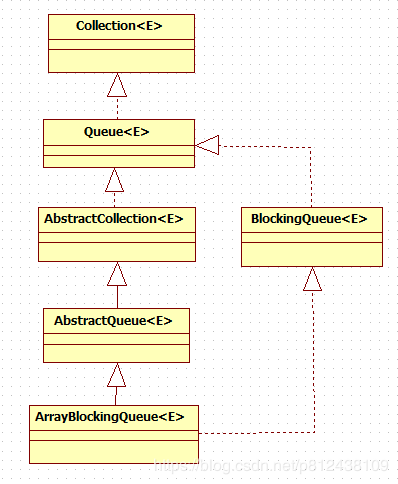
ArrayBlockingQueue源码详解
一)ArrayBlockingQueue简介
ArrayBlockingQueue
1)底层由数组实现。
2)是一个FIFO(先进先出)的阻塞队列。
3)创建时,需指定队列初始容量,指定后不能修改。是一个线程安全的队列。
类图:ArrayBlockingQueue
二)构造方法
1)ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity)
创建具有给定(固定)容量和默认访问策略的 ArrayBlockingQueue,默认为false。
2)ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair)
创建一个 ArrayBlockingQueue具有给定(固定)容量和指定访问策略。
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this(capacity, false); // 调用另一个构造方法
}
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
if (capacity <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.items = new Object[capacity]; // 初始化一个Object数组
lock = new ReentrantLock(fair); // 初始化锁的访问策略
notEmpty = lock.newCondition(); // 消费阻塞条件,当不为空时,才消费
notFull = lock.newCondition(); // 生产阻塞条件,当未满时,才生产
}
三)添加
1)boolean offer(E e)
将指定的元素插入该队列的尾部, 当队列已满时,返回false,否则返回true。
public boolean offer(E e) {
checkNotNull(e); // 如果元素为null, 抛出NullPointerException异常
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; // 获取锁
lock.lock(); // 加锁
try {
if (count == items.length) // 判断队列是否已满
return false; // 队列已满, 返回fase
else {
enqueue(e); // 将元素添加到队列尾部
return true; // 返回true
}
} finally {
lock.unlock(); // 解锁
}
}
private void enqueue(E x) {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[putIndex] == null;
final Object[] items = this.items; // 获取队列
items[putIndex] = x; // 把元素添加到队列尾部
if (++putIndex == items.length) // 判断是否队列已满
putIndex = 0;
count++; // 累计队列数量
notEmpty.signal(); // 唤醒消费者线程,可进行消费
}
2)boolean add(E e)
将指定元素添加到队列尾部,如果队列已满,抛出IllegalStateException异常。
public boolean add(E e) {
return super.add(e); // 调用父类AbstractQueue中add方法,最终是调用offer(E e)方法
}
3)void put(E e)
将指定元素添加到队列尾部,如果队列已满,则等待空间变为可用。
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e); // 判断元素是否为空,如果为空,抛NullPointerException异常
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; // 获取锁
lock.lockInterruptibly(); // 加锁,锁定线程,除非当前线程是interrupted
try {
while (count == items.length) // 判断队列是否已满
notFull.await(); // 队列已满,生产者处于等待
enqueue(e); // 将指定元素添加到队列尾部
} finally {
lock.unlock(); // 解锁
}
}
四)查找
1)boolean contains(Object o)
如果此队列包含指定的元素,则返回 true 。
public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false; // 元素为空,返回false
final Object[] items = this.items; // 获取队列
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; // 获取锁
lock.lock(); // 加锁
try {
if (count > 0) { // 判断队列是否有数据
final int putIndex = this.putIndex; // 获取最后一个元素插入下标位置
int i = takeIndex; // 头部元素下标
do {
if (o.equals(items[i])) // 如果元素查找到,直接返回true
return true;
if (++i == items.length) // 判断元素下标是否属于队列尾部
i = 0;
} while (i != putIndex); // 从队列头部一直扫描到最后元素插入下标位置
}
return false; // 队列没数据或没查找到指定元素,返回false
} finally {
lock.unlock(); // 解锁
}
}
2)E peek()
检索但不删除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null 。
public E peek() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return itemAt(takeIndex); // 获取头部元素
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final E itemAt(int i) {
return (E) items[i]; // 根据下标从队列中获取元素
}
3)E poll()
检索并删除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null 。
public E poll() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return (count == 0) ? null : dequeue(); // 如队列不为null,移除队列头部元素
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private E dequeue() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[takeIndex] != null;
final Object[] items = this.items; // 获取队列
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E x = (E) items[takeIndex]; // 获取队列头部元素
items[takeIndex] = null; // 把头部元素置null
if (++takeIndex == items.length) // 判断队列中是否只有一个元素
takeIndex = 0;
count--; // 累减队列数量
if (itrs != null)
itrs.elementDequeued();
notFull.signal(); // 唤醒生产者线程,进行生产
return x; // 返回队列中移除的头部元素
}
4)E take()
检索并删除此队列的头,如有必要,等待元素可用。如队列没有元素,会一直阻塞。
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0) // 当队列为空时,处于等待状态
notEmpty.await();
return dequeue(); // 移除队列头部元素并返回
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
五)删除
1)void clear()
从这个队列中原子地删除所有的元素。
public void clear() {
final Object[] items = this.items;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int k = count; // 获取队列数量
if (k > 0) {
final int putIndex = this.putIndex; // 获取最后一个插入下标
int i = takeIndex; // 队列头部元素下标
do {
items[i] = null; // 从队列头部元素开始,循环把队列元素置null
if (++i == items.length)
i = 0;
} while (i != putIndex);
takeIndex = putIndex; // 下标初始化
count = 0; // 数量初始化
if (itrs != null)
itrs.queueIsEmpty();
for (; k > 0 && lock.hasWaiters(notFull); k--) // 判断是否有等待的线程,全部唤醒
notFull.signal(); // 唤醒生产者线程
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
2)boolean remove(Object o)
从该队列中删除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在)。
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
final Object[] items = this.items;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (count > 0) { // 判断队列中是否有数据
final int putIndex = this.putIndex;
int i = takeIndex;
do {
if (o.equals(items[i])) {
removeAt(i); // 如果查找到元素, 直接从队列中删除
return true;
}
if (++i == items.length)
i = 0;
} while (i != putIndex);
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
void removeAt(final int removeIndex) {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[removeIndex] != null;
// assert removeIndex >= 0 && removeIndex < items.length;
final Object[] items = this.items;
if (removeIndex == takeIndex) { // 如果移除的元素就是头部元素
// removing front item; just advance
items[takeIndex] = null;
if (++takeIndex == items.length)
takeIndex = 0;
count--;
if (itrs != null)
itrs.elementDequeued();
} else {
// an "interior" remove
// slide over all others up through putIndex.
final int putIndex = this.putIndex;
for (int i = removeIndex;;) { // 循环队列,查找到元素,再移除元素
int next = i + 1;
if (next == items.length)
next = 0;
if (next != putIndex) {
items[i] = items[next];
i = next;
} else {
items[i] = null;
this.putIndex = i;
break;
}
}
count--;
if (itrs != null)
itrs.removedAt(removeIndex);
}
notFull.signal(); // 唤醒生产者线程
}
识别二维码关注个人微信公众号
![]()
本章完结,待续,欢迎转载!
本文说明:该文章属于原创,如需转载,请标明文章转载来源!