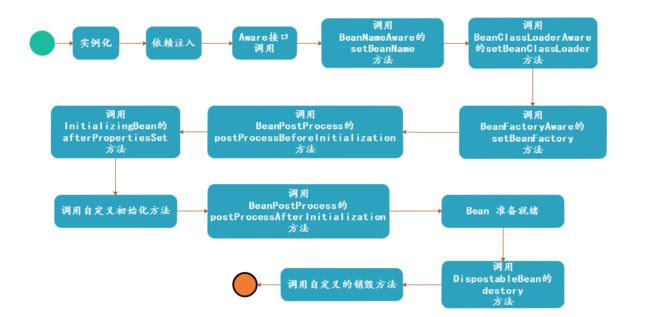
Spring Bean 生命周期
原文发布于: http://blog.ztgreat.cn/article/68
前言
在前面 我们分析了Spring BeanFactory,Spring IOC,Spring AOP,对于IOC的部分,我们跟踪了整个bean的初始化过程:
Spring源码分析:IOC容器初始化(一)
Spring源码分析:IOC容器初始化(二)
这里我们对Spring Bean的生命周期单独做一个总结,也算是梳理知识了。
Spring Bean 生命周期
首先看下生命周期图:
在谈生命周期之前有一点需要先知晓的:
Spring 只帮我们管理单例 Bean 的完整生命周期,对于 prototype 的 bean ,Spring 在创建好交给使用者之后则不会再管理后续的生命周期。
回顾
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory->instantiateBean:
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction更多的内容可以参考 Spring源码分析:IOC容器初始化(二)
初始化过程大致如下:
- 如果 bean 实现了 BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware 或 BeanFactoryAware 接口,则进行 回调
- 通过 PostProcessor 处理器 处理
- 处理 bean 中定义的 init-method,或者如果 bean 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,调用 afterPropertiesSet() 方法
下面我们通过举例来说明每一个步骤
实现 *Aware 接口
在 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory->instantiateBean 中将会调用invokeAwareMethods 方法 :
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader();
if (bcl != null) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl);
}
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}
*Aware 接口可以用于在初始化 bean 时获得 Spring 中的一些对象,如获取 ApplicationContext等。
public class SpringLifeCycleAware implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext ;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext ;
}
}
这样在 springLifeCycleAware 这个 bean 初始化会就会调用 setApplicationContext 方法,并可以获得 applicationContext 对象。
BeanPostProcessor 处理器
实现 BeanPostProcessor 接口,Spring 中所有 bean 在做初始化时都会调用该接口中的两个方法,可以用于对一些特殊的 bean 进行处理:
public class SpringLifeCycleProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//这里 通过名字筛选我们要处理的bean
if ("MyBean".equals(beanName)){
System.out.println("SpringLifeCycleProcessor start beanName:"+beanName);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//这里 通过名字筛选我们要处理的bean
if ("MyBean".equals(beanName)){
System.out.println("SpringLifeCycleProcessor end beanName:"+beanName);
}
return bean;
}
}
InitializingBean, DisposableBean 接口
可以实现 InitializingBean,DisposableBean 这两个接口,也是在初始化以及销毁阶段调用:
public class SpringLifeCycleBean implements InitializingBean,DisposableBean{
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("SpringLifeCycleBean start");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("SpringLifeCycleBean destroy");
}
}
对于 InitializingBean 接口定义如下:
public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
接口只有一个方法afterPropertiesSet,此方法的调用入口是负责加载 spring bean 的AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory,查看 invokeInitMethods:
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
//是否 实现 InitializingBean
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction从这段源码可以得出以下结论:
- spring为bean提供了两种初始化bean的方式,实现InitializingBean接口,实现afterPropertiesSet方法,或者在配置文件中通过init-method指定,两种方式可以同时使用
- 实现InitializingBean接口是直接调用afterPropertiesSet方法,自定义 init-method是通过反射来调用的,但是init-method方式消除了对spring的依赖
- 先调用afterPropertiesSet,再执行 init-method 方法,如果调用afterPropertiesSet方法时出错,则不调用init-method指定的方法。
自定义初始化和销毁方法
也可以自定义方法用于在初始化、销毁阶段调用 来达到同样的效果。:
基于 XML 的配置如下:
注解方式
在 bean 初始化时会经历几个阶段,可以使用注解 @PostConstruct, @PreDestroy 来在 bean 的创建和销毁阶段进行调用:
public class MyBean {
@PostConstruct
public void start(){
System.out.println("MyBean start");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("MyBean destroy");
}
}
对于 @PostConstruct和 @PreDestroy 的实现 是通过 BeanPostProcessor 来实现的,找到类InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
我们先来看这个类的注释:
/**
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor} implementation
* that invokes annotated init and destroy methods. Allows for an annotation
* alternative to Spring's {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean}
* and {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean} callback interfaces.
*
* Spring's {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor}
* supports the JSR-250 {@link javax.annotation.PostConstruct} and {@link javax.annotation.PreDestroy}
* annotations out of the box, as init annotation and destroy annotation, respectively.
* Furthermore, it also supports the {@link javax.annotation.Resource} annotation
* for annotation-driven injection of named beans.
*/
注释说得很清楚了,英语不好,自己慢慢看,我就不翻译了。
对于 @PostConstruct 注解,调用的是如下方法:
InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor->postProcessBeforeInitialization
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass());
metadata.invokeInitMethods(bean, beanName);
//省略 try catch 代码
return bean;
}
对于 @PreDestroy注解,调用的是如下方法:
InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor->postProcessBeforeDestruction
@Override
public void postProcessBeforeDestruction(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass());
metadata.invokeDestroyMethods(bean, beanName);
//省略 try catch 代码
}
总结
简要的将Spring Bean的生命周期过了一篇,虽然在前面Spring IOC 初始化过程中我们基本都提及了,但是比较凌乱,而且不容易理顺知识点,因此这里单独结合前面的IOC 代码把Spring Bean的生命周期走了一遍。