深入分析代理模式——JDK动态代理和CGLib动态代理原理精解版
深入分析代理模式
- 静态代理
- 简单实现,可直接略过
- 现实应用的简单案例【各个省份人员信息在不同数据源中】,通过静态代理切换数据源demo
- 动态代理
- JDK动态代理使用
- JDK动态代理原理分析
- CGLib动态代理使用
- CGLib动态代理原理分析
- JDK与CGLib两种实现方式对比
- 漫谈代理模式与Spring
- 代理模式利弊
静态代理
简单实现,可直接略过
//要找对象的男孩
public class Man implements Person{
public void findLove(){
System.out.println("儿子要求:肤白貌美大长腿");
}
}
//媒婆
public class Matchmaker implements Person {
private Man man;
public Matchmaker(Man man){
this.man = man;
}
public void findLove(){
System.out.println("媒婆整理手中资源");
this.man.findLove();
System.out.println("按照男孩要求物色");
System.out.println("物色到合适的后--善后处理");
}
}
//测试类
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Matchmaker matchmaker = new Matchmaker(new Man());
matchmaker.findLove();
}
}
现实应用的简单案例【各个省份人员信息在不同数据源中】,通过静态代理切换数据源demo
- 基础的新增逻辑【为节省篇幅,忽略了大部分细节,注重思路】
//人员信息
public class PersonInfo {
private String name;
private int age;
}
//mapper层
public interface PersonInfoMapper {
Integer insertPerson(PersonInfo personInfo);
}
//service实现
public class PersonInfoServiceImpl implements PersonInfoService {
PersonInfoMapper personInfoMapper;
public Integer insertPerson(PersonInfo personInfo) {
//新增逻辑
return 1;
}
}
- 切换数据源工具类【众多数据源是提前配置好的,只要根据数据源的名称就可以唯一定位到要使用的数据源】
//切换数据源工具类
public class DynamicDataSourceEntry {
// 默认数据源
public final static String DEFAULT_SOURCE = "默认数据源name";
//当前类为工具类,必须考虑并发,ThreadLocal可以实现线程之间的资源隔离
// 与synchronized【实现线程之间的资源共享】关键字正好相反,不了解者可自行百度
private final static ThreadLocal<String> local = new ThreadLocal<String>();
private DynamicDataSourceEntry(){
}
//清空数据源
public static void clear() {
local.remove();
}
//获取当前数据源的名字
public static String get() {
return local.get();
}
//还原默认数据源
public static void restore() {
local.set(DEFAULT_SOURCE);
}
//根据省份设置数据源
public static void set(String province) {
local.set("DB_" + province);
}
}
- 静态代理类
//相当于媒婆
public class ChangeDataSourceStaticProxy {
//相当于要找对象的男孩
private PersonInfoService personInfoService;
public ChangeDataSourceStaticProxy(PersonInfoService personInfoService) {
this.personInfoService = personInfoService;
}
public Integer insertPersonInfo(PersonInfo personInfo){
//根据当前人所在省份的信息,生成数据源名称 例如:dbName = DB_ + 省份名称
//向ThreadLocal中写入当前要操作的数据源名称
DynamicDataSourceEntry.set("当前要操作的数据源名称dbName");
//切换数据源代码
//执行插入操作
personInfoService.insertPerson(personInfo);
//......此处省略500个方法【在这500个方法中如需获取当前数据源的名称进行操作即可调用DynamicDataSourceEntry.get();】
return 1;
}
}
动态代理
JDK动态代理使用
- 被代理类【小高】,被代理类必须实现接口,JDK通过反射调用接口实现
public class XiaoGaoPerson implements Person {
public boolean findLove() {
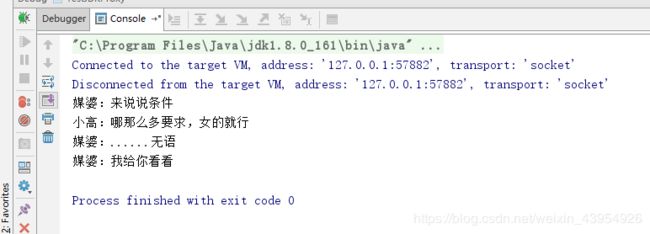
System.out.println("小高:哪那么多要求,女的就行");
return false;
}
}
- 代理类【媒婆】
public class JDKProxy implements InvocationHandler {
//被代理对象
private Object target;
public Object getInstance(Object target){
this.target = target;
Class<?> targetClass = target.getClass();
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(targetClass.getClassLoader(),targetClass.getInterfaces(),this);
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
beforMethod();
Object proxyTarget = method.invoke(this.target, args);
afterMethod();
return proxyTarget;
}
private void beforMethod() {
System.out.println("媒婆:来说说条件");
}
private void afterMethod() {
System.out.println("媒婆:......无语");
System.out.println("媒婆:我给你看看");
}
}
- 测试类
public class TestJDKProxy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = (Person)new JDKProxy().getInstance(new XiaoGaoPerson());
person.findLove();
}
}
JDK动态代理原理分析
有没有感觉很神奇的样子呢?JDK使用的是字节码重组技术,通过生成对象类代理原始对象,并通过调用原始对象的方法。JDK 中有一个规范,在 ClassPath 下只要是$开头的 class 文件一般都是自动生成的。反编译工具
详细步骤为:
- 获取被代理对象的引用及所有接口,接口通过反射获取
- 生成新类,该类实现了被代理类实现的所有接口,并包含了原始业务和扩展后的业务
- 编译生成.class并运行
现在我们获取JDKProxy生成的class进行分析,通过将内存中的字节码文件输出到class中再反编译进行获取
执行如下代码,获取代理后的class文件:
public class ObtainJDKProxyAfterClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = (Person)new JDKProxy().getInstance(new XiaoGaoPerson());
person.findLove();
byte [] bytes = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass("$ProxyGao",new Class[]{Person.class});
FileOutputStream os = null;
try {
os = new FileOutputStream("D://$ProxyGao.class");
os.write(bytes);
os.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这不,我这有,你运行你也有,大家有才是真的有
下面是反编译后的代码:
public final class $ProxyGao extends Proxy
implements Person
{
private static Method m1;
private static Method m3;
private static Method m2;
private static Method m0;
public $ProxyGao()
throws
{
super(paramInvocationHandler);
}
public final boolean equals()
throws
{
try
{
return ((Boolean)this.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[] { paramObject })).booleanValue();
}
catch (RuntimeException localRuntimeException)
{
throw localRuntimeException;
}
catch (Throwable localThrowable)
{
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable);
}
}
public final boolean findLove()
throws
{
try
{
return ((Boolean)this.h.invoke(this, m3, null)).booleanValue();
}
catch (RuntimeException localRuntimeException)
{
throw localRuntimeException;
}
catch (Throwable localThrowable)
{
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable);
}
}
public final String toString()
throws
{
try
{
return ((String)this.h.invoke(this, m2, null));
}
catch (RuntimeException localRuntimeException)
{
throw localRuntimeException;
}
catch (Throwable localThrowable)
{
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable);
}
}
public final int hashCode()
throws
{
try
{
return ((Integer)this.h.invoke(this, m0, null)).intValue();
}
catch (RuntimeException localRuntimeException)
{
throw localRuntimeException;
}
catch (Throwable localThrowable)
{
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable);
}
}
static
{
try
{
m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", new Class[] { Class.forName("java.lang.Object") });
m3 = Class.forName("com.gupaoedu.vip.pattern.proxy.staticproxy.Person").getMethod("findLove", new Class[0]);
m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString", new Class[0]);
m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode", new Class[0]);
return;
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException localNoSuchMethodException)
{
throw new NoSuchMethodError(localNoSuchMethodException.getMessage());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException localClassNotFoundException)
{
throw new NoClassDefFoundError(localClassNotFoundException.getMessage());
}
}
}
通过分析代码我们发现【下面代码取自反编译后的代码】:
- $ProxyGao 继承了 Proxy 类并实现了 Person 接口
public final class $ProxyGao extends Proxy
implements Person
- 静态块中用反射获取了被代理对象的所有方法,并进行了保存
m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", new Class[] { Class.forName("java.lang.Object") });
m3 = Class.forName("com.gupaoedu.vip.pattern.proxy.staticproxy.Person").getMethod("findLove", new Class[0]);
m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString", new Class[0]);
m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode", new Class[0]);
- 重写 findLove()等方法,例如findLove()
- 看这行代码:return ((Boolean)this.h.invoke(this, m3, null)).booleanValue();//通过反射调用
public final boolean findLove()
throws
{
try
{
return ((Boolean)this.h.invoke(this, m3, null)).booleanValue();//通过反射调用
}
catch (RuntimeException localRuntimeException)
{
throw localRuntimeException;
}
catch (Throwable localThrowable)
{
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable);
}
}
CGLib动态代理使用
- 被代理类【小高】,可以不实现接口
public class XiaoGaoPerson {
public boolean findLove() {
System.out.println("小高:哪那么多要求,女的就行");
return false;
}
}
- 代理类,需要实现MethodInterceptor接口
public class CGLibProxy implements MethodInterceptor{
private Object target;
public Object getInstance(Object source){
target = source;
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(this.target.getClass());
enhancer.setCallback(this);
return enhancer.create();
}
//进行业务增强
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
beforMethod();
//此处需要调用被代理的方法
//使用方法1或者方法2均可,但是方法3会造成死循环
//原因在于,方法3调用的是代理之后的方法,相当于在代理之后的方法中再调用代理之后的方法,然后你就会看到它:StackOverflowError
Object obj = methodProxy.invoke(this.target, objects);//方法1
//Object obj = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects); //方法2
//Object obj = methodProxy.invoke(o, objects); //方法3
afterMethod();
return obj;
}
private void beforMethod() {
System.out.println("媒婆:来说说条件");
}
private void afterMethod() {
System.out.println("媒婆:......无语");
System.out.println("媒婆:我给你看看");
}
}
- 测试类
public class CGLibTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
XiaoGaoPerson person = (XiaoGaoPerson)new CGLibProxy().getInstance(XiaoGaoPerson.class);
person.findLove();
}
}
CGLib动态代理原理分析
- 同样的,我们还是先获取内存中生成的class文件,然后反编译查看
- 我们可以在测试类中加入一行代码,利用cglib的代理类可以将内存中的class文件写入到本地磁盘
public class CGLibTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//利用cglib的代理类可以将内存中的class文件写入到本地磁盘
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY,"D://cglib");
XiaoGaoPerson person = (XiaoGaoPerson)new CGLibProxy().getInstance(XiaoGaoPerson.class);
person.findLove();
}
}
package proxy.cglib;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.springframework.cglib.core.ReflectUtils;
import org.springframework.cglib.core.Signature;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Callback;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Factory;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
public class fd16c28d extends XiaoGaoPerson
implements Factory
{
private boolean CGLIB$BOUND;
public static Object CGLIB$FACTORY_DATA;
private static final ThreadLocal CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS;
private static final Callback[] CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS;
private MethodInterceptor CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
private static Object CGLIB$CALLBACK_FILTER;
private static final Method CGLIB$findLove$0$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$findLove$0$Proxy;
private static final Object[] CGLIB$emptyArgs;
private static final Method CGLIB$equals$1$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$equals$1$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$toString$2$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$toString$2$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$hashCode$3$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$hashCode$3$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$clone$4$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy;
static void CGLIB$STATICHOOK1()
{
Class localClass2;
CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS = new ThreadLocal();
CGLIB$emptyArgs = new Object[0];
Class localClass1 = Class.forName("proxy.cglib.XiaoGaoPerson$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$fd16c28d");
Method[] tmp83_80 = ReflectUtils.findMethods(new String[] { "equals", "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z", "toString", "()Ljava/lang/String;", "hashCode", "()I", "clone", "()Ljava/lang/Object;" }, (localClass2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object")).getDeclaredMethods());
CGLIB$equals$1$Method = tmp83_80[0];
CGLIB$equals$1$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(localClass2, localClass1, "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z", "equals", "CGLIB$equals$1");
Method[] tmp103_83 = tmp83_80;
CGLIB$toString$2$Method = tmp103_83[1];
CGLIB$toString$2$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(localClass2, localClass1, "()Ljava/lang/String;", "toString", "CGLIB$toString$2");
Method[] tmp123_103 = tmp103_83;
CGLIB$hashCode$3$Method = tmp123_103[2];
CGLIB$hashCode$3$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(localClass2, localClass1, "()I", "hashCode", "CGLIB$hashCode$3");
Method[] tmp143_123 = tmp123_103;
CGLIB$clone$4$Method = tmp143_123[3];
CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(localClass2, localClass1, "()Ljava/lang/Object;", "clone", "CGLIB$clone$4");
tmp143_123;
Method[] tmp191_188 = ReflectUtils.findMethods(new String[] { "findLove", "()Z" }, (localClass2 = Class.forName("proxy.cglib.XiaoGaoPerson")).getDeclaredMethods());
CGLIB$findLove$0$Method = tmp191_188[0];
CGLIB$findLove$0$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(localClass2, localClass1, "()Z", "findLove", "CGLIB$findLove$0");
tmp191_188;
}
final boolean CGLIB$findLove$0()
{
return super.findLove();
}
public final boolean findLove()
{
MethodInterceptor tmp4_1 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (tmp4_1 == null)
{
tmp4_1;
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
}
MethodInterceptor tmp17_14 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (tmp17_14 == null)
break label52;
label45: label52: if (tmp17_14.intercept(this, CGLIB$findLove$0$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$findLove$0$Proxy) != null)
break label45;
}
final boolean CGLIB$equals$1()
{
return super.equals(paramObject);
}
public final boolean equals()
{
MethodInterceptor tmp4_1 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (tmp4_1 == null)
{
tmp4_1;
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
}
MethodInterceptor tmp17_14 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (tmp17_14 == null)
break label57;
label50: label57: if (tmp17_14.intercept(this, CGLIB$equals$1$Method, new Object[] { paramObject }, CGLIB$equals$1$Proxy) != null)
break label50;
}
final String CGLIB$toString$2()
{
return super.toString();
}
public final String toString()
{
MethodInterceptor tmp4_1 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (tmp4_1 == null)
{
tmp4_1;
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
}
MethodInterceptor tmp17_14 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (tmp17_14 != null)
return ((String)tmp17_14.intercept(this, CGLIB$toString$2$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$toString$2$Proxy));
return super.toString();
}
final int CGLIB$hashCode$3()
{
return super.hashCode();
}
public final int hashCode()
{
MethodInterceptor tmp4_1 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (tmp4_1 == null)
{
tmp4_1;
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
}
MethodInterceptor tmp17_14 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (tmp17_14 == null)
break label52;
label45: label52: if (tmp17_14.intercept(this, CGLIB$hashCode$3$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$hashCode$3$Proxy) != null)
break label45;
}
final Object CGLIB$clone$4()
throws CloneNotSupportedException
{
return super.clone();
}
protected final Object clone()
throws CloneNotSupportedException
{
MethodInterceptor tmp4_1 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (tmp4_1 == null)
{
tmp4_1;
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
}
MethodInterceptor tmp17_14 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (tmp17_14 != null)
return tmp17_14.intercept(this, CGLIB$clone$4$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy);
return super.clone();
}
public static MethodProxy CGLIB$findMethodProxy(Signature paramSignature)
{
String tmp4_1 = paramSignature.toString();
switch (tmp4_1.hashCode())
{
case -508378822:
if (!(tmp4_1.equals("clone()Ljava/lang/Object;")))
break label121;
label121: return CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy;
case 1192015566:
case 1826985398:
case 1913648695:
case 1984935277:
}
}
public static void CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(Callback[] paramArrayOfCallback)
{
CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS.set(paramArrayOfCallback);
}
public static void CGLIB$SET_STATIC_CALLBACKS(Callback[] paramArrayOfCallback)
{
CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS = paramArrayOfCallback;
}
private static final void CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(Object paramObject)
{
fd16c28d localfd16c28d = (fd16c28d)paramObject;
if (localfd16c28d.CGLIB$BOUND)
break label52;
localfd16c28d.CGLIB$BOUND = true;
Object tmp23_20 = CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS.get();
if (tmp23_20 != null)
break label39;
tmp23_20;
Callback[] tmp31_28 = CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS;
if (tmp31_28 != null)
break label39;
tmp31_28;
label39: label52: break label52:
}
public Object newInstance()
{
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(paramArrayOfCallback);
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(null);
return new fd16c28d();
}
public Object newInstance()
{
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(new Callback[] { paramCallback });
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(null);
return new fd16c28d();
}
public Object newInstance(, Object[] paramArrayOfObject, Callback[] paramArrayOfCallback)
{
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(paramArrayOfCallback);
Class[] tmp9_8 = paramArrayOfClass;
switch (tmp9_8.length)
{
case 0:
tmp9_8;
break;
default:
new fd16c28d();
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Constructor not found");
}
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(null);
}
public Callback getCallback()
{
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
switch (paramInt)
{
case 0:
}
return null;
}
public void setCallback(, Callback paramCallback)
{
switch (paramInt)
{
case 0:
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 = ((MethodInterceptor)paramCallback);
}
}
public Callback[] getCallbacks()
{
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
return { this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 };
}
public void setCallbacks()
{
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 = ((MethodInterceptor)paramArrayOfCallback[0]);
}
static
{
CGLIB$STATICHOOK1();
}
}
通过分析代码我们发现【下面代码取自反编译后的代码】:
- 生成的代码中继承了 XiaoGaoPerson类并实现了 Factory 接口
public class fd16c28d extends XiaoGaoPerson
implements Factory
- 请看findLove()方法,通过
tmp17_14.intercept()调用代理类CGLibProxy中的intercept()方法
final boolean CGLIB$findLove$0()
{
return super.findLove();
}
public final boolean findLove()
{
MethodInterceptor tmp4_1 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (tmp4_1 == null)
{
tmp4_1;
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
}
MethodInterceptor tmp17_14 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (tmp17_14 == null)
break label52;
label45: label52: if (tmp17_14.intercept(this, CGLIB$findLove$0$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$findLove$0$Proxy) != null)
break label45;
}
JDK与CGLib两种实现方式对比
- JDK动态代理是实现了被代理对象的接口,CGLib是继承了被代理对象
- JDK和CGLib都是在运行期生成字节码,JDK直接写成Class字节码,CGLib使用ASM框架写Class字节码,CGLib实现更加复杂,生成代理类比JDK效率低。
- JDK是通过反射调用代理方法,CGLib是通过FastClass机制直接调用方法,所以CGLib动态代理的执行效率更高。
漫谈代理模式与Spring
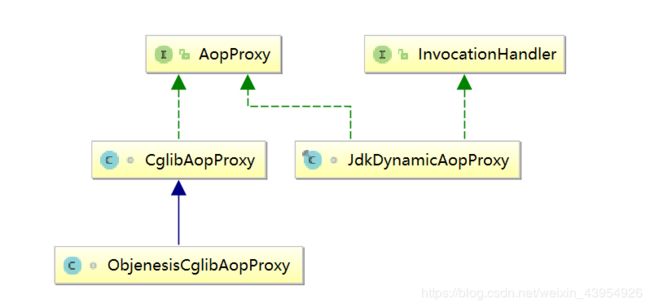
- spring利用动态代理实现AOP有两个关键的类,是JdkDynamicAopProxy和CglibAopProxy,类图如下:
- spring选择两种代理方式的规则是:当Bean实现了接口时使用JDK动态代理;当Bean没有实现接口时使用CGLib动态代理。也可以通过如下配置强制使用CGLib动态代理。【具体原因参见后续的spring源码分析】
代理模式利弊
优点:
- 运用动态代理结合策略模式,可以很好的实现代码的扩展和功能的增强,遵循开闭原则
- 代理模式将代理对象与真实被调用的目标对象分离,降低了耦合度,并且可以保护目标对象
缺点: - 增加了系统和类体系的复杂度
- 客户端和目标对象中间增加了代理对象,降低了访问效率
▄█▀█●各位同仁,如果我的代码对你有帮助,请给我一个赞吧,为了下次方便找到,也可关注加收藏呀
如果有什么意见或建议,也可留言区讨论