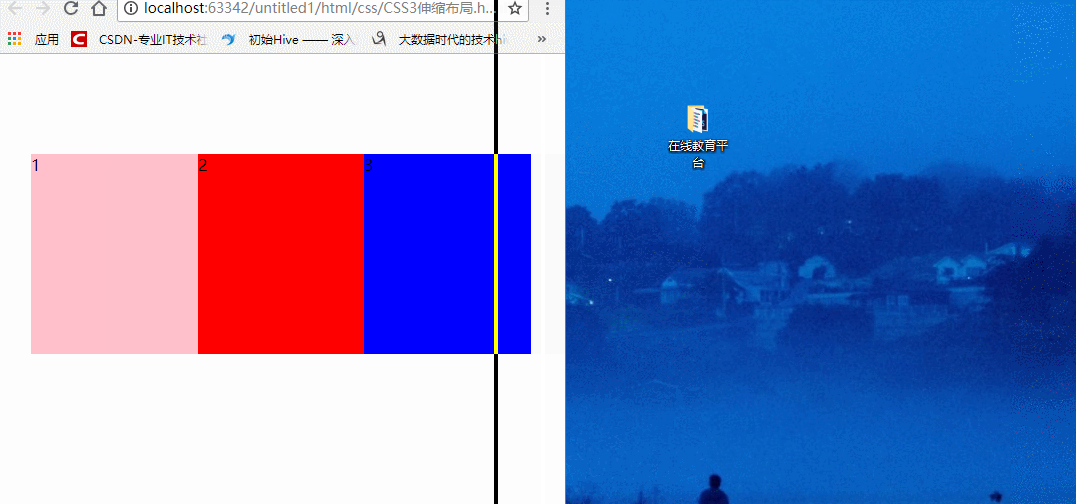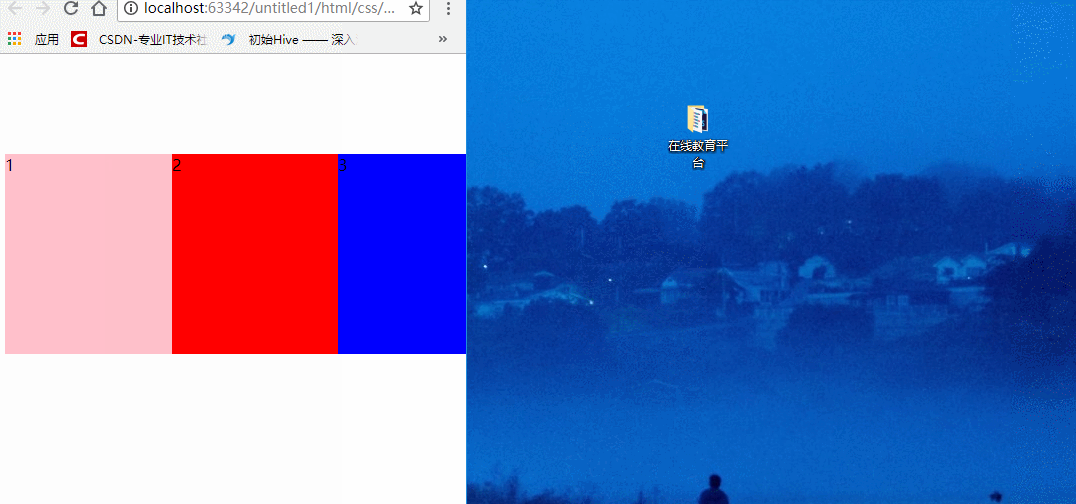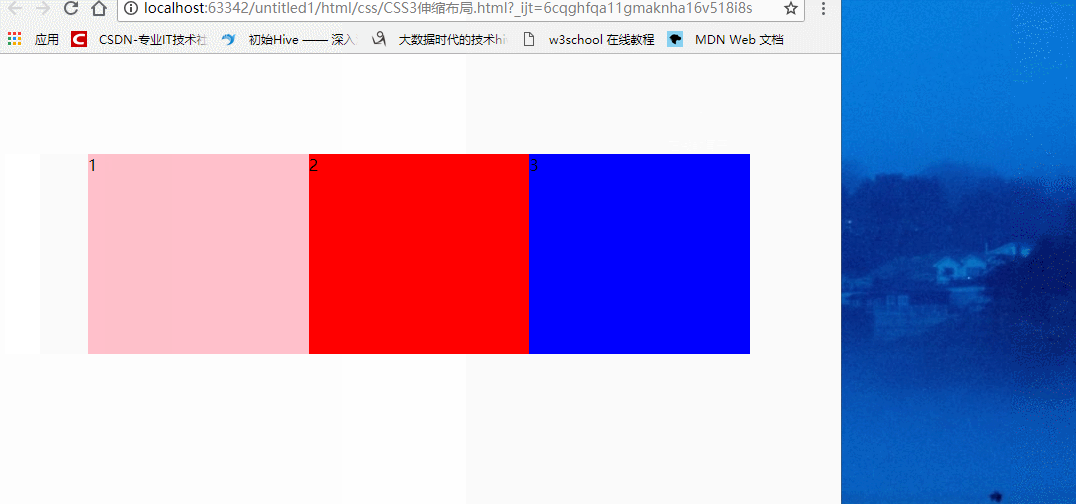
section {
/*注意,伸缩布局父盒子也要用百分比来设定宽度*/
width: 80%;
height: 200px;
margin: 100px auto;
/*在CSS3中,我们引入一个新的伸缩布局*/
display: flex;
/*伸缩布局的宽是不定的,我们伸缩页面,其宽度也会伸缩,但是会一直保持在三等份*/
}
div {
height: 100%;
/*flex指的是每一个div各占一份,也就是三个DIV均分为三等份*/
flex: 1;
}
div:first-child {
background-color: pink;
}
div:nth-child(2) {
background-color: red;
}
div:nth-child(3) {
background-color: blue;
}
1
2
3
效果:
我们也可以各自给盒子添加份数,如:
section {
/*注意,伸缩布局父盒子也要用百分比来设定宽度*/
width: 80%;
height: 200px;
margin: 100px auto;
/*在CSS3中,我们引入一个新的伸缩布局*/
display: flex;
/*伸缩布局的宽是不定的,我们伸缩页面,其宽度也会伸缩,但是会一直保持在三等份*/
}
div {
height: 100%;
/*flex指的是每一个div各占一份,也就是三个DIV均分为三等份*/
flex: 1;
}
div:first-child {
background-color: pink;
/*第一个div占两份,第二个div占一份,第三个div占两份,那么盒子就会变成5份*/
flex: 2;
}
div:nth-child(2) {
background-color: red;
}
div:nth-child(3) {
background-color: blue;
flex: 2;
}
1
2
3
效果:
2.其他属性
(1)伸缩方向(flex-direction)
伸缩方向用来控制伸缩布局的方向,行伸缩或者列伸缩。
属性有:
flex-direction: row 行伸缩,默认属性。
flex-direction: column 列伸缩。
flex-direction: row-reverse 掉转盒子顺序,原先为1 2 3 ,掉转后顺序为3 2 1。
flex-direction: column-reverse 同上。
我们可以为小盒子添加宽度使其固定宽度不再伸缩。
但是在添加固定宽度时,注意自己不能有份数,其他盒子则必须要有份数。
section {
/*注意,伸缩布局父盒子也要用百分比来设定宽度*/
width: 80%;
height: 200px;
margin: 100px auto;
/*在CSS3中,我们引入一个新的伸缩布局*/
display: flex;
/*伸缩布局的宽是不定的,我们伸缩页面,其宽度也会伸缩,但是会一直保持在三等份*/
/*如果我们想要其垂直伸缩分等份,那么我们可以用*/
flex-direction: column;
/*相对应的水平等份是row,不过默认就是row,所以不需要再设置*/
/*还有另外两个属性 row-reverse 和 column-reverse ,它会将我们的子盒子的顺序调转过来,也就是说如果你使用了row-reverse,那么1 2 3排列的三个盒子就会变成3 2 1 排列。*/
}
div {
height: 100%;
/*flex指的是每一个div各占一份,也就是三个DIV均分为三等份*/
flex: 1;
}
div:first-child {
background-color: pink;
}
div:nth-child(2) {
background-color: red;
}
div:nth-child(3) {
background-color: blue;
}
1
2
3
效果:
(2)伸缩极限宽度(max-width/min-width)
控制外盒子的最大/最小伸缩宽度。
section {
/*注意,伸缩布局父盒子也要用百分比来设定宽度*/
width: 80%;
height: 200px;
margin: 100px auto;
/*在CSS3中,我们引入一个新的伸缩布局*/
display: flex;
/*伸缩布局的宽是不定的,我们伸缩页面,其宽度也会伸缩,但是会一直保持在三等份*/
/*我们还可以为父盒子设置最大宽度和最小宽度*/
/*max-width*/
min-width: 500px;
/*这样父盒子缩小到500px就会固定下来,不再缩小*/
}
div {
height: 100%;
/*flex指的是每一个div各占一份,也就是三个DIV均分为三等份*/
flex: 1;
}
div:first-child {
background-color: pink;
}
div:nth-child(2) {
background-color: red;
}
div:nth-child(3) {
background-color: blue;
}
1
2
3
效果:
可以看到盒子缩小到一定大小就固定住,不再缩小了。
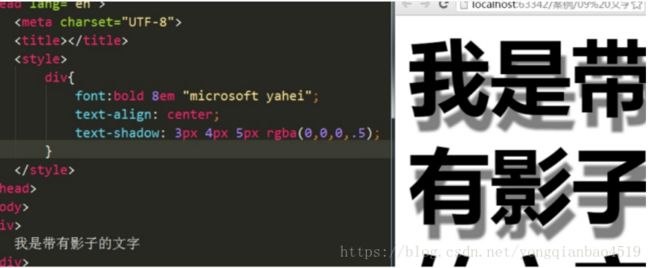
三、CSS3文字阴影
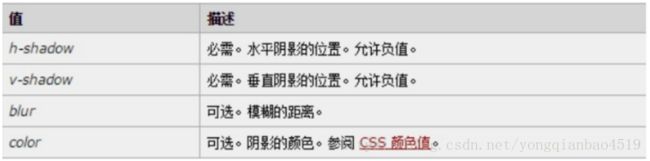
格式:
| text-shadow:水平位置 垂直位置 模糊距离 阴影颜色; |
前两项必写,后两项可以选写。
四、CSS3背景运用
1.背景渐变(了解即可)
就是颜色渐变,但是兼容性非常差,很不常用。
格式:
| background:-webkit-linear-gradient(渐变的起始位置, 起始颜色, 结束颜色); |
| background:-webkit-linear-gradient(渐变的起始位置, 颜色 位置, 颜色位置....); |
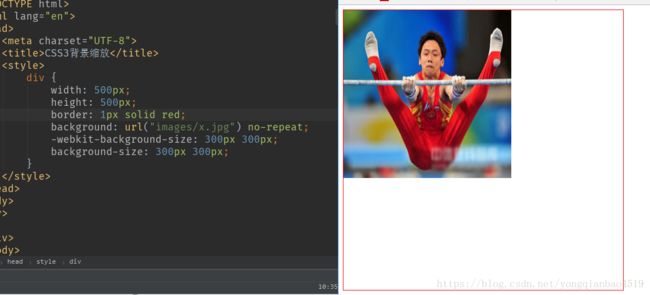
2.CSS3背景缩放
通过background-size来设置背景图片的尺寸,就像设置img的尺寸一样,在移动Web开发中做屏幕适配非常广泛。
因为移动web开发一半都要适用不同系统,比如最主流的IOS和Android,并且屏幕的像素也是需要考虑的因素,所以一般移动Web开发中所用的精灵图会比较大,分辨率比较高,所以就需要用到背景缩放,具体应用可看下方携程网案例。
格式:
(1)可以设置长度单位(px)或百分比(设百分比时以盒子的宽高为参照)。
效果:
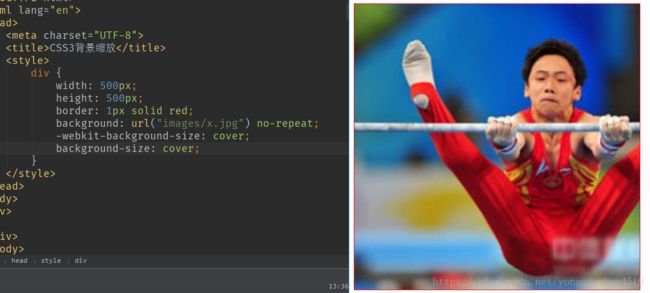
(2)可以设置为cover。
设置为cover时,会自动调整缩放比例,保证背景填满一整个盒子,如有溢出部分则会被隐藏,也就是高跨到极致。cover是最常用的。
效果:
(3)可以设置为contain。
设置为contain时,会自动调整缩放比例,保证图片始终完整显示在背景区域,也就是宽跨到极致。
效果:
3.多背景
以逗号隔开可以设置多背景。
- 一个元素可以设置多重背景图像。
- 每组属性使用逗号分隔。
- 如果设置多重背景图之间存在交集(即重叠关系),则前面的背景图会覆盖在后面的背景图上。
格式:
| background: url(test1.jpg) no-repeat scroll 10px 20px/70px 90px , url(test1.jpg) no-repeat scroll 10px 20px/110px 130px c #aaa; |
案例(泡泡浮动效果):
效果:
图片:
代码:
div {
width: 300px;
height: 80px;
-webkit-border-radius: 20px;
-moz-border-radius: 20px;
border-radius: 20px;
background: url("images/paopao.png") no-repeat top left,url("images/paopao.png") no-repeat right bottom;
/*多背景颜色写在后面,以防被叠加*/
background-color: skyblue;
-webkit-transition: all 3s;
-moz-transition: all 3s;
-ms-transition: all 3s;
-o-transition: all 3s;
transition: all 3s;
}
div:hover {
background-position: right bottom, top left;
}五、综合案例(携程网)
效果:
图片:
代码:
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
html, body {
max-width: 540px;
min-width: 320px;
margin: 0 auto;
font: normal 14px/1.5 Tahoma,"Lucida Grande",Verdana,"Microsoft Yahei",STXihei,hei;
background-color: #F2F2F2;
}
header {
height: 108px;
}
header img {
height: 100%;
width: auto;
}
nav {
width: 100%;
margin-top: 4px;
}
nav a {
text-decoration: none;
color: #F2F2F2;
text-shadow: 1px 1px 1.5px rgba(0, 0, 0, .6);
/*text-shadow:水平位置 垂直位置 模糊距离 阴影颜色;*/
}
.row {
height: 88px;
display: flex;
background-color: #FA6055;
border: 1px solid #F2F2F2;
border-radius: 8px;
overflow: hidden;
}
.flight {
background-color: #4B91ED;
}
.travel {
background-color: #36C3A7;
}
.row div {
height: 100%;
border-right: 1px solid #F2F2F2;
flex: 1;
}
.row div:nth-child(3) {
border: 0;
}
.row div a {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
display: block;
}
.row div em {
text-align: center;
line-height: 45px;
font-style: normal;
display: block;
height: 45px;
}
.row div i {
display: block;
margin: -10px auto;
width: 43px;
height: 43px;
background: url("images/ctrip.png") no-repeat 0 -127px;
-webkit-background-size: 104px;
background-size: 104px;
}
.row div .flight-icon {
background-position: 0 -288px;
}
.row div .travel-icon {
background-position: 0 -178px;
}
.row-d{
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
.row-d a {
text-align: center;
line-height: 44px;
flex: 1;
}
.row-d a:first-child {
border-bottom: 1px solid #F2F2F2;
}