接口自动化测试:mock server之Moco工具
什么是mock server
mock:英文可以翻译为模仿的,mock server是我们用来解除依赖(耦合),假装实现的技术,比如说,前端需要使用某些api进行调试,但是服务端并没有开发完成这些api,那么前端的工作就被服务端阻塞了,那么就可以使用mock server假装实现这些api,能够返回特定的数据,帮助前端进行页面渲染,当然我们为了方便可以需要与服务端进行约定,约定接口的内容是什么。
restful接口规范
转接阮一峰老师的博客—RESTful API 设计指南:http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2014/05/restful_api.html
Moco-约定uri(一)
moco工具是在github开源的一个项目,可以使用moco工具搭一个简单的mock server方便我们进行调试,github地址:https://github.com/dreamhead/moco,下载下来的是一个jar包,目前的版本是0.11.1,首先我们要编写一个config文件,把我们需要“模拟”的请求和响应写入这个配置文件,配置文件是json格式的,接下来我们写一个比较简单的请求,访问 localhost:12306/hello 接口,返回一个纯文本“moco”,moco工具约定了12306端口,不必纠结,就跟tomcat约定8080端口类似,config.json文件如下,而且json文件要与moco的jar包放在同一个文件夹下。比如博主的目录结构:
G:\学习资料\mock\moco-runner-0.11.1-standalone.jar G:\学习资料\mock\config.json
[
{
"request":
{
"uri":"/hello"
},
"response":
{
"text":"moco"
}
}
]配置文件比较简单,我们请求接口,返回一个纯文本,启动指令:
>java -jar moco-runner-0.11.1-standalone.jar http -p 12306 -c config.json
这里的http就是http协议, -p 12306 绑定端口号12306, -c config.json读config文件
看到以上的表现,就说明moco已经顺利启动了,我们访问localhost:12306/hello 看到结果如下就说明mock server顺利返回了我们约定的数据”moco”
Moco-约定uri(二)
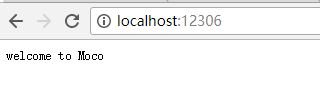
[
{
"request":
{
"uri":"/"
},
"response":
{
"text":"welcome to Moco"
}
},
{
"request":
{
"uri":"/hello"
},
"response":
{
"text":"moco"
}
}
]接下来分别访问localhost:12306和12306:12306/hello,结果如下:

Moco-约定get请求
[
{
"request":
{
"method":"get",
"uri":"/get"
},
"response":
{
"text":"moco get"
}
}
]Moco-约定post请求
[
{
"request":
{
"method":"post",
"uri":"/post"
},
"response":
{
"text":"moco post"
}
}
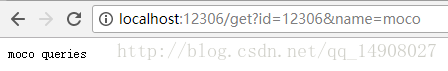
]Moco-约定请求参数
[
{
"request":
{
"method":"get",
"uri":"/get",
"queries":
{
"id":"12306",
"name":"moco"
}
},
"response":
{
"text":"moco queries"
}
}
]Moco-约定请求body必须为json格式
[
{
"request":
{
"method":"post",
"uri":"/post",
"text":
{
"json":"{\"id\":\"12306\",\"name\":\"moco\"}"
}
},
"response":
{
"status":"200"
}
}
]Moco-约定请求头部
[
{
"request":
{
"method":"post",
"uri":"/post",
"headers":
{
"content-type":"application/json",
"Connection":"keep-alive",
"Content-Encoding":"gzip"
}
},
"response":
{
"status":"200"
}
}
]Moco-约定返回内容
前面已经看到了response的集中返回内容如text,和status,下面展示一下返回文件和设置文件格式等
[
{
"request":
{
"method":"post",
"uri":"/post",
},
"response":
{
"file":"data.js",
"charset":"GBK",
"version":"HTTP/1.0"
}
}
]Moco-约定返回状态码
见上述的几个json,里面已经包含了返回状态码的使用方式
Moco-在单元测试中的使用(以Python为例)
[
{
"request":
{
"method":"get",
"uri":"/api/hello"
},
"response":
{
"text":"hello Savitar!",
"status":200
}
}
]这里模拟一个get请求,返回纯文本“hello Savitar!”和状态码200,先在浏览器访问localhost:12306/api/hello 结果如下图:
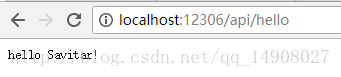
说明接口返回没问题,接下来使用Python requests+unittest写一个简单的接口测试用例
#coding=utf-8
'''
@author=Savitar
'''
import unittest
import requests
class MocoTestApi(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
self.url = "http://localhost:12306"
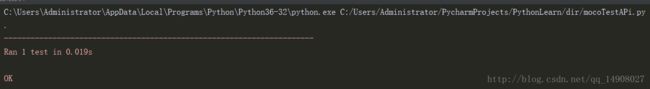
def test_moco_test_api(self):
api = "/api/hello"
url = self.url+api
r = requests.get(url)
self.assertEqual(r.status_code,200)
self.assertEqual(r.text,"hello Savitar!")
def tearDown(self):
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()