创建型模式:原型
原型(Prototype)模式也是解决对象创建常见场景的一种手段,理解起来非常简单,其核心是clone方法,可以围绕着拷贝(浅拷贝+深拷贝)以及序列化等场景进行考虑和展开。
模式场景与说明
类的初始化消耗硬件或者其他资源过多,或者对象准备非常繁琐但是同时有大量重复性的设定等场景,简单来说当我们创建一个对象的时候希望使用copy命令来完成的时候(当然不同语言中的实现是不同的,此处说的是期待的特性),这个时候就是原型模式起作用的时候了。
实现方式
在Java中,由于已经提供了Cloneable接口,实现起来更加简单,Java的原型模式和语言本身已经结合的比较紧密,Java的Cloneable接口是java.lang包下的一个接口,如果确认其内容,会看到如下信息
public interface Cloneable {
}
实现示例
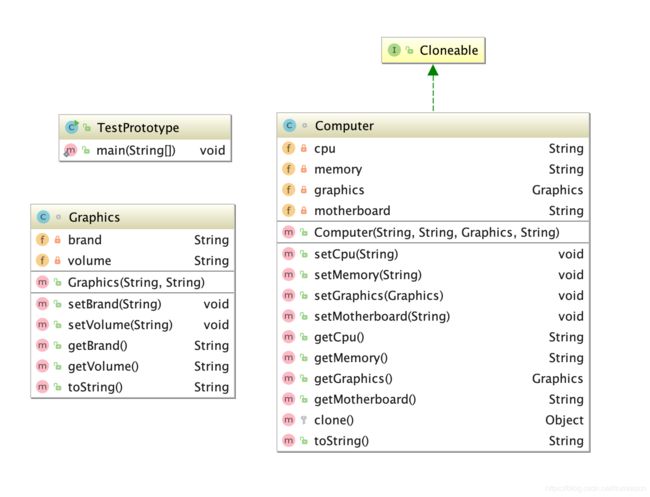
示例代码:浅拷贝
class Graphics {
private String brand;
private String volume;
public Graphics(String brand, String volume) {
this.brand = brand;
this.volume = volume;
System.out.println("Graphics: construct function called.");
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public void setVolume(String volume) {
this.volume = volume;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public String getVolume() {
return volume;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return this.brand + " " + this.volume;
}
}
class Computer implements Cloneable {
private String cpu;
private String memory;
private Graphics graphics;
private String motherboard;
public Computer(String cpu, String memory, Graphics graphics, String motherboard) {
this.cpu = cpu;
this.memory = memory;
this.graphics = graphics;
this.motherboard = motherboard;
System.out.println("Computer: construct function called.");
}
public void setCpu(String cpu) {
this.cpu = cpu;
}
public void setMemory(String memory) {
this.memory = memory;
}
public void setGraphics(Graphics graphics) {
this.graphics = graphics;
}
public void setMotherboard(String motherboard) {
this.motherboard = motherboard;
}
public String getCpu() {
return cpu;
}
public String getMemory() {
return memory;
}
public Graphics getGraphics() {
return graphics;
}
public String getMotherboard() {
return motherboard;
}
@Override
protected Object clone(){
Computer computer = null;
try {
computer = (Computer) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return computer;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Computer information: \n"
+ "CPU: " + this.cpu + "\n"
+ "Memory: " + this.memory + "\n"
+ "Graphics: " + this.graphics + "\n"
+ "Motherboard: " + this.motherboard;
}
}
public class TestPrototype {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Computer computer1 = new Computer("2.5 GHz Quad-Core Intel Core i7", "16 GB 1600 MHz DDR3",
new Graphics("Intel Iris Pro","1536 MB"),"820-00xxx");
System.out.println("clone begins ...");
Computer computer2 = (Computer) computer1.clone();
System.out.println("clone ends ...");
System.out.println("computer1.equals(computer2): " + computer1.equals(computer2));
System.out.println("computer1 == computer2: " + (computer1 == computer2));
System.out.println("computer1.getClass() == computer2.getClass(): " + (computer1.getClass() == computer2.getClass()));
System.out.println("set memory of computer 1:");
computer1.setMemory("32G");
System.out.println(computer1);
System.out.println(computer2);
System.out.println("set Graphics of computer 2:");
computer2.getGraphics().setVolume("3072 MB");
System.out.println(computer1);
System.out.println(computer2);
}
}
执行结果
Graphics: construct function called.
Computer: construct function called.
clone begins ...
clone ends ...
computer1.equals(computer2): false
computer1 == computer2: false
computer1.getClass() == computer2.getClass(): true
set memory of computer 1:
Computer information:
CPU: 2.5 GHz Quad-Core Intel Core i7
Memory: 32G
Graphics: Intel Iris Pro 1536 MB
Motherboard: 820-00xxx
Computer information:
CPU: 2.5 GHz Quad-Core Intel Core i7
Memory: 16 GB 1600 MHz DDR3
Graphics: Intel Iris Pro 1536 MB
Motherboard: 820-00xxx
set Graphics of computer 2:
Computer information:
CPU: 2.5 GHz Quad-Core Intel Core i7
Memory: 32G
Graphics: Intel Iris Pro 3072 MB
Motherboard: 820-00xxx
Computer information:
CPU: 2.5 GHz Quad-Core Intel Core i7
Memory: 16 GB 1600 MHz DDR3
Graphics: Intel Iris Pro 3072 MB
Motherboard: 820-00xxx
结果分析
从上述示例代码的执行结果中可以看到,又如下特点:
- 执行clone时并未触发构建函数
- 对于基本类型的修改并不影响副本的值
- 嵌套类的拷贝上述示例仅实现引用程度的实现,修改其中之一,其副本也会收到影响,这就是所谓的浅拷贝和深拷贝
示例代码:深拷贝
对于其引用的对象也实现Cloneable接口,并在clone实现中加入处理,将代码修改如下:
class Graphics implements Cloneable{
private String brand;
private String volume;
public Graphics(String brand, String volume) {
this.brand = brand;
this.volume = volume;
System.out.println("Graphics: construct function called.");
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public void setVolume(String volume) {
this.volume = volume;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public String getVolume() {
return volume;
}
@Override
protected Object clone(){
Graphics graphics = null;
try {
graphics = (Graphics) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return graphics;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return this.brand + " " + this.volume;
}
}
class Computer implements Cloneable {
private String cpu;
private String memory;
private Graphics graphics;
private String motherboard;
public Computer(String cpu, String memory, Graphics graphics, String motherboard) {
this.cpu = cpu;
this.memory = memory;
this.graphics = graphics;
this.motherboard = motherboard;
System.out.println("Computer: construct function called.");
}
public void setCpu(String cpu) {
this.cpu = cpu;
}
public void setMemory(String memory) {
this.memory = memory;
}
public void setGraphics(Graphics graphics) {
this.graphics = graphics;
}
public void setMotherboard(String motherboard) {
this.motherboard = motherboard;
}
public String getCpu() {
return cpu;
}
public String getMemory() {
return memory;
}
public Graphics getGraphics() {
return graphics;
}
public String getMotherboard() {
return motherboard;
}
@Override
protected Object clone(){
Computer computer = null;
try {
computer = (Computer) super.clone();
computer.setGraphics((Graphics) this.getGraphics().clone());
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return computer;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Computer information: \n"
+ "CPU: " + this.cpu + "\n"
+ "Memory: " + this.memory + "\n"
+ "Graphics: " + this.graphics + "\n"
+ "Motherboard: " + this.motherboard;
}
}
public class TestPrototype {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Computer computer1 = new Computer("2.5 GHz Quad-Core Intel Core i7", "16 GB 1600 MHz DDR3",
new Graphics("Intel Iris Pro","1536 MB"),"820-00xxx");
System.out.println("clone begins ...");
Computer computer2 = (Computer) computer1.clone();
System.out.println("clone ends ...");
System.out.println("computer1.equals(computer2): " + computer1.equals(computer2));
System.out.println("computer1 == computer2: " + (computer1 == computer2));
System.out.println("computer1.getClass() == computer2.getClass(): " + (computer1.getClass() == computer2.getClass()));
System.out.println("set memory of computer 1:");
computer1.setMemory("32G");
System.out.println(computer1);
System.out.println(computer2);
System.out.println("set Graphics of computer 2:");
computer2.getGraphics().setVolume("3072 MB");
System.out.println(computer1);
System.out.println(computer2);
}
}
执行结果
Graphics: construct function called.
Computer: construct function called.
clone begins ...
clone ends ...
computer1.equals(computer2): false
computer1 == computer2: false
computer1.getClass() == computer2.getClass(): true
set memory of computer 1:
Computer information:
CPU: 2.5 GHz Quad-Core Intel Core i7
Memory: 32G
Graphics: Intel Iris Pro 1536 MB
Motherboard: 820-00xxx
Computer information:
CPU: 2.5 GHz Quad-Core Intel Core i7
Memory: 16 GB 1600 MHz DDR3
Graphics: Intel Iris Pro 1536 MB
Motherboard: 820-00xxx
set Graphics of computer 2:
Computer information:
CPU: 2.5 GHz Quad-Core Intel Core i7
Memory: 32G
Graphics: Intel Iris Pro 1536 MB
Motherboard: 820-00xxx
Computer information:
CPU: 2.5 GHz Quad-Core Intel Core i7
Memory: 16 GB 1600 MHz DDR3
Graphics: Intel Iris Pro 3072 MB
Motherboard: 820-00xxx
可以看到,此种方式之下已经实现了所谓深拷贝,返回的computer2中的Graphics对象并不再是一个指向相同地址的引用,修改不再相互影响。
示例代码:序列化
除了通过Cloneable接口,通过Serializable接口也可以非常容易地实现深拷贝,将本文的示例代码简单修正如下:
import java.io.*;
class Graphics implements Serializable {
private String brand;
private String volume;
public Graphics(String brand, String volume) {
this.brand = brand;
this.volume = volume;
System.out.println("Graphics: construct function called.");
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public void setVolume(String volume) {
this.volume = volume;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public String getVolume() {
return volume;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return this.brand + " " + this.volume;
}
}
class Computer implements Serializable {
private String cpu;
private String memory;
private Graphics graphics;
private String motherboard;
public Computer(String cpu, String memory, Graphics graphics, String motherboard) {
this.cpu = cpu;
this.memory = memory;
this.graphics = graphics;
this.motherboard = motherboard;
System.out.println("Computer: construct function called.");
}
public void setCpu(String cpu) {
this.cpu = cpu;
}
public void setMemory(String memory) {
this.memory = memory;
}
public void setGraphics(Graphics graphics) {
this.graphics = graphics;
}
public void setMotherboard(String motherboard) {
this.motherboard = motherboard;
}
public String getCpu() {
return cpu;
}
public String getMemory() {
return memory;
}
public Graphics getGraphics() {
return graphics;
}
public String getMotherboard() {
return motherboard;
}
public Computer copy() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//get current object
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(this);
//create new object
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(byteArrayInputStream);
return (Computer) ois.readObject();
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Computer information: \n"
+ "CPU: " + this.cpu + "\n"
+ "Memory: " + this.memory + "\n"
+ "Graphics: " + this.graphics + "\n"
+ "Motherboard: " + this.motherboard;
}
}
public class TestPrototype {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Computer computer1 = new Computer("2.5 GHz Quad-Core Intel Core i7", "16 GB 1600 MHz DDR3",
new Graphics("Intel Iris Pro","1536 MB"),"820-00xxx");
System.out.println("clone begins ...");
Computer computer2 = null;
try {
computer2 = (Computer) computer1.copy();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("clone ends ...");
System.out.println("computer1.equals(computer2): " + computer1.equals(computer2));
System.out.println("computer1 == computer2: " + (computer1 == computer2));
System.out.println("computer1.getClass() == computer2.getClass(): " + (computer1.getClass() == computer2.getClass()));
System.out.println("set memory of computer 1:");
computer1.setMemory("32G");
System.out.println(computer1);
System.out.println(computer2);
System.out.println("set Graphics of computer 2:");
computer2.getGraphics().setVolume("3072 MB");
System.out.println(computer1);
System.out.println(computer2);
}
}
执行结果
Graphics: construct function called.
Computer: construct function called.
clone begins ...
clone ends ...
computer1.equals(computer2): false
computer1 == computer2: false
computer1.getClass() == computer2.getClass(): true
set memory of computer 1:
Computer information:
CPU: 2.5 GHz Quad-Core Intel Core i7
Memory: 32G
Graphics: Intel Iris Pro 1536 MB
Motherboard: 820-00xxx
Computer information:
CPU: 2.5 GHz Quad-Core Intel Core i7
Memory: 16 GB 1600 MHz DDR3
Graphics: Intel Iris Pro 1536 MB
Motherboard: 820-00xxx
set Graphics of computer 2:
Computer information:
CPU: 2.5 GHz Quad-Core Intel Core i7
Memory: 32G
Graphics: Intel Iris Pro 1536 MB
Motherboard: 820-00xxx
Computer information:
CPU: 2.5 GHz Quad-Core Intel Core i7
Memory: 16 GB 1600 MHz DDR3
Graphics: Intel Iris Pro 3072 MB
Motherboard: 820-00xxx
其他设计模式
- https://liumiaocn.blog.csdn.net/article/details/106954154