- nosql数据库技术与应用知识点
皆过客,揽星河
NoSQLnosql数据库大数据数据分析数据结构非关系型数据库
Nosql知识回顾大数据处理流程数据采集(flume、爬虫、传感器)数据存储(本门课程NoSQL所处的阶段)Hdfs、MongoDB、HBase等数据清洗(入仓)Hive等数据处理、分析(Spark、Flink等)数据可视化数据挖掘、机器学习应用(Python、SparkMLlib等)大数据时代存储的挑战(三高)高并发(同一时间很多人访问)高扩展(要求随时根据需求扩展存储)高效率(要求读写速度快)
- 浅谈MapReduce
Android路上的人
Hadoop分布式计算mapreduce分布式框架hadoop
从今天开始,本人将会开始对另一项技术的学习,就是当下炙手可热的Hadoop分布式就算技术。目前国内外的诸多公司因为业务发展的需要,都纷纷用了此平台。国内的比如BAT啦,国外的在这方面走的更加的前面,就不一一列举了。但是Hadoop作为Apache的一个开源项目,在下面有非常多的子项目,比如HDFS,HBase,Hive,Pig,等等,要先彻底学习整个Hadoop,仅仅凭借一个的力量,是远远不够的。
- Hadoop
傲雪凌霜,松柏长青
后端大数据hadoop大数据分布式
ApacheHadoop是一个开源的分布式计算框架,主要用于处理海量数据集。它具有高度的可扩展性、容错性和高效的分布式存储与计算能力。Hadoop核心由四个主要模块组成,分别是HDFS(分布式文件系统)、MapReduce(分布式计算框架)、YARN(资源管理)和HadoopCommon(公共工具和库)。1.HDFS(HadoopDistributedFileSystem)HDFS是Hadoop生
- Hadoop架构
henan程序媛
hadoop大数据分布式
一、案列分析1.1案例概述现在已经进入了大数据(BigData)时代,数以万计用户的互联网服务时时刻刻都在产生大量的交互,要处理的数据量实在是太大了,以传统的数据库技术等其他手段根本无法应对数据处理的实时性、有效性的需求。HDFS顺应时代出现,在解决大数据存储和计算方面有很多的优势。1.2案列前置知识点1.什么是大数据大数据是指无法在一定时间范围内用常规软件工具进行捕捉、管理和处理的大量数据集合,
- P1228 地毯填补问题
「已注销」
c++数据结构算法
#includeusingnamespacestd;#defineqwdfs(zx+l-1,zy+l-1,zx,zy,l);#definewedfs(zx+l-1,zy+l,zx,zy+l,l);#defineerdfs(zx+l,zy+l-1,zx+l,zy,l);#definertdfs(zx+l,zy+l,zx+l,zy+l,l);voiddfs(intx,int
- hbase介绍
CrazyL-
云计算+大数据hbase
hbase是一个分布式的、多版本的、面向列的开源数据库hbase利用hadoophdfs作为其文件存储系统,提供高可靠性、高性能、列存储、可伸缩、实时读写、适用于非结构化数据存储的数据库系统hbase利用hadoopmapreduce来处理hbase、中的海量数据hbase利用zookeeper作为分布式系统服务特点:数据量大:一个表可以有上亿行,上百万列(列多时,插入变慢)面向列:面向列(族)的
- 洛谷 P1378 油滴扩展
summ1ts
算法
本题可以利用dfs计算,重点是计算某一个油滴可以扩展的半径,并搜索得出所有油滴可以扩展的最大面积。由题意可知:(1):油滴的半径不能越过长方形方框的边界(2):判断当前油滴与其他油滴的关系:是否位于其他油滴内,最多只能与其他油滴相交#includeusingnamespacestd;#definepi3.1415926intn;intxa,ya,xb,yb;structnode{intx,y;do
- HBase介绍
mingyu1016
数据库
概述HBase是一个分布式的、面向列的开源数据库,源于google的一篇论文《bigtable:一个结构化数据的分布式存储系统》。HBase是GoogleBigtable的开源实现,它利用HadoopHDFS作为其文件存储系统,利用HadoopMapReduce来处理HBase中的海量数据,利用Zookeeper作为协同服务。HBase的表结构HBase以表的形式存储数据。表有行和列组成。列划分为
- 【HDFS】【HDFS架构】【HDFS Architecture】【架构】
资源存储库
hdfs架构hadoop
目录1Introduction介绍2AssumptionsandGoals假设和目标HardwareFailure硬件故障StreamingDataAccess流式数据访问LargeDataSets大型数据集SimpleCoherencyModel简单凝聚力模型“MovingComputationisCheaperthanMovingData”“移动计算比移动数据更便宜”PortabilityAc
- Hadoop学习第三课(HDFS架构--读、写流程)
小小程序员呀~
数据库hadoop架构bigdata
1.块概念举例1:一桶水1000ml,瓶子的规格100ml=>需要10个瓶子装完一桶水1010ml,瓶子的规格100ml=>需要11个瓶子装完一桶水1010ml,瓶子的规格200ml=>需要6个瓶子装完块的大小规格,只要是需要存储,哪怕一点点,也是要占用一个块的块大小的参数:dfs.blocksize官方默认的大小为128M官网:https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r3.
- hdfs启动流程
weixin_44352020
hadoophdfshadoop
Namenode1.init()namenode初始化,执行加载配置文件等操作2.loadFsImage()开始加载元数据将FsImage护额徐为目录树,保存在内存中FsImage中主要包含了问价你和数据块的对应关系3.loadEditlog()加载Editlog,将Editlog中记录的元数据修改应用到内存中;4.saveCheckpoint()将内存中最新的目录树持久化为新的FsImage到磁
- hdfs开机启动流程
鸭梨山大哎
hadoophdfs
第一步:加载name目录下最新的那个fsimage_xxx019文件,将里面存储的元数据(目录树结构)维护到内存中,但是还不是关机前的状态第二步:将关机前的最后使用的edits_inprogress_xxxx0160进行重命名edits_0000000000000000160-0000000000000000169操作,然后生成一个最新的edits_inprogress_xxx170文件,并修改s
- hadoop启动HDFS命令
m0_67401228
java搜索引擎linux后端
启动命令:/hadoop/sbin/start-dfs.sh停止命令:/hadoop/sbin/stop-dfs.sh
- 【HDFS主从集群】存在两个独立的问题和解决方案
流辉fglow
大数据#HDFShdfsjavahadoop大数据分布式学习
主从集群存在两个独立的问题和解决方案单点“主”的两个独立的问题以下是解决方案HA高可用方案:解决单点故障导致集群整体不可用问题Federation联邦机制:解决NN压力过大问题总结一般很多技术都是主从结构(最简单的结构)优点:结构相对简单,主与从协作“主”是单点,好处有,缺点也有好处:单点NameNode,数据一致性好掌握 因为一个人管,说一不二的单点“主”的两个独立的问题关键词:独立:两套独立
- 【HDFS】角色的架构设计
流辉fglow
#HDFS大数据hdfshadoop大数据学习分布式
HDFS角色的架构设计前置知识:Windows与Linux文件系统的差异HDFS中的角色及功能HDFS的架构NameNodeDataNodeNameNode元数据的持久化说明:/表示两个词是同一语义,方便你理解的前置知识:Windows与Linux文件系统的差异Windows&LInux虽然都有硬盘/分区、目录,但感受很不同的是:Windows:有很强的分区概念,要先通过不同的“盘符”去找文件在命
- HDFS的启动过程
ffbc2020
HDFSHDFS
HDFS的启动过程HDFS的启动过程分为四个阶段:第一阶段:NameNode读取包含元数据信息的fsimage文件,并加载到内存;第二阶段:NameNode读取体现HDFS最新状态的edits日志文件,并加载到内存中第三阶段:生成检查点,SecondaryNameNode将edits日志中的信息合并到fsimage文件中第四阶段:进入安全模式,检查数据块的完整性HDFS的安全模式什么是安全模式安全
- 集群hdfs启动
sxu~源
hdfshadoopbigdata
1)各个模块分开启动/停止(配置ssh是前提)常用(1)整体启动/停止HDFSstart-dfs.sh/stop-dfs.sh(2)整体启动/停止YARNstart-yarn.sh/stop-yarn.sh2)各个服务组件逐一启动/停止(1)分别启动/停止HDFS组件hdfs--daemonstart/stopnamenode/datanode/secondarynamenode(2)启动/停止Y
- java迷宫问题 华为_深度优先搜索——迷宫问题(华为oj)
刘洛希
java迷宫问题华为
题目描述:定义一个二维数组N*M(其中2=n)38continue;39if(a[tx][ty]==0&&book[tx][ty]==0)40{41xy.x=tx;42xy.y=ty;43way.push_back(xy);44book[tx][ty]=1;45dfs(tx,ty,step+1);46book[tx][ty]=0;47way.pop_back();48}49}50return0;5
- 【蓝桥杯】2.走出迷宫的最少步数——DFS
电次电次
深度优先蓝桥杯算法
1432-【基础】走出迷宫的最少步数题目描述一个迷宫由R行C列格子组成,有的格子里有障碍物,不能走;有的格子是空地,可以走。给定一个迷宫,求从左上角走到右下角最少需要走多少步(数据保证一定能走到)。只能在水平方向或垂直方向走,不能斜着走。输入第一行是两个整数,R和C,代表迷宫的行数和列数。(1usingnamespacestd;intn,m;chara[50][50];//地图intd[50][5
- 数据结构与算法——7-6 列出连通集 (25分)
吃完有点累
数据结构与算法队列算法数据结构DFSBFS
7-6列出连通集(25分)给定一个有N个顶点和E条边的无向图,请用DFS和BFS分别列出其所有的连通集。假设顶点从0到N−1编号。进行搜索时,假设我们总是从编号最小的顶点出发,按编号递增的顺序访问邻接点。输入格式:输入第1行给出2个整数N(0#includetypedefintVertexType;typedefintEdgeType;#defineMAXVEX100#defineINFINITY
- 7-6 列出连通集 (25 分)
胡小涛
DFSBFS
7-6列出连通集(25分)给定一个有N个顶点和E条边的无向图,请用DFS和BFS分别列出其所有的连通集。假设顶点从0到N−1编号。进行搜索时,假设我们总是从编号最小的顶点出发,按编号递增的顺序访问邻接点。输入格式:输入第1行给出2个整数N(0#includeusingnamespacestd;typedefstructGNode{intn;inte;intAdjMatrix[11][11];};s
- spark常用命令
我是浣熊的微笑
spark
查看报错日志:yarnlogsapplicationIDspark2-submit--masteryarn--classcom.hik.ReadHdfstest-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar进入$SPARK_HOME目录,输入bin/spark-submit--help可以得到该命令的使用帮助。hadoop@wyy:/app/hadoop/spark100$bin/spark-submit--
- spark启动命令
学不会又听不懂
spark大数据分布式
hadoop启动:cd/root/toolssstart-dfs.sh,只需在hadoop01上启动stop-dfs.sh日志查看:cat/root/toolss/hadoop/logs/hadoop-root-datanode-hadoop03.outzookeeper启动:cd/root/toolss/zookeeperbin/zkServer.shstart,三台都要启动bin/zkServ
- Redis高可用
確定饿的猫
redis数据库linux
目录持久化主从复制哨兵Cluster集群RDB持久化手动触发自动触发RDB执行流程RDB载入AOF持久化执行流程命令追加文件写入和文件同步appendfsyncalwaysappendfsyncnoappendfsynceverysecond文件重写文件重写流程载入对比nginx、tomcat、mysql等服务都具有预防单点故障、提高整体性能和安全性的功能,当然,Redis也不例外在Redis中,
- 编程常用命令总结
Yellow0523
LinuxBigData大数据
编程命令大全1.软件环境变量的配置JavaScalaSparkHadoopHive2.大数据软件常用命令Spark基本命令Spark-SQL命令Hive命令HDFS命令YARN命令Zookeeper命令kafka命令Hibench命令MySQL命令3.Linux常用命令Git命令conda命令pip命令查看Linux系统的详细信息查看Linux系统架构(X86还是ARM,两种方法都可)端口号命令L
- 使用Python实现多个PDF文件的合并
飘逸高铁侠
工作随笔pythonpdf开发语言
使用Python可以很方便地实现多个PDF文件的合并。我们可以使用PyPDF2库来完成这个任务。以下是一个实现PDF合并的Python脚本:importosfromPyPDF2importPdfMergerdefmerge_pdfs(input_dir,output_filename):#创建一个PdfMerger对象merger=PdfMerger()#获取输入目录中的所有PDF文件pdf_fi
- Hadoop常见面试题整理及解答
叶青舟
Linuxhdfs大数据hadooplinux
Hadoop常见面试题整理及解答一、基础知识篇:1.把数据仓库从传统关系型数据库转到hadoop有什么优势?答:(1)关系型数据库成本高,且存储空间有限。而Hadoop使用较为廉价的机器存储数据,且Hadoop可以将大量机器构建成一个集群,并在集群中使用HDFS文件系统统一管理数据,极大的提高了数据的存储及处理能力。(2)关系型数据库仅支持标准结构化数据格式,Hadoop不仅支持标准结构化数据格式
- 五一的成果
王跃坤txdy
emm。。五一过了有意义的四天。原来简单的图论我也是可以搞出来的原来DFS放进图论真的会使难度变大原来BFS在没有出口的时候会以超指数的爆炸增长原来二叉树并不是很难原来哈希的速度远超数组原来动态规划滚动起来速度真的快原来栈是那么的有用,可惜来不及学了(遇到一个求化学方程式的算法题,我自己写了133行的字符串处理,原来用栈可以缩减3倍的代码)原来很多复杂的问题都可以拆解成很简单的问题比如我好像发现数
- 【每日一题】LeetCode 104.二叉树的最大深度(树、深度优先搜索、广度优先搜索、二叉树)
Chase-Hart
算法leetcode深度优先宽度优先数据结构java
【每日一题】LeetCode104.二叉树的最大深度(树、深度优先搜索、广度优先搜索、二叉树)题目描述给定一个二叉树root,我们需要计算并返回该二叉树的最大深度。二叉树的最大深度是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。思路分析为了解决这个问题,我们可以使用递归的方法。递归的基本思想是从根节点开始,逐层向下遍历树的每个节点,同时记录当前的深度。在递归的过程中,我们会遇到两种情况:当前节点为
- 深度优先算法,广度优先算法,hill climbing,贪心搜索,A*算法,启发式搜索算法是什么,比起一般搜索法算法有什么区别
MIMO. mimo
算法深度优先宽度优先
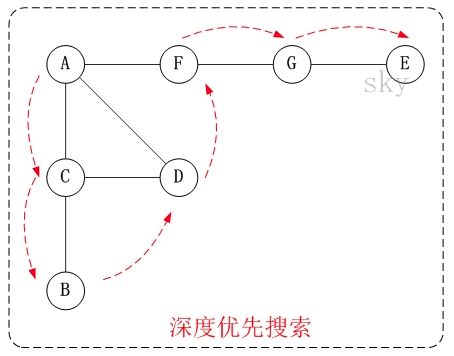
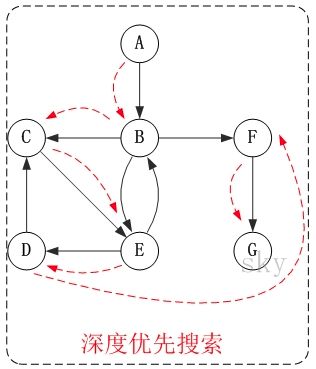
深度优先算法(Depth-FirstSearch,DFS)深度优先搜索是一种用于遍历或搜索树或图的算法。它沿着树的深度遍历树的节点,尽可能深地搜索树的分支。当节点v的所在边都已被探寻过,搜索将回溯到发现节点v的那条边的起始节点。这一过程一直进行到已发现从源节点可达的所有节点为止。如果还存在未被发现的节点,则选择其中一个作为源节点并重复以上过程,直到所有节点都被访问为止。深度优先搜索是一个递归算法,
- VMware Workstation 11 或者 VMware Player 7安装MAC OS X 10.10 Yosemite
iwindyforest
vmwaremac os10.10workstationplayer
最近尝试了下VMware下安装MacOS 系统,
安装过程中发现网上可供参考的文章都是VMware Workstation 10以下, MacOS X 10.9以下的文章,
只能提供大概的思路, 但是实际安装起来由于版本问题, 走了不少弯路, 所以我尝试写以下总结, 希望能给有兴趣安装OSX的人提供一点帮助。
写在前面的话:
其实安装好后发现, 由于我的th
- 关于《基于模型驱动的B/S在线开发平台》源代码开源的疑虑?
deathwknight
JavaScriptjava框架
本人从学习Java开发到现在已有10年整,从一个要自学 java买成javascript的小菜鸟,成长为只会java和javascript语言的老菜鸟(个人邮箱:
[email protected])
一路走来,跌跌撞撞。用自己的三年多业余时间,瞎搞一个小东西(基于模型驱动的B/S在线开发平台,非MVC框架、非代码生成)。希望与大家一起分享,同时有许些疑虑,希望有人可以交流下
平台
- 如何把maven项目转成web项目
Kai_Ge
mavenMyEclipse
创建Web工程,使用eclipse ee创建maven web工程 1.右键项目,选择Project Facets,点击Convert to faceted from 2.更改Dynamic Web Module的Version为2.5.(3.0为Java7的,Tomcat6不支持). 如果提示错误,可能需要在Java Compiler设置Compiler compl
- 主管???
Array_06
工作
转载:http://www.blogjava.net/fastzch/archive/2010/11/25/339054.html
很久以前跟同事参加的培训,同事整理得很详细,必须得转!
前段时间,公司有组织中高阶主管及其培养干部进行了为期三天的管理训练培训。三天的课程下来,虽然内容较多,因对老师三天来的课程内容深有感触,故借着整理学习心得的机会,将三天来的培训课程做了一个
- python内置函数大全
2002wmj
python
最近一直在看python的document,打算在基础方面重点看一下python的keyword、Build-in Function、Build-in Constants、Build-in Types、Build-in Exception这四个方面,其实在看的时候发现整个《The Python Standard Library》章节都是很不错的,其中描述了很多不错的主题。先把Build-in Fu
- JSP页面通过JQUERY合并行
357029540
JavaScriptjquery
在写程序的过程中我们难免会遇到在页面上合并单元行的情况,如图所示
如果对于会的同学可能很简单,但是对没有思路的同学来说还是比较麻烦的,提供一下用JQUERY实现的参考代码
function mergeCell(){
var trs = $("#table tr");
&nb
- Java基础
冰天百华
java基础
学习函数式编程
package base;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Integer a = 4;
// Double aa = (double)a / 100000;
// Decimal
- unix时间戳相互转换
adminjun
转换unix时间戳
如何在不同编程语言中获取现在的Unix时间戳(Unix timestamp)? Java time JavaScript Math.round(new Date().getTime()/1000)
getTime()返回数值的单位是毫秒 Microsoft .NET / C# epoch = (DateTime.Now.ToUniversalTime().Ticks - 62135
- 作为一个合格程序员该做的事
aijuans
程序员
作为一个合格程序员每天该做的事 1、总结自己一天任务的完成情况 最好的方式是写工作日志,把自己今天完成了什么事情,遇见了什么问题都记录下来,日后翻看好处多多
2、考虑自己明天应该做的主要工作 把明天要做的事情列出来,并按照优先级排列,第二天应该把自己效率最高的时间分配给最重要的工作
3、考虑自己一天工作中失误的地方,并想出避免下一次再犯的方法 出错不要紧,最重
- 由html5视频播放引发的总结
ayaoxinchao
html5视频video
前言
项目中存在视频播放的功能,前期设计是以flash播放器播放视频的。但是现在由于需要兼容苹果的设备,必须采用html5的方式来播放视频。我就出于兴趣对html5播放视频做了简单的了解,不了解不知道,水真是很深。本文所记录的知识一些浅尝辄止的知识,说起来很惭愧。
视频结构
本该直接介绍html5的<video>的,但鉴于本人对视频
- 解决httpclient访问自签名https报javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: sun.security.validat
bewithme
httpclient
如果你构建了一个https协议的站点,而此站点的安全证书并不是合法的第三方证书颁发机构所签发,那么你用httpclient去访问此站点会报如下错误
javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path bu
- Jedis连接池的入门级使用
bijian1013
redisredis数据库jedis
Jedis连接池操作步骤如下:
a.获取Jedis实例需要从JedisPool中获取;
b.用完Jedis实例需要返还给JedisPool;
c.如果Jedis在使用过程中出错,则也需要还给JedisPool;
packag
- 变与不变
bingyingao
不变变亲情永恒
变与不变
周末骑车转到了五年前租住的小区,曾经最爱吃的西北面馆、江西水饺、手工拉面早已不在,
各种店铺都换了好几茬,这些是变的。
三年前还很流行的一款手机在今天看起来已经落后的不像样子。
三年前还运行的好好的一家公司,今天也已经不复存在。
一座座高楼拔地而起,
- 【Scala十】Scala核心四:集合框架之List
bit1129
scala
Spark的RDD作为一个分布式不可变的数据集合,它提供的转换操作,很多是借鉴于Scala的集合框架提供的一些函数,因此,有必要对Scala的集合进行详细的了解
1. 泛型集合都是协变的,对于List而言,如果B是A的子类,那么List[B]也是List[A]的子类,即可以把List[B]的实例赋值给List[A]变量
2. 给变量赋值(注意val关键字,a,b
- Nested Functions in C
bookjovi
cclosure
Nested Functions 又称closure,属于functional language中的概念,一直以为C中是不支持closure的,现在看来我错了,不过C标准中是不支持的,而GCC支持。
既然GCC支持了closure,那么 lexical scoping自然也支持了,同时在C中label也是可以在nested functions中自由跳转的
- Java-Collections Framework学习与总结-WeakHashMap
BrokenDreams
Collections
总结这个类之前,首先看一下Java引用的相关知识。Java的引用分为四种:强引用、软引用、弱引用和虚引用。
强引用:就是常见的代码中的引用,如Object o = new Object();存在强引用的对象不会被垃圾收集
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-解释器模式-Interpret
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
package design.pattern;
/*
* 解释器(Interpreter)模式的意图是可以按照自己定义的组合规则集合来组合可执行对象
*
* 代码示例实现XML里面1.读取单个元素的值 2.读取单个属性的值
* 多
- After Effects操作&快捷键
cherishLC
After Effects
1、快捷键官方文档
中文版:https://helpx.adobe.com/cn/after-effects/using/keyboard-shortcuts-reference.html
英文版:https://helpx.adobe.com/after-effects/using/keyboard-shortcuts-reference.html
2、常用快捷键
- Maven 常用命令
crabdave
maven
Maven 常用命令
mvn archetype:generate
mvn install
mvn clean
mvn clean complie
mvn clean test
mvn clean install
mvn clean package
mvn test
mvn package
mvn site
mvn dependency:res
- shell bad substitution
daizj
shell脚本
#!/bin/sh
/data/script/common/run_cmd.exp 192.168.13.168 "impala-shell -islave4 -q 'insert OVERWRITE table imeis.${tableName} select ${selectFields}, ds, fnv_hash(concat(cast(ds as string), im
- Java SE 第二讲(原生数据类型 Primitive Data Type)
dcj3sjt126com
java
Java SE 第二讲:
1. Windows: notepad, editplus, ultraedit, gvim
Linux: vi, vim, gedit
2. Java 中的数据类型分为两大类:
1)原生数据类型 (Primitive Data Type)
2)引用类型(对象类型) (R
- CGridView中实现批量删除
dcj3sjt126com
PHPyii
1,CGridView中的columns添加
array(
'selectableRows' => 2,
'footer' => '<button type="button" onclick="GetCheckbox();" style=&
- Java中泛型的各种使用
dyy_gusi
java泛型
Java中的泛型的使用:1.普通的泛型使用
在使用类的时候后面的<>中的类型就是我们确定的类型。
public class MyClass1<T> {//此处定义的泛型是T
private T var;
public T getVar() {
return var;
}
public void setVa
- Web开发技术十年发展历程
gcq511120594
Web浏览器数据挖掘
回顾web开发技术这十年发展历程:
Ajax
03年的时候我上六年级,那时候网吧刚在小县城的角落萌生。传奇,大话西游第一代网游一时风靡。我抱着试一试的心态给了网吧老板两块钱想申请个号玩玩,然后接下来的一个小时我一直在,注,册,账,号。
彼时网吧用的512k的带宽,注册的时候,填了一堆信息,提交,页面跳转,嘣,”您填写的信息有误,请重填”。然后跳转回注册页面,以此循环。我现在时常想,如果当时a
- openSession()与getCurrentSession()区别:
hetongfei
javaDAOHibernate
来自 http://blog.csdn.net/dy511/article/details/6166134
1.getCurrentSession创建的session会和绑定到当前线程,而openSession不会。
2. getCurrentSession创建的线程会在事务回滚或事物提交后自动关闭,而openSession必须手动关闭。
这里getCurrentSession本地事务(本地
- 第一章 安装Nginx+Lua开发环境
jinnianshilongnian
nginxluaopenresty
首先我们选择使用OpenResty,其是由Nginx核心加很多第三方模块组成,其最大的亮点是默认集成了Lua开发环境,使得Nginx可以作为一个Web Server使用。借助于Nginx的事件驱动模型和非阻塞IO,可以实现高性能的Web应用程序。而且OpenResty提供了大量组件如Mysql、Redis、Memcached等等,使在Nginx上开发Web应用更方便更简单。目前在京东如实时价格、秒
- HSQLDB In-Process方式访问内存数据库
liyonghui160com
HSQLDB一大特色就是能够在内存中建立数据库,当然它也能将这些内存数据库保存到文件中以便实现真正的持久化。
先睹为快!
下面是一个In-Process方式访问内存数据库的代码示例:
下面代码需要引入hsqldb.jar包 (hsqldb-2.2.8)
import java.s
- Java线程的5个使用技巧
pda158
java数据结构
Java线程有哪些不太为人所知的技巧与用法? 萝卜白菜各有所爱。像我就喜欢Java。学无止境,这也是我喜欢它的一个原因。日常
工作中你所用到的工具,通常都有些你从来没有了解过的东西,比方说某个方法或者是一些有趣的用法。比如说线程。没错,就是线程。或者确切说是Thread这个类。当我们在构建高可扩展性系统的时候,通常会面临各种各样的并发编程的问题,不过我们现在所要讲的可能会略有不同。
- 开发资源大整合:编程语言篇——JavaScript(1)
shoothao
JavaScript
概述:本系列的资源整合来自于github中各个领域的大牛,来收藏你感兴趣的东西吧。
程序包管理器
管理javascript库并提供对这些库的快速使用与打包的服务。
Bower - 用于web的程序包管理。
component - 用于客户端的程序包管理,构建更好的web应用程序。
spm - 全新的静态的文件包管
- 避免使用终结函数
vahoa.ma
javajvmC++
终结函数(finalizer)通常是不可预测的,常常也是很危险的,一般情况下不是必要的。使用终结函数会导致不稳定的行为、更差的性能,以及带来移植性问题。不要把终结函数当做C++中的析构函数(destructors)的对应物。
我自己总结了一下这一条的综合性结论是这样的:
1)在涉及使用资源,使用完毕后要释放资源的情形下,首先要用一个显示的方