参考资料:Android开发艺术探索
AsyncTask是一个Android官方提供的一种轻量级的异步任务类,它可以在线程池中执行后台任务,然后把执行的进度和最终结果传递给主线程并在主线程中更新UI。
虽然我们现在用的比较少了,但是掌握下原理还是可以的。
AsyncTask简单介绍
AsyncTask是一个抽象的泛型类,它提供了Params 、Progress和Result这三个泛型参数,其中Params表示参数的类型,Progress表示后台任务执行的进度的类型,而Result则表示后台任务返回的结果的类型。
如下所示
public abstract class AsyncTask {
...
/**
* Override this method to perform a computation on a background thread. The
* specified parameters are the parameters passed to {@link #execute}
* by the caller of this task.
*
* This method can call {@link #publishProgress} to publish updates
* on the UI thread.
*
* @param params The parameters of the task.
*
* @return A result, defined by the subclass of this task.
*
* @see #onPreExecute()
* @see #onPostExecute
* @see #publishProgress
*/
@WorkerThread
protected abstract Result doInBackground(Params... params);
/**
* Runs on the UI thread before {@link #doInBackground}.
*
* @see #onPostExecute
* @see #doInBackground
*/
@MainThread
protected void onPreExecute() {
}
/**
* Runs on the UI thread after {@link #doInBackground}. The
* specified result is the value returned by {@link #doInBackground}.
*
* This method won't be invoked if the task was cancelled.
*
* @param result The result of the operation computed by {@link #doInBackground}.
*
* @see #onPreExecute
* @see #doInBackground
* @see #onCancelled(Object)
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"})
@MainThread
protected void onPostExecute(Result result) {
}
/**
* Runs on the UI thread after {@link #publishProgress} is invoked.
* The specified values are the values passed to {@link #publishProgress}.
*
* @param values The values indicating progress.
*
* @see #publishProgress
* @see #doInBackground
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"})
@MainThread
protected void onProgressUpdate(Progress... values) {
}
}
其中有四个方法对我们使用比较重要 ->
onPreExecute():此方法运行在UI线程中,在开始异步任务之前调用。
doInBackground():此方法运行在子线程中用于执行异步任务,在该方法中调用publishProgress():方法可以在UI线程中更新任务进度。
onProgressUpdate():此方法用于接收任务进度,运行在UI线程中,
onPostExecute(Result result):此方法会将任务结果返回到UI线程中,可以在此更新UI。
使用时有几项注意事项
1.AsyncTask对象必须在UI线程中创建
2.execute方法必须在UI线程中调用
3.不要直接调用onPreExecute,doInBackground,onProgressUpdate,onPostExecute这四个方法
4.一个AsyncTask对象只能执行一次,即只能调用一次execute方法
5.在Android1.6之前,AsyncTask是串行的执行任务的,Android1.6的时候AsyncTask开始采用线程池里处理并行任务,但是从Android3.0开始,为了避免并发错误,AsyncTask又采用一个线程来串行执行任务。不过在Android3.0以及后续的版本中,我们仍然可以通过AsyncTask的executeOnExecutor方法来并行的执行任务。
AsyncTask工作原理
我们先看execute()方法,execute()方法又会调用executeOnExecutor()方法
如下所示
@MainThread
public final AsyncTask execute(Params... params) {
return executeOnExecutor(sDefaultExecutor, params);
}
@MainThread
public final AsyncTask executeOnExecutor(Executor exec,
Params... params) {
if (mStatus != Status.PENDING) {
switch (mStatus) {
case RUNNING:
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:"
+ " the task is already running.");
case FINISHED:
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:"
+ " the task has already been executed "
+ "(a task can be executed only once)");
}
}
mStatus = Status.RUNNING;
onPreExecute();
mWorker.mParams = params;
exec.execute(mFuture);
return this;
}
在上面代码中sDefaultExecutor实际是个串行的线程池,一个线程中所有的AsyncTask全部在这个串行的线程池中排队执行,这个排队的过程后面再分析。
可以看到首先调用了onPreExecute()方法,然后线程池开始执行也就是sDefaultExecutor。
private static class SerialExecutor implements Executor {
final ArrayDeque mTasks = new ArrayDeque();
Runnable mActive;
public synchronized void execute(final Runnable r) {
mTasks.offer(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
r.run();
} finally {
scheduleNext();
}
}
});
if (mActive == null) {
scheduleNext();
}
}
protected synchronized void scheduleNext() {
if ((mActive = mTasks.poll()) != null) {
THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR.execute(mActive);
}
}
}
我们再看一下AsyncTask的构造方法
/**
* Creates a new asynchronous task. This constructor must be invoked on the UI thread.
*/
public AsyncTask() {
this((Looper) null);
}
/**
* Creates a new asynchronous task. This constructor must be invoked on the UI thread.
*
* @hide
*/
public AsyncTask(@Nullable Handler handler) {
this(handler != null ? handler.getLooper() : null);
}
/**
* Creates a new asynchronous task. This constructor must be invoked on the UI thread.
*
* @hide
*/
public AsyncTask(@Nullable Looper callbackLooper) {
mHandler = callbackLooper == null || callbackLooper == Looper.getMainLooper()
? getMainHandler()
: new Handler(callbackLooper);
mWorker = new WorkerRunnable() {
public Result call() throws Exception {
mTaskInvoked.set(true);
Result result = null;
try {
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
//noinspection unchecked
result = doInBackground(mParams);
Binder.flushPendingCommands();
} catch (Throwable tr) {
mCancelled.set(true);
throw tr;
} finally {
postResult(result);
}
return result;
}
};
mFuture = new FutureTask(mWorker) {
@Override
protected void done() {
try {
postResultIfNotInvoked(get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
android.util.Log.w(LOG_TAG, e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("An error occurred while executing doInBackground()",
e.getCause());
} catch (CancellationException e) {
postResultIfNotInvoked(null);
}
}
};
}
可以最终会调用到第三个构造方法,然后我们发现,在创建AsyncTask的时候,在构造里面首先创建了UI线程的Handler,随后创建了WorkerRunnable对象,此对象是个Callable对象,其内部的实现调用了doInBackground()方法,其实就是异步任务的执行过程。
然后又创建了FutureTask对象,会将AsyncTask的Params参数赋值给FutureTask的WorkerRunnable对象。
然后SerialExecutor 的execute方法会将FutureTask对象插入到任务队列mTasks中,如果此时没有正在执行的AsyncTask任务,那么就会调用scheduleNext方法来执行下一个AsyncTask任务。同时当一个AsyncTask执行完后,AsyncTask会继续执行其他任务知道所有任务都执行完为止,从这点可以看出,在默认情况下,AsyncTask是串行执行的。
具体任务的执行是在 scheduleNext()方法中,其中THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR是一个线程池,我们具体来看一下
/**
* An {@link Executor} that can be used to execute tasks in parallel.
*/
public static final Executor THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR;
static {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
CORE_POOL_SIZE, MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE, KEEP_ALIVE_SECONDS, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
sPoolWorkQueue, sThreadFactory);
threadPoolExecutor.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);
THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR = threadPoolExecutor;
}
至此我们发现AsyncTask中有两个线程池SerialExecutor 和THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR,其中SerialExecutor 用于任务的排队,而THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR用于真正的执行任务,InternalHandler则用来发送消息及线程的切换
private static InternalHandler sHandler;
private static class InternalHandler extends Handler {
public InternalHandler(Looper looper) {
super(looper);
}
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "RawUseOfParameterizedType"})
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
AsyncTaskResult result = (AsyncTaskResult) msg.obj;
switch (msg.what) {
case MESSAGE_POST_RESULT:
// There is only one result
result.mTask.finish(result.mData[0]);
break;
case MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS:
result.mTask.onProgressUpdate(result.mData);
break;
}
}
}
可以发现这个sHandler是一个静态变量,会在类加载时就完成加载,所以要求AsyncTask的创建必须在UI线程中进行。
下面我们试验下,AsyncTask是否是串行执行。
public class AsyncTaskM extends AsyncTask{
private static final String TAG = "AsyncTaskM";
@Override
protected void onPreExecute() {
super.onPreExecute();
}
@Override
protected String doInBackground(String... strings) {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return strings[0];
}
@Override
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... values) {
super.onProgressUpdate(values);
}
/**
* 在主线程中执行,在异步任务执行完成后会调用此方法,其中参数是doInBackground的返回值
* @param s
*/
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(String s) {
super.onPostExecute(s);
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Log.e(TAG, "onPostExecute: "+s+"execute finish at "+format.format(new Date()));
}
}
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
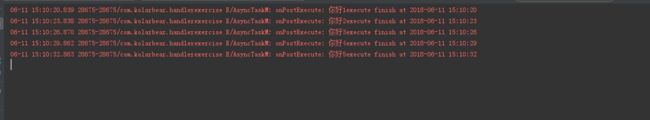
new AsyncTaskM().execute("你好1");
new AsyncTaskM().execute("你好2");
new AsyncTaskM().execute("你好3");
new AsyncTaskM().execute("你好4");
new AsyncTaskM().execute("你好5");
}
}
可以看到时间间隔都是3秒,说明AsyncTask确实是串行执行的(系统5.0)。
那如果想让它并行执行可以吗?
当然
可以
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
new AsyncTaskM().executeOnExecutor(AsyncTask.THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR,"你好1");
new AsyncTaskM().executeOnExecutor(AsyncTask.THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR,"你好2");
new AsyncTaskM().executeOnExecutor(AsyncTask.THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR,"你好3");
new AsyncTaskM().executeOnExecutor(AsyncTask.THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR,"你好4");
new AsyncTaskM().executeOnExecutor(AsyncTask.THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR,"你好5");
}
}
再次运行,
发现变成了并行了。
为什么?
因为
这里传入了AsyncTask.THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR线程池,而不是加入到SerialExecutor负责任务队列的线程池,所以就不存在排队的情况,直接会执行。
以上。