LinkedHashMap源码分析
分析完HashMap后,继续分析它的子类LinkedHasMap
LinkedHashMap与HashMap的区别是,LinkedHashMap记录插入或者访问map元素的顺序,在执行迭代输出元素的时,会按插入的顺序输出
LinkedHashMap用了一个双向链表记录插入或者访问的顺序
先看put方法,LinkedHashMap的put方法是用的父类HashMap的put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}继续看putVal
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node[] tab; Node p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
} 看这个newNode方法
Node newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry p =
new LinkedHashMap.Entry(hash, key, value, e);
linkNodeLast(p);
return p;
} 这里创建一个LinkedHashMap.Entry对象,看看LinkedHashMap.Entry的实现
static class Entry extends HashMap.Node {
Entry before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
} LinkedHashMap.Entry是继承了HashMap.Node,它还有before,after两个成员,说明Entry是用于双向链表的
下面继续看linkNodeLast方法
// link at the end of list
private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry p) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry last = tail;
tail = p;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
} 这个方法就是将Entry对象插入双向链表尾部的一个操作,从而记录了插入的顺序
由此可见,LinkedHashMap是在HashMap的基础上,增加了双向链表用于记录插入或者访问的顺序
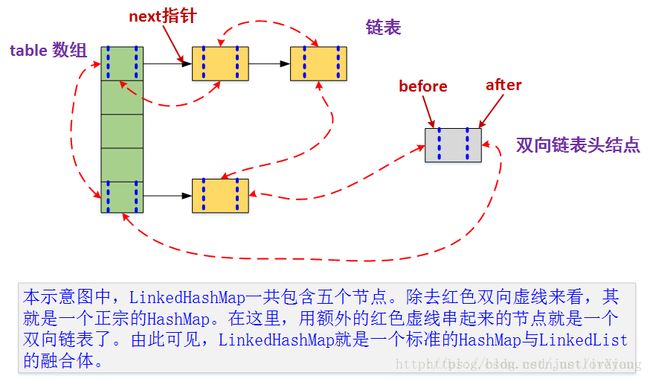
借用别人博客一幅图,可以清楚表现LinkedHashMap的结构