MySQL5.5 中引入了 metadata lock. 顾名思义,metadata lock 不是为了保护表中的数据的,而是保护 database objects(元数据)的。包括表结构、schema、存储过程、函数、触发器、mysql的调度事件(events). 要理解 metadata lock 最重要的一点就是:将 metadata lock放到数据库事务的语义中来理解。metadata lock 的作用就是当一个事务在执行时,事务涉及到的所有元数据(metadata,也就是 database objects),必须是安全的。比如你在一个事物中select一个table,必须保证该table在你的事物完成之前,不会被删除了,或者不会被修改了。
相关文档:http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/metadata-locking.html
- metadata lock 的作用
MySQL uses metadata locking to manage concurrent access to database objects and to ensure data consistency. Metadata locking applies not just to tables, but also to schemas and stored programs (procedures, functions, triggers, and scheduled events).
metadata lock管理对database objects的并发访问,保证数据一致性。
2.metadata lock 会导致性能损耗和锁争用
Metadata locking does involve some overhead, which increases as query volume increases. Metadata contention increases the more that multiple queries attempt to access the same objects.
metadata lock 的引入导致一定的性能损耗。对同一个database object的访问越多,就会越导致该对象上的metadata lock的争用。
Metadata locking is not a replacement for the table definition cache, and its mutexes and locks differ from the LOCK_open mutex.
metadata lock 并不是 为了替代 表定义缓存。其mutex和lock和 LOCK_open mutex不一样。
4.
To ensure transaction serializability, the server must not permit one session to perform a data definition language (DDL) statement on a table that is used in an uncompleted explicitly or implicitly started transaction in another session. The server achieves this by acquiring metadata locks on tables used within a transaction and deferring release of those locks until the transaction ends. A metadata lock on a table prevents changes to the table's structure. This locking approach has the implication that a table that is being used by a transaction within one session cannot be used in DDL statements by other sessions until the transaction ends.
正在运行中的事务,必须要在事务开始时获得它要访问的所有的database objects上的 metadata lock, 然后在事务结束时释放那些database objects上的metadata lock. 事务和metadata lock的关系是极其紧密的:有事务必然就必然有metadata lock,事物结束就释放。metadata lock防止事物中的database objects 被修改,比如阻止事物中的table的结构被修改。所以事务中的database objects上执行DDL会被阻塞,直到事务结束。
5.
This principle applies not only to transactional tables, but also to nontransactional tables. Suppose that a session begins a transaction that uses transactional table t and nontransactional table nt as follows:
START TRANSACTION;
SELECT FROM t;
SELECT FROM nt;
The server holds metadata locks on both t and nt until the transaction ends. If another session attempts a DDL or write lock operation on either table, it blocks until metadata lock release at transaction end. For example, a second session blocks if it attempts any of these operations:
DROP TABLE t;
ALTER TABLE t ...;
DROP TABLE nt;
ALTER TABLE nt ...;
LOCK TABLE t ... WRITE;
metadata lock不仅仅涉及到事务引擎中的table,同样也适用于非事务引擎中的table. metadata lock不仅仅阻塞DDL,同时也阻塞 lock table table_name write 语句。
6.
If the server acquires metadata locks for a statement that is syntactically valid but fails during execution, it does not release the locks early. Lock release is still deferred to the end of the transaction because the failed statement is written to the binary log and the locks protect log consistency.
如果一个sql语句语法正确,但是却执行失败了,其上的metadata lock并不会马上释放,而是要在事务结束之后才释放。这是为了保证日志的一致性。
7.
In autocommit mode, each statement is in effect a complete transaction, so metadata locks acquired for the statement are held only to the end of the statement.
自动提交模式(mysql命令行工具默认是自动提交模式),语句一执行完马上就释放metadata lock,因为他是自动提交的单语句事务。
8.
Metadata locks acquired during a PREPARE statement are released once the statement has been prepared, even if preparation occurs within a multiple-statement transaction.
事务中的metadata lock直到事务结束才释放,但是有一个特例:事务中的prepare(一般用在存储过程中的动态语句)语句一执行完马上释放对应的metadata lock.
9.
Before MySQL 5.5, when a transaction acquired the equivalent of a metadata lock for a table used within a statement, it released the lock at the end of the statement. This approach had the disadvantage that if a DDL statement occurred for a table that was being used by another session in an active transaction, statements could be written to the binary log in the wrong order.
MySQL 5.5 引入了metadata lock,取代了之前版本中的等价物。
但是metadata lock和她之前的等价物有一个区别:metadata lock直到事务结束才释放,而她的等价物是语句执行完就马上释放。metadata lock这样做的目的是为了保证 binary log 顺序的正确。
下面我们实验演示一下:
1.在第一个A会话执行:lock table t write
在第二个会话B中执行select from t;
在第三个会话C中执行 show processlist;
这个时候我们可以看到会话中已经出现了B查询 select from t 出现了 Waiting for table metadata lock,这里是因为A会话已经持有t表metadata lock,排斥B会话再来申请t表的元数据锁。在C会话中执行kill 11 操作
再看B会话,立马会返回结果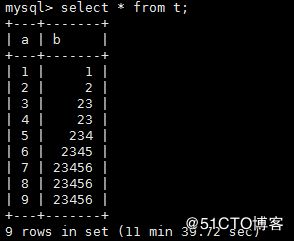
2.下面我们在A会话执行lock table t read 
同样我们在第二个会话中执行select from t;发现会立即返回结果,但是我们执行insert into t(b) value(10000) 会出现等待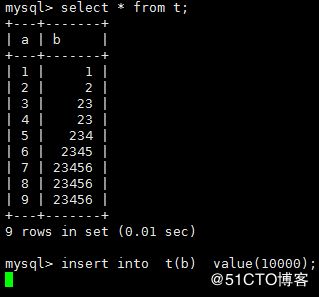
在C会话中执行show processlist 可以看到,同样出现了元数据锁
3.在A会话中执行 set autocommit=0; select from t;
在B会话中执行
在C会话中进行show processlist 中,都可以看到元数据锁,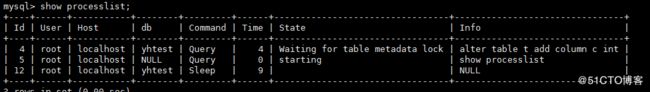
通过上面几种方式,我们看到了产生Waiting for table metadata lock 的原因,很明显,我们在有长时间未提交的事务或者较大事物长时间占用metadata 锁后,都可能导致其他请求该元数据的事务处于等待状态。下面我们再看一个比较常见的原数据锁等待情况。
A会话 同样 set autocommit=0; select from t where a=1;
B会话中执行一个 select from t where a=2;是可以立即返回结果的
在B会话中执行 DDL 操作 alter table t add column d int; 出现等待
在C会话中执行:select * from t where a=2; 也出现了等待![]()
重新开启一个会话D 我们执行show processlist ;可以看到元数据等待情况
通过以上:我们可以看出B会话DDL 操作 alter table t add index idx2(b); 被A话的未提交事物元数据锁阻塞,而B会话对元数据锁的等待,会阻塞所有对该表元数据锁申请的事务,所以C会话也会等待!这个时候我们提交A会话,发现B 会话可以立即获得metadata lock ,然后C也会后的metadata lock ,这说明DDL获得metadata lock 是一个比较短暂的,因为如果DDL 持有metadata是一个比较长的操作,那么C会话应该等B执行完,才有可能获得metadata ,我们在C会话看到的结果应该为
而不是
通过以上测试,我们看出,一个比较小的未提交事务,当遇到DDL元数据锁等待后,可能导致很大的问题,我们在线上应该尽量避免这种情况的发生,针对这样的问题,mysql 也有对应的超时参数,如果进场发生元数据等待情况,我们可以通过设置参数 lock_wait_timeout 来设置元数据超时时间,如果发生元数据锁等待,超过设定时间,便会timeout! 这个参数和innodb_lock_wait_timeout 有很大区别的,我们可以通过官方文档查看!