我们显示必然要使用到component,React.Component 是一个抽象的Class,通常继承该类来构建自定义的Component。 Component可以将U分离成独立的碎片,有点类似于JavaScript的function,它接受一个任意的输入(props)并返回一个React element描述屏幕中的内容。
生命周期及方法
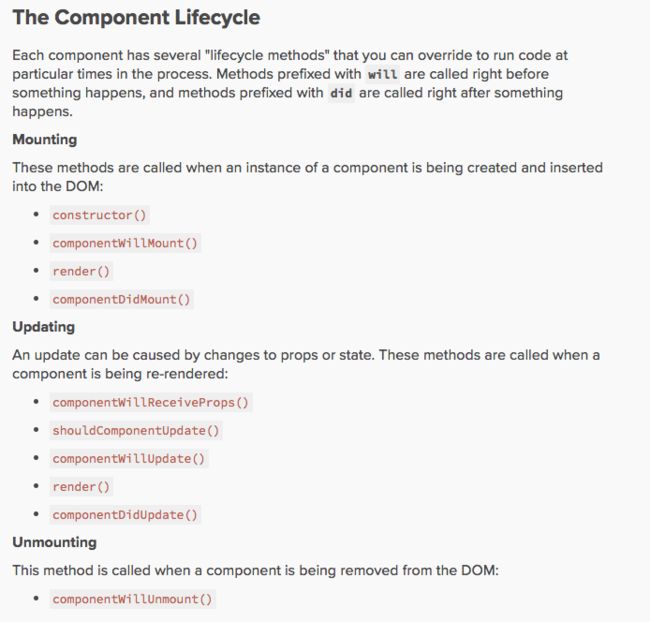
Component和Android中的activity一样,也有一定的生命周期,官网对于其生命周期介绍如下:
基本分为三个阶段:
1、挂载阶段
调用方法:
constructor() //构造函数
componentWillMount()//将要被挂载
render()//渲染
componentDidMount()// 完成挂载
2、更新阶段
调用方法:
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) //作为子空间,在props改变时调用
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps,nextState)//是否允许更新,返回boolean
componentWillUpdate(nextProps,nextState)//将要更新
render()//渲染
componentDidUpdate(prevProps,prevState)//完成更新
3、销毁阶段
调用方法:
componentWillUnmount()//销毁
具体实例
//重新写一个index.js,来演示component的生命周期
//component是从react中来的
importReact, {Component} from 'react';
//Text以及View等都是从react-native中来的
import{AppRegistry,Text}from'react-native'
//定义一个Component,按照ES6的语法来,就和java语法中定义class一样,继承component
class AndroidTestComponent extends Component{
//getDefaultProps() is only supported for classes created using React.createClass. We can use a static property to define defaultProps instead.
// getDefaultProps(){
// console.log("AndroidTestComponent=====getDefaultProps")
// }
// 使用这个方法进行定义props
staticdefaultProps= {
color:'red'
};
//构造函数
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state= {
name:'ruibaobao'
}
console.log("AndroidTestComponent=====constructor")
}
//compoment将要挂载的函数
componentWillMount() {
console.log("AndroidTestComponent=====componentWillMount")
}
//render属性对应的函数会返回一段JSX来表示该组件的结构和布局。该部分是一个组件必不可少的地方,没有这些内容,就无法构成一个组件。
//render方法必须返回单个根元素
//compoment挂载渲染的函数
render() {
console.log("AndroidTestComponent=====render")
return(
{
this.setState({name:'wwoairuibaobao'})
}}style={{backgroundColor:'red'}}>这是一个简单的测试text{this.state.name}
//如何使用props
//forceUpdate 会强制更新component,即使shouldComponentUpdate返回false也会更新
//{this.forceUpdate()}} style={{backgroundColor:this.props.color}} >这只是一个简单的测试t{this.state.name}{this.props.color}
);
}
//compoment已经挂载的函数
componentDidMount() {
console.log("AndroidTestComponent=====componentDidMount")
}
//属性改变时调用,在封装、引用子空间时会触发子空间的这个方法
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {
console.log("AndroidTestComponent=====componentWillReceiveProps")
}
//在props 和 state更新之后,根据返回值判断是否需要更新 true 需要 false 不需要
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
console.log("AndroidTestComponent=====shouldComponentUpdate")
console.log(nextProps)
console.log(nextState)
return true;
}
//component将要更新时调用
componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
console.log("AndroidTestComponent=====componentWillUpdate")
console.log(nextProps)
console.log(nextState)
}
//component更新后调用
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
console.log("AndroidTestComponent=====componentDidUpdate")
console.log(prevProps)
console.log(prevState)
}
//component销毁时调用
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log("AndroidTestComponent=====componentWillUnmount")
}
}
//另一种定义props的方法,如果static defaultProps也定义了,这个会覆盖上面的
// AndroidTestComponent.defaultProps = {
// name:'xiaoerlang'
// }
//进行注册 'RNProject'为项目名称 AndroidTestComponent 为启动的component
AppRegistry.registerComponent('RNProject', () => AndroidTestComponent);
打印log
1、reload
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): AndroidTestComponent=====constructor
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): AndroidTestComponent=====componentWillMount
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): AndroidTestComponent=====render
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): AndroidTestComponent=====componentDidMount
2、点击‘这是一个简单的测试text’
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): AndroidTestComponent=====shouldComponentUpdate
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): { rootTag: 1, color: 'red' }
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): { name: 'wwoairuibaobao' }
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): AndroidTestComponent=====componentWillUpdate
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): { rootTag: 1, color: 'red' }
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): { name: 'wwoairuibaobao' }
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): AndroidTestComponent=====render
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): AndroidTestComponent=====componentDidUpdate
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): { rootTag: 1, color: 'red' }
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): { name: 'ruibaobao' }
如果shouldComponentUpdate返回false即
//在props 和 state更新之后,根据返回值判断是否需要更新 true 需要 false 不需要
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
console.log("AndroidTestComponent=====shouldComponentUpdate")
console.log(nextProps)
console.log(nextState)
return false;
}
点击text后log
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): AndroidTestComponent=====componentWillUpdate
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): { rootTag: 1, color: 'red' }
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): { name: 'wwoairuibaobao' }
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): AndroidTestComponent=====render
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): AndroidTestComponent=====componentDidUpdate
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): { rootTag: 1, color: 'red' }
I/ReactNativeJS(24891): { name: 'wwoairuibaobao' }
这个时候默认是没有进行渲染的,只有调用forceUpdate才会渲染。
参考文章
英文官网
CSDN RN入门简介
CSDN component生命周期
ps:以上网站部分不是最新的语法。