基于TCP协议的网络编程
TCP网络编程
- TCP/IP协议
- 使用Socket通信
- 服务端
- 客户端
- 多线程聊天
- 半关闭Socket
- 使用NIO实现非阻塞式通信
- 使用AIO
TCP/IP协议
TCP/IP 协议是一种可靠的网络协议, 它在通信的两端各建立一个Socket,从而在通信的两端形成网络虚拟链路。
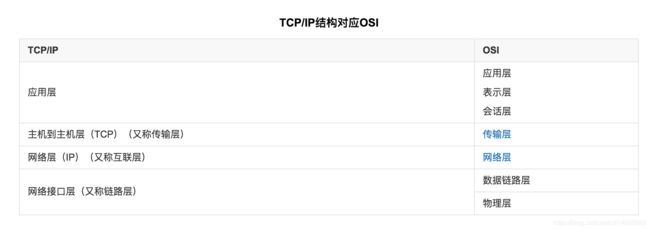
从协议分层模型方面来讲,TCP/IP由四个层次组成:网络接口层、网络层、传输层、应用层。
IP
互联网协议(英语:Internet Protocol ,又译为网际协议),
IP层接收由更低层(网络接口层例如以太网设备驱动程序)发来的数据包,并把该数据包发送到更高层—TCP或UDP层;相反,IP层也把从TCP或UDP层接收来的数据包传送到更低层。IP数据包是不可靠的,因为IP并没有做任何事情来确认数据包是否按顺序发送的或者有没有被破坏,IP数据包中含有发送它的主机的地址(源地址)和接收它的主机的地址(目的地址)。
高层的TCP和UDP服务在接收数据包时,通常假设包中的源地址是有效的。也可以这样说,IP地址形成了许多服务的认证基础,这些服务相信数据包是从一个有效的主机发送来的。IP确认包含一个选项,叫作IP source routing,可以用来指定一条源地址和目的地址之间的直接路径。对于一些TCP和UDP的服务来说,使用了该选项的IP包好像是从路径上的最后一个系统传递过来的,而不是来自于它的真实地点。这个选项是为了测试而存在的,说明了它可以被用来欺骗系统来进行平常是被禁止的连接。那么,许多依靠IP源地址做确认的服务将产生问题并且会被非法入侵。
TCP
TCP(Transmission Control Protocol 传输控制协议)是一种面向连接的、可靠的、基于字节流的传输层通信协议.
TCP是面向连接的通信协议,通过三次握手建立连接,通讯完成时要拆除连接,由于TCP是面向连接的所以只能用于端到端的通讯。
TCP提供的是一种可靠的数据流服务,采用“带重传的肯定确认”技术来实现传输的可靠性。TCP还采用一种称为“滑动窗口”的方式进行流量控制,所谓窗口实际表示接收能力,用以限制发送方的发送速度。
如果IP数据包中有已经封好的TCP数据包,那么IP将把它们向‘上’传送到TCP层。TCP将包排序并进行错误检查,同时实现虚电路间的连接。TCP数据包中包括序号和确认,所以未按照顺序收到的包可以被排序,而损坏的包可以被重传。
TCP将它的信息送到更高层的应用程序,例如Telnet的服务程序和客户程序。应用程序轮流将信息送回TCP层,TCP层便将它们向下传送到IP层,设备驱动程序和物理介质,最后到接收方。
面向连接的服务(例如Telnet、FTP、rlogin、X Windows和SMTP)需要高度的可靠性,所以它们使用了TCP。DNS在某些情况下使用TCP(发送和接收域名数据库),但使用UDP传送有关单个主机的信息。
使用Socket通信
Java使用Socket对象来代表 TCP通信两端的通信端口,并通过Socket产生IO流来进行网络通信。
服务端
使用 ServerSocket创建TCP服务端。
ServerSocket对象用于监听来自客户端的Socket连接,如果没有连接,一直处于等待状态。
public
class ServerSocket implements java.io.Closeable {
/**
* Various states of this socket.
*/
private boolean created = false;
private boolean bound = false;
private boolean closed = false;
private Object closeLock = new Object();
}
Socket accept() : 如果接收到一个客户端连接请求,返回一个与客户端对应的Socket. 否则一直处于等待状态。
ServerSocket 构造器:
ServerSocket(int port): 指定端口port创建一个ServerSocket. 有效端口对整数值: 0 ~ 65535.
public ServerSocket(int port, int backlog):backlog连接队列长度.requested maximum length of the queue of incoming connections
public ServerSocket(int port, int backlog, InetAddress bindAddr) : bindAddr机器存在多个ip情况下,绑定IP地址
客户端
客户端使用Socket的构造器连接到指定服务器
public Socket(String host, int port), 连接远程主机,远程端口。 没有指定本机地址,端口, 默认使用本地主机默认IP地址, 默认使用系统动态分配端口。
public Socket(String host, int port, InetAddress localAddr, int localPort) : 指定本地IP和端口, 适用于本地主机多IP地址情形。
建立Socket连接后, 通过下面方法获取输入输出流:
InputStream getInputStream(): 输入流
OutputStream getOutputStream(): 输出流
Server端:
public class ServerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(10000);
while (true){
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
PrintStream printStream = new PrintStream(socket.getOutputStream());
printStream.println("Hello, message from server");
printStream.close();
socket.close();
}
}
}
client端:
public class ClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10000);
//超时时间, 10s
socket.setSoTimeout(10000);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String line = br.readLine();
System.out.println("server msg : " + line);
br.close();
socket.close();
}
}
//Output
server msg : Hello, message from server
多线程聊天
使用BufferedReader的readLine()方法读取数据时, 该方法返回数据前,线程被阻塞.
为了实现C/S聊天室, 服务端应包含多线程,每个Socket对应一个线程,负责读取客户端的输入流数据。
接收多个客户端消息, 并广播到各个客户端
Server端:
public class ServerTest {
public static List<Socket> sockets = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(10002);
while (true){
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
sockets.add(socket);
new Thread(new ServerThread(socket)).start();
}
}
}
class ServerThread implements Runnable{
Socket socket = null;
BufferedReader bufferedReader = null;
public ServerThread(Socket socket) throws IOException{
this.socket = socket;
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
String content = null;
while ((content = readFromClient()) != null){
//给每个客户端广播消息
for (Socket s : ServerTest.sockets){
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(s.getOutputStream());
ps.println(content);
}
}
}
catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private String readFromClient(){
try {
String line = bufferedReader.readLine();
System.out.println(line);
return line;
}
catch (IOException e){
ServerTest.sockets.remove(socket);
}
return null;
}
}
client端:
public class ClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10002);
new Thread(new ClientThread(socket)).start();
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(socket.getOutputStream());
String line = null;
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){
ps.println(line);
}
}
}
class ClientThread implements Runnable{
private Socket s;
BufferedReader bufferedReader =null;
public ClientThread(Socket s) throws IOException {
this.s = s;
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
String content = null;
while ((content = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(content);
}
}
catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
半关闭Socket
前面例子是以行为最小数据单位,如果通信数据是多行的。
在IO中, 如果表示输出已结束, 可以通过关闭输出流来实现,
在网络通信中,当关闭输出流时,Socket也会关闭, 导致程序无法从该Socket中读取数据。
Socket提供了下面两个半关闭方法, 只关闭Socket的输入输出流, 表示输出数据已发送完成。
- shutdownInput(): 关闭输入流, 还可通过输出流输出数据
- shutdownOutput(): 关闭输出流。 还可通过输入流输入数据
执行后,可通过 isInputShutdown() 是否处于 半读状态(read-half).
isOutputShutdown()是否处于半写状态(write-half)
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(10002);
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(socket.getOutputStream());
ps.println("server first line");
ps.println("server second line");
socket.shutdownOutput();
System.out.println(socket.isClosed());
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(socket.getInputStream());
while (scanner.hasNextLine()){
System.out.println(scanner.nextLine());
}
scanner.close();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
当调用Socket的 shutdownInput() 或 shutdownOutput() 后, 该Socket无法再次打开输入流或输出流。
这种通过不适合用于保持通信的交互式应用, 只适用于一站式通信, 例如HTTP协议, 客户端连接到服务端后, 开始发送数据, 发送完无须再次发送, 只需读取, 读取完后Socket连接也被关闭了。
使用NIO实现非阻塞式通信
前面为阻塞式API, 服务端为每个客户端提供一个独立线程进行处理, 当服务器需要处理大量客户端时,这种会导致性能下降。
使用 NIO API可以让服务器使用一个或有限几个线程来同时处理连接到服务端的所有客户端。
Java 的 NIO 为非阻塞式Socket通信提供下面类:
Selector: 它是 SelectableChannel 对象的多路复用器, 所有希望采用非阻塞式进行通信的Channel都应该注册到 Selector对象。调用 静态方法 open() 创建 Selector 实例。
Selector 同时监控多个 SelectableChannel 的 IO状况, 是非阻塞IO的核心。
一个 Selector 实例有三个 SelectionKey 集合:
keys() : 注册在该 Selector上的 Channel
selectedKeys(): 可通过 select() 方法获取, 需要进行IO处理的Channel。, 另一个集合是被取消注册关系的Channel.
应用程序调用 SelectableChannel 的 register()方法,将其注册到指定的 Selector 上, 当某些SelectableChannel 需要处理IO时, 程序调用 Selector实例的 select() 方法获取他们的数量, 通过selectedKeys()方法返回对应的SelectionKey集合,通过该集合可以获取需要进行IO处理的 SelectableChannel集。
SelectableChannel 对象支持阻塞和非阻塞两种模式, 所有Channel默认为阻塞。
configureBlocking(boolean block): 设置是否采用阻塞
isBlocking() : 返回是否阻塞。
int validOps(): 返回支持的操作
这些操作在 SelectionKey 中定义
public abstract class SelectionKey {
// -- Operation bits and bit-testing convenience methods --
/**
* Operation-set bit for read operations.
*
* Suppose that a selection key's interest set contains
* OP_READ at the start of a selection operation. If the selector
* detects that the corresponding channel is ready for reading, has reached
* end-of-stream, has been remotely shut down for further reading, or has
* an error pending, then it will add OP_READ to the key's
* ready-operation set and add the key to its selected-key set.
*/
public static final int OP_READ = 1 << 0;
/**
* Operation-set bit for write operations.
*
* Suppose that a selection key's interest set contains
* OP_WRITE at the start of a selection operation. If the selector
* detects that the corresponding channel is ready for writing, has been
* remotely shut down for further writing, or has an error pending, then it
* will add OP_WRITE to the key's ready set and add the key to its
* selected-key set.
*/
public static final int OP_WRITE = 1 << 2;
/**
* Operation-set bit for socket-connect operations.
*
* Suppose that a selection key's interest set contains
* OP_CONNECT at the start of a selection operation. If the selector
* detects that the corresponding socket channel is ready to complete its
* connection sequence, or has an error pending, then it will add
* OP_CONNECT to the key's ready set and add the key to its
* selected-key set.
*/
public static final int OP_CONNECT = 1 << 3;
/**
* Operation-set bit for socket-accept operations.
*
* Suppose that a selection key's interest set contains
* OP_ACCEPT at the start of a selection operation. If the selector
* detects that the corresponding server-socket channel is ready to accept
* another connection, or has an error pending, then it will add
* OP_ACCEPT to the key's ready set and add the key to its
* selected-key set.
*/
public static final int OP_ACCEPT = 1 << 4;
SelectionKey : 代表 SelectableChannel 和 Selector 之间的注册关系
ServerSocketChannel: 对应 ServerSocket类,只支持 OP_ACCEPT操作
SocketChannel: 对应 Socket类。
Server端
public class NServer {
//用于检测所有Channel状态的Selector
private Selector selector = null;
static final int PORT = 9000;
private Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
public void init() throws IOException{
selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel server = ServerSocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress isa = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", PORT);
//绑定ip
server.bind(isa);
//非阻塞方式
server.configureBlocking(false);
//注册到Selector
server.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (selector.select() > 0){
//依次处理selector上每个已选择的SelectKey
for(SelectionKey sk : selector.selectedKeys()){
//从已选择的key中删除正在处理的key
selector.selectedKeys().remove(sk);
//如果Channel包含客户端连接请求
if(sk.isAcceptable()){
//产生服务端SocketChannel
SocketChannel sc = server.accept();
//非阻塞模式
sc.configureBlocking(false);
//将 SocketChannel 也注册到 selector
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//将sk对应的Channel设置成准备接收其他请求
sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
}
//如果sk对应的Channel有数据需要读取
if(sk.isReadable()){
//获取该SelectionKey对应的Channel, 该Channel中有可读数据
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) sk.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
String content = "";
//读取数据
try {
while (sc.read(buffer) > 0){
buffer.flip();
content += charset.decode(buffer);
}
System.out.println("read Data:" + content);
//设置成准备下一次读取
sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
catch (IOException e){
//出现异常, 该Channel对应的client出现问题,从Selector中取消sk的注册
sk.cancel();
if(sk.channel() != null){
sk.channel().close();
}
}
//信息不为空
if(content.length() > 0){
//遍历该selector中注册的所有SelectionKey
for (SelectionKey key : selector.keys()){
Channel targetChannel = key.channel();
//如果该Channel是 SocketChannel, 将读到的内容写入该Channel中
if(targetChannel instanceof SocketChannel){
SocketChannel dest = (SocketChannel) targetChannel;
dest.write(charset.encode(content));
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
new NServer().init();
}
}
client端
public class NClient {
private Selector selector = null;
static final int PORT = 9000;
private Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
private SocketChannel sc = null;
public void init() throws IOException{
selector = Selector.open();
InetSocketAddress isa = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", PORT);
sc = SocketChannel.open(isa);
sc.configureBlocking(false);
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//启动读取服务端数据线程
new ClientThread().start();
//创建键盘输入流, 将键盘输入内容输出到SocketChannel中
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNextLine()){
String line = scanner.nextLine();
sc.write(charset.encode(line));
}
}
private class ClientThread extends Thread{
public void run(){
try{
while (selector.select() > 0){
for(SelectionKey sk : selector.selectedKeys()){
selector.selectedKeys().remove(sk);
if(sk.isReadable()){
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) sk.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
String content = "";
while (sc.read(buffer) > 0){
buffer.flip();
content += charset.decode(buffer);
}
System.out.println("get Data:" + content);
sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
}
}
}
catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
new NClient().init();
}
}
使用AIO
NIO.2提供了异步Channel支持, 基于异步Channel的IO机制称为异步IO(Asynchronous IO)。
IO操作分为两步:
- 程序发出IO请求
- 完成实际的IO操作
传统IO和基于Channel的IO都是同步IO, 都是针对第一步, 发出请求是否阻塞线程。
同步IO和异步IO是针对第二步, 实际IO操作由操作系统完成, 再返回给应用程序,这就是异步IO。
如果实际IO需要应用程序本身执行,会阻塞线程,那就是同步IO。
NIO.2提供了一系列以 Asynchronous 开头的Channel接口和类。
AsynchronousSocketChannel 和 AsynchronousServerSocketChannel 是支持TCP通信的异步Channel,
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel是一个负责监听的Channel, 与 ServerSocketChannel 类似。
样例 Server
public class SimpleAIOServer {
static final int PORT = 9001;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
try (
//1. 创建对象
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel =
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open();
){
//2. 绑定端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
while (true){
//3. 循环接收来自client连接
Future<AsynchronousSocketChannel> future = serverSocketChannel.accept();
//连接完成后返回AsynchronousSocketChannel
AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel = future.get();
//输出
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("from AIO server".getBytes("UTF-8"))).get();
}
}
}
}
client :
public class SimpleAIOnClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
try (
//1. 创建对象
AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open();
){
// 2. 连接服务
clientChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9001)).get();
buffer.clear();
// 3. 读取数据
clientChannel.read(buffer).get();
buffer.flip();
String content = charset.decode(buffer).toString();
System.out.println("SERVER:" + content);
}
}
}
服务端和客户端都需要上面样例中3步。
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel的open()方法,还可这样使用
public static AsynchronousSocketChannel open(AsynchronousChannelGroup group)
AsynchronousChannelGroup 是 异步Channel分组管理器, 可以实现资源共享,
//创建一个线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
//指定AsynchronousChannelGroup
AsynchronousChannelGroup channelGroup = AsynchronousChannelGroup.withThreadPool(executorService);
//以线程池创建AsynchronousServerSocketChannel
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(channelGroup)
.bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
当调用 AsynchronousServerSocketChannel 的 accept()方法后,由于异步IO的实际操作交给操作系统完成, 程序并不清楚什么时候完成。也不知道accept()方法什么时候手动客户端请求。为了解决这个异步问题。提供下面两个accept()方法:
Future<\AsynchronousSocketChannel> accept(); 接受客户端请求, 如果程序需要获得连接成功后返回的AsynchronousSocketChannel, 则调用该方法返回的Future对象的 get()方法, get()会阻塞线程。
public abstract <\A> void accept(A attachment,
CompletionHandler
CompletionHandler接口
public interface CompletionHandler<V,A> {
/**
* Invoked when an operation has completed.
*
* @param result
* The result of the I/O operation.
* @param attachment
* The object attached to the I/O operation when it was initiated.
*/
void completed(V result, A attachment);
/**
* Invoked when an operation fails.
*
* @param exc
* The exception to indicate why the I/O operation failed
* @param attachment
* The object attached to the I/O operation when it was initiated.
*/
void failed(Throwable exc, A attachment);
}