Handle-Message的发送和处理
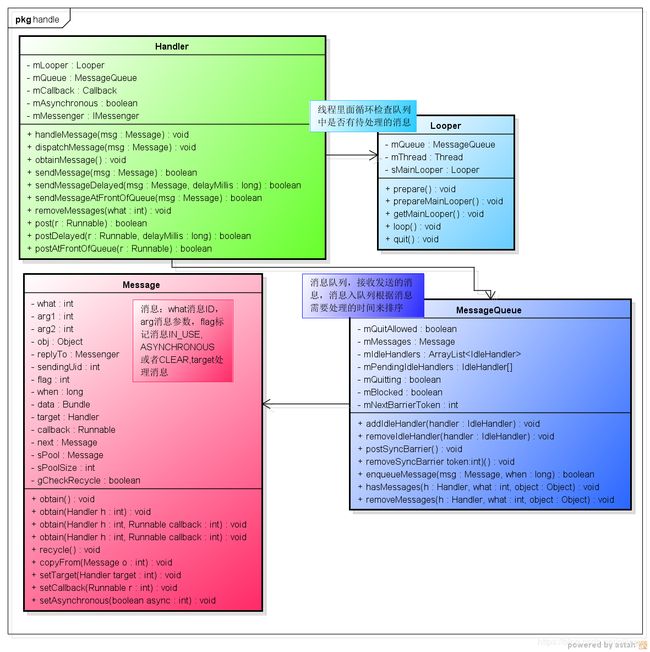
1、Handle,MessageQueue,Message类图
Handle: 处理消息,并提供一系列函数帮忙我们创建消息和插入消息到消息队列中
创建handle实例--PbapClientConnectionHandler
//创建一个线程
mHandlerThread =
new HandlerThread("PBAP PCE handler", Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
mHandlerThread.start();
//将这个线程设置为消息处理Looper线程
mConnectionHandler =
new PbapClientConnectionHandler.Builder().setLooper(mHandlerThread.getLooper())
.setContext(mService)
.setClientSM(PbapClientStateMachine.this)
.setRemoteDevice(mCurrentDevice)
.build();
Looper作用:Looper的prepare函数将Looper和调用prepare的线程绑定在一起,调用线程调用loop函数处理来自该消息队列的消息。
Android 系统的消息队列和消息循环都是针对具体线程的,一个线程可以存在(当然也可以不存在)一个消息队列和一个消息循环(Looper),特定线程的消息只能分发给本线程,不能进行跨线程通讯。但是创建的工作线程默认是没有消息循环和消息队列的,如果想让该线程具有消息队列和消息循环,需要在线程中首先调用Looper.prepare()来创建消息队列,然后调用Looper.loop()进入消息循环
MessageQueue:消息队列,Handle和Looper中使用的是同一个消息队列
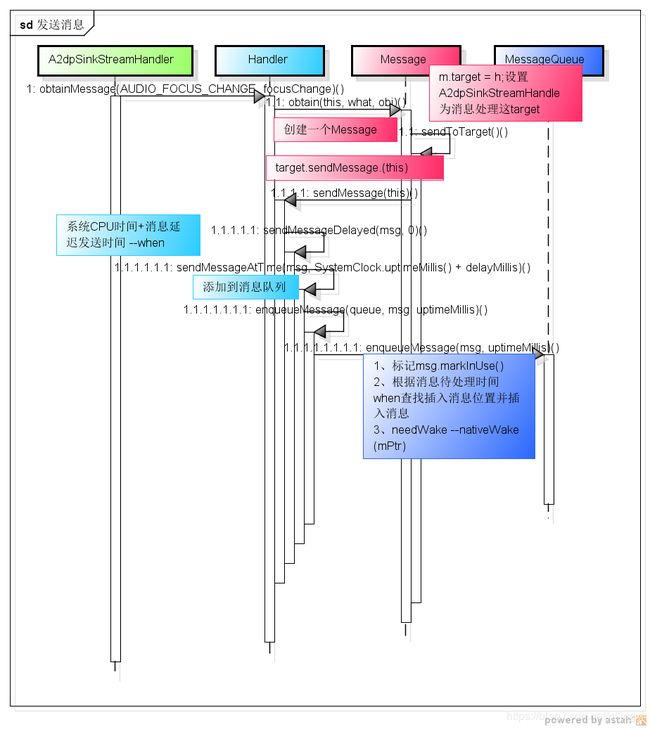
2、发送消息
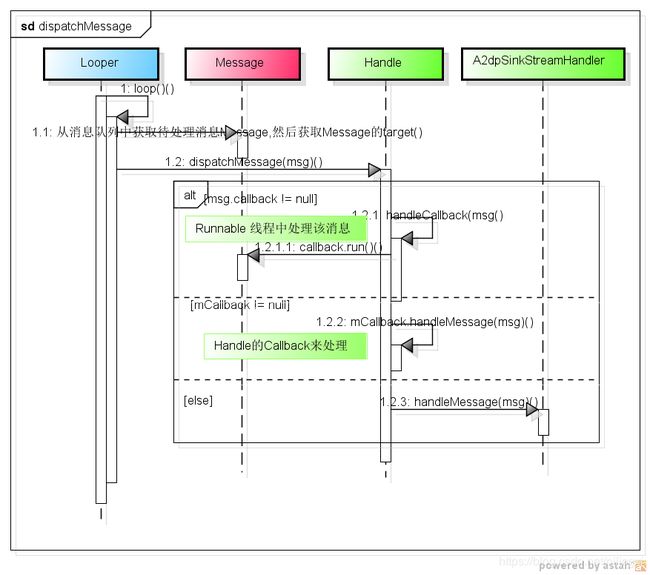
3、处理消息
looper处理消息:
loop 使消息循环起作用,取消息,处理消息
/**
* Run the message queue in this thread. Be sure to call
* {@link #quit()} to end the loop.
*/
public static void loop() {
final Looper me = myLooper();//返回保存在调用线程TLV中的Looper对象
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;//取得Looper对象的消息队列
// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,
// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.
Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block 取消息队列中的一个待处理消息
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
}
// This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger
Printer logging = me.mLogging;
if (logging != null) {
logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +
msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);
}
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);//调用该消息的Handle,交给它的dispatchMessage函数处理
Handle -dispatchMessage
/**
* Handle system messages here.
*/
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.callback != null) {
//Message的callback不为空,则直接调用Message的callback来处理消息
handleCallback(msg);
} else {
if (mCallback != null) {
//Handle的全局Callback不为空
if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
return;
}
}
//调用handle子类的handleMessage来处理消息
handleMessage(msg);
}
}
Message.callback用法:将Runnable当做一个Message
Runnable线程处理使用实例
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
final IBinder b = callbacks.asBinder();
});
}