业务模块化流程编排
背景
项目中经常会遇到一些功能类似,但是各自会多一些少一些功能,这些类似的功能多了,往往会出现上帝类,就是一个类中包含了所有情况,复杂至极,这样的类往往不好维护,最后只能在这个类上往后继续增加业务,最后无比复杂无法维护。还有的是每一种情况就重新写一次定制一个新的,这样虽然可以不回造成类的膨胀,但是这样每次重写造成的很多相似的代码,复用情况差。
业务模块化
针对上述的情况,在一些文章里经常会看到通过模块化处理,像搭积木似的把业务搭建起来。那如何搭这个积木呢?首先要有积木。如何提取这些积木呢?这些模块化的业务就是一些不变的原子业务,也就是DDD中提到的领域模型。以登录注册举例,登录注册功能并不复杂,但是要面对不同的业务线,因此会很多不同的变化,如图

登录注册功能类似,而把他们逐步分割成一个个原子服务模块就是这些:登录密码校验,验证码校验,安全校验token生成等,这些模块不仅登录注册可以用其他也可以用,而这些原子模块往往都有着不可分割,稳定不变的特性,通过不同的编排以应对不同的业务逻辑。
业务的编排
原子模块提取之后,就相当于我们有了积木,我们可以动手自己组装,可是拼装的时候会发现积木无法很好拼接在一起,需要用很多"胶水"粘在一起。胶水用多了总是不太好看,那么又应该怎么做?首先为什么这些积木无法直接组装,因为他们不是一个牌子的(各个代码没有一个统一的接口),因此要统一牌子,都用乐高的(定义统一的接口)。业务的统一抽象接口
/**
* @author maowenlong
*/
public interface IBusinessComponent<T> {
/**
* 业务逻辑执行
*
* @param request 执行请求
*/
void execute(T request);
/**
* 是否执行
* @return
*/
default Boolean executeIs(){
return true;
}
}
各业务模块实现接口,实现接口的统一封装,并定义自己的参数接口
/**
* 注册组件
* @author maowenlong
*/
@Component
public class RegisterComponent implements IBusinessComponent<RegisterRequest> {
@Resource
private AccountRegisterBaseAppService accountRegisterBaseAppService;
@Override
public void execute(RegisterRequest registerRequest) {
//避免重新new,无法渠道AccountId
AccountRegisterParam accountRegisterParam = registerRequest.getAccountRegisterParam();
accountRegisterBaseAppService.register(accountRegisterParam);
registerRequest.setAccountId(accountRegisterParam.getAccountId());
}
}
/**
* @author maowenlong
*/
public interface RegisterRequest {
/**
* 注册入参
* @return
*/
AccountRegisterParam getAccountRegisterParam();
/**
* 回填生成AccountId
* @param accountId
*/
void setAccountId(AccountId accountId);
}
接口统一之后,那么就可以抽象出一个编排流程管理,进行管控,执行各个组件,并对异常进项管控
/**
* 流式管理,
* 类似责任连,命令,stream
* 传统责任连没有外围管理,这样不是太好做一些控制
* 比如 超时,降级,异常
*
* @author maowenlong
*/
@Slf4j
public class Processor<E, T extends ProcessorDomain<E>> {
/**
* 业务组件
*/
List<IBusinessComponent> components = Lists.newArrayList();
/**
* 增加组件
*
* @return
*/
public Processor<E, T> append(IBusinessComponent component) {
components.add(component);
return this;
}
/**
* 执行组件
*
* @param request
* @return
*/
public E doProcess(T request) {
for (IBusinessComponent component : components) {
try {
if (component.executeIs()){
long beforeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
component.execute(request);
long afterMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("{},SUCCESS,耗时{}毫秒", this.getClass().getSimpleName(), (afterMillis - beforeMillis));
}
} catch (BizCheckException e) {
log.info("Process Exception common{}", this.getClass(), e);
exception(e, request);
}
}
return request.getResult();
}
/**
* 判断异常是否忽略
*
* @param e
* @param request
*/
private void exception(BizCheckException e, T request) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(request.getIgnoreException())) {
if (request.getIgnoreException().contains(e.getCode())) {
return;
}
}
throw e;
}
}
通过品牌的积木有了,想在要做的就是把积木拼起来,每个拼接的积木都有一个对应的拼装方式,这些拼装方式都需要实现各个模块的参数接口
/**
* @author maowenlong
*/
public interface ProcessorDomain<T> {
/**
* 获取结果
* @return
*/
T getResult();
/**
* 忽略错误码
* @return
*/
default Set<String> getIgnoreException(){
return null;
}
}
/**
* 1.验证码校验
* 2.用户手机号获取
* 3.白骑士
* 4,注册
* 5,登录
* 6,jwt
* 7,获取VO
* @author maowenlong
*/
public class LoginAndRegWebVerifyCodeProcessorAo implements ProcessorDomain<LoginAndRegWebVerifyCodeVo>,
UserMobileRequest, VerifyCodeCheckRequest, RegisterRequest, LoginRequest, TokenRequest, SecurityCheckRequest {
最后的流式的调用方式
@TraceLog(descn = "验证码web登录注册")
@Override
public RestResult<LoginAndRegWebVerifyCodeVo> loginAndReg(@Valid @RequestBody LoginAndRegWebVerifyCodeVoParam loginAndRegWebVerifyCodeParam) {
LoginAndRegWebVerifyCodeProcessorAo loginAndRegWebVerifyCodeProcessorAo = new LoginAndRegWebVerifyCodeProcessorAo(loginAndRegWebVerifyCodeParam);
return RestResult.successResult(
new Processor<LoginAndRegWebVerifyCodeVo, LoginAndRegWebVerifyCodeProcessorAo>()
.append(verifyCodeCheck)
.append(userMobileWrapper)
.append(securityCheck)
.append(registerComponent)
.append(loginWrapper)
.append(tokenWrapper)
.doProcess(loginAndRegWebVerifyCodeProcessorAo)
);
}
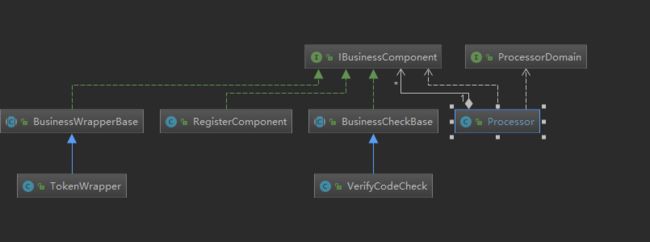
类图:
框架,IBusinessComponent 是组件接口,单还可以细分成 3种:校验,封装,命令
**
LoginAndRegWebVerifyCodeProcessorAo 就是将各个模块连接起来的,实现各个模块的请求接口和流程接口,将各个模块组织起来, 每次拼接都要有个一对应的组装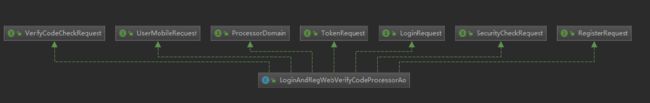
其实模式只是术,只能解决特定问题,对不变业务的理解抽象,业务趋势的把握,以及面向对象思想的理解才是灵活应对多变业务的根本