前言
在Python中,可以方便地使用os模块来运行其他脚本或者程序,这样就可以在脚本中直接使用其他脚本或程序提供的功能,而不必再次编写实现该功能的代码。为了更好地控制运行的进程,
可以使用win32process模块中的函数,如果想进一步控制进程,则可以使用ctype模块,直接调用kernel32.dll中的函数。下面介绍4种方式:
1、os.system()函数
os模块中的system()函数可以方便地运行其他程序或者脚本,模式如下:
os.system(command):command: 要执行的命令,如果要向脚本传递参数,可以使用空格分割程序及多个参数
实例:
#打开记事本 os.system('notepad') #用记事本打开a.txt os.system('notepad a.txt') #a.txt文件必须在当前程序目录 #直接打开a.txt os.system('a.txt') #直接打开Excel文件 os.system('a.xlsx') #直接打开Word文件 os.system('b.docx') filepath='测试.xlsx' #打开包含中文的文件 os.system(filepath.decode('utf8').encode('GBK'))
2、ShellExecute函数
使用win32api模块中的ShellExecute()函数来运行其他程序,格式如下
ShellExecute(hwnd, op, file, args, dir, show)
hwnd: 父窗口的句柄,如果没有父窗口,则为0
op : 要运行的操作,为open,print或者为空
file: 要运行的程序,或者打开的脚本
args: 要向程序传递的参数,如果打开的是文件则为空
dir : 程序初始化的目录
show: 是否显示窗口
使用ShellExecute函数,就相当于在资源管理器中双击文件图标,系统会打开相应程序运行。
引用win32api,需要安装 pywin32, https://sourceforge.net/projects/pywin32/files/pywin32/
实例:
import win32api win32api.ShellExecute(0, 'open', 'notepad.exe', '', '', 0) # 后台执行 win32api.ShellExecute(0, 'open', 'notepad.exe', '', '', 1) # 前台打开 win32api.ShellExecute(0, 'open', 'notepad.exe', 'a.txt', '', 1) # 打开文件 win32api.ShellExecute(0, 'open', 'iexplore.exe', '', '', 1) # 打开IE浏览器 win32api.ShellExecute(0, 'open', 'iexplore.exe', 'https://www.baidu.com/', '', 1) # 用IE浏览器打开百度网址 win32api.ShellExecute(0, 'open', 'mspaint.exe', 'wxqr.png', '', 1) #用系统附件自带的画图打开图片wxqr.png
3、CreateProcess
参考实例:https://www.programcreek.com/python/example/8489/win32process.CreateProcess
3.1、创建进程
为了便于控制通过脚本运行的程序,可以使用win32process模块中的CreateProcess()函数创建一个运行相应程序的进程。其函数格式为:
CreateProcess(appName, cmdLine, proAttr, threadAttr, InheritHandle, CreationFlags, newEnv, currentDir, Attr)
appName 可执行文件名
cmdLine 命令行参数
procAttr 进程安全属性
threadAttr 线程安全属性
InheritHandle 继承标志
CreationFlags 创建标志
currentDir 进程的当前目录
Attr 创建程序的属性
3.2、结束进程
可以使用win32process.TerminateProcess函数来结束已创建的进程, 函数格式如下:
TerminateProcess(handle, exitCode)
handle 要操作的进程句柄
exitCode 进程退出代码
或者使用win32event.WaitForSingleObject等待创建的线程结束,函数格式如下:
WaitForSingleObject(handle, milisecond)
handle : 要操作的进程句柄
milisecond: 等待的时间,如果为-1,则一直等待.
import win32process # 打开记事本,获得其句柄 handle = win32process.CreateProcess(r'C:\Windows\notepad.exe', '', None, None, 0, win32process.CREATE_NO_WINDOW, None, None, win32process.STARTUPINFO()) time.sleep(4) # 终止进程 win32process.TerminateProcess(handle[0], 0) import win32event #等待进程结束 print win32event.WaitForSingleObject(handle[0], -1)
4、使用ctypes调用kernel32.dll中的函数
使用ctypes模块可以让Python调用位于动态链接库的函数。
ctypes模块为Python提供了调用动态链接库中函数的功能。使用ctypes模块可以方便地调用由C语言编写的动态链接库,并向其传递参数。
ctypes模块定义了C语言中的基本数据类型,并且可以实现C语言中的结构体和联合体。ctypes模块可以工作在Windows,Linux,Mac OS等多种操作系统,基本上实现了跨平台。
实例:
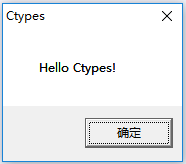
Windows下调用user32.dll中的MessageBoxA函数。
from ctypes import * user32 = windll.LoadLibrary('user32.dll') a = user32.MessageBoxA(0, str.encode('Hello Ctypes!'), str.encode('Ctypes'), 0) print a
ctype模块中含有的基本类型与C语言类似,下面是几个基本的数据类型的对照: