剑指offer 学习笔记 + 程序注释
main.h 头文件中的内容:
#include "iostream"
#include "vector"
#include "string"
#include "list"
#include "deque"
#include "utility"
#include "map"
#include "set"
#include "fstream"
#include "sstream"
#include "algorithm"
#include "numeric"
#include "iterator"
#include "functional"
#include "typeinfo.h"
#include "memory"
using namespace std;
注意各个程序的测试用例,首先想出程序的测试用例
程序·1: 书上 12 页
【把一个字符串转换成为一个数组】#include "D:\worwor\main.h"
// StringToInt.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
// 《剑指Offer——名企面试官精讲典型编程题》代码
// 著作权所有者:何海涛
/*
这个程序是何海涛老师所写的《剑指offer》上的题目的程序代码。特加上注释供以后复习使用。
【把一个字符串转换成为一个数组】
这个程序的作用是输入一个数字组成的字符串 例如: "123456" , char a[]="123456" , char * b ="123456";然后把这个字符串转换成为一个int类型的整数。
比如输入字符串 "123456" 输出整数 : 123456
*/
#include
#include
long long StrToIntCore(const char* str, bool minus);
enum Status { kValid = 0, kInvalid };//valid 有效的 invalid 无效的
int g_nStatus = kValid;
int StrToInt(const char * str)//因为输入的是 "123"这种形式的,所以是const char *
{
g_nStatus = kInvalid;//设置为无效
long long num = 0;//long long 类型是8个字节。
if (str != NULL && *str != '\0')//为了防止输入的str是一个空串 "" 或者是一个空指针NULL。
{
bool minus = false;//判断是否为负数。
if (*str == '+')//如果是一个整数+123那么
str++;
else if (*str == '-')
{
str++;
minus = true;//如果是负数
}
if (*str != '\0')
{
num = StrToIntCore(str, minus);//通过str传递去掉+ / - 号之后的数字,通过minus传递这个数的+ / -。
}
}
return (int)num; //num是一个long long类型 ,强制转换成为int类型之后返回。
}
long long StrToIntCore(const char* digit, bool minus) //digit 数字
{
long long num = 0;
while (*digit != '\0')
{
if (*digit >= '0' && *digit <= '9')
{
int flag = minus ? -1 : 1; //minus等于 true 则返回 -1,否则返回false
num = num * 10 + flag * (*digit - '0');
if ((!minus && num > 0x7FFFFFFF) //负数是true 最大正整数:2147483647
|| (minus && num < (signed int)0x80000000))//有符号整数 最小负整数:-2147483648
{
num = 0;
break;
}
digit++;
}
else
{
num = 0;
break;
}
}
if (*digit == '\0')
/*
比如1a33,第一个 1 是执行完转换了,但是a不满足if (*digit >= '0' && *digit <= '9')所以
前面的while循环停止了,但是整个串并没有真正的转换完毕,只是执行到a就停止了。
所以 *digit == '\0' 不成立 而是 *digit == 'a'所以设置 g_nStatus = kValid ;
*/
{
g_nStatus = kValid;
}
return num;
}
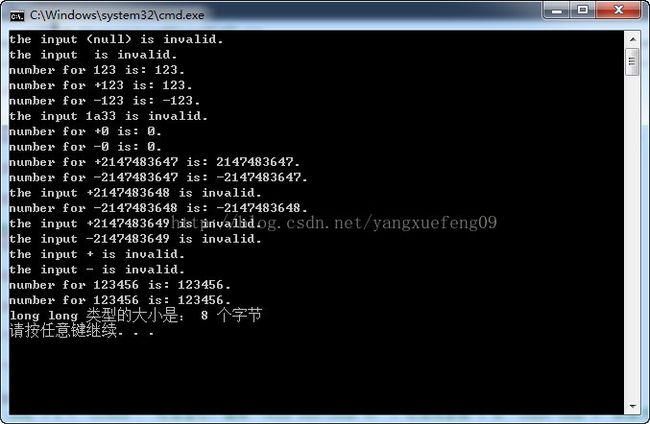
// ====================测试代码====================
void Test(char* string)
{
int result = StrToInt(string);
if (result == 0 && g_nStatus == kInvalid)
printf("the input %s is invalid.\n", string);
else
printf("number for %s is: %d.\n", string, result);
}
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
Test(NULL);
Test("");
Test("123");
Test("+123");
Test("-123");
Test("1a33");
Test("+0");
Test("-0");
//有效的最大正整数, 0x7FFFFFFF
Test("+2147483647"); //int型为有符号32位整数,占4个字节,取值范围在-2,147,483,648~2,147,483,647之间。
Test("-2147483647");
Test("+2147483648");
//有效的最小负整数, 0x80000000
Test("-2147483648");
Test("+2147483649");
Test("-2147483649");
Test("+");
Test("-");
char a[10] = "123456";
//const char * b = "123456"; 无法运行:错误“void Test(char *)”: 无法将参数 1 从“const char *”转换为“char *”
char * b = "123456";
Test(a);
Test(b);
cout <<"long long 类型的大小是: " < 程序2: 书上22页面
空类,有构造函数的类,有虚函数的类,不同的类的大小
#include "D:\C++OBJECT\main.h"
class A0
{
//空类型
};
class A1
{
//有构造函数和析构函数的类型
public:
A1();
~A1();
};
class A2
{
//有虚析构函数
A2();
virtual ~A2();
};
int main()
{
cout<<"空类型,占用内存大小: "<
面试题目1:两个等价的 operator = 的实现。
// AssignmentOperator.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
// 《剑指Offer——名企面试官精讲典型编程题》代码
// 著作权所有者:何海涛
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
class CMyString
{
public:
CMyString(char* pData = NULL);
CMyString(const CMyString& str);
~CMyString(void);
CMyString& operator = (const CMyString& str);
void Print();
private:
char* m_pData;
};
CMyString::CMyString(char *pData)
{
if(pData == NULL)
{
m_pData = new char[1];
m_pData[0] = '\0';
}
else
{
int length = strlen(pData);
m_pData = new char[length + 1];
strcpy(m_pData, pData);
}
}
CMyString::CMyString(const CMyString &str)
{
int length = strlen(str.m_pData);
m_pData = new char[length + 1];
strcpy(m_pData, str.m_pData);
}
CMyString::~CMyString()
{
delete[] m_pData;
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CMyString& CMyString::operator = (const CMyString& str)
{
/*
if(this == &str)
return *this;
delete []m_pData;
m_pData = NULL;
m_pData = new char[strlen(str.m_pData) + 1];
strcpy(m_pData, str.m_pData);
return *this;
*/
if (this!=&str)
{
CMyString strTemp(str);
char * pTemp = strTemp.m_pData;
strTemp.m_pData = m_pData;
m_pData = pTemp;
}
return *this;
}
//最重要的是注意上面两个等价的operator=操作的实现。 面试题2 实现 singleton(单例) 模式 书上是使用C# 实现 ,因为C#一点没有学过。 这里使用C++实现。
转自博客:http://blog.csdn.net/boyxiaolong/article/details/6645681
//单例类的C++实现
#include
using namespace std;
class Singleton
{
private:
Singleton();//注意:构造方法私有
static Singleton* instance;//惟一实例
int var;//成员变量(用于测试)
public:
static Singleton* GetInstance();//工厂方法(用来获得实例)
int getVar();//获得var的值
void setVar(int);//设置var的值
virtual ~Singleton();
};
//构造方法实现
Singleton::Singleton()
{
this->var = 20;
cout << "Singleton Constructor" << endl;
}
Singleton::~Singleton()
{
cout << "Singleton Destructor" << endl;
//delete instance;
}
//初始化静态成员
/*Singleton* Singleton::instance=NULL;
Singleton* Singleton::GetInstance()
{
if(NULL==instance)
instance=new Singleton();
return instance;
}*/
Singleton* Singleton::instance = new Singleton;
Singleton* Singleton::GetInstance()
{
return instance;
}
//seter && getter含数
int Singleton::getVar()
{
return this->var;
}
void Singleton::setVar(int var)
{
this->var = var;
}
//main
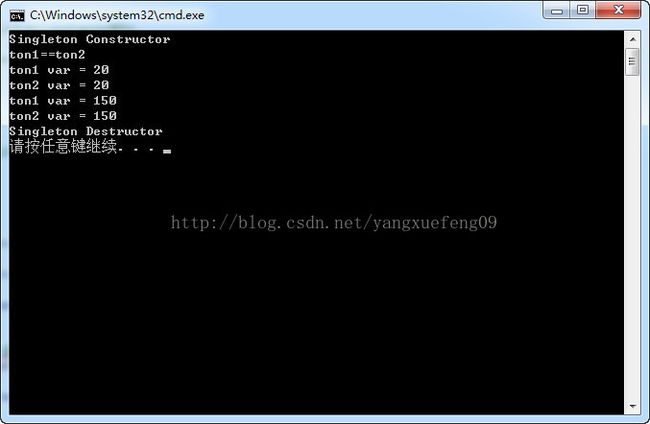
void main()
{
Singleton *ton1 = Singleton::GetInstance();
Singleton *ton2 = Singleton::GetInstance();
if (ton1 == ton2)
cout << "ton1==ton2" << endl;
cout << "ton1 var = " << ton1->getVar() << endl;
cout << "ton2 var = " << ton2->getVar() << endl;
ton1->setVar(150);
cout << "ton1 var = " << ton1->getVar() << endl;
cout << "ton2 var = " << ton2->getVar() << endl;
delete Singleton::GetInstance();//必须显式地删除
} 
程序3 :排序算法,要求时间复杂度是 O(n) 需要的辅助空间的大小是:空间复杂度是 O(1) 常量。对公司所有员工的年龄进行排序,公司的员工约有几万人。
#include "iostream"
#include "D:\worwor\main.h"
void print(int Array[], int length)//对数组进行排序
{
cout << "\n-------------------------------------------------------------" << endl;
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length;++i)
{
cout << Array[i] <<" ";
++j;
if (j==10)
{
cout << endl;
j = 0;
}
}
cout << "\n-------------------------------------------------------------" << endl;
}
void SortAages(int ages[], int length)
{
if (ages == NULL || length <= 0)
return;
const int oldestAge = 9;
int timesOfAge[oldestAge + 1];
print(ages, length);
for (int i = 0; i <= oldestAge;++i)
{
timesOfAge[i] = 0;
}
print(timesOfAge, 9);
for (int i = 0; i < length;++i)
{
int age = ages[i];
if (age<0 || age>oldestAge)
{
throw new std::exception("age out of range.");
}
++timesOfAge[age];
}
print(ages, length);
print(timesOfAge, 9);
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
********************************************//整个程序的最关键的代码部分。*********************************************
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= oldestAge;++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < timesOfAge[i];++j)
{
ages[index] = i;
++index;
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
print(ages, length);
}
int main()
{
int company[30] = { 1,2,5,3,4,5,4,1,5,1,2,8,9,4,5,7,1,2,4,6,4,7,3,6,7 };
SortAages(company, 30);
cout << endl << endl;
print(company, 30);
}
面试题33:把数组排成最小的数
这个代码看了很久主要是 对指向字符串数组的指针没有很好的理解。还有不知道qsort函数的使用方式。
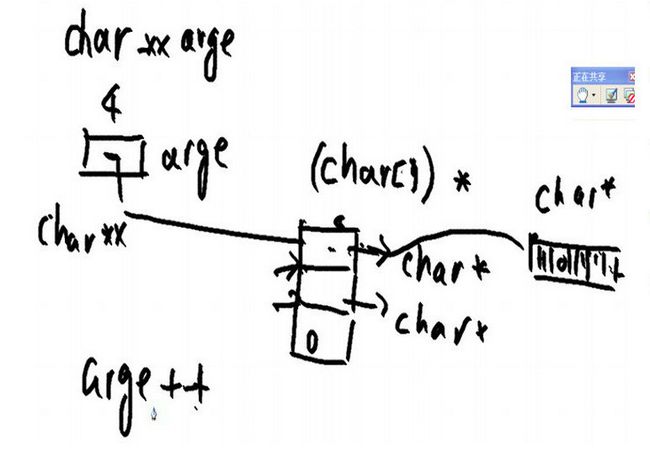
在《Linux高级编程》中第三次课程。老师有讲过 main()函数中通过 参数与获得环境变量的时候。使用了指向字符串数组的指针,也就是二级指针。
其中有(命令行参数argv)和(环境行参数arge) 他们都是字符串数组。通过上面的图,可以看出指向字符串数组的指针的关系。
关于qsort函数在MSDN上有详细的解释,一看就懂:https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/zes7xw0h.aspx
// crt_qsort.c
// arguments: every good boy deserves favor
/* This program reads the command-line
* parameters and uses qsort to sort them. It
* then displays the sorted arguments.
*/
#include
#include
#include
int compare( const void *arg1, const void *arg2 );
int main( int argc, char **argv )
{
int i;
/* Eliminate argv[0] from sort: */
argv++; //这里为什么要减去一。让这个程序在命令行中运行的时候。第一个参数是这个程序本身的名字。所有这个程序名字本身不进行排序所以,要从argv++开始
argc--; //同时要把参数的个数argc减去一
/* Sort remaining args using Quicksort algorithm: */
qsort( (void *)argv, (size_t)argc, sizeof( char * ), compare );
/* Output sorted list: */
for( i = 0; i < argc; ++i )
printf( " %s", argv[i] );
printf( "\n" );
}
int compare( const void *arg1, const void *arg2 )
{
/* Compare all of both strings: */
return _stricmp( * ( char** ) arg1, * ( char** ) arg2 );
} 另外关于 stricmp的使用,如下:https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/k59z8dwe.aspx
int _stricmp(
const char *string1,
const char *string2
);
这样这个代码的运行我就全明白了 !!!
面试题34:书上写的 有些不太明白,但是网友博客写的很明白。http://www.cnblogs.com/xwdreamer/archive/2012/09/25/2701185.html
题目:我们把只包含因子2,3和5的数称作为丑数。求按从小到大的顺序的第1500个丑数。例如6,8都是丑数,但是14不是,因为它包含因子7。习惯上我们把1作为第一个丑数。
方法一:遍历法
使用遍历法求第k个丑数,从1开始遍历,如果是丑数则count++,直到count==k为止。那么如何判断丑数呢?根据丑数的定义,丑数只有2,3,5这三个因子,那么我们就拿数字除以这三个因子。具体算法如下:
- 如果一个数能够被2整除,那么让他继续除以2;
- 如果一个数能够被3整除,那么让他继续除以3;
- 如果一个数能够被5整除,那么让他继续除以5;
- 如果最后这个数变为1,那么这个数就是丑数,否则不是。
代码实现如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
//判断是否为丑数
bool isUgly(int number)
{
while(number%2==0)
number=number/2;
while(number%3==0)
number=number/3;
while(number%5==0)
number=number/5;
return (number==1)?true:false;
}
//获取第k个丑数,假定1为第一个丑数
int getUglyNumber(int index)
{
int number=0;
int count=0;
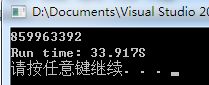
while(count 程序的运行结果如下:
我们发现一共耗时33秒,性能比较低。
方法二:创建丑数数组,用空间还时间
如前所述,我们发现采用遍历法求第K个丑数的效率十分低下,我们在前面求第1500个丑数花去了33秒的时间,这还是在我I7 3770K的电脑上运行的。所以我们考虑有没有一种更加高效的方法。在面试题9:斐波那契数列中我们使用了一种“用空间还时间”的方法来提高求斐波那契数列的速度。这种编程思想也可以应用在这道题目当中,我们为所有求出的丑数创建数组,不在非丑数上面浪费时间。
根据丑数的定义,我们可以知道丑数可以由另外一个丑数乘以2,3或者5得到。因此我们创建一个数组,里面的数字是排好序的丑数,每一个丑数都是前面的丑数乘以2,3或者5得到的。这种思路的关键在于怎样确保数组里面的数字是排序的。
假设丑数数组中已经有若干个排好序的丑数,比如1,2,3,4,5。我们把当前丑数数组中的最大数记为M,这里M=5。我们接下来分析如何生成下一个丑数。根据前面的介绍,我们知道这个丑数肯定是前面丑数数组中的数字乘以2,3,5得到的。所以我们首先考虑把已有的每个丑数乘以2,在乘以2的时候,能够得到若干个小于或者等于M的结果。由于是按照顺序生成的,小于或者等于M的数肯定已经在丑数数组当中了,我们不需要再次考虑;当然还会得到若干大于M的结果,但是我们只需要第一个大于M的结果,因为我们希望丑数是按顺序排列的,所以其他更大的结果可以以后考虑。我们把得到的第一个乘以2以后得到的大于M的结果记为M2。同样,我们把已有的每一个丑数乘以3和5,能得到第一个大于M的结果M3和M5。那么M后面的那一个丑数应该是M2,M3和M5当中的最小值:Min(M2,M3,M5)。比如将丑数数组中的数字按从小到大乘以2,直到得到第一个大于M的数为止,那么应该是2*2=4
前面分析的时候,提到把已有的每个丑数分别都乘以2,3和5。事实上这不是必须的,因为已有的丑数是按顺序存放在数组中的,对乘以2而言,肯定存在某一个丑数T2,排在她之前的每一个丑数乘以2得到的结果都会小于等于(<=)已有最大的丑数,在它之后的每一个丑数乘以2得到的结果都会大于已有的最大丑数。因此我们只需要记下这个丑数的位置,同时每次生成新的丑数的时候去更新这个T2。对于乘以3和5,同样存在这样的T3和T5。
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
//求M2,M3,M5的最小值
int Min(int number1,int number2,int number3)
{
int min=(number1 注意点:在程序最后有delete[] pUglyNumbers;这是因为动态数组与数组变量不同,动态分配的数组将一直存在,直到程序显式释放它为止。普通的数组变量,只要出了数组的作用于,其内存会自动释放。c++提供delete []表达式释放指针所指向的数组空间
面试题目50:
其中有如下的代码,其中的一行,让我感到很迷惑,以为树结点中就有这样的一个成员.m_vChildren.begin()。于是我们去作者附给的代码中找到了答案
bool GetNodePath(TreeNode* pRoot, TreeNode* pNode, list& path)
{
if(pRoot == pNode)
return true;
path.push_back(pRoot);
bool found = false;
vector::iterator i = pRoot->m_vChildren.begin();//**//就是这样的一行代码,让我感到很困惑。//**// 后来在相应的头文件和cpp文件中找到了相应的定义和实现,这样我就看懂了。
while(!found && i < pRoot->m_vChildren.end())
{
found = GetNodePath(*i, pNode, path);
++i;
}
if(!found)
path.pop_back();
return found;
}
struct TreeNode
{
int m_nValue;
std::vector m_vChildren; //在树结点的定义中添加了一个向量vector用来保存,这个树结点的所有的孩子。于是我们就可以通过迭代器iterator 来遍历一个结点的所有的孩子。
};
void ConnectTreeNodes(TreeNode* pParent, TreeNode* pChild)
{//通过这个函数的调用把创建出来的根结点和树中的每一个结点之间建立相应的父子关系。
if(pParent != NULL)
{
pParent->m_vChildren.push_back(pChild);
}
}
// 形状普通的树
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \
// 4 5
// / \ / | \
// 6 7 8 9 10
void Test1()
{
TreeNode* pNode1 = CreateTreeNode(1);
TreeNode* pNode2 = CreateTreeNode(2);
TreeNode* pNode3 = CreateTreeNode(3);
TreeNode* pNode4 = CreateTreeNode(4);
TreeNode* pNode5 = CreateTreeNode(5);
TreeNode* pNode6 = CreateTreeNode(6);
TreeNode* pNode7 = CreateTreeNode(7);
TreeNode* pNode8 = CreateTreeNode(8);
TreeNode* pNode9 = CreateTreeNode(9);
TreeNode* pNode10 = CreateTreeNode(10);
//看上面通过了一系列的调用CreateTreeNode这个函数,就会创建出一系列的结点。然后我们通过上面的定义得ConnectTreeNodes()函数把相应的节点添加到它的父亲结点的vector中。
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode1, pNode2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode1, pNode3);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode2, pNode4);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode2, pNode5);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode4, pNode6);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode4, pNode7);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode5, pNode8);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode5, pNode9);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode5, pNode10);
Test("Test1", pNode1, pNode6, pNode8, pNode2);
}面试题目46:236页面 其中有用static这个关键字来修饰函数指针。代码如下:
typedef unsigned int (*fun)(unsigned int);
unsigned int Solution3_Teminator(unsigned int n)
{
return 0;
}
unsigned int Sum_Solution3(unsigned int n)
{
static fun f[2] = {Solution3_Teminator, Sum_Solution3}; //这里为什么使用static关键字来修饰这个函数指针。关于它的解释见下面的博客。
return n + f[!!n](n - 1);
}
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-22590270-id-3205014.html 这里讲解了用static这个关键字修饰函数指针意义。
剑指offer 纪念版上的题目 面试题55 :
numeric_limits
umeric_limits::max () 是函数,返回编译器允许的 double 型数 最大值。 类似的 numeric_limits ::max () 返回 编译器允许的 int 型数 最大值。 需包含头文件 #include 例子: #include #include using namespace std; main(){ cout << std::numeric_limits ::max () << endl; cout << std::numeric_limits ::max () << endl; }
这个东西就是一个函数,返回编译器允许的最大的类型的数值。
今天做 剑指offer的纪念版本上面的第64题目,出现了堆的使用,完全搞不明白,特查资料如下:
stl中的堆默认是最大堆,要想用最小堆的话,必须要在push_heap,pop_heap,make_heap等每一个函数后面加第三个参数greater
1、make_heap:使序列变成堆
原型:template
void make_heap ( RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last );
template
void make_heap ( RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last,
Compare comp );
// range heap example
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
template void print(T t_begin, T t_end);
int main()
{
int myints[] = { 10, 20, 30, 5, 15 };
vector v(myints, myints + 5);
print(v.begin(), v.end());
make_heap(v.begin(), v.end());
print(v.begin(), v.end());
cout << "initial max heap : " << v.front() << endl;
pop_heap(v.begin(), v.end());
v.pop_back();
print(v.begin(), v.end());
cout << "max heap after pop : " << v.front() << endl;
v.push_back(99);
push_heap(v.begin(), v.end());
cout << "max heap after push: " << v.front() << endl;
sort_heap(v.begin(), v.end());
cout << "final sorted range :";
for (unsigned i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
cout << " " << v[i];
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
template
void print(T t_begin, T t_end)
{
T t_begin1 = t_begin;
while (t_begin1 != t_end)
{
cout << *t_begin1 << " ";
++t_begin1;
}
cout << endl;
} 从上面的程序可以看出,这些堆操作函数,会完全的改变,容器中的数据。我在各个地方使用了print()函数,来进行输出,可以看到输出的vector内容是不同的,所以堆操作的这四个函数会改变堆中的内容。
2、push_heap:压栈(入栈)
原型:
template
void push_heap ( RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last );
template
void push_heap ( RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last,
Compare comp );
3、pop_heap:弹栈(出栈)
原型:
template
void pop_heap ( RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last );
template
void pop_heap ( RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last,
Compare comp ); // range heap example
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
template void print(T t_begin, T t_end);
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int myints[] = { 10, 20, 30, 5, 15 };
vector v(myints, myints + 5);
print(v.begin(), v.end());
vector::iterator it;
make_heap(v.begin(), v.end());
print(v.begin(), v.end());
cout << "initial max heap : " << v.front() << endl;
pop_heap(v.begin(), v.end());
print(v.begin(), v.end());
v.pop_back();
print(v.begin(), v.end());
cout << "max heap after pop : " << v.front() << endl;
v.push_back(99);
print(v.begin(), v.end());
push_heap(v.begin(), v.end());
print(v.begin(), v.end());
cout << "max heap after push: " << v.front() << endl;
sort_heap(v.begin(), v.end());
print(v.begin(), v.end());
cout << "final sorted range :";
for (unsigned i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) cout << " " << v[i];
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
template
void print(T t_begin, T t_end)
{
T t_begin1 = t_begin;
while (t_begin1 != t_end)
{
cout << *t_begin1 << " ";
++t_begin1;
}
cout << endl;
} 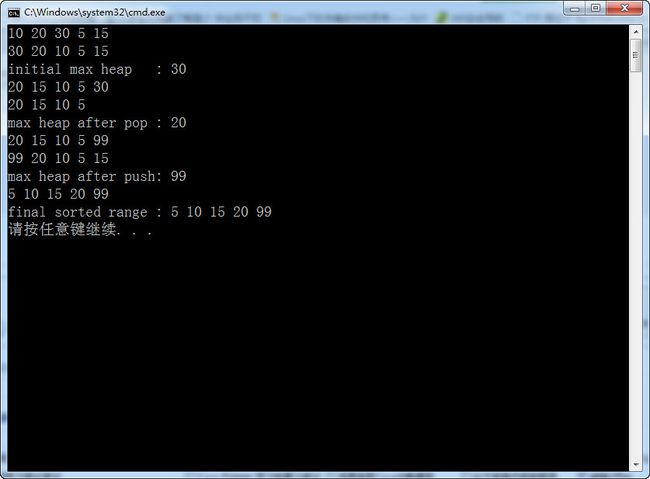
注意看上面的图片,我们可以看到,pop_heap()这个函数只是把堆中应该被弹出的元素,放置到了容器的末尾,并没有真正的从容器中删除这个元素。所以要在堆中真正的弹出这个元素,除了调用pop_heap()函数外,还要在调用这个函数之后再调用容器自身的v.pop_back()函数。这样这个元素就真正的被删除掉了。