基于贪心策略、邻域搜索和遗传算法的设施分配优化问题
基于贪心策略、邻域搜索和遗传算法的设施分配优化问题
算法概论期末项目
文章目录
- 基于贪心策略、邻域搜索和遗传算法的设施分配优化问题
- 摘要
- 1. 导言
- 问题重述
- 贪心算法
- 邻域搜索
- 遗传算法
- 2. 实验过程
- 问题编码
- 代价函数
- 数据读入
- 贪心算法
- 邻域搜索
- 遗传算法
- 初始化种群
- 选择
- 线性排名
- 非线性排名
- 锦标赛法
- $(\mu,\lambda)$选择
- 交叉
- 段交换
- 均匀交换
- 变异
- 批处理
- 3. 结果分析
- 使用数据
- 贪心算法
- 邻域搜索
- 遗传算法
- 4. 感想
- 完整源代码和完整实验结果
- 主要参考文献
摘要
使用贪心算法、邻域搜索(不同邻域方法)和遗传算法(不同选择、变异、交叉方法),解决设施分配优化问题
1. 导言
问题重述
有一些设施,每个设施有不同的承载量,设施承载不能超过这个值
有一些顾客,每个顾客有不同的需求量
没有顾客使用的设施,不需要启动,无需维护费,否则需要维护费
把一名顾客,分配到一台设施,需要一定的调度费
尝试找到一种方案,分配每一个顾客一个设施,使总体费用尽可能最优
贪心算法
该算法不断生成随机解,并与现有最优解进行比较,如果随机解更好就替换之
邻域搜索
该算法从一个初始解出发,通过邻域函数生成解的邻域,再在邻域中 搜索出更优的解来替换当前解,通过不断的迭代过程实现解
遗传算法
该算法模拟生物遗传进化的特点,对问题进行编码,进行选择、交叉、变异操作,不断迭代寻找更优解
2. 实验过程
问题编码
我采用整数编码,即一个解是一个长度为顾客数的数组,对应顾客的数组元素就是该顾客被分配的设施
这样编码可以方便后面的邻域、变异、交叉操作
代价函数
根据题目的定义定义代价函数,即设施开放代价和用户调度代价的总和
特别地,如果一个解使一个设施超出承载量,则它的代价为最大值(MAX_NUM)
计算代价
def get_cost(assign):
if not is_assign_valid(assign):
return MAX_NUM
cost = 0
fset = set()
for i in range(customer_num):
fset.add(assign[i])
cost += allocating_cost[assign[i]][i]
for i in range(facility_num):
if i in fset:
cost += facility_cost[i]
return cost
判断解是否合法:
def is_assign_valid(assign):
real_facility_capacity = [0] * facility_num
for i in range(customer_num):
real_facility_capacity[assign[i]] += customer_demand[i]
for i in range(facility_num):
if real_facility_capacity[i] > facility_capacity[i]:
return False
return True
数据读入
数据71个样例,三种格式,需要处理,使批处理得以运行
def get_data(index):
global facility_num
global customer_num
global facility_capacity
global facility_cost
global allocating_cost
global customer_demand
with open('Instances/p' + str(index), 'r')as f:
lines = f.read()
arr = lines.replace('.', ' ').replace(chr(0), '').replace('\n', ' ').split()
for i in range(len(arr)):
arr[i] = int(arr[i])
facility_num, customer_num = arr[0], arr[1]
facility_capacity, facility_cost = [], []
ind = 2
for i in range(facility_num):
facility_capacity.append(arr[ind])
facility_cost.append(arr[ind + 1])
ind += 2
customer_demand = []
for i in range(customer_num):
customer_demand.append(arr[ind])
ind += 1
# ac[f, c]
allocating_cost = []
for i in range(facility_num):
temp = []
for j in range(customer_num):
temp.append(arr[ind])
ind += 1
allocating_cost.append(temp)
贪心算法
算法流程如下:
- 生成随机解
- 与最佳解比较,如果随机解更好就用它替换最佳解
- 如果最佳解在
TIME_SAVE_STEP步内没有变化,终止算法 - 如果当前
STEP++小于STEP_TOTAL,跳到1
第三步的作用是减少算法运行时间
if __name__ == '__main__':
for ins in range(1, 72):
start = time.time()
init()
get_data(ins)
check()
best_solution = init_assignment()
while not is_assign_valid(best_solution):
best_solution = init_assignment()
best_cost = get_cost(best_solution)
for step in range(STEP_TOTAL):
if step - best_step > TIME_SAVE_STEP:
break
if step % 2000 == 0:
print("running instance: %d, step: %d, min cost:%d"%(ins, step, best_cost))
temp_assign = get_neighbor(best_solution, NEIGHBOR_METHOD)
while not is_assign_valid(temp_assign):
temp_assign = get_neighbor(best_solution, NEIGHBOR_METHOD)
temp_cost = get_cost(temp_assign)
if temp_cost < best_cost:
best_cost = temp_cost
best_solution = temp_assign
best_step = step
running_time = time.time() - start
xls_record.append(['p' + str(ins), best_cost, running_time])
save_result(ins)
邻域搜索
局部搜索其实就是一种贪心策略,通过搜索邻域,每一次都选择评价最高的邻域更新状态
局部搜索框架与贪心算法基本相同,但不生成随机解而是生成邻域解
有两种邻域方法:
- 随机交换两个客户(随机挑选)的选择,即甲选设施A、乙选设施B,变成甲选设施B、乙选设施A
- 随机变换一个用户(随机挑选)的选择,
def get_neighbor(assign, method):
if method == 0:
res = deepcopy(assign)
rana = random.randint(0, customer_num - 1)
ranb = random.randint(0, customer_num - 1)
temp = res[rana]
res[rana] = res[ranb]
res[ranb] = temp
return res
elif method == 1:
res = init_assignment()
while not is_assign_valid(res):
res = init_assignment()
return res
elif NEIGHBOR_METHOD == 2:
res = deepcopy(assign)
rana = random.randint(0, customer_num - 1)
res[rana] = random.randint(0, facility_num - 1)
return res
实测中,第二种邻域方法更加优秀,因为他能探索所有用户都没有选择的设施,并且计算更简单,运算快
遗传算法
初始化种群
随机生成一小部分的随机个体
def init_group():
global group
for _ in range(INITIAL_GROUP_NUM):
group.append(init_assignment())
选择
我尝试了三种选择方法:
- 线性排名
- 非线性排名
- 锦标赛法
线性排名
首先按种群的每个个体的代价从低到高排名:
def sort_function(x, y):
cx = get_cost(x)
cy = get_cost(y)
if cx < cy:
return -1
elif cx == cy:
return 0
else:
return 1
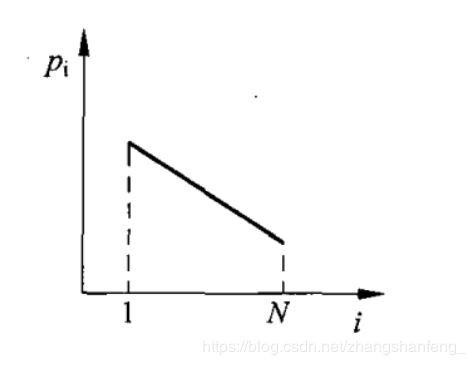
采用线性排名的公式计算
概率分配
total_pro = 0
if SELECT_METHOD == 0:
a = 1.8
b = 2 * (a - 1)
# linear function
for i in range(1, GROUP_NUM + 1):
pro = (a - b * float(i) / (GROUP_NUM + 1)) / GROUP_NUM
total_pro += pro
cost_pro.append(total_pro)
轮盘赌:
temp_group = []
for _ in range(GROUP_SIZE):
random_num = random.random()
for i in range(GROUP_SIZE):
if random_num >= cost_pro[i] and random_num < cost_pro[i+1]:
temp_group.append(group[i])
break
# print(len(temp_group))
group = deepcopy(temp_group)
return res
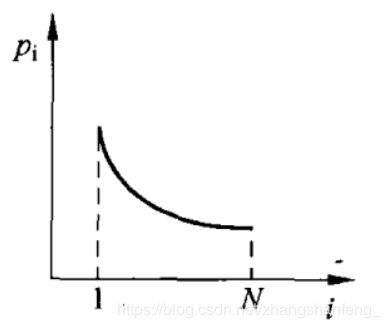
非线性排名
框架与线性排名相同,但使用的公式不同:
概率分配:
使用非线性排名的时候,发现q不可以取太大,否则适应值低的种群几乎不可能生存
elif SELECT_METHOD == 1:
# non-linear function
q = NON_LINEAR_MAX_PRO
for i in range(1, GROUP_NUM + 1):
if i != GROUP_NUM:
pro = q * pow(1 - q, i - 1)
else:
pro = pow(1 - q, i - 1)
total_pro += pro
cost_pro.append(total_pro)
锦标赛法
锦标赛法是基于局部竞争机制的选择,在处理大数据集的时候计算量较小
( μ , λ ) (\mu,\lambda) (μ,λ)选择
使用 ( μ , λ ) (\mu,\lambda) (μ,λ)选择代替传统的变异率
交叉
我尝试了两种交叉方法:
段交换
- 随机交叉父母一段顾客的选择
def OX_crosser(w1, w2):
ran1 = random.randint(0, facility_num - 1)
ran2 = random.randint(0, facility_num - 1)
if ran2 < ran1:
ran1, ran2 = ran2, ran1
offspring1 = deepcopy(w1)
offspring2 = deepcopy(w2)
for i in range(ran1, ran2 + 1):
temp = offspring1[i]
offspring1[i] = offspring2[i]
offspring2[i] = temp
# print(offspring1, offspring2)
return offspring1, offspring2
均匀交换
- 对于父母的每一位的基因,有50%的概率将其交换(均匀交换)
def uniform_crosser(w1, w2):
offspring1 = deepcopy(w1)
offspring2 = deepcopy(w2)
for i in range(len(w1)):
ran = random.random()
if ran < UNIFORM_PRO:
temp = offspring1[i]
offspring1[i] = offspring2[i]
offspring2[i] = temp
return offspring1, offspring2
实测中,两种交换方式在不同的数据集有不同的表现,难分伯仲,但由于第一种方法开销较小,算法运行更快,采用第一种方法
变异
有三种邻域方法:
- 随机交换两个客户(随机挑选)的选择,即甲选设施A、乙选设施B,变成甲选设施B、乙选设施A
- 随机生成一个新解
- 随机变换一个用户(随机挑选)的选择,
def get_neighbor(assign, method):
if method == 0:
res = deepcopy(assign)
rana = random.randint(0, customer_num - 1)
ranb = random.randint(0, customer_num - 1)
temp = res[rana]
res[rana] = res[ranb]
res[ranb] = temp
return res
elif method == 1:
res = init_assignment()
while not is_assign_valid(res):
res = init_assignment()
return res
elif NEIGHBOR_METHOD == 2:
res = deepcopy(assign)
rana = random.randint(0, customer_num - 1)
res[rana] = random.randint(0, facility_num - 1)
return res
经过测试,方法2效果较差,原因是其没有保留优秀的基因,几乎是100%的变异程度,方法1和方法3相比方法3效果稍好
批处理
- 时间度量
- 文件保存
def save_result(ins):
res1 = str(best_cost) + '\n'
res2 = ''
res3 = ''
fset = set()
for i in range(customer_num):
res3 += str(best_solution[i] + 1) + ' '
fset.add(best_solution[i])
res3 += '\n'
for i in range(facility_num):
if i in fset:
res2 += '1 '
else:
res2 += '0 '
res2 += '\n'
with open("Result/genetic_algorithm_details", "a") as f:
f.write(res1 + res2 + res3)
book = xlwt.Workbook(encoding='utf-8', style_compression=0)
sheet = book.add_sheet('sheet1', cell_overwrite_ok=True)
sheet.write(0, 1, 'Result')
sheet.write(0, 2, 'Time(s)')
for i in range(len(xls_record)):
sheet.write(i + 1, 0, xls_record[i][0])
sheet.write(i + 1, 1, xls_record[i][1])
sheet.write(i + 1, 2, xls_record[i][2])
book.save('Result/genetic_algorithm_xls/genetic_algorithm_result.xls' + str(ins) + '.xls')
- 批处理框架
if __name__ == '__main__':
for ins in range(1, 72):
start = time.time()
init()
get_data(ins)
check()
init_group()
for step in range(STEP_TOTAL):
if step - same_step > TIME_SAVE_STEP:
break
min_cost, curr_best_solution = select_group()
if step % 100 == 0:
print("running instance: %d, step %d: min cost: %d" % (ins, step, min_cost))
if min_cost < best_cost:
best_solution = deepcopy(curr_best_solution)
best_cost = min_cost
if min_cost != same_cost:
same_step = step
same_cost = min_cost
cross_over()
mutation()
running_time = time.time() - start
xls_record.append(['p' + str(ins), best_cost, running_time])
save_result(ins)
3. 结果分析
使用数据
提供的71个算例
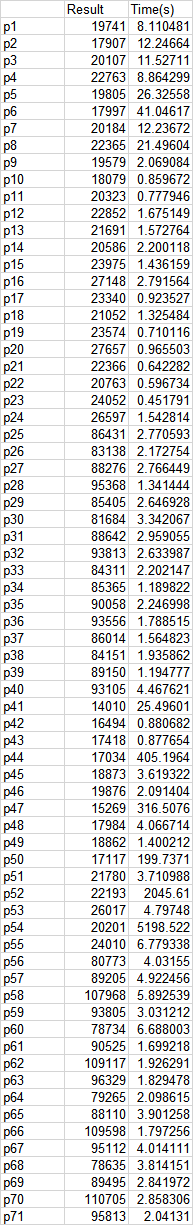
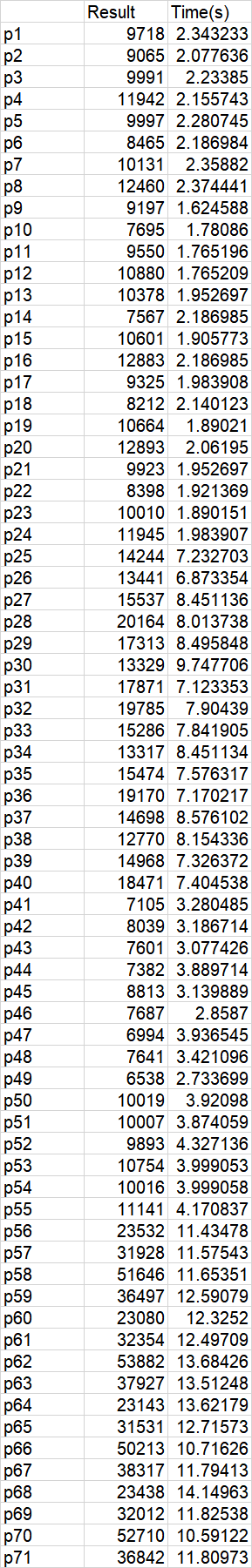
贪心算法
邻域搜索
遗传算法
实验结果显示,朴素的贪心算法,效果比较差;使用邻域搜索改进以后,效果有很大的提升,运算速度也非常快;遗传算法能获得最优的结果,但相应的运算时间也比较长
4. 感想
- 理论基础很重要,要掌握扎实的理论基础,实验中会少遇到很多问题(例如算法中各种参数的意义等)
- 查阅资料时,要结合自己的思考,不可生搬硬套,要弄清楚里面的原理,才能牢固掌握。
- 讨论交流很重要,同学间积极交流可以互通有无,增进理解。
完整源代码和完整实验结果
【链接】
打个星星?
主要参考文献
《人工智能基础教程第二版》,朱福喜