Spring-tx模块分析
Spring-tx模块负责在spring框架中实现事务管理功能。以aop切面的方式将事务注入到业务代码中,并实现不同类型的事务管理器。这篇文章主要介绍Spring-tx模块aop切面的相关实现类型
TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor:使用TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut来确定拦截位置
类型定义:
public class TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor extends AbstractPointcutAdvisor属性:
@Nullable
private TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor;
private final TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut pointcut = new TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut() {
@Override
protected TransactionAttributeSource getTransactionAttributeSource() {
return (transactionInterceptor != null ? transactionInterceptor.getTransactionAttributeSource() : null);
}
};核心方法:
@Override
public Advice getAdvice() {
Assert.state(this.transactionInterceptor != null, "No TransactionInterceptor set");
return this.transactionInterceptor;
}
@Override
public Pointcut getPointcut() {
return this.pointcut;
}TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut具体实现:
abstract class TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcut implements Serializable {
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, @Nullable Class targetClass) {
if (targetClass != null && TransactionalProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) {
if (this == other) {
return true;
}
if (!(other instanceof TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut)) {
return false;
}
TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut otherPc = (TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut) other;
return ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(getTransactionAttributeSource(), otherPc.getTransactionAttributeSource());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut.class.hashCode();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + ": " + getTransactionAttributeSource();
}
/**
* Obtain the underlying TransactionAttributeSource (may be {@code null}).
* To be implemented by subclasses.
*/
@Nullable
protected abstract TransactionAttributeSource getTransactionAttributeSource();
}TransactionAttributeSource:使用策略模式获取事务元数据
/**
* Strategy interface used by {@link TransactionInterceptor} for metadata retrieval.
*
* Implementations know how to source transaction attributes, whether from configuration,
* metadata attributes at source level (such as Java 5 annotations), or anywhere else.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @since 15.04.2003
* @see TransactionInterceptor#setTransactionAttributeSource
* @see TransactionProxyFactoryBean#setTransactionAttributeSource
* @see org.springframework.transaction.annotation.AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource
*/
public interface TransactionAttributeSource {
/**
* Return the transaction attribute for the given method,
* or {@code null} if the method is non-transactional.
* @param method the method to introspect
* @param targetClass the target class (may be {@code null},
* in which case the declaring class of the method must be used)
* @return TransactionAttribute the matching transaction attribute,
* or {@code null} if none found
*/
@Nullable
TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class targetClass);
}
UML结构图如下:
这里重点介绍下AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource和AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource
AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource:根据targetClass和method生成TransactionAttribute
核心方法:
1.getTransactionAttribute
/**
* Determine the transaction attribute for this method invocation.
* Defaults to the class's transaction attribute if no method attribute is found.
* @param method the method for the current invocation (never {@code null})
* @param targetClass the target class for this invocation (may be {@code null})
* @return TransactionAttribute for this method, or {@code null} if the method
* is not transactional
*/
@Override
public TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class targetClass) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return null;
}
// First, see if we have a cached value.
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(method, targetClass);
Object cached = this.attributeCache.get(cacheKey);
if (cached != null) {
// Value will either be canonical value indicating there is no transaction attribute,
// or an actual transaction attribute.
if (cached == NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE) {
return null;
}
else {
return (TransactionAttribute) cached;
}
}
else {
// We need to work it out.
TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
// Put it in the cache.
if (txAttr == null) {
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE);
}
else {
String methodIdentification = ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(method, targetClass);
if (txAttr instanceof DefaultTransactionAttribute) {
((DefaultTransactionAttribute) txAttr).setDescriptor(methodIdentification);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Adding transactional method '" + methodIdentification + "' with attribute: " + txAttr);
}
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, txAttr);
}
return txAttr;
}
}
备注:通过调用computeTransactionAttribute方法来获取TransactionalAttribute
2.computeTransactionAttribute
/**
* Same signature as {@link #getTransactionAttribute}, but doesn't cache the result.
* {@link #getTransactionAttribute} is effectively a caching decorator for this method.
* As of 4.1.8, this method can be overridden.
* @since 4.1.8
* @see #getTransactionAttribute
*/
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttribute computeTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class targetClass) {
// Don't allow no-public methods as required.
if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
return null;
}
// Ignore CGLIB subclasses - introspect the actual user class.
Class userClass = (targetClass != null ? ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass) : null);
// The method may be on an interface, but we need attributes from the target class.
// If the target class is null, the method will be unchanged.
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, userClass);
// If we are dealing with method with generic parameters, find the original method.
specificMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
// First try is the method in the target class.
TransactionAttribute txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod);
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// Second try is the transaction attribute on the target class.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
if (specificMethod != method) {
// Fallback is to look at the original method.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method);
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// Last fallback is the class of the original method.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
}
return null;
}
需要子类扩展的方法如下:
1.protected abstract TransactionAttribute findTransactionAttribute(Method method);
2.protected abstract TransactionAttribute findTransactionAttribute(Class clazz);
AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource:读取类或者方法上的@Transactional注解内容来生成TransactionAttribute
属性:
private static final boolean jta12Present = ClassUtils.isPresent(
"javax.transaction.Transactional", AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource.class.getClassLoader());
private static final boolean ejb3Present = ClassUtils.isPresent(
"javax.ejb.TransactionAttribute", AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource.class.getClassLoader());
private final boolean publicMethodsOnly;
private final Set annotationParsers; 核心方法:
1.findTransactionAttribute
@Override
protected TransactionAttribute findTransactionAttribute(Method method) {
return determineTransactionAttribute(method);
}
@Override
protected TransactionAttribute findTransactionAttribute(Class clazz) {
return determineTransactionAttribute(clazz);
}
/**
* Determine the transaction attribute for the given method or class.
* This implementation delegates to configured
* {@link TransactionAnnotationParser TransactionAnnotationParsers}
* for parsing known annotations into Spring's metadata attribute class.
* Returns {@code null} if it's not transactional.
*
Can be overridden to support custom annotations that carry transaction metadata.
* @param ae the annotated method or class
* @return TransactionAttribute the configured transaction attribute,
* or {@code null} if none was found
*/
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttribute determineTransactionAttribute(AnnotatedElement ae) {
for (TransactionAnnotationParser annotationParser : this.annotationParsers) {
TransactionAttribute attr = annotationParser.parseTransactionAnnotation(ae);
if (attr != null) {
return attr;
}
}
return null;
}
备注:使用TransactionAnnotationParser类型的parseTransactionAnnotation方法进行AnnotatedElement到TransactionAttribute之间的转变
具体可以参考SpringTransactionAnnotationParser
protected TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
RuleBasedTransactionAttribute rbta = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute();
Propagation propagation = attributes.getEnum("propagation");
rbta.setPropagationBehavior(propagation.value());
Isolation isolation = attributes.getEnum("isolation");
rbta.setIsolationLevel(isolation.value());
rbta.setTimeout(attributes.getNumber("timeout").intValue());
rbta.setReadOnly(attributes.getBoolean("readOnly"));
rbta.setQualifier(attributes.getString("value"));
ArrayList rollBackRules = new ArrayList<>();
Class[] rbf = attributes.getClassArray("rollbackFor");
for (Class rbRule : rbf) {
RollbackRuleAttribute rule = new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule);
rollBackRules.add(rule);
}
String[] rbfc = attributes.getStringArray("rollbackForClassName");
for (String rbRule : rbfc) {
RollbackRuleAttribute rule = new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule);
rollBackRules.add(rule);
}
Class[] nrbf = attributes.getClassArray("noRollbackFor");
for (Class rbRule : nrbf) {
NoRollbackRuleAttribute rule = new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule);
rollBackRules.add(rule);
}
String[] nrbfc = attributes.getStringArray("noRollbackForClassName");
for (String rbRule : nrbfc) {
NoRollbackRuleAttribute rule = new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule);
rollBackRules.add(rule);
}
rbta.getRollbackRules().addAll(rollBackRules);
return rbta;
} AnnotationTransactionAspect:通过AspectJ方式根据org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional注解生成事务proxy
UML类图如下:
构造函数如下:
public AnnotationTransactionAspect() {
super(new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource(false));
}备注:使用AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource获取TransactionAttribute
Pointcut定义:
/**
* Matches the execution of any public method in a type with the Transactional
* annotation, or any subtype of a type with the Transactional annotation.
*/
private pointcut executionOfAnyPublicMethodInAtTransactionalType() :
execution(public * ((@Transactional *)+).*(..)) && within(@Transactional *);
/**
* Matches the execution of any method with the Transactional annotation.
*/
private pointcut executionOfTransactionalMethod() :
execution(@Transactional * *(..));
/**
* Definition of pointcut from super aspect - matched join points
* will have Spring transaction management applied.
*/
protected pointcut transactionalMethodExecution(Object txObject) :
(executionOfAnyPublicMethodInAtTransactionalType() || executionOfTransactionalMethod() ) && this(txObject);around方法定义:
@SuppressAjWarnings("adviceDidNotMatch")
Object around(final Object txObject): transactionalMethodExecution(txObject) {
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) thisJoinPoint.getSignature();
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
try {
return invokeWithinTransaction(methodSignature.getMethod(), txObject.getClass(), new InvocationCallback() {
public Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable {
return proceed(txObject);
}
});
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable thr) {
Rethrower.rethrow(thr);
throw new IllegalStateException("Should never get here", thr);
}
}TransactionAspectSupport:实际运行事务的工作类
核心方法:
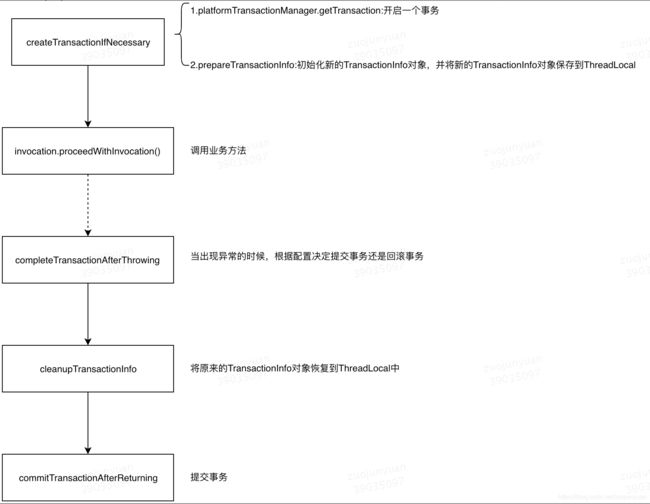
1.invokeWithinTransaction
/**
* General delegate for around-advice-based subclasses, delegating to several other template
* methods on this class. Able to handle {@link CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager}
* as well as regular {@link PlatformTransactionManager} implementations.
* @param method the Method being invoked
* @param targetClass the target class that we're invoking the method on
* @param invocation the callback to use for proceeding with the target invocation
* @return the return value of the method, if any
* @throws Throwable propagated from the target invocation
*/
@Nullable
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal = null;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
else {
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
try {
Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) tm).execute(txAttr, status -> {
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
return invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
}
else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
return new ThrowableHolder(ex);
}
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
});
// Check result: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (result instanceof ThrowableHolder) {
throw ((ThrowableHolder) result).getThrowable();
}
else {
return result;
}
}
catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
}
}备注:
1.通过getTransactionAttributeSource()获取TransactionAttributeSource
2.TransactionAttributeSource根据method和targetClass获取TransactionAttribute
3.根据TransactionAttribute筛选PlatformTransactionManager
4.获取执行方法描述符methodIdentification
5.执行事务(具体流程见下图)
2.determineTransactionManager
/**
* Determine the specific transaction manager to use for the given transaction.
*/
@Nullable
protected PlatformTransactionManager determineTransactionManager(@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr) {
// Do not attempt to lookup tx manager if no tx attributes are set
if (txAttr == null || this.beanFactory == null) {
return getTransactionManager();
}
String qualifier = txAttr.getQualifier();
if (StringUtils.hasText(qualifier)) {
return determineQualifiedTransactionManager(this.beanFactory, qualifier);
}
else if (StringUtils.hasText(this.transactionManagerBeanName)) {
return determineQualifiedTransactionManager(this.beanFactory, this.transactionManagerBeanName);
}
else {
PlatformTransactionManager defaultTransactionManager = getTransactionManager();
if (defaultTransactionManager == null) {
defaultTransactionManager = this.transactionManagerCache.get(DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_KEY);
if (defaultTransactionManager == null) {
defaultTransactionManager = this.beanFactory.getBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class);
this.transactionManagerCache.putIfAbsent(
DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_KEY, defaultTransactionManager);
}
}
return defaultTransactionManager;
}
}
private PlatformTransactionManager determineQualifiedTransactionManager(BeanFactory beanFactory, String qualifier) {
PlatformTransactionManager txManager = this.transactionManagerCache.get(qualifier);
if (txManager == null) {
txManager = BeanFactoryAnnotationUtils.qualifiedBeanOfType(
beanFactory, PlatformTransactionManager.class, qualifier);
this.transactionManagerCache.putIfAbsent(qualifier, txManager);
}
return txManager;
}备注:
1.使用TransactionAttribute的qualifier属性获取PlatformTransactionManager
2.使用transactionManagerCache.get(DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_KEY)获取PlatformTransactionManager
3.使用beanFactory.getBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class)获取PlatformTransactionManager
TransactionInterceptor:业务方法事务拦截器
类型定义:
public class TransactionInterceptor extends TransactionAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable构造器:
/**
* Create a new TransactionInterceptor.
* Transaction manager and transaction attributes still need to be set.
* @see #setTransactionManager
* @see #setTransactionAttributes(java.util.Properties)
* @see #setTransactionAttributeSource(TransactionAttributeSource)
*/
public TransactionInterceptor() {
}
/**
* Create a new TransactionInterceptor.
* @param ptm the default transaction manager to perform the actual transaction management
* @param attributes the transaction attributes in properties format
* @see #setTransactionManager
* @see #setTransactionAttributes(java.util.Properties)
*/
public TransactionInterceptor(PlatformTransactionManager ptm, Properties attributes) {
setTransactionManager(ptm);
setTransactionAttributes(attributes);
}
/**
* Create a new TransactionInterceptor.
* @param ptm the default transaction manager to perform the actual transaction management
* @param tas the attribute source to be used to find transaction attributes
* @see #setTransactionManager
* @see #setTransactionAttributeSource(TransactionAttributeSource)
*/
public TransactionInterceptor(PlatformTransactionManager ptm, TransactionAttributeSource tas) {
setTransactionManager(ptm);
setTransactionAttributeSource(tas);
}
核心方法:
1.invoke
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed);
}TransactionProxyFactoryBean:声明式事务管理Proxy的工厂类,根据transactionManager,transactionAttributes创建事务管理Proxy
类型定义:
public class TransactionProxyFactoryBean extends AbstractSingletonProxyFactoryBean
implements BeanFactoryAwareAbstractSingletonProxyFactoryBean类型定义:
public abstract class AbstractSingletonProxyFactoryBean extends ProxyConfig
implements FactoryBean属性:
private final TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
@Nullable
private Pointcut pointcut;
@Nullable
private Object target;
@Nullable
private Class[] proxyInterfaces;
@Nullable
private Object[] preInterceptors;
@Nullable
private Object[] postInterceptors;
/** Default is global AdvisorAdapterRegistry */
private AdvisorAdapterRegistry advisorAdapterRegistry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance();
@Nullable
private transient ClassLoader proxyClassLoader;
@Nullable
private Object proxy;核心方法:
1.afterPropertiesSet
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (this.target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'target' is required");
}
if (this.target instanceof String) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("'target' needs to be a bean reference, not a bean name as value");
}
if (this.proxyClassLoader == null) {
this.proxyClassLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
if (this.preInterceptors != null) {
for (Object interceptor : this.preInterceptors) {
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(interceptor));
}
}
// Add the main interceptor (typically an Advisor).
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(createMainInterceptor()));
if (this.postInterceptors != null) {
for (Object interceptor : this.postInterceptors) {
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(interceptor));
}
}
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
TargetSource targetSource = createTargetSource(this.target);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
if (this.proxyInterfaces != null) {
proxyFactory.setInterfaces(this.proxyInterfaces);
}
else if (!isProxyTargetClass()) {
// Rely on AOP infrastructure to tell us what interfaces to proxy.
Class targetClass = targetSource.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass != null) {
proxyFactory.setInterfaces(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(targetClass, this.proxyClassLoader));
}
}
postProcessProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
this.proxy = proxyFactory.getProxy(this.proxyClassLoader);
}执行流程如下:
1.创建ProxyFactory对象
2.将preInterceptors的内容添加到ProxyFactory对象的advisors列表中
3.将createMainInterceptor()的返回添加到ProxyFactory对象的advisors列表中
4.将postInterceptors的内容添加到ProxyFactory对象的advisors列表中
5.设置target和proxyInterfaces
6.创建proxy
2.getObject和getObjectType
@Override
public Object getObject() {
if (this.proxy == null) {
throw new FactoryBeanNotInitializedException();
}
return this.proxy;
}
@Override
public Class getObjectType() {
if (this.proxy != null) {
return this.proxy.getClass();
}
if (this.proxyInterfaces != null && this.proxyInterfaces.length == 1) {
return this.proxyInterfaces[0];
}
if (this.target instanceof TargetSource) {
return ((TargetSource) this.target).getTargetClass();
}
if (this.target != null) {
return this.target.getClass();
}
return null;
}3.createMainInterceptor
/**
* Creates an advisor for this FactoryBean's TransactionInterceptor.
*/
@Override
protected Object createMainInterceptor() {
this.transactionInterceptor.afterPropertiesSet();
if (this.pointcut != null) {
return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(this.pointcut, this.transactionInterceptor);
}
else {
// Rely on default pointcut.
return new TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor(this.transactionInterceptor);
}
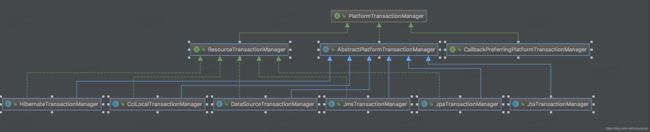
}AbstractPlatformTransactionManager:具体平台事务管理器的抽象基类,使用模板方法设计模式实现Spring的标准事务工作流;
子类必须重写改变事务状态的方法: 1. begin 2. suspend 3.resume 4.commit 5.rollback
UML类图结构如下:
实现功能:
1.确定是否存在现有事务(挂起旧事务和开始新事务);
2.应用适当的事务传播行为;
3.必要时暂停并恢复事务;
4.检查事务提交上的仅回滚(rollback-only)标记;
5.在回滚中(实际回滚或设置回滚(setting rollback-only))进行适当的修改;(todo:两种回滚方式的区别)
6.触发注册的事务同步((Transaction synchronization)回调
7.提交事务
事务同步(Transaction synchronization) 回调详解:
事务同步是注册回调的一种通用机制。一般在事务完成时间调用的。两种应用场景:
1.JDBC、Hibernate、JPA等框架的数据访问支持类在运行JTA事务时使用:事务开始前开启事务同步回调注册,事务结束后关闭 事务同步回调
2.应用程序中的自定义同步需求
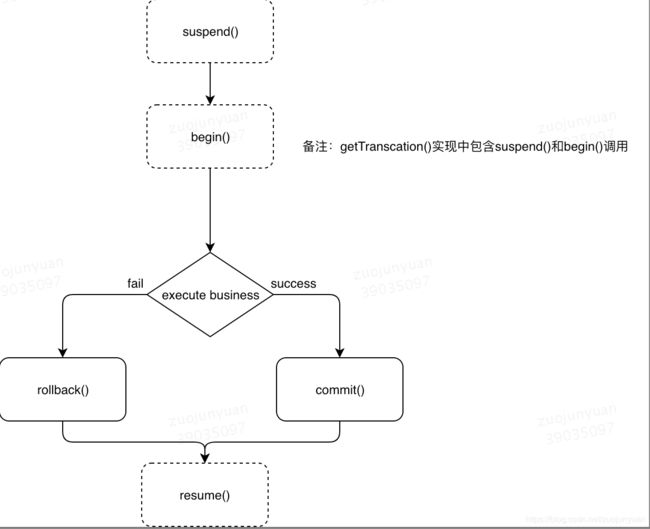
事务执行流程如下:
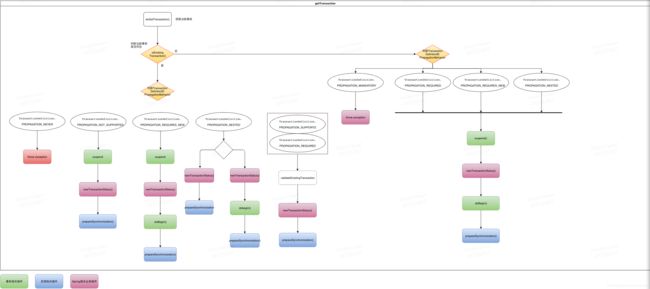
核心方法:
1.getTransaction
2.suspend
@Nullable
protected final SuspendedResourcesHolder suspend(@Nullable Object transaction) throws TransactionException {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
List suspendedSynchronizations = doSuspendSynchronization();
try {
Object suspendedResources = null;
if (transaction != null) {
suspendedResources = doSuspend(transaction);
}
String name = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionName();
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionName(null);
boolean readOnly = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly();
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionReadOnly(false);
Integer isolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel();
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel(null);
boolean wasActive = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive();
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setActualTransactionActive(false);
return new SuspendedResourcesHolder(
suspendedResources, suspendedSynchronizations, name, readOnly, isolationLevel, wasActive);
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
// doSuspend failed - original transaction is still active...
doResumeSynchronization(suspendedSynchronizations);
throw ex;
}
}
else if (transaction != null) {
// Transaction active but no synchronization active.
Object suspendedResources = doSuspend(transaction);
return new SuspendedResourcesHolder(suspendedResources);
}
else {
// Neither transaction nor synchronization active.
return null;
}
} 业务流程如下:
-
挂起列表中的事务同步回调对象(TransactionSynchronization)
-
挂起事务
-
重置TransactionSynchronizationManager内容,返回TransactionSynchronizationManager之前保存的内容
3.newTransactionStatus
protected DefaultTransactionStatus newTransactionStatus(
TransactionDefinition definition, @Nullable Object transaction, boolean newTransaction,
boolean newSynchronization, boolean debug, @Nullable Object suspendedResources) {
boolean actualNewSynchronization = newSynchronization &&
!TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive();
return new DefaultTransactionStatus(
transaction, newTransaction, actualNewSynchronization,
definition.isReadOnly(), debug, suspendedResources);
}备注:返回新的TransactionStatus对象
4.prepareSynchronization
protected void prepareSynchronization(DefaultTransactionStatus status, TransactionDefinition definition) {
if (status.isNewSynchronization()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setActualTransactionActive(status.hasTransaction());
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel(
definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT ?
definition.getIsolationLevel() : null);
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionReadOnly(definition.isReadOnly());
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionName(definition.getName());
TransactionSynchronizationManager.initSynchronization();
}
}备注:将DefaultTransactionStatus和TransactionDefinition内容保存到TransactionSynchronizationManager
DataSourceTransactionManager:描述:针对数据库JDBC connection的事务管理器,通过DataSource的工厂方法来获取JDBC connection。可以做为JtaTransactionManager的替代类
DataSource的获取方式包括:
1.TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy 2.LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy
属性如下:
@Nullable
private javax.sql.DataSource dataSource;
private boolean enforceReadOnly = false;备注:dataSource是必须赋值的
核心方法:
1.dogetTransaction()
@Override
protected Object doGetTransaction() {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = new DataSourceTransactionObject();
txObject.setSavepointAllowed(isNestedTransactionAllowed());
ConnectionHolder conHolder =
(ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(obtainDataSource());
txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder, false);
return txObject;
}具体流程如下:
-
初始化DataSourceTransactionObject对象(该对象在整个事务执行流程中作为上下文存在)
-
DataSourceTransactionObject对象绑定DataSource在threadlocal保存的Connection
2.isExistingTransaction(Object transaction)
@Override
protected boolean isExistingTransaction(Object transaction) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
return (txObject.hasConnectionHolder() && txObject.getConnectionHolder().isTransactionActive());
}备注:判断当前connection是否存在并且是否开启了事务
3.doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition)
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
Connection con = null;
try {
if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() ||
txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
Connection newCon = obtainDataSource().getConnection();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Acquired Connection [" + newCon + "] for JDBC transaction");
}
txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true);
}
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition);
txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel);
// Switch to manual commit if necessary. This is very expensive in some JDBC drivers,
// so we don't want to do it unnecessarily (for example if we've explicitly
// configured the connection pool to set it already).
if (con.getAutoCommit()) {
txObject.setMustRestoreAutoCommit(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Switching JDBC Connection [" + con + "] to manual commit");
}
con.setAutoCommit(false);
}
prepareTransactionalConnection(con, definition);
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTransactionActive(true);
int timeout = determineTimeout(definition);
if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout);
}
// Bind the connection holder to the thread.
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(obtainDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder());
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, obtainDataSource());
txObject.setConnectionHolder(null, false);
}
throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction", ex);
}主要业务流程如下:
-
如果DataSourceTransactionObject的connection为空或者connection的事务同步(SynchronizedWithTransaction)已经开启, DataSourceTransactionObject对象设置新的connection
-
DataSourceTransactionObject的connection开启事务同步(SynchronizedWithTransaction),保存当前的隔离级别,设置是否开启自动提交(默认开启)
根据TransactionDefinition.isReadOnly属性生成优化语句("SET TRANSACTION READ ONLY")
-
DataSourceTransactionObject的connection设置成拥有事务(TransactionActive)
4. 如果DataSourceTransactionObject的connection是新生成的,将datasource和connection的对应关系保存到threadlocal
5.doSuspend
@Override
protected Object doSuspend(Object transaction) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
txObject.setConnectionHolder(null);
return TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(obtainDataSource());
}6.doResume
@Override
protected void doResume(@Nullable Object transaction, Object suspendedResources) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(obtainDataSource(), suspendedResources);
}7.doCommit
@Override
protected void doCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Committing JDBC transaction on Connection [" + con + "]");
}
try {
con.commit();
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new TransactionSystemException("Could not commit JDBC transaction", ex);
}
}8.doCleanupAfterCompletion
@Override
protected void doCleanupAfterCompletion(Object transaction) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
// Remove the connection holder from the thread, if exposed.
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(obtainDataSource());
}
// Reset connection.
Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
try {
if (txObject.isMustRestoreAutoCommit()) {
con.setAutoCommit(true);
}
DataSourceUtils.resetConnectionAfterTransaction(con, txObject.getPreviousIsolationLevel());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.debug("Could not reset JDBC Connection after transaction", ex);
}
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Releasing JDBC Connection [" + con + "] after transaction");
}
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, this.dataSource);
}
txObject.getConnectionHolder().clear();
}备注:进行资源清理等操作