C语言基础之文件
1,Makefile
意义:解决多文件编译模块化的问题
格式:
main:(目标)main.0 (依赖)
(一个TAB)gcc main.o -o main (命令)
makefile文件名必须为makefile或者Makefile,其余文件名要使用make -f 文件名命令告诉系统去哪找makefile文件
gcc命令:
gcc -c 编译到目标代码,不进行链接 (gcc -c 文件.c 生成 文件.o)
gcc -o <文件> 输出到<文件> (gcc -o 目标文件名.o 文件.o)
Makefile 实例应用
建立一个小项目,有main.c student.c class.c三个文件,
main.c:

class.c:

student.c:

class.h:

student.h:
![]()
此项目实现的功能很简单就是打印10个学生序号
可以使用脚本语言.sh完成
build.sh:

这时,我们使用这个脚本,就能成功编译和链接:
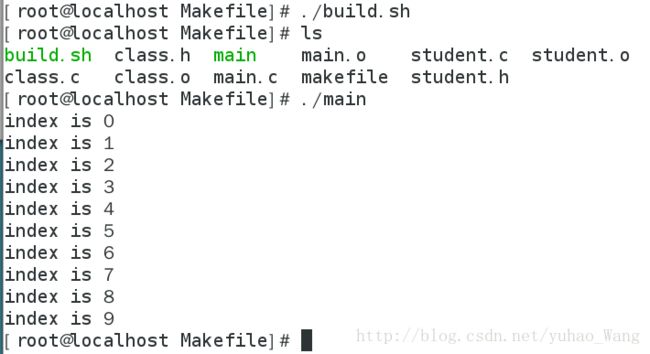
但是,如果文件特别多,在只改动一个文件的情况下,我们不希望全部文件编译,只编译改动文件,这就需要用到Makefile
Makefile:

这时,我们只改动student.c文件,并查看时间戳,makefile执行也是根据时间戳的更改来完成,如果目标晚于依赖文件的时间戳,则执行对应语句:
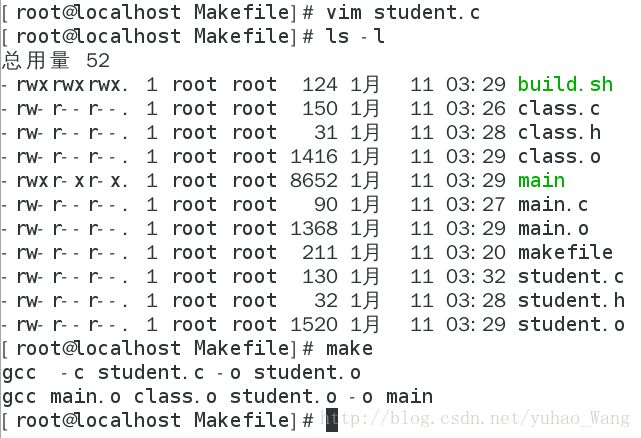
执行make可以看到,只执行了与student.c文件有关的语句,其余的语句则没有重新编译,大大提高了编译效率
2,静态文件与动态文件
1、静态文件(inode)
硬盘中的文件,就是静态文件。文件都是以多个块和多个扇区组成的。一般情况,一个扇区(512字节),64个扇区组成一个块。在硬盘中,对文件管理有一个特定规则(文件管理表+真实的内容):文件管理表,这个表中是以文件为单位提供了各个文件的所有信息 (每一个文件信息表就对应一个结构体,这个结构体就称之为inode,也叫i节点,这个文件的包含的多少块、多少扇区),而我们通过查找这个表就可以找到我们所需要文件的内容。
我们找文件,通过(文件名字)找的。第一步:在文件管理表中,找到这个文件的名字,第二部,访问这个文件。U盘格式化:1、快速格式化,清除了你的文件管理表,文件系统就找不到你所需要的文件名字 ,你的真实内容还在硬盘里,可以部分恢复 2、彻底格式化,这个就是把文件真实内容也清除掉了,u盘不能通过软件技术恢复了,必须借助国家安全机构(通过物理机制,通过硬件的记忆恢复)。
联系:生活中,处理小文件的一个手段,文件压缩。把扇区的空余字节都利用起来,减少了占用硬盘上的空间。硬盘喜欢大文件。
2、动态文件(vnode)(在内存中)
一个程序的运行就是一个进程,而我们打开的文件就属于这个进程。而操作系统对于每一个进程都有一个结构体进行管理,这个管理当前进程所有信息的结构体,我们就叫做(进程信息表)。这个表中有一个指针指向我们的文件管理表,这个文件管理表就包含了本进程打开的所有文件,通过查找文件管理表的index(文件描述符fd,相当于这个结构体数组的下标),就得到了我们的文件所有信息的结构体(Vnode,V节点),而这个结构体的指针就是文件指针。
3,打印系统时间的小项目
#include 4,两个文件描述符来写文件(dup)
#include 5,模仿ls-l的小程序
#include