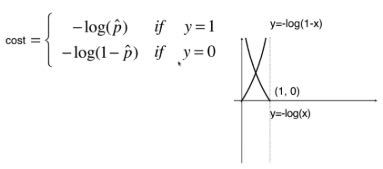初识机器学习 | 6.逻辑回归
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib
%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
Using matplotlib backend: MacOSX
逻辑回归(Logistic Regression), 是使用回归的实现的分类算法,只能解决二分类问题. 在Kaggle竞赛中,LR算法以63.5,荣获"出场率最高算法"
p ^ = f ( x ) y ^ = { 1 , p ^ ≥ 0.5 0 , p ^ ≤ 0.5 \hat{p}=f(x) \quad \hat{y}=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} 1, & \hat{p} \geq 0.5 \\ 0, & \hat{p} \leq 0.5 \end{array}\right. p^=f(x)y^={1,0,p^≥0.5p^≤0.5
假定f(x)为一个线性回归问题,他的值域(-infinity,+infinity)
f ( x ) = x b ⋅ θ f(x)= x_{b} \cdot \theta f(x)=xb⋅θ
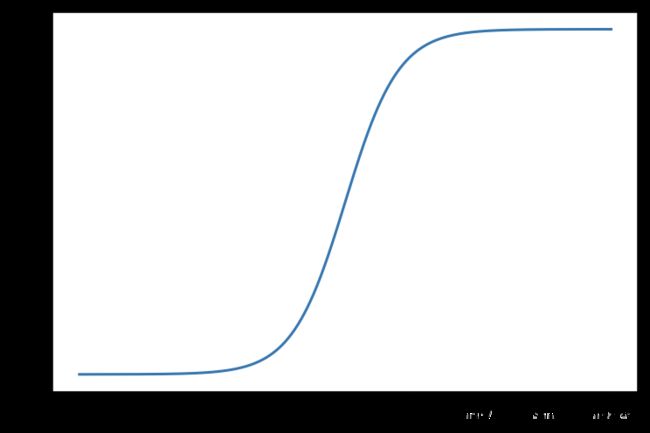
使用Sigmoid函数限定为概率的值域[0,1]
σ ( t ) = 1 1 + e − t \sigma(t)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-t}} σ(t)=1+e−t1
Sigmoid函数
σ ( t ) = 1 1 + e − t \sigma(t)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-t}} σ(t)=1+e−t1
值域(0,1)
- t0时候, p=0.5
- t>0时候, p>0.5
- t<0时候, p<0.5
# 返回e的幂次方,e是一个常数为2.71828。将线性方程转化为0-1之间的概率。
def sigmoid(t):
return 1.0 / (1+np.exp(-t))
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 500)
plt.plot(x, sigmoid(x))
plt.show()
实现逻辑回归
逻辑回归的模型
p ^ = σ ( f ( x ) ) = σ ( x b ⋅ θ ) = 1 1 + e x b ⋅ θ \hat{p}=\sigma\left(f(x)\right)=\sigma\left(x_{b} \cdot {\theta}\right)=\frac{1}{1+e^{x_{b} \cdot {\theta}}} p^=σ(f(x))=σ(xb⋅θ)=1+exb⋅θ1
y ^ = { 1 , p ^ ≥ 0.5 0 , p ^ ≤ 0.5 \hat{y}=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} 1, & \hat{p} \geq 0.5 \\ 0, & \hat{p} \leq 0.5 \end{array}\right. y^={1,0,p^≥0.5p^≤0.5
问题: 给定的样本集X,y, 如何找到对应的参数Theta(使用梯度下降搜索),是的最大程度获得样本数据集X对应的分类输出y?
解决方法: 最小话损失函数,使用梯度下降找到对应的Theta
假设损失函数
从逻辑回归的模型可看出
- 当y=1时, p值越小,损失越大;p值越大,损失越小。
- 当y=0时, p值越小,损失越小;p值越大,损失越大。
进一步推导:
cost = − y log ( p ^ ) − ( 1 − y ) log ( 1 − p ^ ) \operatorname{cost}=-y \log (\hat{p})-(1-y) \log (1-\hat{p}) cost=−ylog(p^)−(1−y)log(1−p^)
=>
J ( θ ) = − 1 m ∑ i = 1 m y ( i ) log ( p ^ ( i ) ) + ( 1 − y ( i ) ) log ( 1 − p ^ ( i ) ) J(\theta)=-\frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m} y^{(i)} \log \left(\hat{p}^{(i)}\right)+\left(1-y^{(i)}\right) \log \left(1-\hat{p}^{(i)}\right) J(θ)=−m1i=1∑my(i)log(p^(i))+(1−y(i))log(1−p^(i))
=>
J ( θ ) = − 1 m ∑ i = 1 m y ( i ) log ( σ ( X b ( i ) θ ) ) + ( 1 − y ( i ) ) log ( 1 − σ ( X b ( i ) θ ) ) J(\theta)=-\frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m} y^{(i)} \log \left(\sigma\left(X_{b}^{(i)} \theta\right)\right)+\left(1-y^{(i)}\right) \log \left(1-\sigma\left(X_{b}^{(i)} \theta\right)\right) J(θ)=−m1i=1∑my(i)log(σ(Xb(i)θ))+(1−y(i))log(1−σ(Xb(i)θ))
∇ J ( θ ) = 1 m ⋅ ( ∑ i = 1 m ( y ^ ( i ) − y ( i ) ) ∑ i = 1 m ( y ^ ( i ) − y ( i ) ) ⋅ X 1 ( i ) ∑ i = 1 m ( y ^ ( i ) − y ( i ) ) ⋅ X 2 ( i ) ⋯ ∑ i = 1 m ( y ^ ( i ) − y ( i ) ) ⋅ X n ( i ) ) = 1 m ⋅ X b T ⋅ ( σ ( X b θ ) − y ) \nabla J(\theta)=\frac{1}{m} \cdot\left(\begin{array}{c} \sum_{i=1}^{m}\left(\hat{y}^{(i)}-y^{(i)}\right) \\ \sum_{i=1}^{m}\left(\hat{y}^{(i)}-y^{(i)}\right) \cdot X_{1}^{(i)} \\ \sum_{i=1}^{m}\left(\hat{y}^{(i)}-y^{(i)}\right) \cdot X_{2}^{(i)} \\ \cdots \\ \sum_{i=1}^{m}\left(\hat{y}^{(i)}-y^{(i)}\right) \cdot X_{n}^{(i)} \\ \end{array}\right) =\frac{1}{m} \cdot X_{b}^{T} \cdot\left(\sigma\left(X_{b} \theta\right)-y\right) ∇J(θ)=m1⋅⎝⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎛∑i=1m(y^(i)−y(i))∑i=1m(y^(i)−y(i))⋅X1(i)∑i=1m(y^(i)−y(i))⋅X2(i)⋯∑i=1m(y^(i)−y(i))⋅Xn(i)⎠⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎞=m1⋅XbT⋅(σ(Xbθ)−y)
以上方程无公式解, 只能使用梯度下降法求解
import numpy as np
class LogisticRegression:
def __init__(self):
self._thetas = None
# 截距
self.intercept = None
# 参数系数
self.coefs = None
@staticmethod
def sigmoid(t):
return 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-t))
def j(self, x, y, theta):
"""目标函数"""
try:
sig = self.sigmoid(x.dot(theta))
return -(np.sum(y.dot(np.log(sig)) + (1-y).dot(1-sig))) / len(x)
except:
# 当数据特别大,报错时,返回无穷大。
return float('inf')
def dj_debug(self, x, y, theta, epsilon=0.01):
"""梯度调试"""
res = np.empty(len(theta))
for i in range(len(theta)):
theta_1 = theta.copy()
theta_1[i] += epsilon
theta_2 = theta.copy()
theta_2[i] -= epsilon
res[i] = (self.j(theta_1, x, y) - self.j(theta_2, x, y)) / (2 * epsilon)
return res
def dj(self, x, y, thetas):
"""求导(梯度)"""
sig = self.sigmoid(x.dot(thetas))
return (x.T).dot(sig-y)
def gradient_descent(self, dj, x, y, initial_thetas, eta, epsilon, max_iters):
"""梯度下降"""
thetas = initial_thetas
while max_iters > 0:
# 梯度gradient
gradient = dj(x, y, thetas)
last_thetas = thetas
thetas = thetas - eta * gradient
if(abs(self.j(x, y, thetas) - self.j(x, y, last_thetas)) < epsilon):
break
max_iters -= 1
self._thetas = thetas
self.intercept = thetas[0]
self.coefs = thetas[1:]
def fit(self, x_train, y_train, eta=0.01, epsilon=1e-8, max_iters=1e4, debug=False):
"""训练"""
# 加上一列全为1
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(x_train), 1)), x_train])
initial_thetas = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1])
if debug:
self.gradient_descent(self.dj_debug, X_b, y_train, initial_thetas, eta, epsilon, max_iters)
else:
self.gradient_descent(self.dj, X_b, y_train, initial_thetas, eta, epsilon, max_iters)
def predict(self, x_predict):
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(x_predict), 1)), x_predict])
p = self.sigmoid(X_b.dot(self._thetas))
p[p >= 0.5] = 1
p[p < 0.5] = 0
return p
def score(self, x, y):
"""accuracy=正确的数据量 / 样本量"""
y_predict = self.predict(x)
return np.sum(y == y_predict) / len(y)
from sklearn import datasets
# 只使用两种莺尾花和两个特征
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
X = X[y < 2, : 2]
y = y[y < 2]
# 训练模型
log_reg = LogisticRegression()
log_reg.fit(X, y)
print('coefs: ', log_reg.coefs)
print('intercept: ', log_reg.intercept)
print('Score: ', log_reg.score(X, y))
coefs: [ 9.91317105 -11.51345535]
intercept: -17.935266908864193
Score: 0.99
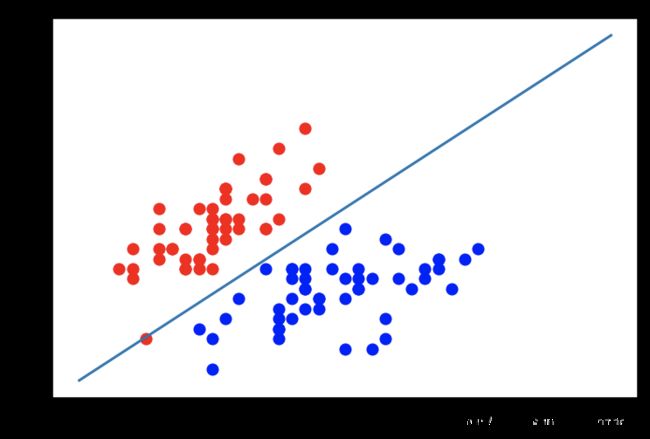
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1], color="red")
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1], color="blue")
# 绘制分隔线
# x1 = np.arange(4, 8, 0.01)
x1 = np.linspace(4, 8, 1000)
y1 = x1 * (log_reg.coefs[0]/(-log_reg.coefs[1])) + (log_reg.intercept/-log_reg.coefs[1])
plt.plot(x1, y1)
plt.show()
决策边界绘制
def plot_decision_boundary(model, axis):
""" 决策边界绘制函数(2D)
"""
# x轴: axis[0]~axis[1]; y轴: axis[0]~axis[1]
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1]-axis[0])*100)).reshape(-1, 1),
np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3]-axis[2])*100)).reshape(-1, 1),
)
X_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()]
y_predict = model.predict(X_new)
zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape)
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A','#FFF59D','#90CAF9'])
plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap)
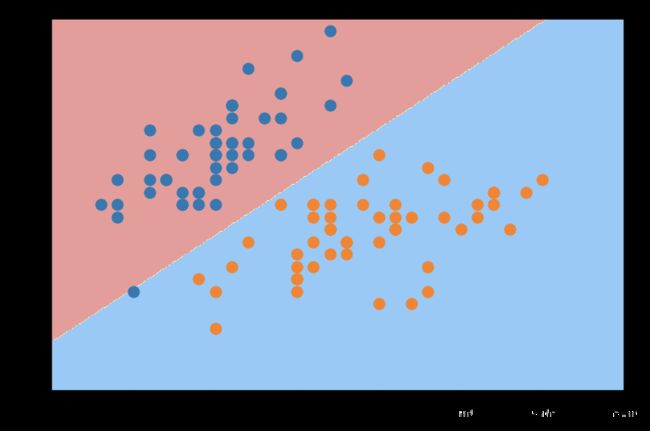
两类莺尾花决策边界绘制(两个特征)
plot_decision_boundary(log_reg, axis=[4, 7.5, 1.5, 4.5])
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1])
plt.show()
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:17: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth'
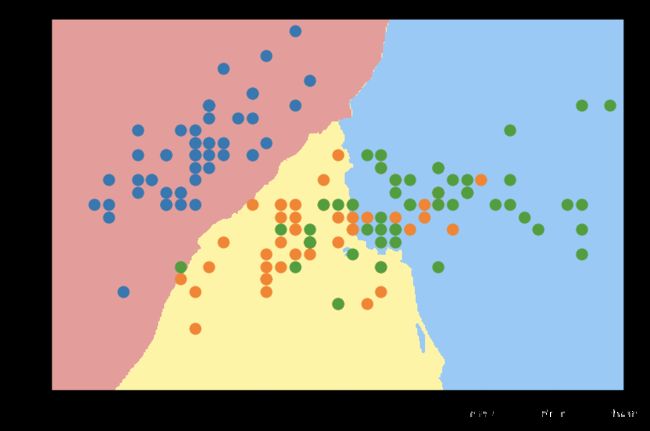
三类莺尾花决策边界绘制(两个特征)
# 全部类别的莺尾花(两个特征),因为有三类,而逻辑回归只能解决二分类问题,所以使用knn解决
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
# 只使用两种莺尾花和两个特征
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X_all = (iris.data)[:,:2]
y_all = iris.target
# 调整n_neighbors, 控制拟合度
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=30)
knn.fit(X_all, y_all)
print('Score: ', knn.score(X_all, y_all))
# 绘制预测值和决策边界
plot_decision_boundary(knn, axis=[4, 8, 1.5, 4.5])
plt.scatter(X_all[y_all==0,0], X_all[y_all==0,1])
plt.scatter(X_all[y_all==1,0], X_all[y_all==1,1])
plt.scatter(X_all[y_all==2,0], X_all[y_all==2,1])
plt.show()
Score: 0.84
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:17: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth'
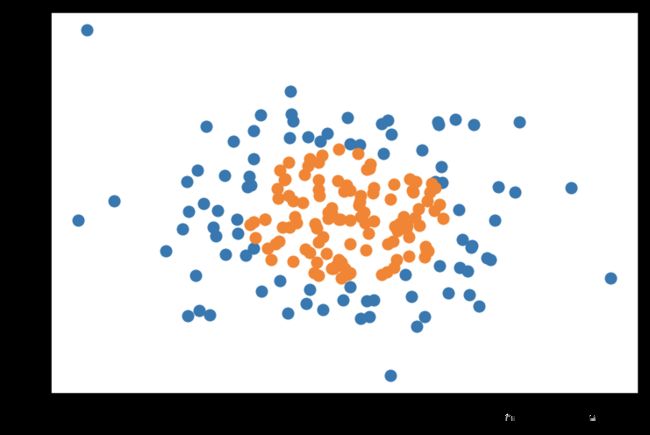
逻辑回归中添加多项式特征
np.random.seed(666)
X = np.random.normal(0, 1, size=(200, 2))
y = np.array((X[:,0]**2+X[:,1]**2)<1.5, dtype='int')
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1])
plt.show()
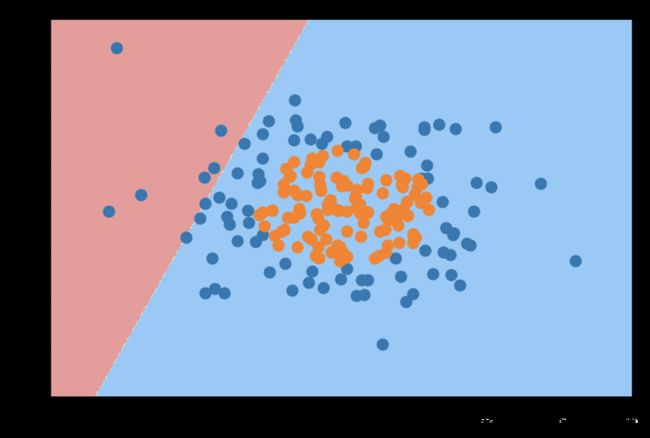
单纯使用逻辑回归
如下,因为现实中边界类似于圆, 而逻辑回归得到的边界是条直线,拟合很差。从而使得分比较低。
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
log_reg = LogisticRegression()
log_reg.fit(X, y)
print('Score', log_reg.score(X, y))
Score 0.605
# 绘制预测值和决策边界
plot_decision_boundary(log_reg, axis=[-4, 4, -4, 4])
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1])
plt.show()
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:17: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth'
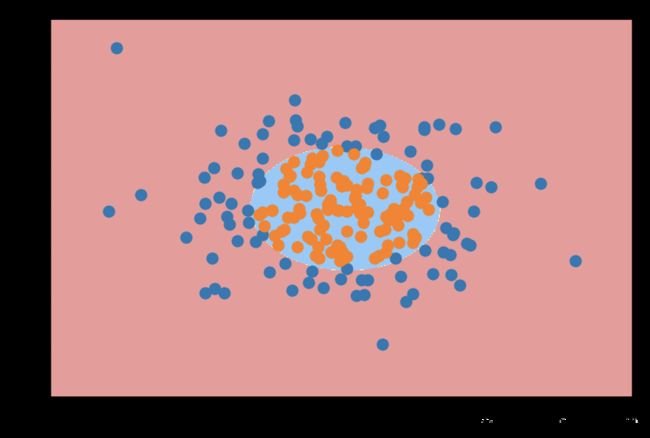
加入多项式特性
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
def PolynomialLogisticRegression(degree):
return Pipeline([
('poly', PolynomialFeatures(degree=degree)),
('log_reg', LogisticRegression())
])
poly_log_reg = PolynomialLogisticRegression(degree=2)
poly_log_reg.fit(X, y)
print('score: ', poly_log_reg.score(X, y))
score: 0.975
plot_decision_boundary(poly_log_reg, axis=[-4, 4, -4, 4])
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1])
plt.show()
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:17: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth'
多分类问题
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, :2]
y = iris.target
log_reg = LogisticRegression()
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1])
plt.show()
OVR
from sklearn.multiclass import OneVsRestClassifier
ovr = OneVsRestClassifier(log_reg)
ovr.fit(X, y )
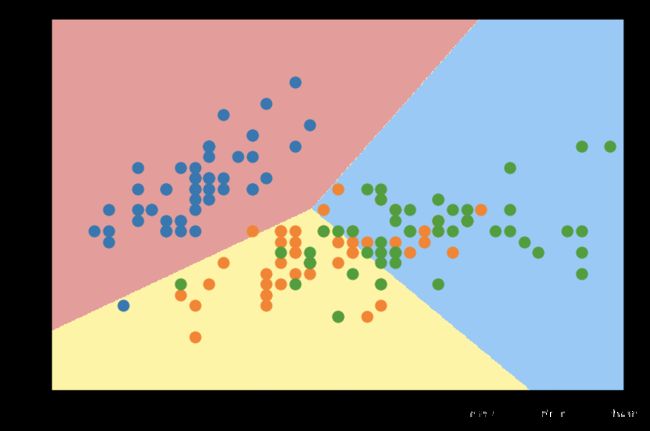
print('Score: ', ovr.score(X, y))
Score: 0.8066666666666666
# 绘制预测值和决策边界
plot_decision_boundary(ovr, axis=[4, 8, 1.5, 5])
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==2,0], X[y==2,1])
plt.show()
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:17: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth'
OVO
from sklearn.multiclass import OneVsOneClassifier
ovo = OneVsOneClassifier(log_reg)
ovo.fit(X, y )
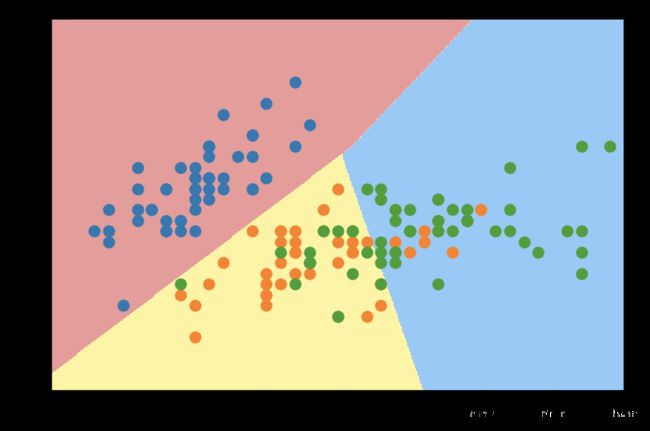
print('Score: ', ovo.score(X, y))
Score: 0.8333333333333334
# 绘制预测值和决策边界
plot_decision_boundary(ovo, axis=[4, 8, 1.5, 5])
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==2,0], X[y==2,1])
plt.show()
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:17: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth'