深入浅出低功耗蓝牙(BLE)协议栈,使用Ubertooth one扫描嗅探低功耗蓝牙
BLE协议栈为什么要分层?怎么理解BLE“连接”?如果BLE协议只有ATT层没有GATT层会发生什么?
深入浅出低功耗蓝牙BLE协议栈
- 1. 协议栈框架
- 2. 如何通过无线发送一个数据包
- 2.1 广播方式
- 2.2 连接方式
- 3. PHY和LL层协议栈编写
- 3.1 基本概念
- (1)链路层状态机
- (2)协议栈
- (3)通信信道
- 3.2 LL层协议
- 3.3 跳频算法
- 4. 嗅探测试
- 4.1 环境搭建
- (1)安装lib库
- (2)安装libbtbb
- (3)安装ubertooth
- (4)安装wireshark
- (5)安装kismet
- (6)安装BLE解密工具crackle
- 4.2 嗅探扫描
- (1)spectool
- (2)hcitool
- (3)gatttool
- (4)ubertooth-scan
- (5)ubertooth-btle
- (6)crackle
- 5. 参考 && 感谢
1. 协议栈框架
一般而言,我们把某个协议的实现代码称为协议栈(protocol stack),BLE协议栈就是实现低功耗蓝牙协议的代码,理解和掌握BLE协议是实现BLE协议栈的前提。在深入BLE协议栈各个组成部分之前,我们先看一下BLE协议栈整体架构。
如上图所述,要实现一个BLE应用,首先需要一个支持BLE射频的芯片,然后还需要提供一个与此芯片配套的BLE协议栈,最后在协议栈上开发自己的应用。可以看出BLE协议栈是连接芯片和应用的桥梁,是实现整个BLE应用的关键。那BLE协议栈具体包含哪些功能呢?简单来说,BLE协议栈主要用来对你的应用数据进行层层封包,以生成一个满足BLE协议的空中数据包,也就是说,把应用数据包裹在一系列的帧头(header)和帧尾(tail)中。具体来说,BLE协议栈主要由如下几部分组成:
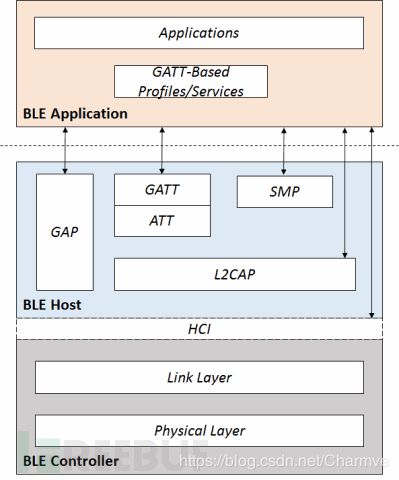
- PHY层(Physical layer物理层)。PHY层用来指定BLE所用的无线频段,调制解调方式和方法等。PHY层做得好不好,直接决定整个BLE芯片的功耗,灵敏度以及selectivity等射频指标。
- LL层(Link Layer链路层)。LL层是整个BLE协议栈的核心,也是BLE协议栈的难点和重点。像Nordic的BLE协议栈能同时支持20个link(连接),就是LL层的功劳。LL层要做的事情非常多,比如具体选择哪个射频通道进行通信,怎么识别空中数据包,具体在哪个时间点把数据包发送出去,怎么保证数据的完整性,ACK如何接收,如何进行重传,以及如何对链路进行管理和控制等等。LL层只负责把数据发出去或者收回来,对数据进行怎样的解析则交给上面的GAP或者GATT。
- HCI(Host controller interface主机控制接口层)。HCI是可选的(具体请参考文章: 三种蓝牙架构实现方案(蓝牙协议栈方案)),HCI主要用于2颗芯片实现BLE协议栈的场合,用来规范两者之间的通信协议和通信命令等。
- GAP层(Generic access profile)。GAP是对LL层payload(有效数据包)如何进行解析的两种方式中的一种,而且是最简单的那一种。GAP简单的对LL payload进行一些规范和定义,因此GAP能实现的功能极其有限。GAP目前主要用来进行广播,扫描和发起连接等。
- L2CAP层(Logic link control and adaptation protocol逻辑链路控制及自适应协议层)。L2CAP对LL进行了一次简单封装,LL只关心传输的数据本身,L2CAP就要区分是加密通道还是普通通道,同时还要对连接间隔进行管理。
- SMP(Secure manager protocol安全管理协议层)。SMP用来管理BLE连接的加密和安全的,如何保证连接的安全性,同时不影响用户的体验,这些都是SMP要考虑的工作。
- ATT(Attribute protocol属性协议层)。简单来说,ATT层用来定义用户命令及命令操作的数据,比如读取某个数据或者写某个数据。BLE协议栈中,开发者接触最多的就是ATT。BLE引入了attribute概念,用来描述一条一条的数据。Attribute除了定义数据,同时定义该数据可以使用的ATT命令,因此这一层被称为ATT层。
- GATT(Generic attribute profile 通用属性配置文件层)。GATT用来规范attribute中的数据内容,并运用group(分组)的概念对attribute进行分类管理。没有GATT,BLE协议栈也能跑,但互联互通就会出问题,也正是因为有了GATT和各种各样的应用profile,BLE摆脱了ZigBee等无线协议的兼容性困境,成了出货量最大的2.4G无线通信产品。
视频参考,可只看第二集。
【CC2540】TI官方低功耗蓝牙BLE协议栈说明(TI官方)
我相信很多人看了上面的介绍,还是不懂BLE协议栈的工作原理,以及每一层具体干什么的,为什么要这么分层。下面我以如何发送一个数据包为例来讲解BLE协议栈各层是如何紧密配合,以完成发送任务的。
2. 如何通过无线发送一个数据包
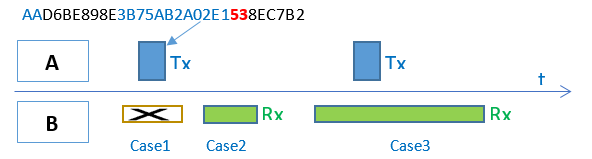
假设有设备A和设备B,设备A要把自己目前的电量状态83%(十六进制表示为0x53)发给设备B,该怎么做呢?作为一个开发者,他希望越简单越好,对他而言,他希望调用一个简单的API就能完成这件事,比如send(0x53),实际上我们的BLE协议栈就是这样设计的,开发者只需调用send(0x53)就可以把数据发送出去了,其余的事情BLE协议栈帮你搞定。很多人会想,BLE协议栈是不是直接在物理层就把0x53发出去,就如下图所示:
这种方式初看起来挺美的,但由于很多细节没有考虑到,实际是不可行的。首先,它没有考虑用哪一个射频信道来进行传输,在不更改API的情况下,我们只能对协议栈进行分层,为此引入LL层,开发者还是调用send(0x53),send(0x53)再调用send_LL(0x53,2402M)(注:2402M为信道频率)。这里还有一个问题,设备B怎么知道这个数据包是发给自己的还是其他人的,为此BLE引入access address概念,用来指明接收者身份,其中,0x8E89BED6这个access address比较特殊,它表示要发给周边所有设备,即广播。如果你要一对一的进行通信(BLE协议将其称为连接),即设备A的数据包只能设备B接收,同样设备B的数据包只能设备A接收,那么就必须生成一个独特的随机access address以标识设备A和设备B两者之间的连接。
2.1 广播方式
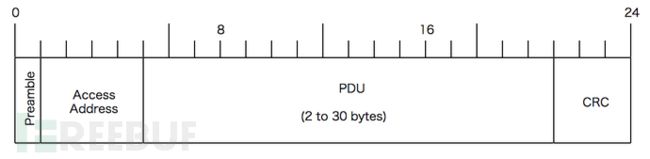
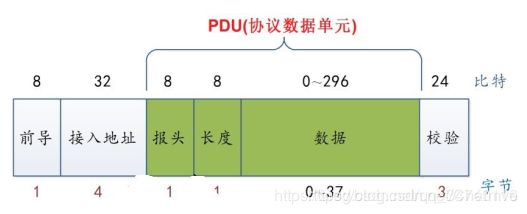
我们先来看一下简单的广播情况,这种情况下,我们把设备A叫advertiser(广播者),设备B叫scanner或者observer(扫描者)。广播状态下设备A的LL层API将变成send_LL(0x53,2402M, 0x8E89BED6)。由于设备B可以同时接收到很多设备的广播,因此数据包还必须包含设备A的device address(0xE1022AAB753B)以确认该广播包来自设备A,为此send_LL参数需要变成(0x53,2402M, 0x8E89BED6, 0xE1022AAB753B)。LL层还要检查数据的完整性,即数据在传输过程中有没有发生窜改,为此引入CRC24对数据包进行检验 (假设为0xB2C78E) 。同时为了调制解调电路工作更高效,每一个数据包的最前面会加上1个字节的preamble(前导帧),preamble一般为0x55或者0xAA。这样,整个空中包就变成:(注:空中包用小端模式表示!)
上面这个数据包还有如下问题:
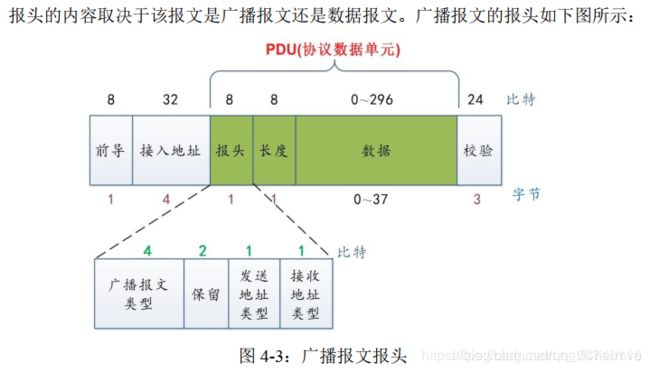
- 没有对数据包进行分类组织,设备B无法找到自己想要的数据0x53。 为此我们需要在access address之后加入两个字段:LL header和长度字节。LL header用来表示数据包的LL类型,长度字节用来指明payload的长度
- 设备B什么时候开启射频窗口以接收空中数据包? 如上图case1所示,当设备A的数据包在空中传输的时候,设备B把接收窗口关闭,此时通信将失败;同样对case2来说,当设备A没有在空中发送数据包时,设备B把接收窗口打开,此时通信也将失败。只有case3的情况,通信才能成功,即设备A的数据包在空中传输时,设备B正好打开射频接收窗口,此时通信才能成功,换句话说,LL层还必须定义通信时序。
- 当设备B拿到数据0x53后,该如何解析这个数据呢? 它到底表示湿度还是电量,还是别的意思?这个就是GAP层要做的工作,GAP层引入了LTV(Length-Type-Value)结构来定义数据,比如020105,02-长度,01-类型(强制字段,表示广播flag,广播包必须包含该字段),05-值。由于广播包最大只能为31个字节,它能定义的数据类型极其有限,像这里说的电量,GAP就没有定义,因此要通过广播方式把电量数据发出去,只能使用供应商自定义数据类型0xFF,即04FF590053,其中04表示长度,FF表示数据类型(自定义数据),0x0059是供应商ID(自定义数据中的强制字段),0x53就是我们的数据(设备双方约定0x53就是表示电量,而不是其他意思)。
最终空中传输的数据包将变成:
- AA – 前导帧(preamble)
- D6BE898E – 访问地址(access address)
- 60 – LL帧头字段(LL header)
- 0E – 有效数据包长度(payload length)
- 3B75AB2A02E1 – 广播者设备地址(advertiser address)
- 02010504FF590053 – 广播数据
- 8EC7B2 – CRC24值
关于报头第三部分还会详细介绍。
有了PHY,LL和GAP,就可以发送广播包了,但广播包携带的信息极其有限,而且还有如下几大限制:
- 无法进行一对一双向通信 (广播是一对多通信,而且是单方向的通信)
- 由于不支持组包和拆包,因此无法传输大数据
- 通信不可靠及效率低下。广播信道不能太多,否则将导致扫描端效率低下。为此,BLE只使用37(2402MHz) /38(2426MHz) /39(2480MHz)三个信道进行广播和扫描,因此广播不支持跳频。由于广播是一对多的,所以广播也无法支持ACK。这些都使广播通信变得不可靠。
- 扫描端功耗高。由于扫描端不知道设备端何时广播,也不知道设备端选用哪个频道进行广播,扫描端只能拉长扫描窗口时间,并同时对37/38/39三个通道进行扫描,这样功耗就会比较高。
而连接则可以很好解决上述问题,下面我们就来看看连接是如何将0x53发送出去的。
2.2 连接方式
到底什么叫连接(connection)? 像有线UART,很容易理解,就是用线(Rx和Tx等)把设备A和设备B相连,即为连接。用“线”把两个设备相连,实际是让2个设备有共同的通信媒介,并让两者时钟同步起来。蓝牙连接有何尝不是这个道理,所谓设备A和设备B建立蓝牙连接,就是指设备A和设备B两者一对一“同步”成功,其具体包含以下几方面:
- 设备A和设备B对接下来要使用的物理信道达成一致
- 设备A和设备B双方建立一个共同的时间锚点,也就是说,把双方的时间原点变成同一个点
- 设备A和设备B两者时钟同步成功,即双方都知道对方什么时候发送数据包什么时候接收数据包
如上图所示,一旦设备A和设备B连接成功(此种情况下,我们把设备A称为Master或者Central,把设备B称为Slave或者Peripheral),设备A将周期性以CI(connection interval)为间隔向设备B发送数据包,而设备B也周期性地以CI为间隔打开射频接收窗口以接收设备A的数据包。同时按照蓝牙spec要求,设备B收到设备A数据包150us后,设备B切换到发送状态,把自己的数据发给设备A;设备A则切换到接收状态,接收设备B发过来的数据。由此可见,连接状态下,设备A和设备B的射频发送和接收窗口都是周期性地有计划地开和关,而且开的时间非常短,从而大大降低系统功耗并大大提高系统效率。
现在我们看看连接状态下是如何把数据0x53发送出去的,从中大家可以体会到蓝牙协议栈分层的妙处。
- 对开发者来说,很简单,他只需要调用send(0x53)
- GATT层定义数据的类型和分组,方便起见,我们用0x0013表示电量这种数据类型,这样GATT层把数据打包成130053 (小端模式!)
- ATT层用来选择具体的通信命令,比如读/写/notify/indicate等,这里选择notify命令0x1B,这样数据包变成了:1B130053
- L2CAP用来指定connection interval(连接间隔),比如每10ms同步一次(CI不体现在数据包中),同时指定逻辑通道编号0004(表示ATT命令),最后把ATT数据长度0x0004加在包头,这样数据就变为:040004001B130053
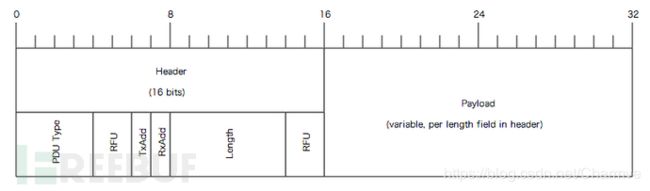
- LL层要做的工作很多,首先LL层需要指定用哪个物理信道进行传输(物理信道不体现在数据包中),然后再给此连接分配一个Access address(0x50655DAB)以标识此连接只为设备A和设备B直连服务,然后加上LL header和payload length字段,LL header标识此packet为数据packet,而不是control packet等,payload length为整个L2CAP字段的长度,最后加上CRC24字段,以保证整个packet的数据完整性,所以数据包最后变成:
- AA – 前导帧(preamble)
- 0x50655DAB – 访问地址(access address)
- 1E – LL帧头字段(LL header)
- 08 – 有效数据包长度(payload length)
- 04000400 – ATT数据长度,以及L2CAP通道编号
- 1B – notify command
- 0x0013 – 电量数据handle
- 0x53 – 真正要发送的电量数据
- 0xF650D5 – CRC24值
虽然开发者只调用了 send(0x53),但由于低功耗蓝牙协议栈层层打包,最后空中实际传输的数据将变成下图所示的模样,这就既满足了低功耗蓝牙通信的需求,又让用户API变得简单,可谓一箭双雕!

关于报头第三部分还会详细介绍。
上面只是对BLE协议栈实现原理做了一个简单概述,即便如此,由于都是关于BLE协议栈底层的东西,很多开发者还是会觉得比较枯燥和晦涩,而且对很多开发者来说,他们也不关心BLE协议栈是如何实现的,他们更关心的是BLE协议栈的使用,即怎么开发一个BLE应用。BLE应用是实打实的东西,不能像上面讲述协议栈一样泛泛而谈,必须结合具体的蓝牙芯片和蓝牙协议栈来讲解,为此后面将以Nordic芯片及协议栈作为范例,来具体讲解如何开发BLE应用,以及如何通过代码去理解BLE协议中定义的一些概念和术语。
标签: ATT, GAP, Link layer, GATT, L2CAP, BLE stack, 广播, 连接, BLE协议栈, 链路层
3. PHY和LL层协议栈编写
3.1 基本概念
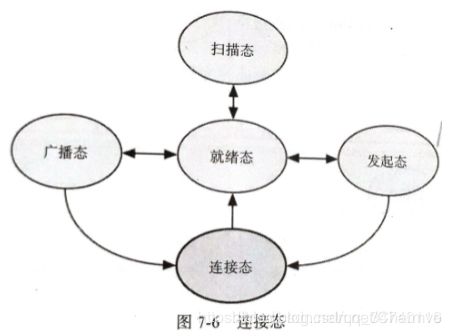
(1)链路层状态机
共有5中状态:
(2)协议栈
协议栈内容请参考:Understanding Bluetooth Advertising Packets一文。
中文版:http://blog.csdn.net/ooakk/article/details/7302425
(3)通信信道
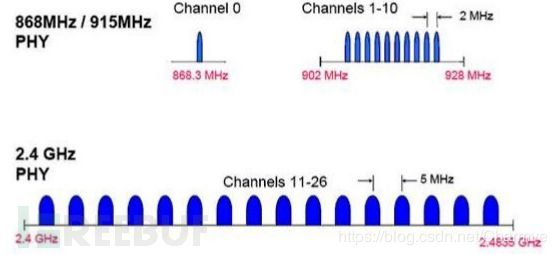
BLE 工作在 ISM 频带,定义了两个频段,2.4GHz 频段和 896/915MHz 频带。在IEEE802.15.4 中共规定了 27 个信道:
在 2.4GHz 频段,共有 16 个信道,信道通信速率为 250kbps:
在 915MHz 频段,共有 10 个信道,信道通信速率为 40kbps:
在 868MHz 频段,有 1 个信道,信道通信速率为 20kbpS。
BLE 工作在 2.4GHz 频段,仅适用 3 个广播通道,适用所有蓝牙规范版本通用的自适应调频技术。
BlueTooth 有79个射频信道,按0-78排序,并于2402 MHz开始,以1 MHz分隔:
channel 00 : 2.402000000 Ghz
channel 01 : 2.403000000 Ghz
…
channel 78 : 2.480000000 Ghz
BTLE有40个频道(也称为信道),按37在第一个,后面由0-36,然后第39信道(那么38呢 )第38信道位于10和11之间:
channel 37 : 2.402000000 Ghz
channel 00 : 2.404000000 Ghz
channel 01 : 2.406000000 Ghz
channel 02 : 2.408000000 Ghz
channel 03 : 2.410000000 Ghz
channel 04 : 2.412000000 Ghz
channel 05 : 2.414000000 Ghz
channel 06 : 2.416000000 Ghz
channel 07 : 2.418000000 Ghz
channel 08 : 2.420000000 Ghz
channel 09 : 2.422000000 Ghz
channel 10 : 2.424000000 Ghz
channel 38 : 2.426000000 Ghz
channel 11 : 2.428000000 Ghz
channel 12 : 2.430000000 Ghz
channel 13 : 2.432000000 Ghz
channel 14 : 2.434000000 Ghz
channel 15 : 2.436000000 Ghz
channel 16 : 2.438000000 Ghz
channel 17 : 2.440000000 Ghz
channel 18 : 2.442000000 Ghz
channel 19 : 2.444000000 Ghz
channel 20 : 2.446000000 Ghz
channel 21 : 2.448000000 Ghz
channel 22 : 2.450000000 Ghz
channel 23 : 2.452000000 Ghz
channel 24 : 2.454000000 Ghz
channel 25 : 2.456000000 Ghz
channel 26 : 2.458000000 Ghz
channel 27 : 2.460000000 Ghz
channel 28 : 2.462000000 Ghz
channel 29 : 2.464000000 Ghz
channel 30 : 2.466000000 Ghz
channel 31 : 2.468000000 Ghz
channel 32 : 2.470000000 Ghz
channel 33 : 2.472000000 Ghz
channel 34 : 2.474000000 Ghz
channel 35 : 2.476000000 Ghz
channel 36 : 2.478000000 Ghz
channel 39 : 2.480000000 Ghz
40个频道中:37、38、39为广播信道,另外37个频道用于数据的传输:
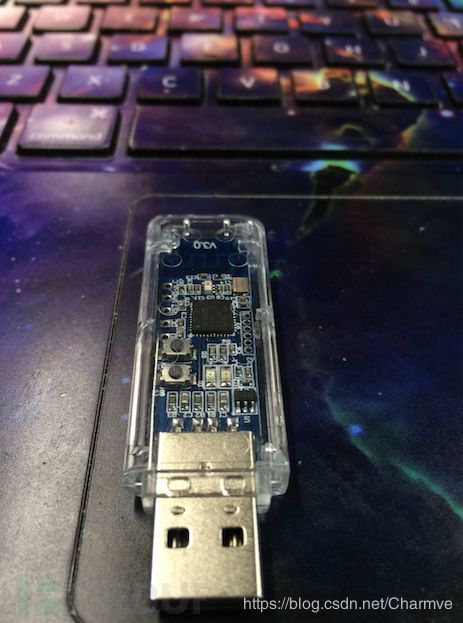
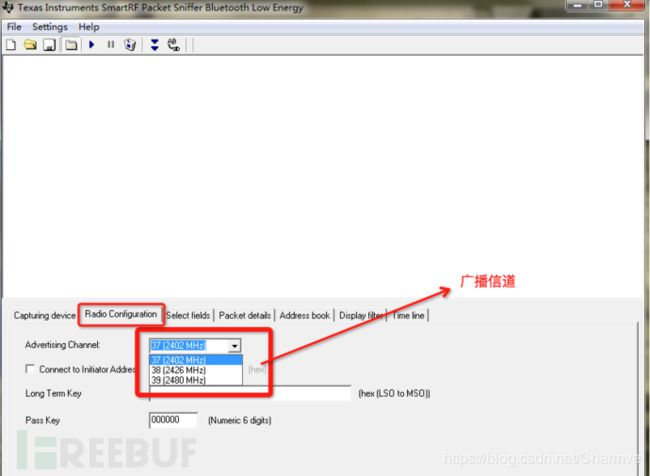
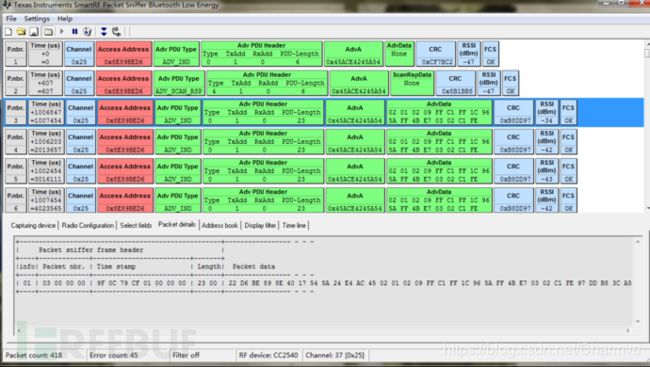
使用德州仪器(TI)CC2540蓝牙低功耗模块配合官方的SmartRF协议软件包监听器:PACKET-SNIFFER,可对三个蓝牙广播信道进行嗅探。
使用方法可参考:Ti.com.cn/packet-sniffer 这种嗅探方案优点是廉价,不足是只能嗅探到广播信道的数据包,无法捕获连接完成后也就是设备通信过程中的数据包:
基于HackRF嗅探蓝牙数据包实际上也是可行的:
其方法参考jxj童鞋的BTLE packet sniffer based on HACKRF (function and performance similar to TI’s packet sniffer)
HackRF.NET 中文版:基于HACKRF的低功耗蓝牙(BTLE)packet sniffer/scanner
关于其他LL层的相关概念,可以参考这篇博文,限于文章篇幅。
BLE-3の蓝牙4.0协议栈の空口包格式 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34740116/article/details/106274889
3.2 LL层协议
详解BLE空口包格式—兼BLE Link layer协议解析
3.3 跳频算法
蓝牙跳频算法分析【经典蓝牙 vs BLE 4.x vs BT 5.0 BLE部分】
4. 嗅探测试
4.1 环境搭建
上面介绍了数据包和各层协议,接下来我们将使用Ubertooth One来捕获通信过程中的蓝牙数据包。
(1)安装lib库
apt-get install python-software-properties
add-apt-repository ppa:pyside
apt-get update
apt-get install libnl-dev libusb-1.0-0-dev pyside-tools
(2)安装libbtbb
wget https://github.com/greatscottgadgets/libbtbb/archive/2015-09-R2.tar.gz -O libbtbb-2015-09-R2.tar.gz
tar xf libbtbb-2015-09-R2.tar.gz
cd libbtbb-2015-09-R2
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
sudo make install
(3)安装ubertooth
wget https://github.com/greatscottgadgets/ubertooth/releases/download/2015-09-R2/ubertooth-2015-09-R2.tar.xz -O ubertooth-2015-09-R2.tar.xz
tar xf ubertooth-2015-09-R2.tar.xz
cd ubertooth-2015-09-R2/host
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
sudo make install
sudo ldconfig
(4)安装wireshark
sudo apt-get install checkinstallwget https://www.wireshark.org/download/src/wireshark-2.0.3.tar.bz2tar -xvf wireshark-2.0.3.tar.bz2cd wireshark-2.0.3./configuremakemake install
(5)安装kismet
wget https://kismetwireless.net/code/kismet-2013-03-R1b.tar.xz
tar xf kismet-2013-03-R1b.tar.xz
cd kismet-2013-03-R1b
ln -s ../ubertooth-2015-09-R2/host/kismet/plugin-ubertooth .
./configure
make && make plugins
sudo make suidinstall
sudo make plugins-install
(6)安装BLE解密工具crackle
crackle (开源项目地址)
git clone https://github.com/mikeryan/crackle.git
cd crackle
make
make install
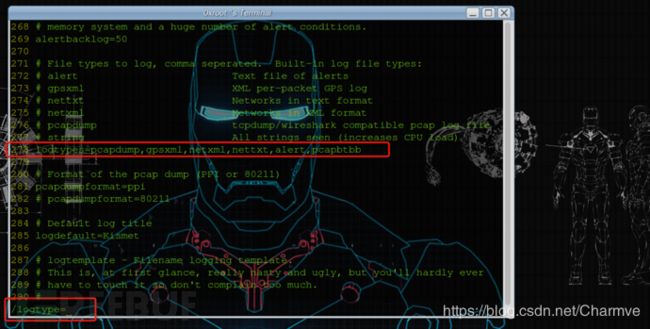
找到kismet的配置文件kismet.conf ,把"pcapbtbb"加入到kismet.conf的logtypes= 里边
4.2 嗅探扫描
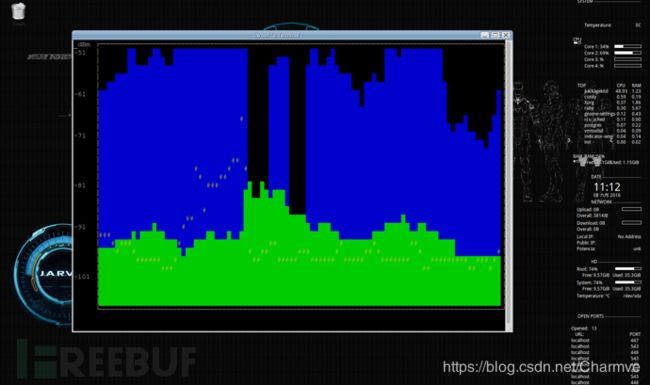
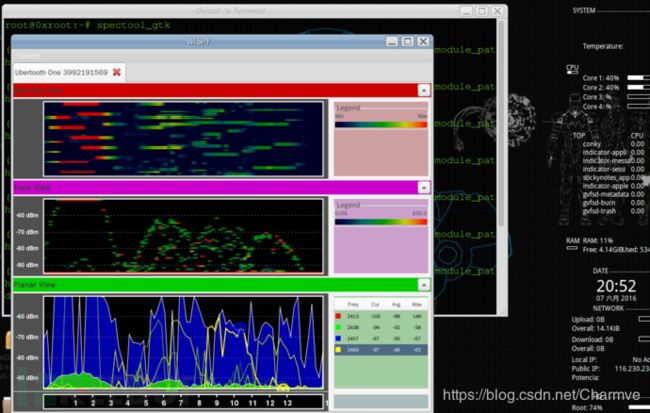
(1)spectool
spectool_curses
spectool_raw RAW中文解释是“原材料”或“未经处理的东西”,这里猜测是显示设备捕获到的未经处理的信号数据:
spectool_net 将Ubertooth One作为一台“硬件服务器”,并监听TCP:30569端口,局域网内任何可以跟主机建立通信的PC可通过Ubertoothe主机IP+30569共享设备。连接方式:在另外一台主机终端上执行:spectool_gtk
—>选择Open Network Device —>输入ip、端口。
(2)hcitool
root@0xroot:~# hcitool --help
hcitool - HCI Tool ver 4.99
Usage:
hcitool [options] [command parameters]
Options:
--help Display help
-i dev HCI device
Commands:
dev Display local devices
inq Inquire remote devices
scan Scan for remote devices
name Get name from remote device
info Get information from remote device
spinq Start periodic inquiry
epinq Exit periodic inquiry
cmd Submit arbitrary HCI commands
con Display active connections
cc Create connection to remote device
dc Disconnect from remote device
sr Switch master/slave role
cpt Change connection packet type
rssi Display connection RSSI
lq Display link quality
tpl Display transmit power level
afh Display AFH channel map
lp Set/display link policy settings
lst Set/display link supervision timeout
auth Request authentication
enc Set connection encryption
key Change connection link key
clkoff Read clock offset
clock Read local or remote clock
lescan Start LE scan
lewladd Add device to LE White List
lewlrm Remove device from LE White List
lewlsz Read size of LE White List
lewlclr Clear LE White list
lecc Create a LE Connection
ledc Disconnect a LE Connection
lecup LE Connection Update
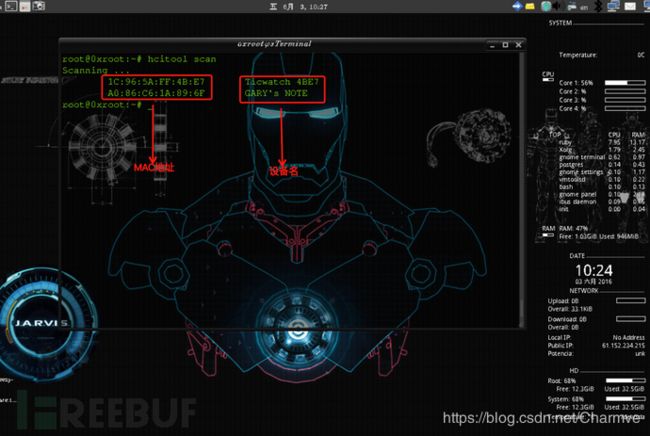
hcitool scan :扫描附近蓝牙设备
hcitool lescan :扫描附近低功耗蓝牙设备
(3)gatttool
root@0xroot:~# gatttool -h
Usage:
gatttool [OPTION...]
Help Options:
-h, --help Show help options
--help-all Show all help options
--help-gatt Show all GATT commands
--help-params Show all Primary Services/Characteristics arguments
--help-char-read-write Show all Characteristics Value/Descriptor Read/Write arguments
Application Options:
-i, --adapter=hciX Specify local adapter interface
-b, --device=MAC Specify remote Bluetooth address
-m, --mtu=MTU Specify the MTU size
-p, --psm=PSM Specify the PSM for GATT/ATT over BR/EDR
-l, --sec-level=[low | medium | high] Set security level. Default: low
-I, --interactive Use interactive mode
gatttool -b 1C:96:5A:FF:4B:E7 -I
[ ][1C:96:5A:FF:4B:E7][LE]> help
help Show this help
exit Exit interactive mode
quit Exit interactive mode
connect [address] Connect to a remote device
disconnect Disconnect from a remote device
primary [UUID] Primary Service Discovery
characteristics [start hnd [end hnd [UUID]]] Characteristics Discovery
char-desc [start hnd] [end hnd] Characteristics Descriptor Discovery
char-read-hnd [offset] Characteristics Value/Descriptor Read by handle
char-read-uuid [start hnd] [end hnd] Characteristics Value/Descriptor Read by UUID
char-write-req Characteristic Value Write (Write Request)
char-write-cmd Characteristic Value Write (No response)
sec-level [low | medium | high] Set security level. Default: low
mtu Exchange MTU for GATT/ATT
[ ][1C:96:5A:FF:4B:E7][LE]>
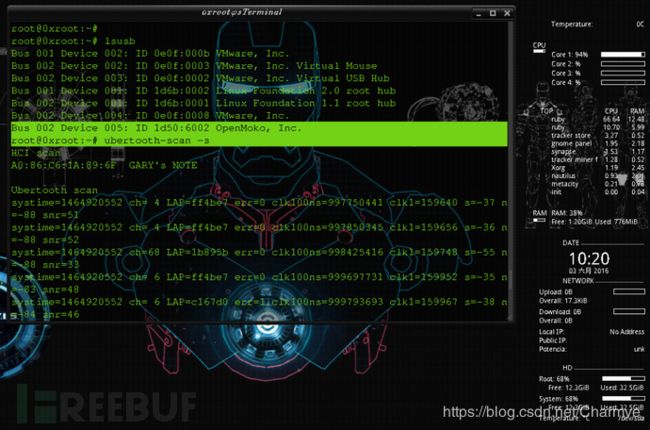
(4)ubertooth-scan
root@0xroot:~# ubertooth-scan --help
ubertooth-scan: invalid option -- '-'
ubertooth-scan - active(bluez) device scan and inquiry supported by Ubertooth
Usage:
-h this Help
-U<0-7> set ubertooth device to use
-s hci Scan - perform HCI scan
-t scan Time (seconds) - length of time to sniff packets. [Default: 20s]
-x eXtended scan - retrieve additional information about target devices
-b Bluetooth device (hci0)
ubertooth-scan -s
(5)ubertooth-btle
ubertooth-btle - passive Bluetooth Low Energy monitoring
Usage:
-h this help
Major modes:
-f follow connections
-p promiscuous: sniff active connections
-a[address] get/set access address (example: -a8e89bed6)
-s faux slave mode, using MAC addr (example: -s22:44:66:88:aa:cc)
-t set connection following target (example: -t22:44:66:88:aa:cc)
Interference (use with -f or -p):
-i interfere with one connection and return to idle
-I interfere continuously
Data source:
-U<0-7> set ubertooth device to use
Misc:
-r capture packets to PCAPNG file
-q capture packets to PCAP file (DLT_BLUETOOTH_LE_LL_WITH_PHDR)
-c capture packets to PCAP file (DLT_PPI)
-A advertising channel index (default 37)
-v[01] verify CRC mode, get status or enable/disable
-x allow n access address offenses (default 32)
If an input file is not specified, an Ubertooth device is used for live capture.
In get/set mode no capture occurs.
ubertooth-btle -f -c test.pcap抓包&保存到本地
使用这条命令我们可以把设备捕获到的数据包保存到本地,完成后可导入wireshark进行数据包、协议分析。
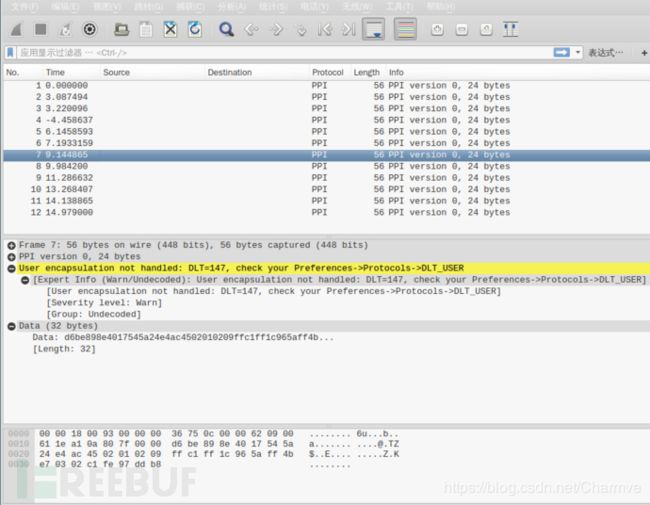
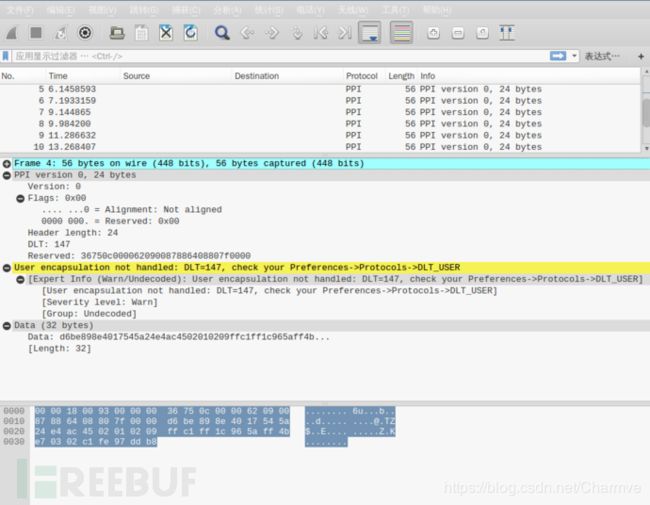
wireshark导入嗅探到的蓝牙数据包需要处理一下才能正常查看,不然无法正常分析数据:
Edit → Preferences → Protocols → DLT_USER → Edit → New
在payload protocol中输入btle
使用规则过滤数据包:参考Capturing BLE in Wireshark
btle.data_header.length > 0 || btle.advertising_header.pdu_type == 0x05
(6)crackle
如果捕获到足够的数据包尤其是btsmp,那接下来便可以用crackle来破解tk和ltk:
crackle -i .pcap>
解密数据包,并把解密后的包另存:
crackle -i .pcap> -o .pcap>
crackle -i .pcap> -o .pcap> -l
5. 参考 && 感谢
参考书:Robin Heydon. Bluetooth Low Energy the Developer’s Handbook 《低功耗蓝牙开发权威指南》,网盘密码公众号回复“8001” 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1xneDTzdejtA91go5YuDhnQ
Sniffing and decoding NRF24L01+ and Bluetooth LE packets for under $30
Bluetooth sniffing with Ubertooth : https://dominicspill.com/kiwicon/Spill-Ubertooth-Kiwicon-2012.pdf
Now I wanna sniff some Bluetooth: Sniffing and Cracking Bluetooth with the UbertoothOne
http://j2abro.blogspot.com.au/2014/06/understanding-bluetooth-advertising.html
路人甲@乌云drops:Bluetooth Low Energy 嗅探
疯狗@乌云drops:物联网安全拔“牙”实战——低功耗蓝牙(BLE)初探
http://j2abro.blogspot.com.au/2014/06/understanding-bluetooth-advertising.html
http://j2abro.blogspot.com.au/2014/06/analyzing-bluetooth-advertising-with.html
http://cerescontrols.com/tutorials-3/sniffing-bluetooth-packets-with-kismet-and-wireshark-in-ubuntu-12-04/
https://github.com/greatscottgadgets/ubertooth/wiki/Build-Guide
https://github.com/greatscottgadgets/ubertooth/wiki/Capturing-BLE-in-Wireshark
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/23877761/sniffing-logging-your-own-android-bluetooth-traffic
https://lacklustre.net/bluetooth/wireshark.html
https://blog.lacklustre.net/posts/BLE_Fun_With_Ubertooth:_Sniffing_Bluetooth_Smart_and_Cracking_Its_Crypto/
http://superuser.com/questions/947593/how-can-i-sniff-bluetooth-traffic-coming-from-my-and-another-device
http://www.backtrack-linux.org/forums/showthread.php?t=41552
http://www.splitbits.com/2014/05/14/ubertooth-spectools-chromebook/
http://ubertooth.sourceforge.net/usage/start/
http://hackerific.net/2012/01/28/Spectrum-Tools-and-Ubertooth-One/
https://penturalabs.wordpress.com/2014/02/20/ubertooth-updated-for-2014/
https://blog.lacklustre.net/
推荐阅读(点击标题可跳转阅读)
[1] 机器学习实战 | 逻辑回归应用之“Kaggle房价预测”
[2] 机器学习实战 | 逻辑回归应用之“Kaggle泰坦尼克之灾”
[3] 本科生晋升GM记录:Kaggle比赛进阶技巧分享
[4] 表情识别FER | 基于深度学习的人脸表情识别系统(Keras)
[5] PyTorch实战 | 使用卷积神经网络对CIFAR10图片进行分类(附源码)
[6] 有了这些珍藏的实用工具/学习网站,自学更快乐!
关注公众号迈微电子研发社,文章首发与公众号。
![]()
知识星球:社群旨在分享AI算法岗的秋招/春招准备攻略(含刷题)、面经和内推机会、学习路线、知识题库等。
![]()
![]()