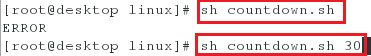shell中的脚本程序(四)(for语句,if语句,while语句脚本)
1.for语句实验:
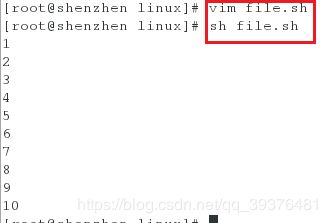
<1>新建一个脚本,正序输出1~10
[root@shenzhen linux]# vim file.sh
[root@shenzhen linux]# sh file.sh
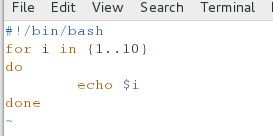
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..10}
do
echo $i
done
#!/bin/bash
for i in `seq 1 10`
do
echo $i
done
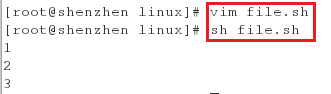
[root@shenzhen linux]# vim file.sh
[root@shenzhen linux]# sh file.sh
#!/bin/bash
for i in 1 2 3
do
echo $i
done

<3>新建一个脚本,利用for循环输出/mnt目录下的文件或子目录
[root@shenzhen linux]# vim file.sh
[root@shenzhen linux]# sh file.sh
#!/bin/bash
for i in `ls /mnt`
do
echo $i
done

<4>新建一个脚本,利用seq设置步长,即输出1~10的内容,但每隔两个数字输出
[root@shenzhen linux]# vim file.sh
[root@shenzhen linux]# sh file.sh
#!/bin/bash
for i in `seq 1 2 10`
do
echo $i
done
2.利用for语句编写一个脚本,设计一个30秒倒计时的定时器
<1>编写脚本
[root@desktop linux]# vim countdown.sh
![]()
脚本中的内容如下:
#!/bin/bash
[ -z "$1" ] && {
echo ERROR
exit
}
clear
for ((SEC=$1;SEC>0;SEC--))
do
echo -n "After ${SEC}s is end "
echo -ne "\r"
sleep 1
done

<2>运行脚本,不输入秒数时会出现报错,输入秒数后,会切换到一个新的界面进行倒计时,且在计时完毕后,会自动关闭
[root@desktop linux]# sh countdown.sh
[root@desktop linux]# sh countdown.sh 30
注意:
1.两位和一位差一个空格,所以需要在echo -n "After ${SEC}s is end "的“end”后输入一个空格,否则当执行两位秒数时不会报错,执行一位秒数时会有错误,显示的错误结果如下:
=====================20
3.利用if语句编写一个脚本,设计一个1分10秒倒计时的定时器
编写脚本并执行脚本
[root@desktop linux]# vim monitor.sh
[root@desktop linux]# sh monitor.sh
#!/bin/bash
SEC=10
MIN=1
clear
for ((;SEC>=0;SEC--))
do
if
[ "$SEC" -eq "0" -a "$MIN" -eq "0" ]
then
exit 0
elif
[ "$SEC" -eq "0" -a "$MIN" -ge "0" ]
then
echo -n "After $MIN:$SEC is end "
echo -ne "\r"
SEC=59
((MIN--))
sleep 1
fi
echo -n "After $MIN:$SEC is end "
echo -ne "\r"
sleep 1
done
4.比较if语句和case语句(if查询的效率要远低于case,因为if是一个一个查询,而case只查询想要查询的内容)
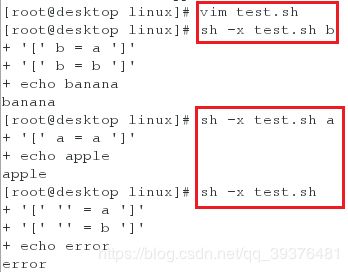
<1>编写一个脚本,利用if语句依次查询,当输入a时输出apple,当输入b时,输出banana,当输入其他字符时,输出error(查看其运行脚本时的过程,会发现,其优先顺序取决于脚本中所写的顺序)
[root@desktop linux]# vim test.sh
[root@desktop linux]# sh -x test.sh b ##系统在脚本中比较两次后才可以输出b所对应的输出结果
[root@desktop linux]# sh -x test.sh a ##系统在脚本中比较两次后才可以输出a所对应的输出结果
[root@desktop linux]# sh -x test.sh ##系统在脚本中比较两次后才可以输出除了特定设置的值以外所对应的输出结果
#!/bin/bash
if
[ "$1" = "a" ]
then
echo apple
elif
[ "$1" = "b" ]
then
echo banana
else
echo error
fi

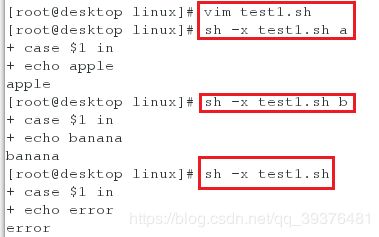
<2>编写一个脚本,利用case语句依次查询,当输入a时输出apple,当输入b时,输出banana,当输入其他字符时,输出error(查看其运行脚本时的过程,会发现,case语句中没有优先顺序)
[root@desktop linux]# vim test1.sh
[root@desktop linux]# sh -x test1.sh a ##系统在脚本中比较一次后可以输出a所对应的输出结果
[root@desktop linux]# sh -x test1.sh b ##系统在脚本中比较一次后可以输出a所对应的输出结果
[root@desktop linux]# sh -x test1.sh ##系统在脚本中比较一次后可以输出除了特定设置的值以外所对应的输出结果
#!/bin/bash
case $1 in
a)
echo apple
;;
b)
echo banana
;;
*)
echo error
esac
5.编写一个脚本,使其在没有输入任何内容时提示please input content,且在连通主机时输出可以连通的主机的ip is up!,没有连通主机时无法连通的输出主机的ip is dowm!
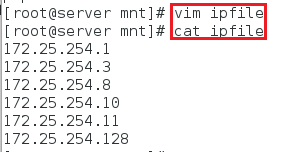
<1>首先在一个文件中写入几个需要连接的ip并进行查看
[root@server mnt]# vim ipfile
[root@server mnt]# cat ipfile
[root@server mnt]# vim check_ip.sh
![]()
<3>运行shell脚本,会发现不输入内容时会出现错误信息,输入要查询的文件名后,会显示运行成功的信息
[root@server mnt]# sh check_ip.sh
[root@server mnt]# sh check_ip.sh ipfile
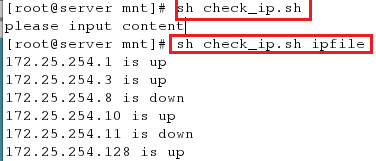
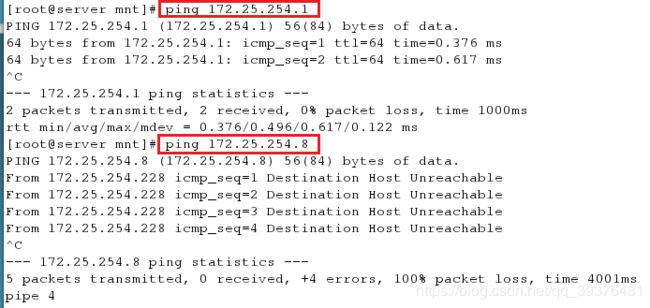
<4>检测运行脚本后的结果是否正确(分别连接一个成功连接上的主机和一个没有成功连接上的主机)
[root@server mnt]# ping 172.25.254.1
[root@server mnt]# ping 172.25.254.8
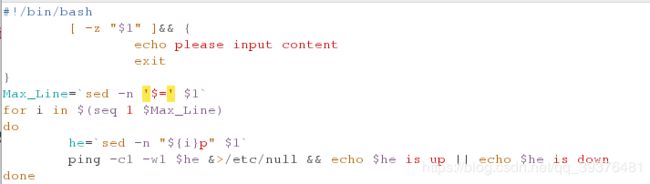
#!/bin/bash
[ -z "$1" ]&& {
echo please input content
exit
}
Max_Line=`sed -n '$=' $1`
for i in $(seq 1 $Max_Line)
do
he=`sed -n "${i}p" $1`
ping -c1 -w1 $he &>/etc/null && echo $he is up || echo $he is down
done
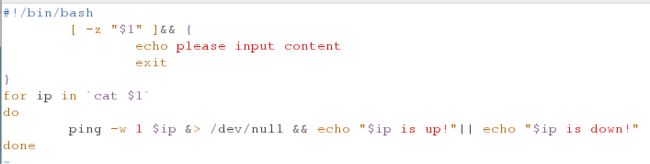
#!/bin/bash
[ -z "$1" ]&& {
echo please input content
exit
}
for ip in `cat $1`
do
ping -w 1 $ip &> /dev/null && echo "$ip is up!"|| echo "$ip is down!"
done
6.while语句实验
编写一个脚本,使其利用while语句读取输入的值并输出,当输入exit时退出
[root@desktop linux]# vim test.sh
[root@desktop linux]# sh test.sh
#!/bin/bash
while true ##当条件成立时执行
do
read -p "Please input a word: " WORD
while [ "$WORD" = "exit" ]
do
echo bye
exit 0
done
echo $WORD
done
#!/bin/bash
until false ##直到条件不成立时不执行
do
read -p "Please input a word: " WORD
while [ "$WORD" = "exit" ]
do
echo bye
exit 0
done
echo $WORD
done
7.if语句实验
<1>编写一个脚本,当输入a时输出apple,当输入b时,输出banana,当输入其他字符时,输出error
[root@desktop linux]# vim test.sh ##编写脚本
[root@desktop linux]# sh test.sh ##运行脚本
[root@desktop linux]# sh test.sh a
[root@desktop linux]# sh test.sh b
#!/bin/bash
if
[ "$1" = "a" ]
then
echo apple
elif
[ "$1" = "b" ]
then
echo banana
else
echo error
fi

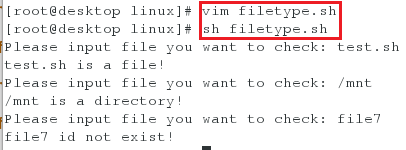
<2>编写一个脚本,当输入一个文件时,判断其文件类型是什么,并进行输出
编写脚本,并执行,会发现当输入文件的名称后,会输出文件的类型
[root@desktop linux]# vim filetype.sh
[root@desktop linux]# sh filetype.sh
#!/bin/bash
while true
do
read -p "Please input file you want to check: " Input
[ -e "$Input" ] || {
echo "$Input id not exist!"
exit
}
if
[ -d "$Input" ]
then
echo "$Input is a directory!"
elif
[ -f "$Input" ]
then
echo "$Input is a file!"
elif
[ -L "$Input" ]
then
echo "$Input is a link!"
elif
[ -s "$Input" ]
then
echo "$Input is a socket!"
elif
[ -b "$Input" ]
then
echo "$Input is a block!"
elif
[ -c "$Input" ]
then
echo "$Input is a character!"
fi
done
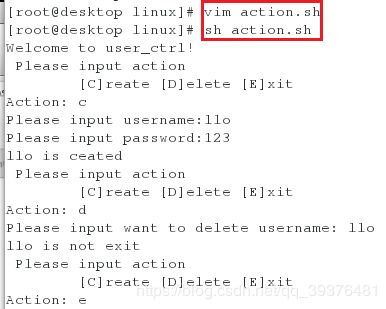
8.脚本升级(使用while语句)
编写脚本并运行该脚本(该脚本在之前的博客中有,在这里只是将结构更加标准化,使用while语句可以使其效率更高点)
[root@desktop linux]# vim action.sh
[root@desktop linux]# sh action.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo "Welcome to user_ctrl!"
while true
do
echo " Please input action
[C]reate [D]elete [E]xit"
read -p "Action: " Input_Action
ACTION=`echo $Input_Action | tr 'A-Z' 'a-z'`
[ "$ACTION" != "c" -a "$ACTION" != "d" -a "$ACTION" != "e" ] && {
echo Input wrong action!!
}
while [ "$ACTION" = "c" ]
do
read -p "Please input username:" USERNAME
id $USERNAME &>/dev/null && {
echo "$USERNAME is exist!!"
}||{
read -p "Please input password:" PASSWORD
useradd $USERNAME
echo $PASSWORD | passwd --stdin $USERNAME &> /dev/null && {
echo $USERNAME is ceated
}
}
break
done
while [ "$ACTION" = "d" ]
do
read -p "Please input want to delete username: " DELUSER
id $DELUSER &>/dev/null &&{
echo "$DELUSER is not exit"
}||{
userdel -r $DELUSER
echo "username is deleted!!"
}
break
done
while [ "$ACTION" = "e" ]
do
exit
break
done
done