- 【编译原理】方舟编译技术课程 — 词法分析
CSU_THU_SUT
编译原理编译器编译原理llvm
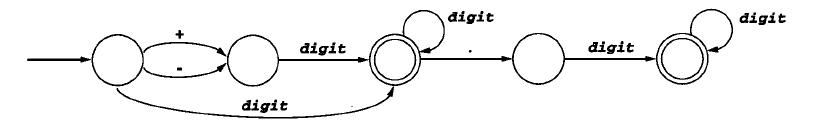
打开目录阅读更佳参考视频:方舟·编译技术入门与实战以及西交冯博琴老师的相关视频编译的过程包括词法分析(分析程序符号)、语法分析(分析语法单位)、中间代码生成、代码优化和目标代码生成。一、编译过程各部分的任务(1)词法分析:输入源程序,扫描分解源程序字符串,识别五类符号,包括定义符、标识符、运算符、界符和常数,转为单词符号。(2)语法分析:在词法分析基础上,将单词符号转为语法单位(如短句、子句、句子
- 包含所有的计算机视频教程
rart2008
程序人生windows移动开发企业应用网络分布式应用asp.net
计算机视频教程http://www.study66.cn/soft/show.asp?id=1237北京师范大-多媒体视频http://www.study66.cn/soft/show.asp?id=1240北京理工大学编译原理串讲http://www.study66.cn/soft/show.asp?id=1241北京大学计算机网络视频教程http://www.study66.cn/soft/s
- 程序员心中的一道坎:主存的编址与计算和串并联系统!
冰河团队
写在前面很多小伙伴认为程序员就是写写代码,不需要了解计算机底层的知识和原理。其实,这种观点是错误的。如果你想突破程序员的职业发展瓶颈,计算机硬件、操作系统原理、编译原理等是一定要掌握的知识。而【冰河技术】微信公众号的【程序员进阶系列】专题就是要系统的向大家分享程序员进阶需要掌握的各项知识技能。今天,我们来聊聊一个让程序员很头疼的话题:计算机中的主存是如何进行编址和计算的?主存编址与计算这里,小伙伴
- 树数据结构(Tree Data Structures)的全面指南:深度解析、算法实战与应用案例
Chauvin912
数据结构科普数据结构算法
树数据结构(TreeDataStructures)的全面指南:深度解析、算法实战与应用案例引言树数据结构(TreeDataStructures)作为计算机科学中的基石之一,以其独特的层次结构和分支特性,在众多领域发挥着关键作用。从文件系统的组织到数据库的索引,从编译原理的语法分析到人工智能的决策制定,树数据结构无处不在。本文将深入探讨树数据结构的基本概念、类型、遍历方式及其在实际应用中的广泛案例。
- 2018-09-07
Maymomo
编译原理Ch1概念编译程序本质上是一个翻译程序,将一门源语言(高级语言)翻译成功能等价的低级语言(汇编语言,机器语言等)的程序。编译程序由八部分组成:词法分析程序语法分析程序语义分析程序中间代码生成程序代码优化程序目标代码生成程序表格管理程序出错处理程序词法分析顺序读入源程序文件,解析出一个个的单词.我的理解是将语言的保留字,标识符,运算符和数值等提取出来。如下简单的C代码(假设不经历预处理器处理
- C++竞赛初阶L1-14-第六单元-数组(31~33课)541: T456471 计算书费
麓小墨哥
c++免费文章c++开发语言青少年编程算法数据结构
题目内容下面是一个图书的单价表:计算概论28.9元/本数据结构与算法32.7元/本数字逻辑45.6元/本C++程序设计教程78元/本人工智能35元/本计算机体系结构86.2元/本编译原理27.8元/本操作系统43元/本计算机网络56元/本JAVA程序设计65元/本依次给定每种图书购买的数量,编程计算应付的总费用。输入格式输入一行,含10个非负整数,每两个整数之间有一个空格。第i个整数表示要购买上述
- Vue 模版编译原理
I will.874
vue.jsjavascript前端
当我们使用Vue编写完一个组件以后,Vue会根据模版编译一个render函数,调用render函数生成虚拟DOM,然后将虚拟DOM映射成真实DOM当数据发生变化时,Vue会触发更新视图,调用render函数返回新的虚拟DOM,对比新旧虚拟DOM,修改真实DOM,从而更新页面在此期间,有以下4个关键步骤:模版编译。生成渲染函数render执行render函数生成虚拟DOM首次渲染,根据虚拟DOM生成
- 【编译原理】一篇就够了——学习笔记与课程实验超详细整理
一棵___大树
编译原理学习笔记学习算法
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐Github主页https://github.com/A-BigTree更多学习笔记链接https://github.com/A-BigTree/college_assignment编译原理实验https://github.com/A-BigTree/college_assignment/compiler_Experiment如果可以,麻烦各位看官顺手点个star~如果文章对你有所帮助
- 解析器模式详解
d303577562
设计模式设计模式
1.简介在软件开发中,会遇到有些问题多次重复出现,而且有一定的相似性和规律性。如果将它们归纳成一种简单的语言,那么这些问题实例将是该语言的一些句子,这样就可以用“编译原理”中的解释器模式来实现了。虽然使用解释器模式的实例不是很多,但对于满足以上特点,且对运行效率不是很高的应用实例,如果用解释器模式来实现,其效果是非常好的。2.定义解释器(Interpreter)模式的定义:给分析对象定义一个语言,
- 用python+pyqt5手工编写一个含交互界面的简易的词法分析器
x1Nge.
学习记录python
python+pyqt5手工编写一个含交互界面的简易词法分析器@author:x1nge.编译原理基础实验基础在之前的一篇博文中我记录了一个不含交互界面的简易词法分析器程序编写内容点击此处查看在本文我将用pyqt5写一个简单的交互界面,也修改了部分代码使得程序更加完整。具体实验分析本文全部源码见本文末尾,上次编写的不含交互界面的源码也可点此处下载交互界面可以用QtDesigner快速编写,或者自己
- 今日总结
薛灵均
1.今日工作感觉还行吧。2.刷了抖音和知乎,练了口语。3.读了《线》10-12章4.做了一会儿矫正动作5.听了歌,印象比较深刻的是《大地》《女人花》《月亮惹的祸》《花心》《心如止水》《屋顶》《我曾》6.看了一点点java和编译原理7.决定明天开始恢复excel的学习8.今天吃的鸭翅好吃9.成年人了,该学会哭过就整理好情绪好好反省自己。10.明天做学编译原理吧,相信自己。还要开始着手面试的事了。按自
- java设计模式之解释器模式
劉鵬杰
JAVA设计模式java设计模式解释器模式
解释器模式(InterpreterPattern)1.基本介绍在编译原理中,一个算术表达式通过词法分析器形成词法单远,而这些词法单远再通过语法分析器构建语法分析树,最终形成一颗抽象的语法分析树,(词法分析器和语法分析器都可以看做是解释器)解释器模式是指给定一个语言(表达式),定义它的文法的一种表示,并定义一个解释器,使用该解释器来解释语言中的句子(表达式)。2.应用场景可以将一个需要解释执行的语言
- 程序员泛滥的时代,怎么样才能让自己脱颖而出?
Java自闭师
由于LZ本人是Java后端开发出身,因此所推荐的学习内容是JavaWeb和Java后端开发的路线,非JavaWeb和Java后端开发的同学请适当参考其学习思想即可,切勿照搬。2、下面的推荐内容,目的是让你尽快成为一个可以参加工作的Java开发者,更适用于处于待业状态,准备转行Java的同学。如果你是在校学生,务必要在学好基础(比如计算机系统、算法、编译原理等等)的前提下,再考虑去进行下面的学习。对
- 编译原理(三)词法分析
Cookie__C
词法分析词法分析是编译的第一个阶段,它的主要任务是从左到右逐个字符地对源程序进行扫描,产生一个个单词序列。词法分析阶段设计的主要问题是字符串(单词)的识别问题。具体说,如何判定任意的一个字符串是否为合法字符串(单词)的问题。字符串(单词)集合可用不同的工具来表示,常见的有:单词的描述技术:正规式。识别机制:有穷自动机(有限自动机)。因此,要研究如何从正规表达式或自动机构造出相应的单词识别器的问题。
- STM32必备知识点(面试和工作用的到)
树的编程知识屋
嵌入式基础stm32求职招聘单片机
STM32必备知识点(面试和工作用的到)文章目录STM32必备知识点(面试和工作用的到)前言嵌入式C基础一、位操作1.不改变其他位的值的状况下,对某几个位进行设值2.移位操作提高代码的可读性:将第pinpos位设置为13.~取反操作使用技巧4.举例:二、ifdef条件编译三、extern变量申明二、编译原理1、Gcc编译的C语言程序占用的内存分为哪几个部分?三、STM32资料1、常用小知识2、基础
- 编译原理-递归下降分析法-c简单实现
都灵的夏天_
一、实验目的:根据某一文法编制调试递归下降分析程序,以便对任意输入的符号串进行分析。本次实验的目的主要是加深对递归下降分析法的理解。二、实验预习提示1、递归下降分析法的功能词法分析器的功能是利用函数之间的递归调用模拟语法树自上而下的构造过程。2、递归下降分析法的前提改造文法:消除二义性、消除左递归、提取左因子,判断是否为LL(1)文法,3、递归下降分析法实验设计思想及算法为G的每个非终结符号U构造
- 深入了解C++:底层编译原理
程韬123
linux运维c++缓存开发语言
进程的虚拟空间划分任何编程语言,都会产生两样东西,指令和数据。.exe程序运行的时候会从磁盘被加载到内存中,但是不能直接加载到物理内存中。Linux会给当前进程分配一块空间,比如x8632位linux环境下会给进程分配2^32(4G)大小的空间,这个空间被叫做【进程的虚拟地址空间】,进程的虚拟地址空间其实并不存在,从底层来看它不过是内核创建的一系列数据结构而已。以x8632位linux为例,讲解进
- 深入了解C++:底层编译原理(二)
程韬123
c++开发语言
C++文件需要经历编译和链接两大步骤才能生成可执行文件。编译会生成二进制可重定位的目标文件,其中的重定位指的是符号重定位,发生了链接阶段。二进制可重定位的目标文件:也就是我们通常所说的.o,.obj文件。二进制文件构成:二进制文件就是.o文件,其中的内容除了elf文件头,还由各个段组成,有些段和内存空间个段可以匹配,比如.text,.data.,.bss段。objdump-s和readelf-S是
- (三)JVM成神路之全面详解执行引擎子系统与JIT即时编译原理
竹子爱熊猫
JVMjava高并发编程架构
引言执行引擎子系统是JVM的重要组成部分之一,在JVM系列的开篇曾提到:JVM是一个架构在平台上的平台,虚拟机是一个相似于“物理机”的概念,与物理机一样,都具备代码执行的能力。但虚拟机与物理机最大的不同在于:物理机的执行引擎是直接建立在处理器、高速缓存、平台指令集与操作系统层面上的,物理机的执行引擎可以直接调用各处资源对代码进行直接执行,而虚拟机则是建立在软件层面上的平台,它的执行引擎则是负责解释
- JVM成神路之全面详解执行引擎子系统、JIT即时编译原理与分派实现
头顶假发
程序员Java编程jvmjavalinux
引言执行引擎子系统是JVM的重要组成部分之一,在JVM系列的开篇曾提到:JVM是一个架构在平台上的平台,虚拟机是一个相似于“物理机”的概念,与物理机一样,都具备代码执行的能力。但虚拟机与物理机最大的不同在于:物理机的执行引擎是直接建立在处理器、高速缓存、平台指令集与操作系统层面上的,物理机的执行引擎可以直接调用各处资源对代码进行直接执行,而虚拟机则是建立在软件层面上的平台,它的执行引擎则是负责解释
- 疫情爆发前 我因流感被隔离了
冷冷的方格田
时间:2019年末记录初衷:可能因为印象比较深刻,给我身体和精神上带来了较大的折磨,并且紧挨着就发生了新冠(以下是正文,没有太多修辞,仅仅是个人经历的一次记录)12月9日daybegin早上起来忽然感觉头昏脑胀,喉咙不知不明的痛。不过,作为一个在校大学生,作业任务让我很快压过了生病的念头。今天的计划是把编译原理的实验报告写完,这事就算结束了。早早的起床,洗漱吃饭,到自习室。实验报告写了一半,困意来
- Makefile编译原理 make 中的路径搜索_2
嵌入式_笔记
Linux驱动linux
一.make中的路径搜索VPATH变量和vpath关键字同时指定搜索路径。实验1VPATH和vpath同时指定搜索路径mhr@ubuntu:~/work/makefile1/18$tree.├──inc│└──func.h├──main.c├──makefile├──src1│└──func.c└──src2└──func.cmakefileVPATH:=src1CFLAGS:=-Iincvpat
- Makefile编译原理 make 中的路径搜索_1
嵌入式_笔记
Linux驱动linux
一.make中的路径搜索问题:在实际的工程项目中,所有的源文件和头文件都放在同一个文件夹中吗?实验1:VPATH引子mhr@ubuntu:~/work/makefile1/17$lltotal28drwxrwxr-x4mhrmhr4096Apr2200:46./drwxrwxr-x7mhrmhr4096Apr2200:32../drwxrwxrwx2mhrmhr4096Jan232018inc/-
- Makefile编译原理 make的隐性规则
嵌入式_笔记
Linux驱动数据库服务器运维
一.makefile中的同名目标下面程序怎么执行?为什么?实验1:makefile中出现同名目标时.PHONY:allall:@echo"command-1"all:@echo"command-2"VAR:=testall:@echo"all:$(VAR)"mhr@ubuntu:~/work/makefile1$makeallmakefile:12:warning:overridingrecipe
- 【软件设计师】——编译原理
栉风沐雪
软件设计师开发语言汇编软件工程
编译系统的结构词法分析/扫描(Scanning)从左向右逐行扫描源程序的字符,识别出各个单词,确定单词的类型。将识别出的单词转换成统一的机内表示,词法单元(token)形式:token:单词类型种别种别码关键字program,if,else…一词一码标识符变量名,数组名,记录名…多词一码常量整型,浮点型,字符型…一型一码运算符算术、关系、逻辑一词\一型一码界限符;()={}…一词一码语法分析(pa
- 《编译原理》
曹元_
第一章编译引论1、编译程序:将某一种程序设计语言写的程序翻译成等价的另一种语言的程序的程序2、源语言:用来编写源程序的语言(汇编,高级程序设计语言)3、源程序:用源语言写的程序4、目标语言:目标程序描述的语言5、目标程序:源程序经过编译后生成的程序6、宿主语言:编译程序的实现语言7、宿主机:编译程序的运行环境8、分类:解释程序【接受某语言的源程序将其直接翻译成目标代码且执行】;编译程序【接受某语言
- 编译原理研究性学习专题 2——递归下降语法分析设计原理与实现
dor.yang
课程作业记录博客学习java前端编译原理递归下降
1实验内容完成以下描述赋值语句的LL(1)文法的递归下降分析程序G[S]:S→V=EE→TE’E’→ATE’|eT→FT’T’→MFT’|EF→(E)|iA→+|-M→*|/V→i设计说明:终结符号i为用户定义的简单变量,即标识符的定义。2实验要求(1)输入串应是词法分析的输出二元式序列,即某算术表达式“专题1”的输出结果,输出为输入串是否为该文法定义的算术表达式的判断结果;(2)递归下降分析程序
- 编译原理(九)——递归下降法
很注重数学和821
编译原理
背景:自定向下的语法分析方法,LL(1)是一种非常直观的方法,它的分析过程是按照句子的定义来进行的,也就是说从开始符出发对要分析的串进行推导,如果推导成功就证明这个被分析的串是一个合法的句子,否则的话就有语法错误,但是在推导过程中,对文法进行了一些限定,保证推导过程是唯一的。总体上说,LL(1)就是在选择规则的时候加入了约束条件,考虑到输入流中的第一个符号,以及推导过程中的非终极符的规则选择,只有
- 编译原理 实验2 语法分析——递归下降分析器
学而时习之,不亦说乎?
目录标题一、核心代码1.题目要求2.代码实现3.运行结果:二、实现加,减,乘,除运算的表达式文法1.题目要求2.代码实现3.运行结果一、核心代码1.题目要求练习构造递归下降语法分析程序的方法,熟悉上下文无关文法的使用,加深对课堂教学的理解;提高语法分析方法的实践能力文法G[E]:E→E+T|TT→T*F|FF→i|(E)消除左递归后:E→TXX→+TX|^T→FYY→*FY|^F→i|(E)要求:
- 编译原理——实验贰——递归下降语法分析器的构建
赴约如期
一、实验要求运用递归下降法,针对给定的上下文无关文法,给出实验方案。预估实验中可能出现的问题。二、实验方案1、构造LL(1),通过设计、编制、调试递归下降语法分析程序,对输入的符号串进行分析匹配,观察输入符号串是否为给定文法的句子。2、根据LL(1)写程序三、预估问题预估问题:LL(1)构造失败,程序报错理论基础:1、递归下降分析程序的实现思想是:识别程序由一组子程序组成。每个子程序对应于一个非终
- VMware Workstation 11 或者 VMware Player 7安装MAC OS X 10.10 Yosemite
iwindyforest
vmwaremac os10.10workstationplayer
最近尝试了下VMware下安装MacOS 系统,
安装过程中发现网上可供参考的文章都是VMware Workstation 10以下, MacOS X 10.9以下的文章,
只能提供大概的思路, 但是实际安装起来由于版本问题, 走了不少弯路, 所以我尝试写以下总结, 希望能给有兴趣安装OSX的人提供一点帮助。
写在前面的话:
其实安装好后发现, 由于我的th
- 关于《基于模型驱动的B/S在线开发平台》源代码开源的疑虑?
deathwknight
JavaScriptjava框架
本人从学习Java开发到现在已有10年整,从一个要自学 java买成javascript的小菜鸟,成长为只会java和javascript语言的老菜鸟(个人邮箱:
[email protected])
一路走来,跌跌撞撞。用自己的三年多业余时间,瞎搞一个小东西(基于模型驱动的B/S在线开发平台,非MVC框架、非代码生成)。希望与大家一起分享,同时有许些疑虑,希望有人可以交流下
平台
- 如何把maven项目转成web项目
Kai_Ge
mavenMyEclipse
创建Web工程,使用eclipse ee创建maven web工程 1.右键项目,选择Project Facets,点击Convert to faceted from 2.更改Dynamic Web Module的Version为2.5.(3.0为Java7的,Tomcat6不支持). 如果提示错误,可能需要在Java Compiler设置Compiler compl
- 主管???
Array_06
工作
转载:http://www.blogjava.net/fastzch/archive/2010/11/25/339054.html
很久以前跟同事参加的培训,同事整理得很详细,必须得转!
前段时间,公司有组织中高阶主管及其培养干部进行了为期三天的管理训练培训。三天的课程下来,虽然内容较多,因对老师三天来的课程内容深有感触,故借着整理学习心得的机会,将三天来的培训课程做了一个
- python内置函数大全
2002wmj
python
最近一直在看python的document,打算在基础方面重点看一下python的keyword、Build-in Function、Build-in Constants、Build-in Types、Build-in Exception这四个方面,其实在看的时候发现整个《The Python Standard Library》章节都是很不错的,其中描述了很多不错的主题。先把Build-in Fu
- JSP页面通过JQUERY合并行
357029540
JavaScriptjquery
在写程序的过程中我们难免会遇到在页面上合并单元行的情况,如图所示
如果对于会的同学可能很简单,但是对没有思路的同学来说还是比较麻烦的,提供一下用JQUERY实现的参考代码
function mergeCell(){
var trs = $("#table tr");
&nb
- Java基础
冰天百华
java基础
学习函数式编程
package base;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Integer a = 4;
// Double aa = (double)a / 100000;
// Decimal
- unix时间戳相互转换
adminjun
转换unix时间戳
如何在不同编程语言中获取现在的Unix时间戳(Unix timestamp)? Java time JavaScript Math.round(new Date().getTime()/1000)
getTime()返回数值的单位是毫秒 Microsoft .NET / C# epoch = (DateTime.Now.ToUniversalTime().Ticks - 62135
- 作为一个合格程序员该做的事
aijuans
程序员
作为一个合格程序员每天该做的事 1、总结自己一天任务的完成情况 最好的方式是写工作日志,把自己今天完成了什么事情,遇见了什么问题都记录下来,日后翻看好处多多
2、考虑自己明天应该做的主要工作 把明天要做的事情列出来,并按照优先级排列,第二天应该把自己效率最高的时间分配给最重要的工作
3、考虑自己一天工作中失误的地方,并想出避免下一次再犯的方法 出错不要紧,最重
- 由html5视频播放引发的总结
ayaoxinchao
html5视频video
前言
项目中存在视频播放的功能,前期设计是以flash播放器播放视频的。但是现在由于需要兼容苹果的设备,必须采用html5的方式来播放视频。我就出于兴趣对html5播放视频做了简单的了解,不了解不知道,水真是很深。本文所记录的知识一些浅尝辄止的知识,说起来很惭愧。
视频结构
本该直接介绍html5的<video>的,但鉴于本人对视频
- 解决httpclient访问自签名https报javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: sun.security.validat
bewithme
httpclient
如果你构建了一个https协议的站点,而此站点的安全证书并不是合法的第三方证书颁发机构所签发,那么你用httpclient去访问此站点会报如下错误
javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path bu
- Jedis连接池的入门级使用
bijian1013
redisredis数据库jedis
Jedis连接池操作步骤如下:
a.获取Jedis实例需要从JedisPool中获取;
b.用完Jedis实例需要返还给JedisPool;
c.如果Jedis在使用过程中出错,则也需要还给JedisPool;
packag
- 变与不变
bingyingao
不变变亲情永恒
变与不变
周末骑车转到了五年前租住的小区,曾经最爱吃的西北面馆、江西水饺、手工拉面早已不在,
各种店铺都换了好几茬,这些是变的。
三年前还很流行的一款手机在今天看起来已经落后的不像样子。
三年前还运行的好好的一家公司,今天也已经不复存在。
一座座高楼拔地而起,
- 【Scala十】Scala核心四:集合框架之List
bit1129
scala
Spark的RDD作为一个分布式不可变的数据集合,它提供的转换操作,很多是借鉴于Scala的集合框架提供的一些函数,因此,有必要对Scala的集合进行详细的了解
1. 泛型集合都是协变的,对于List而言,如果B是A的子类,那么List[B]也是List[A]的子类,即可以把List[B]的实例赋值给List[A]变量
2. 给变量赋值(注意val关键字,a,b
- Nested Functions in C
bookjovi
cclosure
Nested Functions 又称closure,属于functional language中的概念,一直以为C中是不支持closure的,现在看来我错了,不过C标准中是不支持的,而GCC支持。
既然GCC支持了closure,那么 lexical scoping自然也支持了,同时在C中label也是可以在nested functions中自由跳转的
- Java-Collections Framework学习与总结-WeakHashMap
BrokenDreams
Collections
总结这个类之前,首先看一下Java引用的相关知识。Java的引用分为四种:强引用、软引用、弱引用和虚引用。
强引用:就是常见的代码中的引用,如Object o = new Object();存在强引用的对象不会被垃圾收集
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-解释器模式-Interpret
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
package design.pattern;
/*
* 解释器(Interpreter)模式的意图是可以按照自己定义的组合规则集合来组合可执行对象
*
* 代码示例实现XML里面1.读取单个元素的值 2.读取单个属性的值
* 多
- After Effects操作&快捷键
cherishLC
After Effects
1、快捷键官方文档
中文版:https://helpx.adobe.com/cn/after-effects/using/keyboard-shortcuts-reference.html
英文版:https://helpx.adobe.com/after-effects/using/keyboard-shortcuts-reference.html
2、常用快捷键
- Maven 常用命令
crabdave
maven
Maven 常用命令
mvn archetype:generate
mvn install
mvn clean
mvn clean complie
mvn clean test
mvn clean install
mvn clean package
mvn test
mvn package
mvn site
mvn dependency:res
- shell bad substitution
daizj
shell脚本
#!/bin/sh
/data/script/common/run_cmd.exp 192.168.13.168 "impala-shell -islave4 -q 'insert OVERWRITE table imeis.${tableName} select ${selectFields}, ds, fnv_hash(concat(cast(ds as string), im
- Java SE 第二讲(原生数据类型 Primitive Data Type)
dcj3sjt126com
java
Java SE 第二讲:
1. Windows: notepad, editplus, ultraedit, gvim
Linux: vi, vim, gedit
2. Java 中的数据类型分为两大类:
1)原生数据类型 (Primitive Data Type)
2)引用类型(对象类型) (R
- CGridView中实现批量删除
dcj3sjt126com
PHPyii
1,CGridView中的columns添加
array(
'selectableRows' => 2,
'footer' => '<button type="button" onclick="GetCheckbox();" style=&
- Java中泛型的各种使用
dyy_gusi
java泛型
Java中的泛型的使用:1.普通的泛型使用
在使用类的时候后面的<>中的类型就是我们确定的类型。
public class MyClass1<T> {//此处定义的泛型是T
private T var;
public T getVar() {
return var;
}
public void setVa
- Web开发技术十年发展历程
gcq511120594
Web浏览器数据挖掘
回顾web开发技术这十年发展历程:
Ajax
03年的时候我上六年级,那时候网吧刚在小县城的角落萌生。传奇,大话西游第一代网游一时风靡。我抱着试一试的心态给了网吧老板两块钱想申请个号玩玩,然后接下来的一个小时我一直在,注,册,账,号。
彼时网吧用的512k的带宽,注册的时候,填了一堆信息,提交,页面跳转,嘣,”您填写的信息有误,请重填”。然后跳转回注册页面,以此循环。我现在时常想,如果当时a
- openSession()与getCurrentSession()区别:
hetongfei
javaDAOHibernate
来自 http://blog.csdn.net/dy511/article/details/6166134
1.getCurrentSession创建的session会和绑定到当前线程,而openSession不会。
2. getCurrentSession创建的线程会在事务回滚或事物提交后自动关闭,而openSession必须手动关闭。
这里getCurrentSession本地事务(本地
- 第一章 安装Nginx+Lua开发环境
jinnianshilongnian
nginxluaopenresty
首先我们选择使用OpenResty,其是由Nginx核心加很多第三方模块组成,其最大的亮点是默认集成了Lua开发环境,使得Nginx可以作为一个Web Server使用。借助于Nginx的事件驱动模型和非阻塞IO,可以实现高性能的Web应用程序。而且OpenResty提供了大量组件如Mysql、Redis、Memcached等等,使在Nginx上开发Web应用更方便更简单。目前在京东如实时价格、秒
- HSQLDB In-Process方式访问内存数据库
liyonghui160com
HSQLDB一大特色就是能够在内存中建立数据库,当然它也能将这些内存数据库保存到文件中以便实现真正的持久化。
先睹为快!
下面是一个In-Process方式访问内存数据库的代码示例:
下面代码需要引入hsqldb.jar包 (hsqldb-2.2.8)
import java.s
- Java线程的5个使用技巧
pda158
java数据结构
Java线程有哪些不太为人所知的技巧与用法? 萝卜白菜各有所爱。像我就喜欢Java。学无止境,这也是我喜欢它的一个原因。日常
工作中你所用到的工具,通常都有些你从来没有了解过的东西,比方说某个方法或者是一些有趣的用法。比如说线程。没错,就是线程。或者确切说是Thread这个类。当我们在构建高可扩展性系统的时候,通常会面临各种各样的并发编程的问题,不过我们现在所要讲的可能会略有不同。
- 开发资源大整合:编程语言篇——JavaScript(1)
shoothao
JavaScript
概述:本系列的资源整合来自于github中各个领域的大牛,来收藏你感兴趣的东西吧。
程序包管理器
管理javascript库并提供对这些库的快速使用与打包的服务。
Bower - 用于web的程序包管理。
component - 用于客户端的程序包管理,构建更好的web应用程序。
spm - 全新的静态的文件包管
- 避免使用终结函数
vahoa.ma
javajvmC++
终结函数(finalizer)通常是不可预测的,常常也是很危险的,一般情况下不是必要的。使用终结函数会导致不稳定的行为、更差的性能,以及带来移植性问题。不要把终结函数当做C++中的析构函数(destructors)的对应物。
我自己总结了一下这一条的综合性结论是这样的:
1)在涉及使用资源,使用完毕后要释放资源的情形下,首先要用一个显示的方