字节跳动专场:力扣第 197 场周赛
1、好数对的数目
1、题目描述
2、题解:
方法1:暴力法
两次循环,找满足条件的对数
class Solution:
def numIdenticalPairs(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
#暴力法
res = 0
for i in range(len(nums)-1):
for j in range(i+1,len(nums)):
if nums[i] == nums[j]:
res += 1
return res方法2:哈希表法:
先建立哈希表,统计每个数出现几次;
遍历,计算好数对:对于每个单词出现的次数,计算好数对:v*(v-1)//2
class Solution:
def numIdenticalPairs(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
#哈希表法
# hashmap = {}
hashmap = collections.defaultdict(int)
#遍历,建立哈希表,统计每个数出现几次
for num in nums:
hashmap[num] += 1
#遍历,计算好数对
res = 0
for key,v in hashmap.items():
if v > 1:
res += v*(v-1)//2
return res2、仅含 1 的子串数
1、题目描述:
2、题解:
方法1:从后往前遍历
class Solution:
def numSub(self, s: str) -> int:
x = 0
res = 0
for i in range(len(s) - 1,-1,-1):
if s[i] == '0':
x = 0
else:
x += 1
res += x
return int(res % (1e9 + 7))方法2:双指针法
class Solution:
def numSub(self, s: str) -> int:
#双指针
ln = len(s)
left,right = 0,0
res = 0
while right < ln:
if '1' not in s[right+1:]:
if '0' not in s[left:right+1]:
res += sum(range(1,right-left+2))
left = right + 1
break
if '0' not in s[left:right+1] and s[right+1] == '0':
res += sum(range(1,right-left+2))
left = right+1
if left >= ln:
break
if s[left] == '0':
left += 1
right += 1
return res %1000000007遍历,求连续1的个数,用公式v(v+1)//2*
class Solution:
def numSub(self, s: str) -> int:
#双指针
left,right = 0,1
if not s:return 0
n = len(s)
res = 0
while left < n and right < n:
if s[left] == '1':
right = left + 1
while right < n and s[right] == '1':
right += 1
temp = right - left
res += temp * (temp + 1) // 2
left = right
else:
left += 1
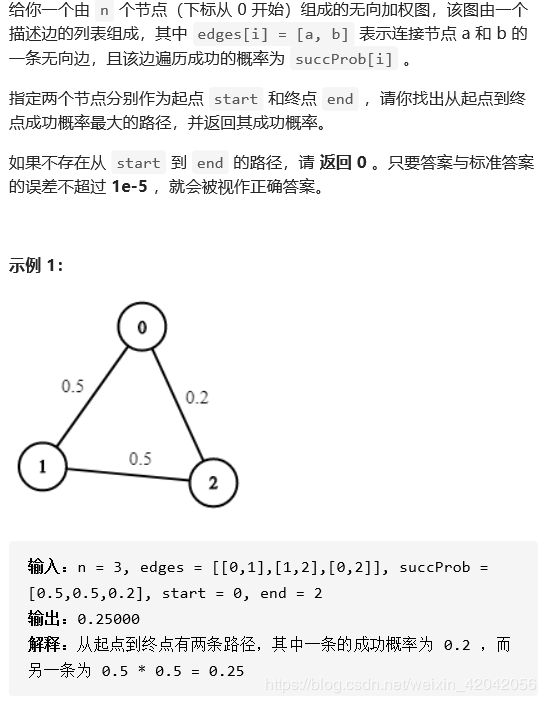
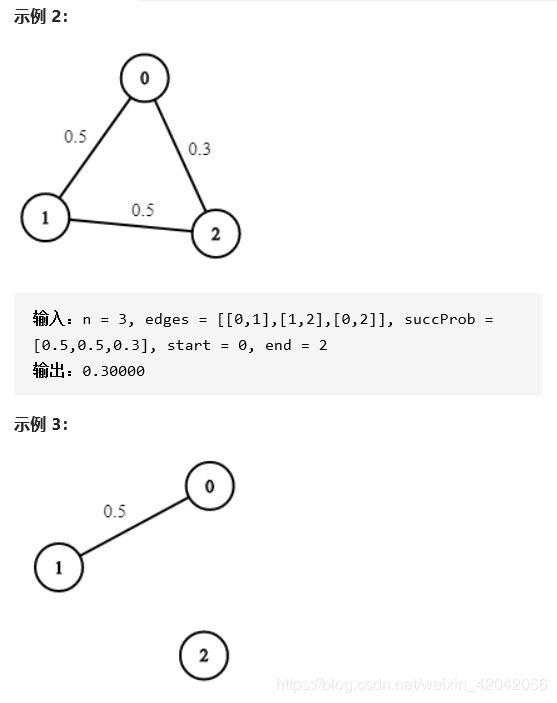
return int(res % (1e9 + 7))3、概率最大的路径
1、题目描述:
2、题解:
class Solution:
def maxProbability(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], succProb: List[float], start: int, end: int) -> float:
#BFS
if not edges or not edges[0]: return 0
# 构造节点邻接表
from collections import defaultdict
st_maps = defaultdict(list)
for i, (s, e) in enumerate(edges):
st_maps[s].append((e, succProb[i]))
st_maps[e].append((s, succProb[i]))
ans = 0
queue = deque([(start, 1)])
visited = {start: 0}
while queue:
# 当前节点
cur_node, cur_prob = queue.popleft()
for next_node, p in st_maps[cur_node]:
# 下一个待遍历的节点
next_prob = cur_prob * p
if next_node == end:
ans = max(ans, next_prob)
continue
# 剪枝和去重:如果下一个待遍历节点的概率大于ans && (该节点为遍历过 或 遍历过该节点但是上次的概率比现在小)
if next_prob > ans and (next_node not in visited or visited[next_node] < next_prob):
visited[next_node] = next_prob
queue.append((next_node, next_prob))
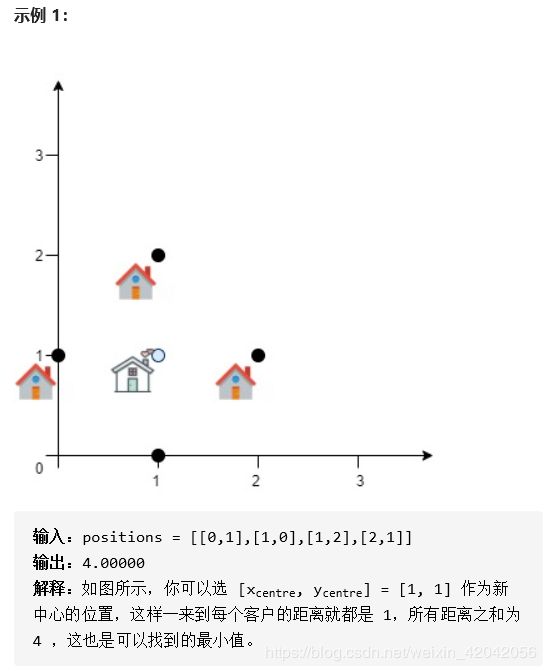
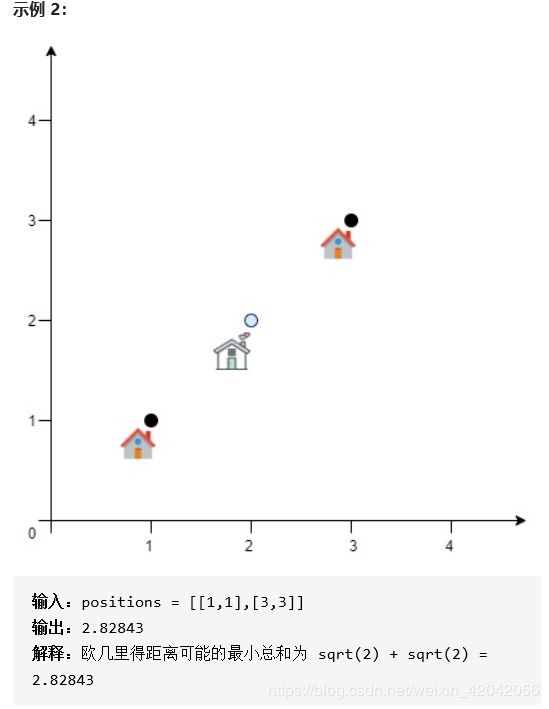
return ans4、服务中心的最佳位置
1、题目描述:
2、题解:
class Solution:
def getMinDistSum(self, positions: List[List[int]]) -> float:
# 到各点距离之和
def dis(x, y):
return sum([((px - x) ** 2 + (py - y) ** 2) ** 0.5 for px, py in positions])
# 三分找最小
def three_divide(l, r, f, eps=1e-6):
while r - l > eps:
m = l + (r - l) / 3
mm = r - (r - l) / 3
if f(m) < f(mm):
r = mm
else:
l = m
return (l + r) / 2
# 左右边界
lmin, rmax = 0, 100
# 外层查x,x=mx时最小距离
def xf(mx):
# 内层查y,x=mx且y=my的距离
def yf(my): return dis(mx, my)
return dis(mx, three_divide(lmin, rmax, yf))
x = three_divide(lmin, rmax, xf)
y = three_divide(lmin, rmax, lambda my: dis(x, my))
return dis(x, y)