Neutron印象3:neutron-l3-agent
一.Layer-3 Networking Extension
neutron l3作为一种API扩展,向租户提供了路由和NAT功能。
l3扩展包含两种资源:
- router:在不同内部子网中转发数据包;通过指定内部网关做NAT。每一个子网对应router上的一个端口,这个端口的ip就是子网的网关。
- floating ip:代表一个外部网络的IP,映射到内部网络的端口上。当网络的router:external属性为True时,floating ip才能定义。
这两种资源都对应有不同的属性。支持CRUD操作。
二.代码分析
既然neutron中支持了l3扩展,那么怎样通过API来创建router或者floating ip,以提供路由以及NAT的功能的呢?
主要有以下几个步骤:
1.租户通过horizon,nova命令或者自定义的脚本,发送与router或floating ip相关的操作。
2.这些API请求发送到neutron server,通过neutron提供的API extension相对应。
3.实现这些API extension的操作,比如说create_router,则由具体的plugin和database来共同完成。
4.plugin会通过rpc机制与计算网络节点上运行的l3 agent来执行l3 转发和NAT的功能。
l3.py
源代码目录:neutron/extensions/l3.py
class RouterPluginBase(object): @abc.abstractmethod def create_router(self, context, router): pass @abc.abstractmethod def update_router(self, context, id, router): pass @abc.abstractmethod def get_router(self, context, id, fields=None): pass @abc.abstractmethod def delete_router(self, context, id): pass @abc.abstractmethod def get_routers(self, context, filters=None, fields=None, sorts=None, limit=None, marker=None, page_reverse=False): pass @abc.abstractmethod def add_router_interface(self, context, router_id, interface_info): pass @abc.abstractmethod def remove_router_interface(self, context, router_id, interface_info): pass @abc.abstractmethod def create_floatingip(self, context, floatingip): pass @abc.abstractmethod def update_floatingip(self, context, id, floatingip): pass @abc.abstractmethod def get_floatingip(self, context, id, fields=None): pass @abc.abstractmethod def delete_floatingip(self, context, id): pass @abc.abstractmethod def get_floatingips(self, context, filters=None, fields=None, sorts=None, limit=None, marker=None, page_reverse=False): pass def get_routers_count(self, context, filters=None): raise NotImplementedError() def get_floatingips_count(self, context, filters=None): raise NotImplementedError()
l3_db.py
源码目录:/neutron/db/l3_db.py
这个模块中,class L3_NAT_db_mixin继承了上面l3模块的class RouterPluginBase,因此在RouterPluginBase中定义的抽象方法就要在这里实现了。
类注释中写道,Mixin class to add L3/NAT router methods to db_plugin_base_v2。
在类的开始,有这样一段代码:
@property def l3_rpc_notifier(self): if not hasattr(self, '_l3_rpc_notifier'): self._l3_rpc_notifier = l3_rpc_agent_api.L3AgentNotifyAPI() return self._l3_rpc_notifier
l3_rpc_agent_api模块源码在/neutron/api/rpc/agentnotifiers/l3_rpc_agent_api.py。
class L3AgentNotifyAPI(n_rpc.RpcProxy): """API for plugin to notify L3 agent.""" BASE_RPC_API_VERSION = '1.0' def __init__(self, topic=topics.L3_AGENT): super(L3AgentNotifyAPI, self).__init__( topic=topic, default_version=self.BASE_RPC_API_VERSION) def _notification_host(self, context, method, payload, host): """Notify the agent that is hosting the router.""" ... def _agent_notification(self, context, method, router_ids, operation, data): """Notify changed routers to hosting l3 agents.""" ... def _notification(self, context, method, router_ids, operation, data): """Notify all the agents that are hosting the routers.""" ...def _notification_fanout(self, context, method, router_id): """Fanout the deleted router to all L3 agents.""" ...def agent_updated(self, context, admin_state_up, host): self._notification_host(context, 'agent_updated', {'admin_state_up': admin_state_up}, host) def router_deleted(self, context, router_id): self._notification_fanout(context, 'router_deleted', router_id) def routers_updated(self, context, router_ids, operation=None, data=None): if router_ids: self._notification(context, 'routers_updated', router_ids, operation, data) def router_removed_from_agent(self, context, router_id, host): self._notification_host(context, 'router_removed_from_agent', {'router_id': router_id}, host) def router_added_to_agent(self, context, router_ids, host): self._notification_host(context, 'router_added_to_agent', router_ids, host)
这个类主要用于plugin发送rpc通知给l3 agent。
rpc处理
在上面的l3_db.py中,会将涉及router和floating ip的处理读取或者写入到数据中。但是还有一些操作不仅如此,还需要通过rpc(通过调用l3_rpc_agent_api中的函数,这些操作大部分会去 调用routers_updated),通知l3 agent进行处理。
这些需要处理的地方包括:update_router,delete_router,add_router_interface,remove_router_interface,create_floatingip,update_floatingip,delete_floatingip,disassociate_floatingips等操作。
l3_agent.py
源码目录:neutron/agent/l3_agent.py
l3 agent使用Linux ip协议栈和iptables来实现router和NAT的功能。
这时候,如果在horizon的界面创建一个路由,不进行任何操作的话,plugin只会操作数据库,l3 agent不会作处理。而当update router,如设置外部网关时,l3才会去处理请求。
l3 agent使用service框架启动服务,其manager类为neutron.agent.l3_agent.L3NATAgentWithStateReport,该类继承自L3NATAgent,主要实现了基于rpc的_report_state向PluginReportStateAPI(topic为q-plugin)汇报状态信息,这些信息由各个plugin来处理(比如ml2中通过start_rpc_listeners来注册该topic的消费者)。
L3NATAgent类是最主要的L3 Manager类,该类继承关系为 class L3NATAgent(firewall_l3_agent.FWaaSL3AgentRpcCallback, manager.Manager) ;FWaaSL3AgentRpcCallback主要是加载防火墙驱动,并创建RPC与Plugin通信。
再来看L3NATAgent的创建过程:
def __init__(self, host, conf=None): if conf: self.conf = conf else: self.conf = cfg.CONF self.root_helper = config.get_root_helper(self.conf) self.router_info = {} self._check_config_params() try: # import driver from l3_agent.init # Example: interface_driver = neutron.agent.linux.interface.OVSInterfaceDriver self.driver = importutils.import_object( self.conf.interface_driver, self.conf ) except Exception: msg = _("Error importing interface driver " "'%s'") % self.conf.interface_driver LOG.error(msg) raise SystemExit(1) self.context = context.get_admin_context_without_session() # Agent side of the l3 agent RPC API, topic is 'q-l3-plugin' self.plugin_rpc = L3PluginApi(topics.L3PLUGIN, host) self.fullsync = True self.updated_routers = set() self.removed_routers = set() self.sync_progress = False self._clean_stale_namespaces = self.conf.use_namespaces # Start RPC Loop self.rpc_loop = loopingcall.FixedIntervalLoopingCall( self._rpc_loop) self.rpc_loop.start(interval=RPC_LOOP_INTERVAL) super(L3NATAgent, self).__init__(conf=self.conf) self.target_ex_net_id = None
上面的self.plugin_rpc会处理neutron-server转发过来的请求,这个请求是通过service_plugins的方式处理的:
neutron.service_plugins = dummy = neutron.tests.unit.dummy_plugin:DummyServicePlugin router = neutron.services.l3_router.l3_router_plugin:L3RouterPlugin firewall = neutron.services.firewall.fwaas_plugin:FirewallPlugin lbaas = neutron.services.loadbalancer.plugin:LoadBalancerPlugin aas = neutron.services..plugin:VPNDriverPlugin metering = neutron.services.metering.metering_plugin:MeteringPlugin
self.rpc_loop会循环检测从plugin发送过来的rpc请求:
@lockutils.synchronized('l3-agent', 'neutron-') def _rpc_loop(self): # _rpc_loop and _sync_routers_task will not be # executed in the same time because of lock. # so we can clear the value of updated_routers # and removed_routers, but they can be updated by # updated_routers and removed_routers rpc call try: LOG.debug(_("Starting RPC loop for %d updated routers"), len(self.updated_routers)) if self.updated_routers: # 保存了需要本次处理的router信息 # We're capturing and clearing the list, and will # process the "captured" updates in this loop, # and any updates that happen due to a context switch # will be picked up on the next pass. updated_routers = set(self.updated_routers) self.updated_routers.clear() router_ids = list(updated_routers) routers = self.plugin_rpc.get_routers( self.context, router_ids) # routers with admin_state_up=false will not be in the fetched fetched = set([r['id'] for r in routers]) #不在fetched中而在updated_routers中,说明需删除 self.removed_routers.update(updated_routers - fetched) self._process_routers(routers) self._process_router_delete() LOG.debug(_("RPC loop successfully completed")) except Exception: LOG.exception(_("Failed synchronizing routers")) self.fullsync = True
_process_routers
如果有rpc请求过来,即需要更新路由信息,或者添加路由子接口,创建floating ip等操作,都会在这里执行。这个函数里会去调用_process_routers函数,在_process_routers函数中会去创建绿色线程,执行process_router函数。可以说,l3 agent调用网络设备的工作都会在process_router中进行。
def process_router(self, ri): ri.iptables_manager.defer_apply_on() ex_gw_port = self._get_ex_gw_port(ri) internal_ports = ri.router.get(l3_constants.INTERFACE_KEY, []) existing_port_ids = set([p['id'] for p in ri.internal_ports]) current_port_ids = set([p['id'] for p in internal_ports if p['admin_state_up']]) new_ports = [p for p in internal_ports if p['id'] in current_port_ids and p['id'] not in existing_port_ids] old_ports = [p for p in ri.internal_ports if p['id'] not in current_port_ids] for p in new_ports: self._set_subnet_info(p) self.internal_network_added(ri, p['network_id'], p['id'], p['ip_cidr'], p['mac_address']) ri.internal_ports.append(p) for p in old_ports: self.internal_network_removed(ri, p['id'], p['ip_cidr']) ri.internal_ports.remove(p) existing_devices = self._get_existing_devices(ri) current_internal_devs = set([n for n in existing_devices if n.startswith(INTERNAL_DEV_PREFIX)]) current_port_devs = set([self.get_internal_device_name(id) for id in current_port_ids]) stale_devs = current_internal_devs - current_port_devs for stale_dev in stale_devs: LOG.debug(_('Deleting stale internal router device: %s'), stale_dev) self.driver.unplug(stale_dev, namespace=ri.ns_name, prefix=INTERNAL_DEV_PREFIX) # Get IPv4 only internal CIDRs internal_cidrs = [p['ip_cidr'] for p in ri.internal_ports if netaddr.IPNetwork(p['ip_cidr']).version == 4] # TODO(salv-orlando): RouterInfo would be a better place for # this logic too ex_gw_port_id = (ex_gw_port and ex_gw_port['id'] or ri.ex_gw_port and ri.ex_gw_port['id']) interface_name = None if ex_gw_port_id: interface_name = self.get_external_device_name(ex_gw_port_id) if ex_gw_port and ex_gw_port != ri.ex_gw_port: self._set_subnet_info(ex_gw_port) self.external_gateway_added(ri, ex_gw_port, interface_name, internal_cidrs) elif not ex_gw_port and ri.ex_gw_port: self.external_gateway_removed(ri, ri.ex_gw_port, interface_name, internal_cidrs) stale_devs = [dev for dev in existing_devices if dev.startswith(EXTERNAL_DEV_PREFIX) and dev != interface_name] for stale_dev in stale_devs: LOG.debug(_('Deleting stale external router device: %s'), stale_dev) self.driver.unplug(stale_dev, bridge=self.conf.external_network_bridge, namespace=ri.ns_name, prefix=EXTERNAL_DEV_PREFIX) # Process static routes for router self.routes_updated(ri) # Process SNAT rules for external gateway ri.perform_snat_action(self._handle_router_snat_rules, internal_cidrs, interface_name) # Process SNAT/DNAT rules for floating IPs fip_statuses = {} try: if ex_gw_port: existing_floating_ips = ri.floating_ips self.process_router_floating_ip_nat_rules(ri) ri.iptables_manager.defer_apply_off() # Once NAT rules for floating IPs are safely in place # configure their addresses on the external gateway port fip_statuses = self.process_router_floating_ip_addresses( ri, ex_gw_port) except Exception: # TODO(salv-orlando): Less broad catching # All floating IPs must be put in error state for fip in ri.router.get(l3_constants.FLOATINGIP_KEY, []): fip_statuses[fip['id']] = l3_constants.FLOATINGIP_STATUS_ERROR if ex_gw_port: # Identify floating IPs which were disabled ri.floating_ips = set(fip_statuses.keys()) for fip_id in existing_floating_ips - ri.floating_ips: fip_statuses[fip_id] = l3_constants.FLOATINGIP_STATUS_DOWN # Update floating IP status on the neutron server self.plugin_rpc.update_floatingip_statuses( self.context, ri.router_id, fip_statuses) # Update ex_gw_port and enable_snat on the router info cache ri.ex_gw_port = ex_gw_port ri.enable_snat = ri.router.get('enable_snat')
1.处理内部接口
这个是在router添加和删除子接口时工作。它会调用internal_network_added和internal_network_removed这个两个函数。
在internal_network_added和internal_network_removed这个两个函数会去调用OVSInterfaceDriver的plug和unplug函数,这两个函数最终会用ip link 和ip addr的命令去处理接口和ip地址。
2.处理外部网关
router添加和删除外部网关。调用external_gateway_added和external_gateway_removed函数,同样也会调用plug和unplug函数,用ip link 和ip addr的命令进行最终处理
3.为外部网关做SNAT
调用_handle_router_snat_rules函数,使用iptables来加链和删除链。
在我的测试网络中,router上有3个接口,外部网关地址为192.168.39.2,内部两个子网的网关为10.1.0.1,10.2.0.1。iptables规则如下:
|
1
2
3
|
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING ! -i qg-fcb1a762-1f ! -o qg-fcb1a762-1f -m conntrack ! --ctstate DNAT -j ACCEPT
iptables -t nat -A snat -s 10.2.0.1
/24
-j SNAT --to-
source
192.168.39.2
iptables -t nat -A snat -s 10.1.0.1
/24
-j SNAT --to-
source
192.168.39.2
|
qg-fcb1a762-1f为外部网关接口的索引,使用ip netns exec $namespace ip link list可查看。
4.为floating ip做SNAT/DNAT
和浮动IP相关,如创建,更新,删除,绑定到一个云主机的接口,解绑定等。
不同neutron版本这部分的处理不同,这里是基于Icehouse rc1版本的,在havava stable版本,只有一个函数来处理iptables规则和floating ip。
process_router_floating_ip_nat_rules :当floating ip与云主机绑定时,会先清除已有的floating_ip规则,再加上要添加的iptables规则,同时重新加载清除的iptables规则。
比如,一个云主机10.1.0.2上绑定了一个floating ip(192.168.39.5)。那么最终会在iptable不同的链中添加iptables规则,float-snat为neutron自定义链。
|
1
2
3
|
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -d 192.168.39.5 -j DNAT --to 10.1.0.2
iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -d 192.168.39.5 -j DNAT --to 10.1.0.2
iptables -t nat -A float-snat -s 10.1.0.2 -j SNAT --to 192.168.39.5
|
process_router_floating_ip_addresses:
将floating ip和云主机绑定时,使用ip addr add命令添加ip地址。
解除floating ip和云主机绑定时,使用ip addr del命令将floating ip删除。
类图
本文转自http://squarey.me/cloud-virtualization/neutron-l3-analyse.html,有部分删改。
1. keepalived vrrp/conntrackd
High availability features will be implemented as extensions or drivers.A first extension/driver will be based on VRRP.
A new scheduler will be also added in order to be able to spawn multiple instances of a same router in many places.
Conntrackd will be used to maintain the TCP sessions going through the router. One instance of conntrackd per virtual router, then one per namespace.
Blueprints: https://blueprints.launchpad.net/neutron/+spec/l3-high-availability
wiki: https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Neutron/L3_High_Availability_VRRP
analysis: http://blog.csdn.net/quqi99/article/details/18799877
2. neutron DVR based multi-host l3-agent
Provide Distributed Virtual Routing functionality with OVS, to improve the performance.
在Openstack中L3router会造成流量集中的问题。不论东西向还是南北向的流量都需要流过网络节点的虚拟路由器。为了解决流量集中的问题,社区正在开打分布式虚拟路由器(DVR)的feature。
https://blueprints.launchpad.net/neutron/+spec/neutron-ovs-dvr
https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Neutron/DVR_L2_Agent
http://m.blog.csdn.net/blog/maoliping455mlp455/36899391
http://blog.csdn.net/quqi99/article/details/20711303
3. Neutron Multi-host DHCP and L3
Goal here is to have a DHCP implementation that provides the same properties as nova-network's "multi_host" functionality, where the DHCP server for a particular VM runs directly on the same hypervisor as the VM itself (with the exception of when a VM migrates).
This blueprints is in drafting, and will not merge in upstream.
https://blueprints.launchpad.net/neutron/+spec/quantum-multihost
4. crontab using neutron-client
http://m.blog.csdn.net/blog/maoliping455mlp455/23428897
So this when we neutron-l3-agent is down, we can see that it will not affect the existed VMs. And we can easily use monitd to make process "neutron-l3-agent" is always alive. We can use the following script, and run a crontab(every 10 sec) on the server which installed neutronclient (But not on the controller nodes):
#!/usr/bin/python from neutronclient.v2_0 import client as neutronclient TENANT_NAME="admin" USERNAME="admin" PASSWORD="admin" AUTH_URL="https://10.224.159.107:443/v2.0/" neutron = neutronclient.Client(auth_url=AUTH_URL, username=USERNAME, password=PASSWORD, tenant_name=TENANT_NAME) agents = neutron.list_agents() alive_l3_agents = [] dead_l3_agents = [] for agent in agents['agents']: if agent['binary'] == 'neutron-l3-agent' and agent['alive'] == True: alive_l3_agents.append(agent) if agent['binary'] == 'neutron-l3-agent' and agent['alive'] != True: dead_l3_agents.append(agent) if len(alive_l3_agents) == 0 : print "No active L3" if len(dead_l3_agents) == 0 : print "No dead L3" routers = neutron.list_routers() dead_routers = [] for dead_l3_agent in dead_l3_agents: dead_routers = neutron.list_routers_on_l3_agent(dead_l3_agent['id']) for dead_router in dead_routers['routers']: neutron.remove_router_from_l3_agent(dead_l3_agent['id'], dead_router['id']) print "remove_router_from_l3_agent : L3 id is %s, router id is %s" %(dead_l3_agent['id'], dead_router['id']) # Currently, only add to the first alive agent neutron.add_router_to_l3_agent(alive_l3_agents[0]['id'], {"router_id":dead_router['id']}) print "add_router_to_l3_agent : L3 id is %s, router id is %s" %(alive_l3_agents[0]['id'], dead_router['id'])
5. HA of other components
(1) Database: active-passive (pacemarker + DRBD); active-active (Galera)
http://blog.csdn.net/quqi99/article/details/9392789
(2) MQ: MQ cluster
http://blog.csdn.net/quqi99/article/details/9394121
(3) Cinder: Local File System (Raid10 + LVM); Distrubte File System (Ceph)
http://blog.csdn.net/quqi99/article/details/9396413
http://blog.csdn.net/quqi99/article/details/10894833
(4) All stateless services, like (keystone|glance|nova|neutron)-api, nova-schedule etc (haproxy + pacemarker)
(5) l3-agent: VRRP + keeplived + ip conntracked
https://blueprints.launchpad.net/neutron/+spec/l3-high-availability
http://blog.csdn.net/quqi99/article/details/18799877
当neutron启用L3 agent时,如果在配置文件中配置了external_network_bridge,从这个bridge上出去的包只能是untag的。但在DC中,极有可能被分配的是某一vlan。这种情况下,在配置文件中就要如下设置:
- /etc/neutron/l3_agent.ini
- # Name of bridge used for external network traffic. This should be set to
- # empty value for the linux bridge
- external_network_bridge = ""
设定external网络可以参照以下命令:
- # ovs-vsctl show
- 418f4819-8ad6-4fe5-a959-3605eee4852b
- Bridge "br-eth1"
- Port "phy-br-eth1"
- Interface "phy-br-eth1"
- Port "br-eth1"
- Interface "br-eth1"
- type: internal
- Port "eth1"
- Interface "eth1"
- Bridge br-int
- Port "tapa570fb69-fb"
- tag: 5
- Interface "tapa570fb69-fb"
- type: internal
- Port "qr-f01fed18-ad"
- tag: 5
- Interface "qr-f01fed18-ad"
- type: internal
- Port br-int
- Interface br-int
- type: internal
- Port "tapa7b25e2f-ad"
- tag: 1
- Interface "tapa7b25e2f-ad"
- type: internal
- Port "qg-d2f9cb0b-11"
- tag: 3
- Interface "qg-d2f9cb0b-11"
- type: internal
- Port "tapa85a86f8-c1"
- tag: 3
- Interface "tapa85a86f8-c1"
- type: internal
- Port "int-br-eth1"
- Interface "int-br-eth1"
- ovs_version: "1.11.0"
qr-XXX和qg-YYY都在br-eth1上,qg-YYY和qr-XXX之间是L3 agent通过iptables的nat转换来实现的。
转:
Openstack Neutron Provider Network虚机数据流
本文分析了一下neutron provider network的环境下虚拟机数据流。
实验环境如下:
Openstack : Havana (Neutron ML2+openvswitch agent, Vlan模式)
Provider Network : Vlan 100, 网段 100.100.100.0/24, 网关100.100.100.1
虚机网络拓扑环境如下:
我们以在虚拟机中ping 8.8.8.8为例说明数据流。
在虚机中当我们敲下ping 8.8.8.8以后, 我们的kernel会查找路由表看看我们有没有8.8.8.8的路由。
在虚机中ifconfig和ip route的结果如下:
# ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr FA:16:3E:2E:FD:E1
inet addr:100.100.100.2 Bcast:100.100.100.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:1906 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:1709 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:147567 (144.1 KiB) TX bytes:233064 (227.6 KiB)
# ip route show
169.254.169.254 via 100.100.100.3 dev eth0 proto static
100.100.100.0/24 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 100.100.100.2
169.254.0.0/16 dev eth0 scope link metric 1002
default via 100.100.100.1 dev eth0
我们发现在虚机中并没有到8.8.8.8的直连路由,因此我们会把包发送给默认网关100.100.100.1。
此时我们首先会发送ARP广播请求默认网关的MAC。当默认网关会应我们ARP请求后,我们就得到了需要的默认网关的MAC。
我们会将ICMP Request包发出,这个包源IP是100.100.100.2,目的IP是8.8.8.8,源MAC是FA:16:3E:2E:FD:E1,目的MAC是默认网关的MAC。
之后这个包就被发送到了tapdfc176e4-5a。
下面是tapdfc176e4-5a在计算节点上的相关配置:
# ifconfig tapdfc176e4-5a
tapdfc176e4-5a Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr FE:16:3E:2E:FD:E1
inet6 addr: fe80::fc16:3eff:fe2e:fde1/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:217 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:249 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:500
RX bytes:28180 (27.5 KiB) TX bytes:21472 (20.9 KiB)
# brctl show
bridge name bridge idSTP enabledinterfaces
qbr6750eac8-57 8000.d6c128fae672noqvb6750eac8-57
tap6750eac8-57
qbrdfc176e4-5a 8000.7e07e8dd1cf6noqvbdfc176e4-5a
tapdfc176e4-5a
virbr0 8000.525400e75eaayesvirbr0-nic
目前Security Group是用iptables实现的。在iptables中有一个feature叫做bridge-nf-call-iptables,可以过滤桥上的流。我们可以通过以下命令查看是否开启:
# cat /proc/sys/net/bridge/bridge-nf-call-iptables
1
我们可以使用iptables -nvL 查看这个VM在filter表中的Security Group:
Chain neutron-openvswi-idfc176e4-5 (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 DROP all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state INVALID
318 20107 RETURN all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
1 60 RETURN tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:22
0 0 RETURN udp -- * * 100.100.100.3 0.0.0.0/0 udp spt:67 dpt:68
0 0 RETURN udp -- * * 100.100.100.4 0.0.0.0/0 udp spt:67 dpt:68
0 0 neutron-openvswi-sg-fallback all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain neutron-openvswi-odfc176e4-5 (2 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 RETURN udp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 udp spt:68 dpt:67
299 31689 neutron-openvswi-sdfc176e4-5 all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 DROP udp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 udp spt:67 dpt:68
0 0 DROP all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state INVALID
295 31365 RETURN all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
4 324 RETURN all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 neutron-openvswi-sg-fallback all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
在Neutron中会对进入/流出虚机的流量进行过滤,neutron-openvswi-idfc176e4-5链是进入虚机流的访问控制规则。neutron-openvswi-odfc176e4-5链是流出虚机流的访问控制规则。
这两个连是在neutron-openvswi-sg-chain中被调用的:
Chain neutron-openvswi-sg-chain (4 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
319 20167 neutron-openvswi-idfc176e4-5 all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 PHYSDEV match --physdev-out tapdfc176e4-5a --physdev-is-bridged
299 31689 neutron-openvswi-odfc176e4-5 all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 PHYSDEV match --physdev-in tapdfc176e4-5a --physdev-is-bridged
在packet从桥和Security Group流出后,他会来到br-int的qvodfc176e4-5a,这个接口可以看到是"tag: 2",这表示这个接口是"Access口",vlan id是2。
OVS输出如下:
# ovs-vsctl show
47115847-b828-47f3-bbdb-e18d4b0fd11e
Bridge br-int
Port "tap39b2b891-3b"
tag: 2
Interface "tap39b2b891-3b"
type: internal
Port br-int
Interface br-int
type: internal
Port "qvo6750eac8-57"
tag: 1
Interface "qvo6750eac8-57"
Port "qvodfc176e4-5a"
tag: 2
Interface "qvodfc176e4-5a"
Port "int-br-eth2"
Interface "int-br-eth2"
Port "qr-441abe6b-8b"
tag: 1
Interface "qr-441abe6b-8b"
type: internal
Bridge br-ex
Port br-ex
Interface br-ex
type: internal
Port "qg-019b0743-e4"
Interface "qg-019b0743-e4"
type: internal
Port "eth3"
Interface "eth3"
Bridge "br-eth2"
Port "eth2"
Interface "eth2"
Port "br-eth2"
Interface "br-eth2"
type: internal
Port "phy-br-eth2"
Interface "phy-br-eth2"
ovs_version: "1.11.0"
虚拟交换机br-int会将packet从int-br-eth2发送出去,而"int-br-eth2"和"phy-br-eth2"是veth pair,因此包会从phy-br-eth2流入br-eth2,以下是OVS的openflow输出:
# ovs-ofctl show br-eth2
OFPT_FEATURES_REPLY (xid=0x2): dpid:00000800270731f9
n_tables:254, n_buffers:256
capabilities: FLOW_STATS TABLE_STATS PORT_STATS QUEUE_STATS ARP_MATCH_IP
actions: OUTPUT SET_VLAN_VID SET_VLAN_PCP STRIP_VLAN SET_DL_SRC SET_DL_DST SET_NW_SRC SET_NW_DST SET_NW_TOS SET_TP_SRC SET_TP_DST ENQUEUE
1(eth2): addr:08:00:27:07:31:f9
config: 0
state: 0
speed: 0 Mbps now, 0 Mbps max
2(phy-br-eth2): addr:a2:e1:41:5c:cc:bf
config: 0
state: 0
current: 10GB-FD COPPER
speed: 10000 Mbps now, 0 Mbps max
LOCAL(br-eth2): addr:08:00:27:07:31:f9
config: 0
state: 0
speed: 0 Mbps now, 0 Mbps max
OFPT_GET_CONFIG_REPLY (xid=0x4): frags=normal miss_send_len=0
# ovs-ofctl dump-flows br-eth2
NXST_FLOW reply (xid=0x4):
cookie=0x0, duration=3968.876s, table=0, n_packets=20, n_bytes=2052, idle_age=1947, priority=4,in_port=2,dl_vlan=1 actions=mod_vlan_vid:1001,NORMAL
cookie=0x0, duration=3967.173s, table=0, n_packets=218, n_bytes=28424, idle_age=502, priority=4,in_port=2,dl_vlan=2 actions=mod_vlan_vid:100,NORMAL
cookie=0x0, duration=3972.688s, table=0, n_packets=10, n_bytes=764, idle_age=1986, priority=2,in_port=2 actions=drop
cookie=0x0, duration=3976.268s, table=0, n_packets=411, n_bytes=77162, idle_age=14, priority=1 actions=NORMAL
我们需要特别关注以下openflow条目:
cookie=0x0, duration=3967.173s, table=0, n_packets=218, n_bytes=28424, idle_age=502, priority=4,in_port=2,dl_vlan=2 actions=mod_vlan_vid:100,NORMAL
"dl_vlan=2" 是说当packet的vlan tag为2。我们的packet是从Tag为2的"Access口"进来的,因此会带有tag为2的vlan头。
"action = mod_vlan_vid:100" 执行修改vlan头的action,将vlan id改为100。
"NORMAL" 执行标准交换机动作。
也就是说在br-eth2上的openflow规则会将我们的packet转为vlan id为100的packet。我们回过头来看br-int的openflow条目,会发现也有类似规则,不过是将vlan id从100改为2。
下面是br-int上的openflow条目:
# ovs-ofctl show br-int
OFPT_FEATURES_REPLY (xid=0x2): dpid:000032774807d443
n_tables:254, n_buffers:256
capabilities: FLOW_STATS TABLE_STATS PORT_STATS QUEUE_STATS ARP_MATCH_IP
actions: OUTPUT SET_VLAN_VID SET_VLAN_PCP STRIP_VLAN SET_DL_SRC SET_DL_DST SET_NW_SRC SET_NW_DST SET_NW_TOS SET_TP_SRC SET_TP_DST ENQUEUE
1(int-br-eth2): addr:4e:1d:f3:fe:23:12
config: 0
state: 0
current: 10GB-FD COPPER
speed: 10000 Mbps now, 0 Mbps max
2(qvodfc176e4-5a): addr:36:92:d2:25:b7:8d
config: 0
state: 0
current: 10GB-FD COPPER
speed: 10000 Mbps now, 0 Mbps max
3(qr-441abe6b-8b): addr:f6:01:00:00:00:00
config: PORT_DOWN
state: LINK_DOWN
speed: 0 Mbps now, 0 Mbps max
4(qvo6750eac8-57): addr:fe:63:44:8b:9d:28
config: 0
state: 0
current: 10GB-FD COPPER
speed: 10000 Mbps now, 0 Mbps max
7(tap39b2b891-3b): addr:f6:01:00:00:00:00
config: PORT_DOWN
state: LINK_DOWN
speed: 0 Mbps now, 0 Mbps max
LOCAL(br-int): addr:32:77:48:07:d4:43
config: 0
state: 0
speed: 0 Mbps now, 0 Mbps max
OFPT_GET_CONFIG_REPLY (xid=0x4): frags=normal miss_send_len=0
# ovs-ofctl dump-flows br-int
NXST_FLOW reply (xid=0x4):
cookie=0x0, duration=3960.902s, table=0, n_packets=2, n_bytes=748, idle_age=1949, priority=3,in_port=1,dl_vlan=1001 actions=mod_vlan_vid:1,NORMAL
cookie=0x0, duration=3959.222s, table=0, n_packets=242, n_bytes=21940, idle_age=494, priority=3,in_port=1,dl_vlan=100 actions=mod_vlan_vid:2,NORMAL
cookie=0x0, duration=3965.248s, table=0, n_packets=166, n_bytes=54124, idle_age=6, priority=2,in_port=1 actions=drop
cookie=0x0, duration=3969.286s, table=0, n_packets=608, n_bytes=69908, idle_age=494, priority=1 actions=NORMAL
当我们的packet在br-eth2上被转发到eth2,并带有vlan id 100从eth2上发送出去,就会发送到物理交换机上。物理交换机与compute节点是通过trunk连接的,只要配置了vlan100就能将包转发到网关上,最后由网关将包转发出去
转:
Neutron L3 Agent packet flow
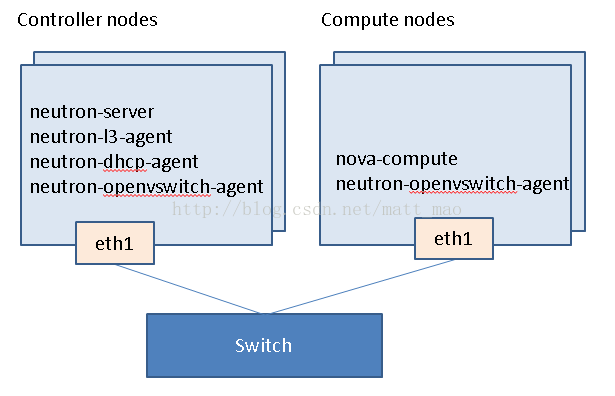
部署环境如下:
目前我们将neutron-l3-agent放在controller节点上,之后会将其移至专属的network节点,专属的network节点的网卡能力更强些。
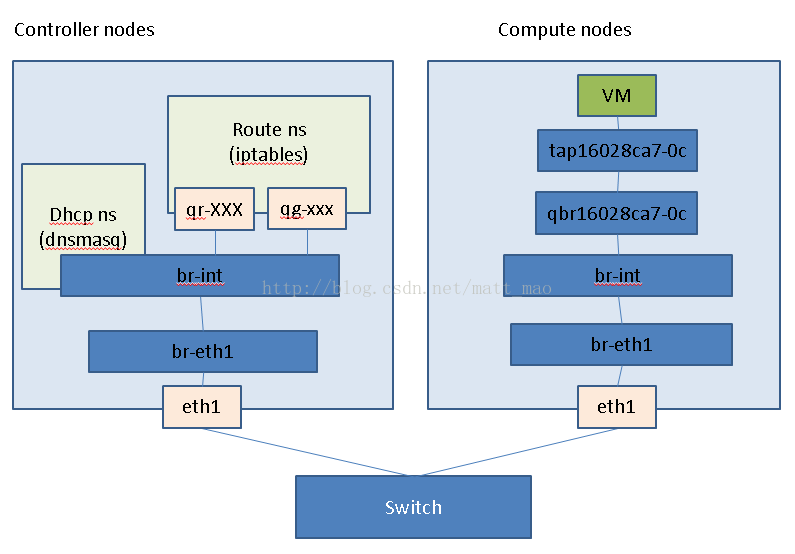
以下是网络逻辑拓扑:
从虚机到计算节点的eth1的packet flow与provider network是一致的,可以参照:
http://blog.csdn.net/matt_mao/article/details/17231045
不同的地方是虚机获取的网关地址是qr-XXX的ip地址。这样虚机的数据流就会进入controller节点。
例如:
- # ip netns exec qrouter-942b3c47-0c90-44c9-b01d-8c6c7f4368a1 ifconfig
- lo Link encap:Local Loopback
- inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
- inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
- UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
- RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
- TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
- collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
- RX bytes:0 (0.0 b) TX bytes:0 (0.0 b)
- qg-123e8e11-94 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr FA:16:3E:5F:96:A1
- inet addr:10.224.159.170 Bcast:10.224.159.191 Mask:255.255.255.224
- inet6 addr: fe80::f816:3eff:fe5f:96a1/64 Scope:Link
- UP BROADCAST RUNNING MTU:1500 Metric:1
- RX packets:899 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
- TX packets:12 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
- collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
- RX bytes:56096 (54.7 KiB) TX bytes:941 (941.0 b)
- qr-f1977c17-37 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr FA:16:3E:F6:C9:36
- inet addr:192.168.76.1 Bcast:192.168.76.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
- inet6 addr: fe80::f816:3eff:fef6:c936/64 Scope:Link
- UP BROADCAST RUNNING MTU:1500 Metric:1
- RX packets:25 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
- TX packets:13 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
- collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
- RX bytes:2375 (2.3 KiB) TX bytes:1208 (1.1 KiB)
虚机的默认网关地址是qr-f1977c17-37的ip地址,数据流就会进入controller的这个netns, 然后经过内核的netfilter进行SNAT后,如果你没有设置floating ip,则源地址变为qg-123e8e11-94的地址。
- [root@ci91szcmp001 ~]# ip netns exec qrouter-942b3c47-0c90-44c9-b01d-8c6c7f4368a1 iptables -nvL -t nat
- Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 960 packets, 46441 bytes)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 960 46441 neutron-l3-agent-PREROUTING all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
- Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 3 221 neutron-l3-agent-POSTROUTING all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
- 3 221 neutron-postrouting-bottom all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
- Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 0 0 neutron-l3-agent-OUTPUT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
- Chain neutron-l3-agent-OUTPUT (1 references)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- Chain neutron-l3-agent-POSTROUTING (1 references)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 0 0 ACCEPT all -- !qg-123e8e11-94 !qg-123e8e11-94 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ! ctstate DNAT
- Chain neutron-l3-agent-PREROUTING (1 references)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 0 0 REDIRECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 169.254.169.254 tcp dpt:80 redir ports 9697
- Chain neutron-l3-agent-float-snat (1 references)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- Chain neutron-l3-agent-snat (1 references)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 3 221 neutron-l3-agent-float-snat all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
- 3 221 SNAT all -- * * 192.168.76.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 to:10.224.159.170
- Chain neutron-postrouting-bottom (1 references)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 3 221 neutron-l3-agent-snat all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
如果设置了floating ip,则在接口qg-123e8e11-94上可以找到这个floating ip:
- # ip netns exec qrouter-942b3c47-0c90-44c9-b01d-8c6c7f4368a1 ip route
- 10.224.159.160/27 dev qg-123e8e11-94 proto kernel scope link src 10.224.159.170
- 192.168.76.0/24 dev qr-f1977c17-37 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.76.1
- default via 10.224.159.161 dev qg-123e8e11-94
并且会添加以下SNAT和DNAT规则:
- [root@ci91szcmp001 ~]# ip netns exec qrouter-942b3c47-0c90-44c9-b01d-8c6c7f4368a1 iptables -nvL -t nat
- Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 1101 packets, 53272 bytes)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 1101 53272 neutron-l3-agent-PREROUTING all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
- Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 6 428 neutron-l3-agent-POSTROUTING all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
- 6 428 neutron-postrouting-bottom all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
- Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 0 0 neutron-l3-agent-OUTPUT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
- Chain neutron-l3-agent-OUTPUT (1 references)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 0 0 DNAT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 10.224.159.171 to:192.168.76.2
- Chain neutron-l3-agent-POSTROUTING (1 references)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 0 0 ACCEPT all -- !qg-123e8e11-94 !qg-123e8e11-94 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ! ctstate DNAT
- Chain neutron-l3-agent-PREROUTING (1 references)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 0 0 REDIRECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 169.254.169.254 tcp dpt:80 redir ports 9697
- 0 0 DNAT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 10.224.159.171 to:192.168.76.2
- Chain neutron-l3-agent-float-snat (1 references)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 0 0 SNAT all -- * * 192.168.76.2 0.0.0.0/0 to:10.224.159.171
- Chain neutron-l3-agent-snat (1 references)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 6 428 neutron-l3-agent-float-snat all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
- 0 0 SNAT all -- * * 192.168.76.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 to:10.224.159.170
- Chain neutron-postrouting-bottom (1 references)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 6 428 neutron-l3-agent-snat all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
接口qg-123e8e11-94会被连接到br-int上:
- [root@ci91szcmp001 ~]# ovs-vsctl show
- b1c45d14-3a2b-4d80-9d14-60c50770d7e1
- Bridge "br-eth1"
- Port "br-eth1"
- Interface "br-eth1"
- type: internal
- Port "phy-br-eth1"
- Interface "phy-br-eth1"
- Port "eth1"
- Interface "eth1"
- Bridge br-int
- Port "qr-f1977c17-37"
- tag: 10
- Interface "qr-f1977c17-37"
- type: internal
- Port "int-br-eth1"
- Interface "int-br-eth1"
- Port "qg-123e8e11-94"
- tag: 5
- Interface "qg-123e8e11-94"
- type: internal
- Port br-int
- Interface br-int
- type: internal
- ...
接口qg-123e8e11-94来自于一个external网络,此处这个external网络也是一个provider 网络。可参照: http://blog.csdn.net/matt_mao/article/details/19088127