数据结构与算法 迷宫问题
迷宫问题问题描述:
栈的实现在这篇博客中:https://blog.csdn.net/zj1131190425/article/details/87991662
迷宫是一个矩形区域,有一个出口和入口,迷宫内部包含不能穿越的墙壁和障碍物。
1.用矩阵来描述迷宫。入口是(0, 0), 出口是(m,n),现在需要在迷宫中选找一条路径,穿过迷宫。位置(i,j)=1表示有障碍。0表示无障碍。
思路:
1.出发点处,定义四个方向的坐标偏移量,搜索等四个方向,直到找到一个可行的方向,按照可行的方向移动到下一个位置,将前一个位置坐标压入栈中(保存路径),且将此位置设置为1(放置障碍物,防止往回退的时候又重新搜索这个方向)
2. 如果在某个位置没有找到可行的方向,则将当前这个位置设置为1(这个位置不可再回来),从栈顶弹出一个坐标,作为当前坐标(相当于走回头路),继续搜索其他的方向是否可行。
3. 如此往复
采用自顶向下设计的方法设计代码:
(1)输入迷宫
(2)寻找路径
(3)输出路径
#include
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\sparseMatrix\external_file\arraystack.h"
#include
using namespace std;
// 迷宫
template
void print_array(T a[][12])
{
for(int i=0; i<12; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<12; j++)
{
cout << a[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
class position // 存储位置坐标
{
public:
int row;
int col;
position()
{
row = 0;
col = 0;
}
position(int row, int col)
{
this->row = row;
this->col = col;
}
void add_offset(position& ps)
{
row += ps.row;
col += ps.col;
}
};
void find_path(bool map[][12])
{
int map_1[12][12];
// 保存map()的一个副本
for(int i=0; i<12; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<12; j++)
{
map_1[i][j] = (int)map[i][j];
}
}
// 寻找迷宫的路径
arrayStack path; // 存储路径信息
// 偏移量
position offset[4];
// 向右偏移 index=0
offset[0].row = 0;
offset[0].col = 1;
// 向下偏移 index=1
offset[1].row = 1;
offset[1].col = 0;
// 向左偏移 index=2
offset[2].row = 0;
offset[2].col = -1;
// 向上偏移 index=3
offset[3].row = -1;
offset[3].col = 0;
position current_position(1,1); // 初始化当前位置
int option = 0; //初始化选的方向,右,下,左,上=(0,1,2,3)
int max_otion = 3; // 方向的选择范围
map[1][1] = 1; // 在(1,1)位置放置障碍
cout << "current position: " << current_position.row << " " << current_position.col << endl;
while(current_position.row!=10 || current_position.col!=10)
{
int r,c;
while(option<=max_otion)
{
r = current_position.row + offset[option].row;
c = current_position.col + offset[option].col;
if(map[r][c]==0) // 新的位置可行
{
break;
}
option++;
}
if(option<=max_otion) // 找到了可行的方向
{
path.push(current_position);
//current_position.add_offset(offset[position]); // current_position更新
current_position.row = r; // 移动到新的位置
current_position.col = c;
map[r][c] = 1; // 放置障碍物 避免回退时又选到这个方向
option = 0;
}
else // 选择的位置走不通
{
if(path.empty())
{
cout << "The puzzle has no solution" << endl;
return;
}
position next = path.top();
path.pop();
// 计算返回后的搜索方向:
// 按照前面对方向的定义,返回后应该搜索未搜索过的两个方向:
// map[currentRow][currentCol] = 1; // 走不通的位置设置障碍,避免重复搜索
map[current_position.row][current_position.col] = 1; // 当前的位置是死路
option = 0;
current_position = next; // 浅复制即可 这个类默认的拷贝构造函数
}
cout << "(r,c)= " << r << "," << c << endl;
}
position tmp;
while(!path.empty())
{
// cout << "revise the map" << endl;
tmp = path.top();
path.pop();
map_1[tmp.row][tmp.col] = 2;
}
// 结果输出
char result[12][12];
for(int i=0; i<12; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<12; j++)
{
if(map_1[i][j]==1)
{
result[i][j]='1';
}
else if(map_1[i][j]==0)
{
result[i][j]='0';
}
else
{
result[i][j]='*';
}
}
}
print_array(result);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//int a[12][12];
bool a[][12] = {
{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1},
{1,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1},
{1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,1},
{1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1},
{1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1},
{1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,1},
{1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,1},
{1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,1},
{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}
};
//print_array(a);
find_path(a);
return 0;
}
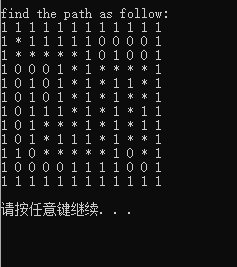
运行结果:
迷宫问题最短路径
可以使用队列来实现寻找最短路径的操作
首先介绍C++ 实现队列:关于队列的实现参考博客: https://blog.csdn.net/zj1131190425/article/details/88090905,下面的队列是对https://blog.csdn.net/zj1131190425/article/details/88090905中队列的改进,主要是改经了ensureCapacity()函数,因为原来的队列中ensureCapacity()函数有点小的bug.
定义一个队列的基类,queueABC
queueABC.h文件
#ifndef QUEUE_ABC_H
#define QUEUE_ABC_H
using namespace std;
// 定义抽象类
template
class queueABC
{
public:
// virtual ~queue();
virtual bool empty() const=0; // 纯虚函数 只读
virtual int size() const=0; // 返回队列中元素的个数
virtual T& front() = 0; // 返回队首元素
virtual T& back() = 0; // 返回队尾元素
virtual void pop() = 0; // 删除队首的元素
virtual void push(T x) = 0; // 队尾插入元素
};
#endif
queue.h
#ifndef QUEUE_H
#define QUEUE_H
#include
#include
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\dequeue\external_file\queueABC.h" // 包含ABC文件
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\dequeue\external_file\queueemptyEx.h" // 包含异常类文件
using namespace std;
template
class queue : public queueABC
{
private:
int arrayLength; // 数组的长度
int queueSize; // 队列中元素的个数
int queueFront; // 队首元素所在的位置
int queueBack; // 队尾元素所在的位置
T* element;
void ensureArrayLength(); // 进行数组扩容
public:
queue(int arrayLength=10); // 构造函数
~queue(); // 析构函数
queue(const queue& q); // 拷贝构造函数
// ADT
bool empty() const;
int size() const;
T& front();
T& back();
void pop();
void push(T x);
void display_queue() const; // 打印输出队列中的元素
};
template
queue::queue(int arrayLength)
{
this->arrayLength = arrayLength;
this->queueSize = 0;
this->queueFront = 0;
this->queueBack = 0;
element = new T[arrayLength];
}
template
queue::~queue()
{
delete [] element;
}
template
queue::queue(const queue& q)
{
arrayLength = q.arrayLength;
queueSize = q.queueSize;
queueFront = q.queueFront;
queueBack = q.queueBack;
element = new T[arrayLength];
for(int i=0; i
bool queue::empty() const
{
return queueSize==0;
}
template
int queue::size() const
{
return queueSize;
}
template
T& queue::front()
{
return element[(queueFront+1)%arrayLength]; // queueFront是队首元素的前一个位置,+1是表示队首元素的位置
}
template
T& queue::back()
{
return element[queueBack%arrayLength]; // queueback队尾元素的位置
}
/*
template
void queue::ensureArrayLength()
{
// 如果需要,增加数组长度
if((queueBack+1)%arrayLength==queueFront) // 环形的数组
{
T* old;
old = element;
//delete element;
// arrayLength = arrayLength*2; // 增加分配的内存长度
element = new T[2*arrayLength];
// 环形数组重新布局
// 先将数组复制过来
//更新关于数组复制
int index_tmp;
for(int i=0; i
void queue::ensureArrayLength()
{
if((queueBack+1)%arrayLength==queueFront) // 环形的数组
{
T* new_element = new T[2*arrayLength];
int start = (queueFront+1)%arrayLength;
if(start<2) // 没有形成环
{
copy(element+start, element+start+arrayLength-1, new_element); // 复制操作
}
else // 形成环
{
copy(element+start, element+arrayLength, new_element);
copy(element, element+queueBack+1, new_element+arrayLength-start);
}
queueFront = 2*arrayLength-1;
queueBack = arrayLength-2;
arrayLength *= 2;
delete[] element;
element = new_element;
}
}
// push()操作:
template
void queue::push(T x)
{
ensureArrayLength(); // 先保证数组长度满足条件
queueSize++;
//queueBack = (queueBack+1)%arrayLength;
//element[queueBack] = x;
queueBack++;
element[queueBack%arrayLength] = x;
}
//pop()操作
template
void queue::pop()
{
if(empty())
throw queueEmptyException(0);
queueFront++;
queueSize--;
// element[queueFront].~T;
}
template
void queue::display_queue() const
{
//int tmp = queueFront;
// int start_pos = (tmp+1)%arrayLength;
if(empty())
{
cout << "The queue is empty!" << endl;
return;
}
for(int i=0; i 自定义的异常类:
queueemptyException:
// 自定义异常类
#ifndef QUEUE_EMPTY_EXCEPTION
#define QUEUE_EMPTY_EXCEPTION
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class queueEmptyException : public runtime_error
{
private:
int queueSize;
public:
queueEmptyException(int queueSize) : runtime_error("The queue empty!")
{
this->queueSize = queueSize;
}
void display_error_info()
{
cout << "The queue size is " << queueSize << endl;
}
};
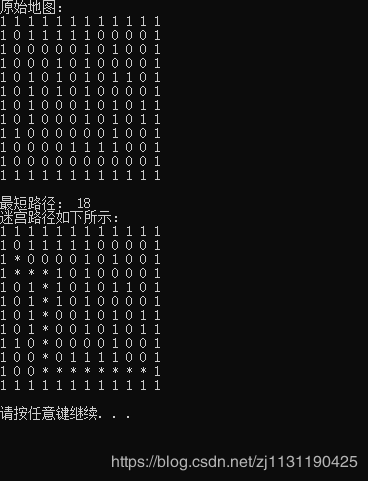
#endif 寻找最短路径的算法思路:
从上面的迷宫中,找一条从入口到出口的最短路径,要有两个过程:
1. 一个是距离标记过程
2. 另一个是路径标记过程
在距离标记过程中,把能从入口到达的相邻位置标记为1,然后把从编号为1可到达的相邻位置标记为2(表示与入口相距为2),直到到达出口或者没有可标记的相邻位置为止。
在路径标记过程中,从出口开始,首先移动到比出口的编号小1的位置,再从当前位置移动到比其编号小1的位置上,直到到达起点为止,这便是最短的路径
3.按照上述思路编写代码实现:
main.cpp
#include
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\dequeue\external_file\queue.h"
using namespace std;
// 迷宫
template
void print_array(T **a, int size)
{
for(int i=0; irow = row;
this->col = col;
}
/*
void add_offset(position& ps)
{
row += ps.row;
col += ps.col;
}
*/
};
void findPath(int** map, int mapSize=10)
{
// 这里默认起始点为(0,0),终点为(9,9)
// 给地图添加围墙:
int** new_map = new int*[mapSize+2];
for(int i=0; i q; // 队列,用于存放标记的位置
while(true)
{
// 给相邻位置做标记
for(int i=0; i q_path; // 存储路径
current_position = end_position; // 从终点回溯
for(int i=pathLength-1; i>=0; i--)
{
// path[i] = current_position;
q_path.push(current_position); // 当前的位置放入队列中
for(int j=0; j1))
{
result[i][j] = '0';
}
}
}
// 输出迷宫路径
cout << "最短路径: " << pathLength << endl;
cout << "迷宫路径如下所示: " << endl;
print_array(result, mapSize+2);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int map_size = 10;
int input_map[10][10] = {
{0,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0},
{0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0},
{0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,0},
{0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0},
{0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1},
{0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0}
};
// 数据转换
int** map_in = new int*[map_size];
for(int i=0; i 算法的运行结果如下图所示:
---------------------------------------------------end----------------------------------------------------------