VINS-Mono源码分析2— vins_estimator1(预积分)
VINS-Mono源码分析2— vins_estimator1
ros::init(argc, argv, "vins_estimator");
ros::NodeHandle n("~");
ros::console::set_logger_level(ROSCONSOLE_DEFAULT_NAME, ros::console::levels::Info);
vins_estimator包的入口程序,主要是ROS方面的一些基本操作,大多数ROS代码开始都会做的一种工作。
readParameters(n);
void readParameters(ros::NodeHandle &n)
{
std::string config_file;
config_file = readParam<std::string>(n, "config_file");
cv::FileStorage fsSettings(config_file, cv::FileStorage::READ);
......
}
读取参数文件,设置相关参数,默认参数文件为~/VINS-Mono/config/euroc文件夹下的euroc_config.yaml文件。特别注意config_file读取的是来自~/VINS-Mono/vins_estimator/launch文件夹下的euroc.launch文件。
estimator.setParameter();
void Estimator::setParameter()
{
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++)
{
tic[i] = TIC[i];
ric[i] = RIC[i];
}
f_manager.setRic(ric);
ProjectionFactor::sqrt_info = FOCAL_LENGTH / 1.5 * Matrix2d::Identity();
ProjectionTdFactor::sqrt_info = FOCAL_LENGTH / 1.5 * Matrix2d::Identity(); //1.5是像素坐标的协方差开方
td = TD;
}
NUM_OF_CAM=1,tic[0]和ric[0]分别为 p c b p^b_c pcb和 q c b q^b_c qcb,f_manager的tic[0]也设为 p c b p^b_c pcb,设置非线性优化的重投影误差部分的信息矩阵sqrt_info。
registerPub(n);
void registerPub(ros::NodeHandle &n)
{
pub_latest_odometry = n.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry>("imu_propagate", 1000);
pub_path = n.advertise<nav_msgs::Path>("path", 1000);
pub_relo_path = n.advertise<nav_msgs::Path>("relocalization_path", 1000);
pub_odometry = n.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry>("odometry", 1000);
pub_point_cloud = n.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud>("point_cloud", 1000);
pub_margin_cloud = n.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud>("history_cloud", 1000);
pub_key_poses = n.advertise<visualization_msgs::Marker>("key_poses", 1000);
pub_camera_pose = n.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry>("camera_pose", 1000);
pub_camera_pose_visual = n.advertise<visualization_msgs::MarkerArray>("camera_pose_visual", 1000);
pub_keyframe_pose = n.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry>("keyframe_pose", 1000);
pub_keyframe_point = n.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud>("keyframe_point", 1000);
pub_extrinsic = n.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry>("extrinsic", 1000);
pub_relo_relative_pose= n.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry>("relo_relative_pose", 1000);
cameraposevisual.setScale(1);
cameraposevisual.setLineWidth(0.05);
keyframebasevisual.setScale(0.1);
keyframebasevisual.setLineWidth(0.01);
}
定义了许多个用于可能被RVIZ订阅的ROS话题,以及一些涂涂画画的参数。
ros::Subscriber sub_imu = n.subscribe(IMU_TOPIC, 2000, imu_callback, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());
ros::Subscriber sub_image = n.subscribe("/feature_tracker/feature", 2000, feature_callback);
ros::Subscriber sub_restart = n.subscribe("/feature_tracker/restart", 2000, restart_callback);
ros::Subscriber sub_relo_points = n.subscribe("/pose_graph/match_points", 2000, relocalization_callback);
订阅一些话题,执行一些回调函数。先看回调函数 imu_callback(),
void imu_callback(const sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr &imu_msg)
{
......
}
if (imu_msg->header.stamp.toSec() <= last_imu_t)
{
ROS_WARN("imu message in disorder!");
return;
}
last_imu_t = imu_msg->header.stamp.toSec();
m_buf.lock();
imu_buf.push(imu_msg);
m_buf.unlock();
con.notify_one();
先根据IMU数据的时间戳,判断数据的有序性,如果有序,就把IMU数据添加到imu_buf里,需要上锁。
last_imu_t = imu_msg->header.stamp.toSec();
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lg(m_state);
predict(imu_msg);
std_msgs::Header header = imu_msg->header;
header.frame_id = "world";
if (estimator.solver_flag == Estimator::SolverFlag::NON_LINEAR)
pubLatestOdometry(tmp_P, tmp_Q, tmp_V, header);
}
根据当前的imu_msg以及之前的tmp_P, tmp_Q, tmp_V计算现在的tmp_P, tmp_Q, tmp_V,具体代码实现看下面的predict()函数。如果现在系统的状态是非线性化,则将tmp_P, tmp_Q, tmp_V,通过pubLatestOdometry发布出去,发布过程不详解。
void predict(const sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr &imu_msg)
{
double t = imu_msg->header.stamp.toSec();
if (init_imu)
{
latest_time = t;
init_imu = 0;
return;
}
double dt = t - latest_time;
latest_time = t;
double dx = imu_msg->linear_acceleration.x;
double dy = imu_msg->linear_acceleration.y;
double dz = imu_msg->linear_acceleration.z;
Eigen::Vector3d linear_acceleration{dx, dy, dz};
double rx = imu_msg->angular_velocity.x;
double ry = imu_msg->angular_velocity.y;
double rz = imu_msg->angular_velocity.z;
Eigen::Vector3d angular_velocity{rx, ry, rz};
Eigen::Vector3d un_acc_0 = tmp_Q * (acc_0 - tmp_Ba) - estimator.g;
Eigen::Vector3d un_gyr = 0.5 * (gyr_0 + angular_velocity) - tmp_Bg;
tmp_Q = tmp_Q * Utility::deltaQ(un_gyr * dt);
Eigen::Vector3d un_acc_1 = tmp_Q * (linear_acceleration - tmp_Ba) - estimator.g;
Eigen::Vector3d un_acc = 0.5 * (un_acc_0 + un_acc_1);
tmp_P = tmp_P + dt * tmp_V + 0.5 * dt * dt * un_acc;
tmp_V = tmp_V + dt * un_acc;
acc_0 = linear_acceleration;
gyr_0 = angular_velocity;
}
上面的代码对应崔华坤大神的文章《VINS论文推导及代码解析》的第5页的2.2的内容。
接下来分析feature_callback()回调函数,
void feature_callback(const sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr &feature_msg)
{
if (!init_feature)
{
//skip the first detected feature, which doesn't contain optical flow speed
init_feature = 1;
return;
}
m_buf.lock();
feature_buf.push(feature_msg);
m_buf.unlock();
con.notify_one();
}
从第二帧特征点信息开始,将特征点信息feature_msg存储在feature_buf,需要上锁。
void restart_callback(const std_msgs::BoolConstPtr &restart_msg)
{
if (restart_msg->data == true)
{
ROS_WARN("restart the estimator!");
m_buf.lock();
while(!feature_buf.empty())
feature_buf.pop();
while(!imu_buf.empty())
imu_buf.pop();
m_buf.unlock();
m_estimator.lock();
estimator.clearState();
estimator.setParameter();
m_estimator.unlock();
current_time = -1;
last_imu_t = 0;
}
return;
}
其实它就是把feature_buf和imu_buf全部清空,将整个系统重置。
void relocalization_callback(const sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr &points_msg)
{
//printf("relocalization callback! \n");
m_buf.lock();
relo_buf.push(points_msg);
m_buf.unlock();
}
系统检测到回环并且参数文件euroc_config.yaml下的fast_relocalization值置为1时,才会执行这个回调函数。
接下来的process()函数才是核心
std::thread measurement_process{process};
std::vector<std::pair<std::vector<sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr>, sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr>> measurements;
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lk(m_buf);
con.wait(lk, [&]
{
return (measurements = getMeasurements()).size() != 0;
});
lk.unlock();
这段代码主要的功能是将IMU信息和视觉信息对齐,具体代码请看getMeasurements()函数,
std::vector<std::pair<std::vector<sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr>, sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr>>
getMeasurements()
{
std::vector<std::pair<std::vector<sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr>, sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr>> measurements;
while (true)
{
if (imu_buf.empty() || feature_buf.empty())
return measurements;
if (!(imu_buf.back()->header.stamp.toSec() > feature_buf.front()->header.stamp.toSec() + estimator.td))
{
//ROS_WARN("wait for imu, only should happen at the beginning");
sum_of_wait++;
return measurements;
}
if (!(imu_buf.front()->header.stamp.toSec() < feature_buf.front()->header.stamp.toSec() + estimator.td))
{
ROS_WARN("throw img, only should happen at the beginning");
feature_buf.pop();
continue;
}
sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr img_msg = feature_buf.front();
feature_buf.pop();
std::vector<sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr> IMUs;
while (imu_buf.front()->header.stamp.toSec() < img_msg->header.stamp.toSec() + estimator.td)
{
IMUs.emplace_back(imu_buf.front());
imu_buf.pop();
}
IMUs.emplace_back(imu_buf.front());
if (IMUs.empty())
ROS_WARN("no imu between two image");
measurements.emplace_back(IMUs, img_msg);
}
return measurements;
}
measurements是一个容器,里面有多个元素,它的一个元素包含多个IMU信息帧和一个图像信息帧。这段代码的意思可以用下图表示,
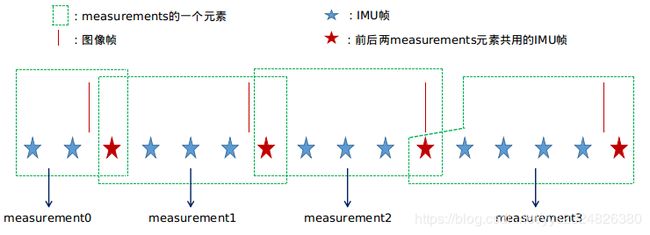
对一个measurements元素中的多个IMU帧进行处理,具体代码如下,
auto img_msg = measurement.second;
double dx = 0, dy = 0, dz = 0, rx = 0, ry = 0, rz = 0;
for (auto &imu_msg : measurement.first)
{
double t = imu_msg->header.stamp.toSec();
double img_t = img_msg->header.stamp.toSec() + estimator.td;
if (t <= img_t)
{
if (current_time < 0)
current_time = t;
double dt = t - current_time;
ROS_ASSERT(dt >= 0);
current_time = t;
dx = imu_msg->linear_acceleration.x;
dy = imu_msg->linear_acceleration.y;
dz = imu_msg->linear_acceleration.z;
rx = imu_msg->angular_velocity.x;
ry = imu_msg->angular_velocity.y;
rz = imu_msg->angular_velocity.z;
estimator.processIMU(dt, Vector3d(dx, dy, dz), Vector3d(rx, ry, rz));
}
else
{
double dt_1 = img_t - current_time;
double dt_2 = t - img_t;
current_time = img_t;
ROS_ASSERT(dt_1 >= 0);
ROS_ASSERT(dt_2 >= 0);
ROS_ASSERT(dt_1 + dt_2 > 0);
double w1 = dt_2 / (dt_1 + dt_2);
double w2 = dt_1 / (dt_1 + dt_2);
dx = w1 * dx + w2 * imu_msg->linear_acceleration.x;
dy = w1 * dy + w2 * imu_msg->linear_acceleration.y;
dz = w1 * dz + w2 * imu_msg->linear_acceleration.z;
rx = w1 * rx + w2 * imu_msg->angular_velocity.x;
ry = w1 * ry + w2 * imu_msg->angular_velocity.y;
rz = w1 * rz + w2 * imu_msg->angular_velocity.z;
estimator.processIMU(dt_1, Vector3d(dx, dy, dz), Vector3d(rx, ry, rz));
}
}
这部分的代码就是求多个IMU帧的预积分,求预积分的核心代码在estomator.cpp的processIMU()函数中,
void Estimator::processIMU(double dt, const Vector3d &linear_acceleration, const Vector3d &angular_velocity)
{
if (!first_imu)
{
first_imu = true;
acc_0 = linear_acceleration;
gyr_0 = angular_velocity;
}
if (!pre_integrations[frame_count])
{
pre_integrations[frame_count] = new IntegrationBase{acc_0, gyr_0, Bas[frame_count], Bgs[frame_count]};
}
if (frame_count != 0)
{
pre_integrations[frame_count]->push_back(dt, linear_acceleration, angular_velocity);
//if(solver_flag != NON_LINEAR)
tmp_pre_integration->push_back(dt, linear_acceleration, angular_velocity);
dt_buf[frame_count].push_back(dt);
linear_acceleration_buf[frame_count].push_back(linear_acceleration);
angular_velocity_buf[frame_count].push_back(angular_velocity);
int j = frame_count;
Vector3d un_acc_0 = Rs[j] * (acc_0 - Bas[j]) - g;
Vector3d un_gyr = 0.5 * (gyr_0 + angular_velocity) - Bgs[j];
Rs[j] *= Utility::deltaQ(un_gyr * dt).toRotationMatrix();
Vector3d un_acc_1 = Rs[j] * (linear_acceleration - Bas[j]) - g;
Vector3d un_acc = 0.5 * (un_acc_0 + un_acc_1);
Ps[j] += dt * Vs[j] + 0.5 * dt * dt * un_acc;
Vs[j] += dt * un_acc;
}
acc_0 = linear_acceleration;
gyr_0 = angular_velocity;
}
当frame_count=0时,只是定义了pre_integrations[0],并没有进行实际的预积分操作。
当frame_count不等于0时,才会执行预积分操作。预积分操作的执行在push_back()函数中,并且会计算jacobian和covariance,这部分的主要实现代码在factor文件夹的integration_base.h中,代码理论知识请看崔华坤大神的文章《VINS论文推导及代码解析》的2.3~2.8的内容,此处不在详述。
接着就是计算Rs[j]、Ps[j] 和Vs[j]的过程,这里计算的这三个量是前后两图像帧间,即frame_count帧间的相对量。
返回到estimator_node.cpp中,继续往下阅读代码,
sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr relo_msg = NULL;
while (!relo_buf.empty())
{
relo_msg = relo_buf.front();
relo_buf.pop();
}
if (relo_msg != NULL)
{
vector<Vector3d> match_points;
double frame_stamp = relo_msg->header.stamp.toSec();
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < relo_msg->points.size(); i++)
{
Vector3d u_v_id;
u_v_id.x() = relo_msg->points[i].x;
u_v_id.y() = relo_msg->points[i].y;
u_v_id.z() = relo_msg->points[i].z;
match_points.push_back(u_v_id);
}
Vector3d relo_t(relo_msg->channels[0].values[0], relo_msg->channels[0].values[1], relo_msg->channels[0].values[2]);
Quaterniond relo_q(relo_msg->channels[0].values[3], relo_msg->channels[0].values[4], relo_msg->channels[0].values[5], relo_msg->channels[0].values[6]);
Matrix3d relo_r = relo_q.toRotationMatrix();
int frame_index;
frame_index = relo_msg->channels[0].values[7];
estimator.setReloFrame(frame_stamp, frame_index, match_points, relo_t, relo_r);
}
当系统检测到回环,执行了重定位操作后,这段代码才会执行,否则跳过。
这段代码其实就是对回环帧做了一些处理,核心代码在setReloFrame()函数中,
void Estimator::setReloFrame(double _frame_stamp, int _frame_index, vector<Vector3d> &_match_points, Vector3d _relo_t, Matrix3d _relo_r)
{
relo_frame_stamp = _frame_stamp;
relo_frame_index = _frame_index;
match_points.clear();
match_points = _match_points;
prev_relo_t = _relo_t;
prev_relo_r = _relo_r;
for(int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE; i++)
{
if(relo_frame_stamp == Headers[i].stamp.toSec())
{
relo_frame_local_index = i;
relocalization_info = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < SIZE_POSE; j++)
relo_Pose[j] = para_Pose[i][j];
}
}
}
上面代码完成的事情,就是把回环帧的一些有用信息存储到相应的变量中。
接下来,对一个measurements元素中的一个图像帧进行处理,具体代码如下,
map<int, vector<pair<int, Eigen::Matrix<double, 7, 1>>>> image;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < img_msg->points.size(); i++)
{
int v = img_msg->channels[0].values[i] + 0.5;
int feature_id = v / NUM_OF_CAM;
int camera_id = v % NUM_OF_CAM;
double x = img_msg->points[i].x;
double y = img_msg->points[i].y;
double z = img_msg->points[i].z;
double p_u = img_msg->channels[1].values[i];
double p_v = img_msg->channels[2].values[i];
double velocity_x = img_msg->channels[3].values[i];
double velocity_y = img_msg->channels[4].values[i];
ROS_ASSERT(z == 1);
Eigen::Matrix<double, 7, 1> xyz_uv_velocity;
xyz_uv_velocity << x, y, z, p_u, p_v, velocity_x, velocity_y;
image[feature_id].emplace_back(camera_id, xyz_uv_velocity);
}
estimator.processImage(image, img_msg->header);
这里面有个数据结构image,可参考崔华坤大神的文章《VINS论文推导及代码解析》中的第15页的内容理解一下。在这里要特别强调一下,因为VINS-mono的相机是单目的,所以camera id只有一个。
将图像特征点消息img_msg赋值给image后,核心的处理函数为processImage()。由于它所涉及的代码量巨大,故单独写了一篇博客《VINS-Mono源码分析3— vins_estimator2》对其进行分析。