spring框架中的AOP
在spring框架中学习与测试AOP。
第一步:需要导入对应的所需要的jar包:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1KrhAz-gP2U0j1PTrO5MS4Q 密码:zcqb
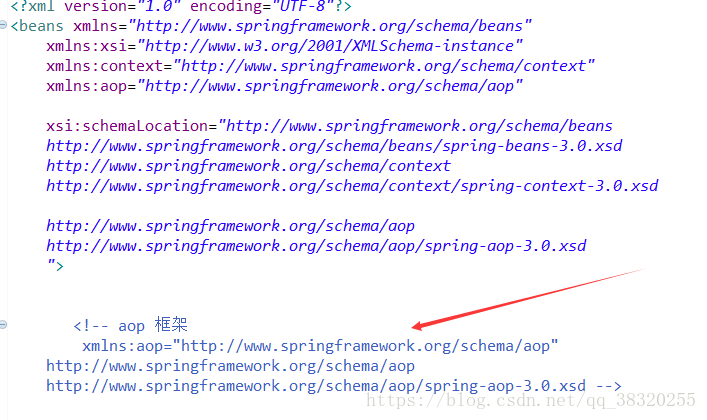
第二步:在Beans.xml文件中进行配置(命名标签的配置):
注意:要在配置中加入我注释的那三行。
第一次把第一行漏掉了,导致我在接下来的步骤中报错,直接无法找到对应的命名标签。
第三步:即可对AOP进行实例操作了。
由于才开始学,以下是我对AOP的粗浅理解,以及操作。可能会有错误,还请指正。
Spring框架的AOP框架是面向方面。而不是面向对象编程,即它不是针对对象。也就是说多个对象
都有可能触发它。在粗浅的理解,对象进行操作时都会触发它,如日志,每当任何对象有操作时,
日志都会打印相关信息,以便维护人员观察。而日志的打印不是根据对象。而是根据操作。无论哪个对象,
只要它有动作,就会打印。
根据这个Spring方面有5种通知:
1.前置通知:当某个对象要执行一个方法时,执行会通知,即AOP会执行相关操作。
2.后置通知:当某个对象执行完一个方法时,不考虑结果,AOP会执行相关操作。
3.返回后通知:当某个对象执行完方法之后,只有在方法成功完成时,才能执行通知。
4.抛出异常后通知:当某个对象执行完方法之后,只有在方法退出抛出异常时,才能执行通知。
5.环绕通知:在建议方法调用之前和之后,执行通知。
接下来先给出相应的实例类,然后在分析AOP
1.logging类:相当于日志,每当有方法执行时,它都会被通知到,并作出响应。
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class Logging {
/**
* This is the method which I would like to execute
* before a selected method execution.
*/
public void beforeAdvice(){
System.out.println("Going to setup student profile.");
}
/**
* This is the method which I would like to execute
* after a selected method execution.
*/
public void afterAdvice(){
System.out.println("Student profile has been setup.");
}
/**
* This is the method which I would like to execute
* when any method returns.
*/
public void afterReturningAdvice(Object retVal){
System.out.println("Returning:" + retVal.toString() );
}
/**
* This is the method which I would like to execute
* if there is an exception raised.
*/
public void AfterThrowingAdvice(IllegalArgumentException ex){
System.out.println("There has been an exception: " + ex.toString());
}
}2.Student类,是我们一会将要有执行方法的类。
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class Student {
private Integer age;
private String name;
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getAge() {
System.out.println("Age : " + age );
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
System.out.println("Name : " + name );
return name;
}
public void printThrowException(){
System.out.println("Exception raised");
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
}3.MainApp类:主程序运行的类:在该类中执行方法。
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println("-----------");
student.getName();
System.out.println("------------");
student.getAge();
System.out.println("-------------");
}
}}4.Beans.xml
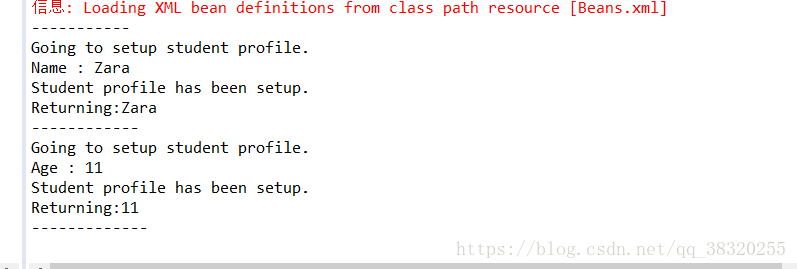
以下是代码运行结果,然后我们在进行分析:
分析:
1.我们先分析一下Beans.xml中对aop的配置
1.是aop的配置的声明:表明该标签中是aop的配置信息。
2. aop:aspect id="log" ref="logging" :
aspect:声明一个aop模块,该模块的id为:“log”。 ref则是引用的到类的名称,即当aop有执行时,它执行的是“logging”中 的方法。
3.
pointcut :表明应用程序中的一个点,该点名称是“selectAll”,并且相关联的是com.tutorialspoint.*.*(..)),也就是说当 com.tutorialspoint包中的所有对象有方法执行时,AOP都会被通知,并且响应。(由此我们可以理解AOP并不是针对某个对象,而是所有。)
4.而第四部分则4种通知,它执行的方法则是对应的logging中的4个对应方法。
2.我们来根据执行,分析一下结果:
1.先打印:“-----------------”
2.我们要执行student对象中getName方法。而该对象属于com.tutorialspoint,根据配置我们可以看到它会触发AOPbefore的通知,
而配置中,before通知指向的是logging中的beforeAdvice()方法,则会执行该方法,并输出:
“Going to setup student profile.”
3.getNmae方法才开始真正执行,于是输出:“Name : Zara” (该参数是在Beans.xml中已配置)。
4.getNmae方法执行完成,根据配置又会后置通知,而后置通知根据配置执行的是logging类中的
afterAdvice()方法,于是打印:“Student profile has been setup.”。
5.由于getName执行成功并有返回值,于是返回后通知也开始执行,对应的是logging中的afterReturningAdvice(Object retVal)
方法,于是打印:“Returning:Zara ”;
6.则第一个getNmae算是执行完全。
7.第二个getAge也是同样!
由此可以得到输出结果:
以上!