GreenDao多线程查询
GreenDao号称最快的ORM数据操作。特别是多线程中,因为他在多线程查询中,在每个线程中定义一个属于当前线程的查询对象,这样子每个线程之间都互相不干扰,比对对象加锁进行同步操作的性能提高了很多,节省了加锁的开销。
先用最普通的方法在线程中访问对象读取数据。
private void queryThread() {
final Query query = sonDao.queryBuilder().build();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
List sonList = query.list();
Log.d("son",sonList.get(0).getName());
}
}).start();
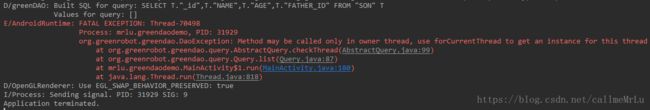
} 运行程序会抛出一个异常。
信息提示方法使用应该仅在当前线程,使用forCurrentThread()方法为这个线程获得一个事例。(该方法返回一个查询类Query)
现在添加这个方法。
private void queryThread() {
final Query query = sonDao.queryBuilder().build();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//forCurrentThread()该方法返回一个Query对象
List sonList = query.forCurrentThread().list();
Log.d("son",sonList.get(0).getName());
}
}).start();
} 运行成功。
接下来了解下如何多线程查询的,以及了解这个方法。
还记得上一篇讲到的四个查询方法吗?因为查询方法中都有线程检查的方法。
protected void checkThread() {
if (Thread.currentThread() != ownerThread) {
throw new DaoException(
"Method may be called only in owner thread, use forCurrentThread to get an instance for this thread");
}
}很熟悉,异常就是这个方法抛出的。下面来看查询正确的过程是怎样实现多线程查询的。
点进去方法forCurrentThread(),以下就是多线程查询的核心代码:
/**
* Just an optimized version, which performs faster if the current thread is already the query's owner thread.
* Note: all parameters are reset to their initial values specified in {@link QueryBuilder}.
*/
Q forCurrentThread(Q query) {
if (Thread.currentThread() == query.ownerThread) {
System.arraycopy(initialValues, 0, query.parameters, 0, initialValues.length);
return query;
} else {
return forCurrentThread();
}
}
/**
* Note: all parameters are reset to their initial values specified in {@link QueryBuilder}.
*/
Q forCurrentThread() {
// Process.myTid() seems to have issues on some devices (see Github #376) and Robolectric (#171):
// We use currentThread().getId() instead (unfortunately return a long, can not use SparseArray).
// PS.: thread ID may be reused, which should be fine because old thread will be gone anyway.
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
synchronized (queriesForThreads) {
WeakReference queryRef = queriesForThreads.get(threadId);
Q query = queryRef != null ? queryRef.get() : null;
if (query == null) {
gc();
query = createQuery();
queriesForThreads.put(threadId, new WeakReference(query));
} else {
System.arraycopy(initialValues, 0, query.parameters, 0, initialValues.length);
}
return query;
}
}
意思就是:只是一个优化版本,如果当前线程已经是查询的所有者线程,则执行速度更快。
注意:所有参数都重置为{@link QueryBuilder}中指定的初始值
讲解一下。
先判断线程是否是当前线程,如果是的话,就copy query的信息到一个数组中,并且返回一个query。其实这个方法就是源码里面说的当前线程的话执行速度更快,指的就是这个,因为if包含的这段代码是判断为主线程成立运行的。
否则的话(当前线程不是主线程)就调用下面的forCurrentThread()方法。
注释说:Process.myTid()在一些设备上有为题;我们使用了currentThread().getId()代替了旧版本,返回一个long;线程ID可以重复使用,这应该没问题,因为旧线程无论如何都会消失。
(我写下这段的时候也有点懵逼-----。。。。。)
方法先记录线程ID,然后加线程锁,锁的是一个final Map
所以,forCurrentThread()方法返回一个query类给用户,然后我们就可以进行查询了。