java设计模式之——状态模式
状态模式
在状态模式(State Pattern)中,类的行为是基于它的状态改变的。这种类型的设计模式属于行为型模式。
在状态模式中,我们创建表示各种状态的对象和一个行为随着状态对象改变而改变的 context 对象。
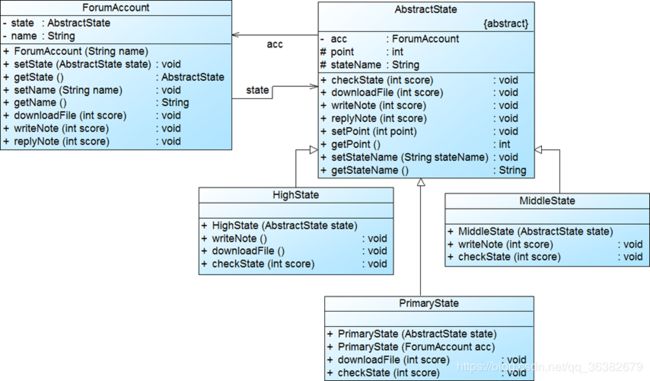
模式结构

状态模式包含如下角色:
1 上下文环境(Context):它定义了客户程序需要的接口并维护一个具体状态角色的实例,将与状态相关的操作委托给当前的Concrete State对象来处理。
2 抽象状态(State):定义一个接口以封装使用上下文环境的的一个特定状态相关的行为。
3 具体状态(Concrete State):实现抽象状态定义的接口。
模式分析
用于解决系统中复杂对象的状态转换以及不同状态下行为的封装问题
将一个对象的状态从该对象中分离出来,封装到专门的状态类中,使得对象状态可以灵活变化
对于客户端而言,无须关心对象状态的转换以及对象所处的当前状态,无论对于何种状态的对象,客户端都可以一致处理
具体案例
状态模式优点:
1、封装了转换规则。
2、枚举可能的状态,在枚举状态之前需要确定状态种类。
3、将所有与某个状态有关的行为放到一个类中,并且可以方便地增加新的状态,只需要改变对象状态即可改变对象的行为。
4、允许状态转换逻辑与状态对象合成一体,而不是某一个巨大的条件语句块。
5、可以让多个环境对象共享一个状态对象,从而减少系统中对象的个数。
状态模式缺点:
1、状态模式的使用必然会增加系统类和对象的个数。
2、状态模式的结构与实现都较为复杂,如果使用不当将导致程序结构和代码的混乱。
3、状态模式对"开闭原则"的支持并不太好,对于可以切换状态的状态模式,增加新的状态类需要修改那些负责状态转换的源代码,否则无法切换到新增状态,而且修改某个状态类的行为也需修改对应类的源代码。
在以下情况下可以使用状态模式:
对象的行为依赖于它的状态(例如某些属性值),状态的改变将导致行为的变化
在代码中包含大量与对象状态有关的条件语句,这些条件语句的出现会导致代码的可维护性和灵活性变差,不能方便地增加和删除状态,并且导致客户类与类库之间的耦合增强
具体案例代码实现
1 定义 State: 抽象状态类
package state;
public abstract class AbstractState
{
protected ForumAccount acc;
protected int point;
protected String stateName;
public abstract void checkState(int score);
public void downloadFile(int score)
{
System.out.println(acc.getName() + "下载文件,扣除" + score + "积分。");
this.point-=score;
checkState(score);
System.out.println("剩余积分为:" + this.point + ",当前级别为:" + acc.getState().stateName + "。");
}
public void writeNote(int score)
{
System.out.println(acc.getName() + "发布留言" + ",增加" + score + "积分。");
this.point+=score;
checkState(score);
System.out.println("剩余积分为:" + this.point + ",当前级别为:" + acc.getState().stateName + "。");
}
public void replyNote(int score)
{
System.out.println(acc.getName() + "回复留言,增加" + score + "积分。");
this.point+=score;
checkState(score);
System.out.println("剩余积分为:" + this.point + ",当前级别为:" + acc.getState().stateName + "。");
}
public void setPoint(int point) {
this.point = point;
}
public int getPoint() {
return (this.point);
}
public void setStateName(String stateName) {
this.stateName = stateName;
}
public String getStateName() {
return (this.stateName);
}
}
2 定义ConcreteState: 具体状态类
package state;
public class HighState extends AbstractState
{
public HighState(AbstractState state)
{
this.acc=state.acc;
this.point=state.getPoint();
this.stateName="专家";
}
public void writeNote(int score)
{
System.out.println(acc.getName() + "发布留言" + ",增加" + score + "*2个积分。");
this.point+=score*2;
checkState(score);
System.out.println("剩余积分为:" + this.point + ",当前级别为:" + acc.getState().stateName + "。");
}
public void downloadFile(int score)
{
System.out.println(acc.getName() + "下载文件,扣除" + score + "/2积分。");
this.point-=score/2;
checkState(score);
System.out.println("剩余积分为:" + this.point + ",当前级别为:" + acc.getState().stateName + "。"); }
public void checkState(int score)
{
if(point<0)
{
System.out.println("余额不足,文件下载失败!");
this.point+=score;
}
else if(point<=100)
{
acc.setState(new PrimaryState(this));
}
else if(point<=1000)
{
acc.setState(new MiddleState(this));
}
}
}
package state;
public class MiddleState extends AbstractState
{
public MiddleState(AbstractState state)
{
this.acc=state.acc;
this.point=state.getPoint();
this.stateName="高手";
}
public void writeNote(int score)
{
System.out.println(acc.getName() + "发布留言" + ",增加" + score + "*2个积分。");
this.point+=score*2;
checkState(score);
System.out.println("剩余积分为:" + this.point + ",当前级别为:" + acc.getState().stateName + "。");
}
public void checkState(int score)
{
if(point>=1000)
{
acc.setState(new HighState(this));
}
else if(point<0)
{
System.out.println("余额不足,文件下载失败!");
this.point+=score;
}
else if(point<=100)
{
acc.setState(new PrimaryState(this));
}
}
}
package state;
public class PrimaryState extends AbstractState
{
public PrimaryState(AbstractState state)
{
this.acc=state.acc;
this.point=state.getPoint();
this.stateName="新手";
}
public PrimaryState(ForumAccount acc)
{
this.point=0;
this.acc=acc;
this.stateName="新手";
}
public void downloadFile(int score)
{
System.out.println("对不起," + acc.getName() + ",您没有下载文件的权限!");
}
public void checkState(int score)
{
if(point>=1000)
{
acc.setState(new HighState(this));
}
else if(point>=100)
{
acc.setState(new MiddleState(this));
}
}
}
3 定义Context: 环境类
package state;
public class ForumAccount
{
private AbstractState state;
private String name;
public ForumAccount(String name)
{
this.name=name;
this.state=new PrimaryState(this);
System.out.println(this.name + "注册成功!");
System.out.println("---------------------------------------------");
}
public void setState(AbstractState state)
{
this.state=state;
}
public AbstractState getState()
{
return this.state;
}
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name=name;
}
public String getName()
{
return this.name;
}
public void downloadFile(int score)
{
state.downloadFile(score);
}
public void writeNote(int score)
{
state.writeNote(score);
}
public void replyNote(int score)
{
state.replyNote(score);
}
}
4 测试
package state;
public class Client
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
ForumAccount account=new ForumAccount("张三");
account.writeNote(20);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
account.downloadFile(20);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
account.replyNote(100);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
account.writeNote(40);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
account.downloadFile(80);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
account.downloadFile(150);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
account.writeNote(1000);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
account.downloadFile(80);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
}
}