cv2最强仿射变换(支持n点对齐,可进行人脸对齐)
人脸识别过程中,人脸对齐往往是最重要的一步,对齐的结果往往影响之后提取人脸特征的准确率,opencv内置的仿射变换仅仅需要三个点,而需对齐的人脸关键点一般是5个、68个、128个,本文提供一种n点对齐的放射变换点,以5个关键点的对齐为例:
归一化的五点坐标为:
[(0.31556875000000000, 0.4615741071428571),
(0.68262291666666670, 0.4615741071428571),
(0.50026249999999990, 0.6405053571428571),
(0.34947187500000004, 0.8246919642857142),
(0.65343645833333330, 0.8246919642857142)]
假如要裁剪的face大小为(112, 96),即:(height, width),则face的最终location点为:(xwidth, yheight)
[(30.2946, 51.6963),
(65.5318, 51.6963),
(48.0252, 71.7366),
(33.5493, 92.3655),
(62.7299, 92.3655)]
代码参考来源:https://matthewearl.github.io/2015/07/28/switching-eds-with-python/
#coding=utf-8
import os,cv2,numpy
import logging
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.DEBUG,
format='%(asctime)s %(levelname)s: %(message)s',
datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'
)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
imgSize = [112, 96];
coord5point = [[30.2946, 51.6963],
[65.5318, 51.6963],
[48.0252, 71.7366],
[33.5493, 92.3655],
[62.7299, 92.3655]]
face_landmarks = [[259, 137],
[319, 150],
[284, 177],
[253, 206],
[297, 216]]
def transformation_from_points(points1, points2):
points1 = points1.astype(numpy.float64)
points2 = points2.astype(numpy.float64)
c1 = numpy.mean(points1, axis=0)
c2 = numpy.mean(points2, axis=0)
points1 -= c1
points2 -= c2
s1 = numpy.std(points1)
s2 = numpy.std(points2)
points1 /= s1
points2 /= s2
U, S, Vt = numpy.linalg.svd(points1.T * points2)
R = (U * Vt).T
return numpy.vstack([numpy.hstack(((s2 / s1) * R,c2.T - (s2 / s1) * R * c1.T)),numpy.matrix([0., 0., 1.])])
def warp_im(img_im, orgi_landmarks,tar_landmarks):
pts1 = numpy.float64(numpy.matrix([[point[0], point[1]] for point in orgi_landmarks]))
pts2 = numpy.float64(numpy.matrix([[point[0], point[1]] for point in tar_landmarks]))
M = transformation_from_points(pts1, pts2)
dst = cv2.warpAffine(img_im, M[:2], (img_im.shape[1], img_im.shape[0]))
return dst
def main():
pic_path = r'D:\20171117190537959.jpg'
img_im = cv2.imread(pic_path)
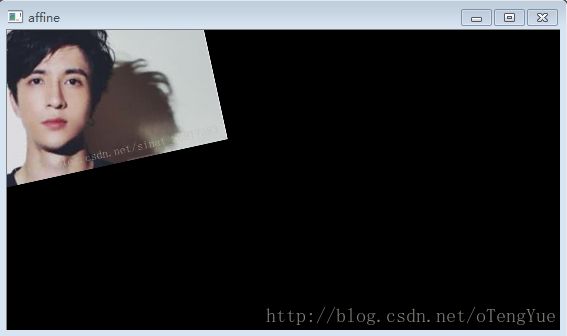
cv2.imshow('affine_img_im', img_im)
dst = warp_im(img_im, face_landmarks, coord5point)
cv2.imshow('affine', dst)
crop_im = dst[0:imgSize[0], 0:imgSize[1]]
cv2.imshow('affine_crop_im', crop_im)
if __name__=='__main__':
main()
cv2.waitKey()
pass