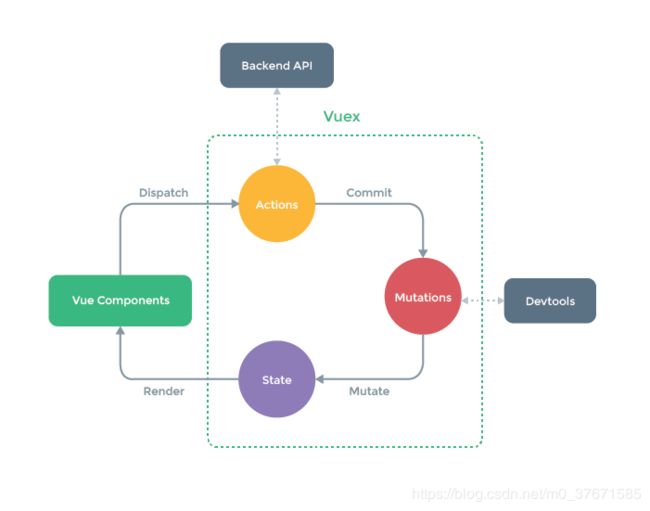
Vuex学习笔记
这里写自定义目录标题
- 使用的原因
- 原理
- Store
- State
- mapState 辅助函数
- Getter
- 1、Getter 接受 state 作为其第一个参数:
- 2、Getter 也可以接受其他 getter 作为第二个参数:
- 3、也可以通过让 getter 返回一个函数,来实现给 getter 传参。在对 store 里的数组进行查询时非常有用。
- Mutation
- 提交载荷(Payload)
- 使用常量替代 Mutation 事件类型
- Mutation 必须是同步函数
- 在组件中提交 Mutation
- Action
- 分发 Action
- mapActions
- Module
- 模块的局部状态
- 双向绑定的计算属性
- 热重载
使用的原因
多组件共用同一个状态时,确保单向数据流不被破坏。
原理
Store
store包含着应用中大部分的状态 (state)
1、Vuex 的状态存储是响应式的。当 Vue 组件从 store 中读取状态的时候,若 store 中的状态发生变化,
那么相应的组件也会相应地得到高效更新。
2、不可以直接改变 store 中的状态。改变 store 中的状态的唯一途径就是显式地提交 (commit) mutation。
这样使得我们可以方便地跟踪每一个状态的变化,从而让我们能够实现一些工具帮助我们更好地了解我们的应用。
在组件中调用 store 中的状态需要在计算属性(computed)中返回。触发变化需要在组件的 methods 中提交 mutation。
在根实例中全局注册store,就可以在任意组件中通过 this.$store.state 获取状态属性
State
mapState 辅助函数
当一个组件需要获取多个状态的时候,将这些状态都声明为计算属性会有些重复和冗余。为了解决这个问题,我们可以使用 mapState 辅助函数帮助我们生成计算属性,如果需要和局部状态响应只能使用普通函数,不可使用箭头函数否则this会获取不到vue实例:
computed: mapState({
// 箭头函数可使代码更简练
count: state => state.count,
// 传字符串参数 'count' 等同于 `state => state.count`
countAlias: 'count',
// 为了能够使用 `this` 获取局部状态,必须使用常规函数
countPlusLocalState (state) {
return state.count + this.localCount
}
})
当映射的计算属性的名称与 state 的子节点名称相同时,我们也可以给 mapState 传一个字符串数组:
computed: mapState([
// 映射 this.count 为 store.state.count
'count' 这里使用的是ES6的简写语法 当属性名和属性值相同是就可以只简写属性名
])
通过 …mapState()可以将多个对象合并为一个,此时函数参数为一个对象
Getter
有时候我们需要从 store 中的 state 中派生出一些状态,Vuex 允许我们在 store 中定义“getter”(可以认为是 store 的计算属性)。就像计算属性一样,getter 的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算,Getter 会暴露为 store.getters 对象,可以以属性的形式访问。辅助函数传参区别:参数为【】时,内部可以使用简写,参数为{}时内部不可以使用简写
1、Getter 接受 state 作为其第一个参数:
getters: {
doneTodos: state => {
return state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done)
}
}
2、Getter 也可以接受其他 getter 作为第二个参数:
getters: {
doneTodosCount: (state, getters) => {
return getters.doneTodos.length
}
}
3、也可以通过让 getter 返回一个函数,来实现给 getter 传参。在对 store 里的数组进行查询时非常有用。
getter 在通过方法访问时,每次都会去进行调用,而不会缓存结果。
getters: {
getTodoById: (state) => (id) => { 此处通过箭头函数返回一个新箭头函数
return state.todos.find(todo => todo.id === id)
}
}
mapGetters 辅助函数
...mapGetters({
// 把 `this.doneCount` 映射为 `this.$store.getters.doneTodosCount`
doneCount: 'doneTodosCount'
})
Mutation
更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation。Vuex 中的 mutation 非常类似于事件:每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的 事件类型 (type) 和 一个 回调函数 (handler)。这个回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 1
},
mutations: {
increment (state) {
// 变更状态
state.count++
}
}
})
不能直接调用一个 mutation handler。这个选项更像是事件注册:“当触发一个类型为 increment 的 mutation 时,调用此函数。”要唤醒一个 mutation handler,你需要以相应的 type 调用 store.commit 方法:
store.commit('increment')
提交载荷(Payload)
可以向 store.commit 传入额外的参数,即 mutation 的 载荷(payload):
mutations: {
increment (state, n) {
state.count += n
}
}
store.commit('increment', 10)
使用常量替代 Mutation 事件类型
// mutation-types.js
export const SOME_MUTATION = 'SOME_MUTATION'
// store.js
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import { SOME_MUTATION } from './mutation-types'
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: { ... },
mutations: {
// 我们可以使用 ES2015 风格的计算属性命名功能来使用一个常量作为函数名
[SOME_MUTATION] (state) {
// mutate state
}
}
})
Mutation 必须是同步函数
在组件中提交 Mutation
你可以在组件中使用 this.$store.commit(‘xxx’) 提交 mutation,或者使用 mapMutations 辅助函数将组件中的 methods 映射为 store.commit 调用(需要在根节点注入 store)。
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapMutations([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
// `mapMutations` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapMutations({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
})
}
}
Action
Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
- Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。
- Action 可以包含任意异步操作
Action 函数接受一个与 store 实例具有相同方法和属性的 context 对象(并不是store实例),因此你可以调用 context.commit 提交一个 mutation,或者通过 context.state 和 context.getters 来获取 state 和 getters。
actions: {
increment (context) {
context.commit('increment')
}
}
// 解构赋值方式
actions: {
increment ({ commit }) {
commit('increment')
}
}
分发 Action
Action 通过 store.dispatch 方法触发:
- store.dispatch(‘increment’)
Actions 支持同样的载荷方式和对象方式进行分发:
// 以载荷形式分发
store.dispatch('incrementAsync', {
amount: 10
})
// 以对象形式分发
store.dispatch({
type: 'incrementAsync',
amount: 10
})
mapActions
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapActions([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
// `mapActions` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapActions({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
})
}
}
Module
Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割:
const moduleA = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态
store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
模块的局部状态
对于模块内部的 mutation 和 getter,接收的第一个参数是模块的局部状态对象。
const moduleA = {
state: { count: 0 },
mutations: {
increment (state) {
// 这里的 `state` 对象是模块的局部状态
state.count++
}
},
getters: {
doubleCount (state) {
return state.count * 2
}
}
}
同样,对于模块内部的 action,局部状态通过 context.state 暴露出来,根节点状态则为 context.rootState:
const moduleA = {
// ...
actions: {
incrementIfOddOnRootSum ({ state, commit, rootState }) {
if ((state.count + rootState.count) % 2 === 1) {
commit('increment')
}
}
}
}
对于模块内部的 getter,根节点状态会作为第三个参数暴露出来:
const moduleA = {
// ...
getters: {
sumWithRootCount (state, getters, rootState) {
return state.count + rootState.count
}
}
}
双向绑定的计算属性
<input v-model="message">
computed: {
message: {
get () {
return this.$store.state.obj.message
},
set (value) {
this.$store.commit('updateMessage', value)
}
}
}
mutations: {
updateMessage (state, message) {
state.obj.message = message
}
}
热重载
// store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import mutations from './mutations'
import moduleA from './modules/a'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const state = { ... }
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations,
modules: {
a: moduleA
}
})
if (module.hot) {
// 使 action 和 mutation 成为可热重载模块
module.hot.accept(['./mutations', './modules/a'], () => {
// 获取更新后的模块
// 因为 babel 6 的模块编译格式问题,这里需要加上 `.default`
const newMutations = require('./mutations').default
const newModuleA = require('./modules/a').default
// 加载新模块
store.hotUpdate({
mutations: newMutations,
modules: {
a: newModuleA
}
})
})
}