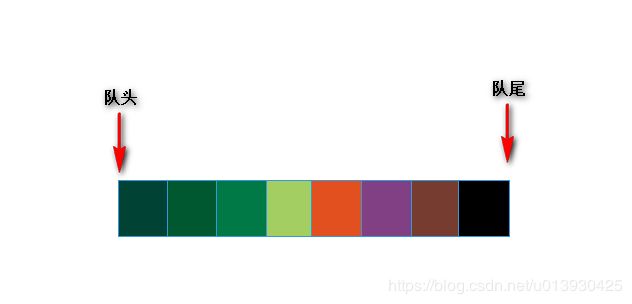2.2 栈和队列—队列
什么是队列
队列是一种先进先出(FIFO:First In First Out)的线性表,只允许从一端插入,从另一端删除,允许插入的一端叫队尾(rear),允许删除的一端叫队头(front)。
队列的模型
队列可以用数组或者链表进行实现,我这边使用链表进行实现。通过链表实现的队列叫链式队列,通过数组实现的队列叫顺序队列,需要注意的是还有一种特殊的队列叫循环队列,实现循环队列。
操作
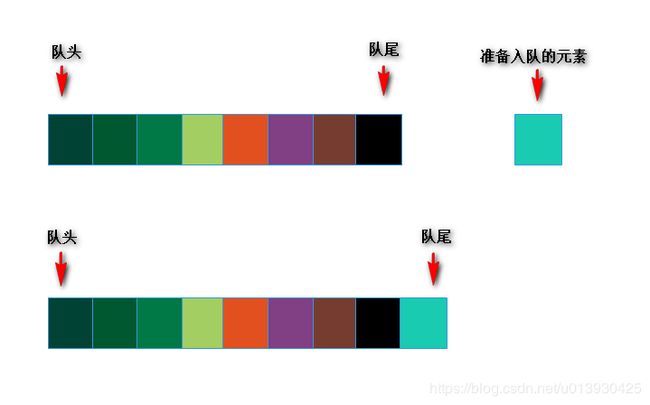
入队: public void enQueue(E e)
入队操作就是将新加入的节点放入队尾即可,也就是链表的 add() 方法。
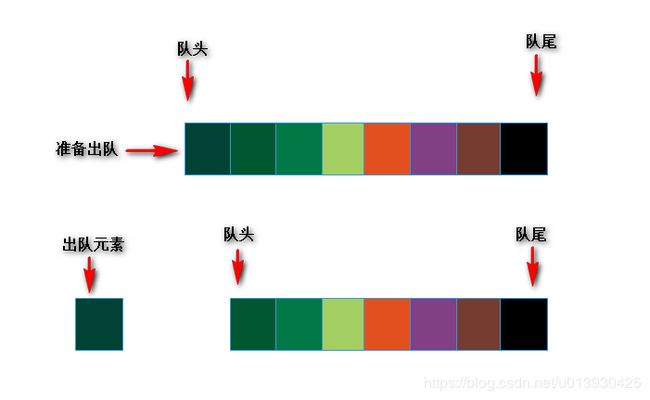
出队:public E deQueue()
出队操作就是将队头节点移除,然后对头节点向后移动移位,对于链表来说,也就是移除链表头节点的过程。
获取队列大小: public int size()
直接获取属性链表的大小即可。
判断队列是否为空:public boolean isEmpty()
直接判断属性链表是否为空即可。
完整代码
package com.qucheng.qingtian.wwjd.datastructure;
/**
* 队列
*
* @author 阿导
* @CopyRight 万物皆导
* @Created 2019-12-12 11:08:00
*/
public class DaoLinkQueue<E> {
/**
* 队列中链表属性
*/
private DaoDoubleLinkedList<E> linkedList;
/**
* 构造函数
*
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/12/12 :00
* @return
*/
public DaoLinkQueue() {
this.linkedList = new DaoDoubleLinkedList<>();
}
/**
* 入队
*
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/12/12 :00
* @param e
* @return void
*/
public void enQueue(E e) {
this.linkedList.add(e);
}
/**
* 出队
*
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/12/12 :00
* @return boolean
*/
public E deQueue() {
if(this.isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列中元素已空");
}
return this.linkedList.remove(0);
}
/**
* 判断是否为空
*
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/12/12 :00
* @return boolean
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.linkedList.isEmpty();
}
/**
* 获取大小
*
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/12/12 :00
* @return int
*/
public int size() {
return this.linkedList.size();
}
}
线程池中的队列
我们学习线程池的时候,线程池没有空闲线程时,新任务请求线程资源时,线程池里面时何如处理的?
基于这个问题,一般有两种处理方式,第一种时非阻塞的处理方式,直接拒绝任务请求,另一种时阻塞的处理方式,将请求排队,等到有空闲线程的时候再取出排队的请求进行处理,这里面就涉及到用队列存储请求的问题。接下来看看基于数组和链表实现的队列的区别。
基于链表实现的链式队列,可以实现一个支持无限排队的无界队列(unbounded queue),但是可能会导致过多的请求排队等待,请求处理的响应时间过长。所以针对响应时间比较敏感的系统,基于链表实现的无限排队的线程池是不合适的。
基于数组实现的有界队列(bounded queue),队列大小有限,所以线程池中排队的请求超过队列大小时,接下来的请求就会被拒绝,这种方式队响应时间敏感的系统来说,就相对更为合理。所以设置队列的大小很是关键,设置合理才能最大限度的利用系统资源发挥其性能,也不会让更多的请求阻塞,等待很长时间。
LinkedBlockingQueue
先看看 JDK 中队列的 UML 图
下面我们来剖析一下 LinkedBlockingQueue 源码,其它源码感兴趣的可自行研究,另外阿导说的不好的地方请多多包含和指教。
首先里面有个内部静态类 Node 存储节点信息的,没啥好说的。具体代码如下:
/**
* Linked list node class
*/
static class Node<E> {
E item;
/**
* One of:
* - the real successor Node
* - this Node, meaning the successor is head.next
* - null, meaning there is no successor (this is the last node)
*/
Node<E> next;
Node(E x) { item = x; }
}
下面看看 LinkedBlockingQueue 里面的属性
public class LinkedBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
/** The capacity bound, or Integer.MAX_VALUE if none */
// capacity 设置队列的边界,默认为 Integer.MAX_VALUE
private final int capacity;
/** Current number of elements */
// 统计队列里面的元素个数
private final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger();
/**
* Head of linked list.
* Invariant: head.item == null
*
* 链表的头节点,里面元素为空是不变的
*
*/
transient Node<E> head;
/**
* Tail of linked list.
* Invariant: last.next == null
*
* 链表的尾节点,里面下一个节点为 null 是不变的
*/
private transient Node<E> last;
/** Lock held by take, poll, etc */
// 协助 tabke ,poll 等操作的可重入锁
private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();
/** Wait queue for waiting takes */
// 执行 takes 操作进行阻塞辅助
private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition();
/** Lock held by put, offer, etc */
// 协助 put,offer 等操作的可重入锁
private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();
/** Wait queue for waiting puts */
// 执行 puts 操作进行阻塞辅助
private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition();
}
下面才是重头戏,阿导将逐一讲解其里面的方法,阿导就从源码的顺序往下说。
构造方法:public LinkedBlockingQueue()、public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity)、public LinkedBlockingQueue(Collection c)
/**
* Creates a {@code LinkedBlockingQueue} with a capacity of
* {@link Integer#MAX_VALUE}.
*/
public LinkedBlockingQueue() {
// 调用 public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity),默认是整型的最大值
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
/**
* Creates a {@code LinkedBlockingQueue} with the given (fixed) capacity.
*
* @param capacity the capacity of this queue
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code capacity} is not greater
* than zero
*/
public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
// 阈值校验
if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// 赋值给阈值
this.capacity = capacity;
// 新增头尾节点,但里面元素均为空,显然空队列的时候,头尾指针指向的是同一个节点
last = head = new Node<E>(null);
}
/**
* Creates a {@code LinkedBlockingQueue} with a capacity of
* {@link Integer#MAX_VALUE}, initially containing the elements of the
* given collection,
* added in traversal order of the collection's iterator.
*
* @param c the collection of elements to initially contain
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection or any
* of its elements are null
*
* 这个构造方法传入了一个集合,
*/
public LinkedBlockingQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) {
// 第一步调用 public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity),阈值是整型的最大值
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 获取 putLock 锁对象
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
// 声明时虽然还没开始竞争,但是针对可见性是必要的
putLock.lock(); // Never contended, but necessary for visibility
try {
// 默认队列元素为空
int n = 0;
// 遍历集合
for (E e : c) {
// 元素非空判断是有必要的
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// 进行阈值判断
if (n == capacity)
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");
// 新节点入队操作
enqueue(new Node<E>(e));
// 统计值自加 1
++n;
}
// 设置队列的大小
count.set(n);
} finally {
// 最后释放锁
putLock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Links node at end of queue.
* 入队操作
* @param node the node
*/
private void enqueue(Node<E> node) {
// assert putLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
// assert last.next == null;
// 这个操作可拆分为 last.next = node; last = node;
last = last.next = node;
}
获取队列的大小:public int size()
/**
* Returns the number of elements in this queue.
*
* count 是 AtomicInteger 类型,保证其原子性,里面是通过 unsafe 里面的 CAS 来实现的
*
* @return the number of elements in this queue
*/
public int size() {
return count.get();
}
获取队列可用容量:public int remainingCapacity()
/**
* Returns the number of additional elements that this queue can ideally
* (in the absence of memory or resource constraints) accept without
* blocking. This is always equal to the initial capacity of this queue
* less the current {@code size} of this queue.
*
* Note that you cannot always tell if an attempt to insert
* an element will succeed by inspecting {@code remainingCapacity}
* because it may be the case that another thread is about to
* insert or remove an element.
*
* capacity 为最大容量,count.get()为当前已使用数量,它们之差即为队列剩余节点数量
*/
public int remainingCapacity() {
return capacity - count.get();
}
入队(阻塞):public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue, waiting if
* necessary for space to become available.
*
* @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
// 校验元素可用性
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// Note: convention in all put/take/etc is to preset local var
// holding count negative to indicate failure unless set.
// 临时变量,进行和阈值判断,给初始值 -1 不知有什么特殊含义
int c = -1;
// 构造一个新节点
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
// 获取 putLock 锁对象
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
// 获取 count 对象
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
// 首先获取 putLock 的锁,保证 putLock 的线程安全性
putLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
/*
* Note that count is used in wait guard even though it is
* not protected by lock. This works because count can
* only decrease at this point (all other puts are shut
* out by lock), and we (or some other waiting put) are
* signalled if it ever changes from capacity. Similarly
* for all other uses of count in other wait guards.
*/
// 若是队列达到阈值,则阻塞等待,当消费者消费的时候会调用 notFull.signal()
while (count.get() == capacity) {
notFull.await();
}
// 入队操作
enqueue(node);
// count 先赋值给临时变量 c,然后自增加 1
c = count.getAndIncrement();
// 当前线程入队成功,释放 notFull 信号量
if (c + 1 < capacity)
notFull.signal();
} finally {
// 最后要释放锁
putLock.unlock();
}
// 队列空到不空的状态,释放 notEmpty 信号量,主要是唤起消费者进行消费(出队)
if (c == 0)
signalNotEmpty();
}
/**
* Signals a waiting take. Called only from put/offer (which do not
* otherwise ordinarily lock takeLock.)
*
* 释放 notEmpty 信号量,唤起消费者消费,这个方法是从 put 和 offer 方法进行调用的
*
*/
private void signalNotEmpty() {
// 获取 takeLock 锁对象
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
// 获取锁
takeLock.lock();
try {
// 释放 notEmpty 信号量
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
// 释放 takeLock 锁
takeLock.unlock();
}
}
入队(非阻塞),并返回入队结果: public boolean offer(E e)
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue if it is
* possible to do so immediately without exceeding the queue's capacity,
* returning {@code true} upon success and {@code false} if this queue
* is full.
* When using a capacity-restricted queue, this method is generally
* preferable to method {@link BlockingQueue#add add}, which can fail to
* insert an element only by throwing an exception.
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
// 这特么都不等,要是队列满了,直接返回失败
if (count.get() == capacity)
return false;
// 这里赋值为 -1 还是有点意义的,要是入队失败,在返回结果时 c>=0 为 false
int c = -1;
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
putLock.lock();
try {
// 这边没有进行阻塞操作,所以,可能再多线程(也就是说在 putLock.lock(); 之前正好最后一个元素进入导致队满)的情况下,最后一个位置存在竞争导致入队失败。
if (count.get() < capacity) {
enqueue(node);
c = count.getAndIncrement();
if (c + 1 < capacity)
notFull.signal();
}
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
if (c == 0)
signalNotEmpty();
return c >= 0;
}
入队(等待超时),并设置超时时间,并返回入队结果:public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue, waiting if
* necessary up to the specified wait time for space to become available.
*
* @return {@code true} if successful, or {@code false} if
* the specified waiting time elapses before space is available
* @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*
* 参数依次代表的含义是 入队信息,超时时间,时间类型
*/
public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 转换时间为毫微秒(NANOSECONDS)
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
int c = -1;
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
putLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count.get() == capacity) {
// 若超时,返回 false 表示入队未成功
if (nanos <= 0)
return false;
// 获取本次循环后的剩余时间
nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
enqueue(new Node<E>(e));
c = count.getAndIncrement();
if (c + 1 < capacity)
notFull.signal();
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
if (c == 0)
signalNotEmpty();
// 入队成功则返回 true
return true;
}
出队(阻塞):public E take()
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
// 声明结果
E x;
// 临时变量 c 存储队列数目变化,进行判断是否释放 notEmpty 信号量
int c = -1;
// 获取 队列中元素
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
// 获取 takeLock 锁对象
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
// 获取 takeLock 锁
takeLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 队列为空,则阻塞,等待生产者(入队成功)释放信号量
while (count.get() == 0) {
notEmpty.await();
}
// 出队操作
x = dequeue();
// 首先将 count 赋值给 c, 然后 count 自减
c = count.getAndDecrement();
// 若在移除之前不为空,则释放 notEmpty 信号量,可进行出队操作
if (c > 1)
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
// 释放 takeLock 锁
takeLock.unlock();
}
// 阈值的元素已出队,队列从满到不满的状态,说明可释放入队的信号量
if (c == capacity)
signalNotFull();
// 返回出队元素内容
return x;
}
/**
* Removes a node from head of queue.
*
* @return the node
*/
private E dequeue() {
// assert takeLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
// assert head.item == null;
// 获取头节点
Node<E> h = head;
// 第一个节点为头节点的后继节点
Node<E> first = h.next;
// 头节点下一个节点指向本身辅助垃圾回收
h.next = h; // help GC
// 头节点指向第一个节点
head = first;
// 获取第一个节点的元素
E x = first.item;
// 头节点元素置空
first.item = null;
// 返回元素
return x;
}
/**
* Signals a waiting put. Called only from take/poll.
* 原先队列已满,达到阈值,调用此方法说明已经出队了一个元素,释放 notFull 信号,通知生产者可入队。
*/
private void signalNotFull() {
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
// 获取 putLock 锁
putLock.lock();
try {
// 释放 notFull 信号量
notFull.signal();
} finally {
// 释放锁
putLock.unlock();
}
}
出队(不阻塞):public E poll()
public E poll() {
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
// 若队空,则直接返回 null
if (count.get() == 0)
return null;
E x = null;
int c = -1;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lock();
try {
// 队列不为空方可进行出队操作
if (count.get() > 0) {
x = dequeue();
c = count.getAndDecrement();
if (c > 1)
notEmpty.signal();
}
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
if (c == capacity)
signalNotFull();
return x;
}
出队(等待超时):public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
E x = null;
int c = -1;
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 进行自旋
while (count.get() == 0) {
// 超时后返回 null,表示队空
if (nanos <= 0)
return null;
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
x = dequeue();
c = count.getAndDecrement();
if (c > 1)
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
if (c == capacity)
signalNotFull();
return x;
}
获取队头元素,但不出队:public E peek()
public E peek() {
// 队空没元素可获取
if (count.get() == 0)
return null;
// 获取 takeLock 锁对象
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
// 获取 takeLock 锁
takeLock.lock();
try {
// 第一个元素,并返回结果
Node<E> first = head.next;
if (first == null)
return null;
else
return first.item;
} finally {
// 释放锁
takeLock.unlock();
}
}
移除元素:public boolean remove(Object o)
/**
* Removes a single instance of the specified element from this queue,
* if it is present. More formally, removes an element {@code e} such
* that {@code o.equals(e)}, if this queue contains one or more such
* elements.
* Returns {@code true} if this queue contained the specified element
* (or equivalently, if this queue changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this queue, if present
* @return {@code true} if this queue changed as a result of the call
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
// 元素为空,直接返回 false
if (o == null) return false;
// 移除操作需要锁住出入队操作
fullyLock();
try {
// 进行遍历节点查找匹配的位置
for (Node<E> trail = head, p = trail.next;
p != null;
trail = p, p = p.next) {
// 若是查询到元素
if (o.equals(p.item)) {
// 删除节点操作
unlink(p, trail);
// 返回成功
return true;
}
}
// 返回 false
return false;
} finally {
// 释放出入队锁
fullyUnlock();
}
}
/**
* Locks to prevent both puts and takes.
*
* 先锁住入队,可有效利用资源
*/
void fullyLock() {
// 入队锁
putLock.lock();
// 出队锁
takeLock.lock();
}
/**
* Unlocks to allow both puts and takes.
* 先释放出队锁,有利于释放资源
*/
void fullyUnlock() {
// 释放出队锁
takeLock.unlock();
// 释放入队锁
putLock.unlock();
}
/**
* Unlinks interior Node p with predecessor trail.
* 删除节点 p
*/
void unlink(Node<E> p, Node<E> trail) {
// assert isFullyLocked();
// p.next is not changed, to allow iterators that are
// traversing p to maintain their weak-consistency guarantee.
p.item = null;
// 直接将 p 的前驱节点的后继节点设置为 p 的后继节点
trail.next = p.next;
// 若 p 为队尾,需要将队尾指针指向 p 的前驱节点
if (last == p)
last = trail;
// 若是正好从阈值删除一个节点,需要唤起入队操作
if (count.getAndDecrement() == capacity)
notFull.signal();
}
包含元素:public boolean contains(Object o)
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this queue contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this queue contains
* at least one element {@code e} such that {@code o.equals(e)}.
*
* @param o object to be checked for containment in this queue
* @return {@code true} if this queue contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
// null 则无须查找
if (o == null) return false;
// 需要锁住出入队操作,若是一直都有出入队操作,可能会造成死循环
fullyLock();
try {
// 遍历节点查找匹配的元素,若查询到则返回 true,否则返回 false
for (Node<E> p = head.next; p != null; p = p.next)
if (o.equals(p.item))
return true;
return false;
} finally {
// 释放出入队操作
fullyUnlock();
}
}
转换成数组:public Object[] toArray()
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue, in
* proper sequence.
*
* The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it are
* maintained by this queue. (In other words, this method must allocate
* a new array). The caller is thus free to modify the returned array.
*
*
This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based
* APIs.
*
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this queue
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
// 锁住出入队操作
fullyLock();
try {
// 获取队列大小
int size = count.get();
// 声明结果数组
Object[] a = new Object[size];
int k = 0;
// 遍历队列中每一个节点,然后赋值给数组
for (Node<E> p = head.next; p != null; p = p.next)
a[k++] = p.item;
// 返回结果数组
return a;
} finally {
// 释放出入队操作
fullyUnlock();
}
}
转换成指定类型的数组:public T[] toArray(T[] a)
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue, in
* proper sequence; the runtime type of the returned array is that of
* the specified array. If the queue fits in the specified array, it
* is returned therein. Otherwise, a new array is allocated with the
* runtime type of the specified array and the size of this queue.
*
* If this queue fits in the specified array with room to spare
* (i.e., the array has more elements than this queue), the element in
* the array immediately following the end of the queue is set to
* {@code null}.
*
*
Like the {@link #toArray()} method, this method acts as bridge between
* array-based and collection-based APIs. Further, this method allows
* precise control over the runtime type of the output array, and may,
* under certain circumstances, be used to save allocation costs.
*
*
Suppose {@code x} is a queue known to contain only strings.
* The following code can be used to dump the queue into a newly
* allocated array of {@code String}:
*
*
{@code String[] y = x.toArray(new String[0]);}
*
* Note that {@code toArray(new Object[0])} is identical in function to
* {@code toArray()}.
*
* @param a the array into which the elements of the queue are to
* be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the
* same runtime type is allocated for this purpose
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this queue
* @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array
* is not a supertype of the runtime type of every element in
* this queue
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified array is null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
fullyLock();
try {
int size = count.get();
// 传入的数组容量不够,这边似乎有个风险,若 a 为 null 则会出现空指针异常,因为底层扩容是 native 方法,所以这边加了 unchecked ,注释上也说明了会有空指针的情况
if (a.length < size)
a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance
(a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);
int k = 0;
// 遍历队并一一赋值
for (Node<E> p = head.next; p != null; p = p.next)
a[k++] = (T)p.item;
// 这种情况可能出现在 a.length 大于 count.get 的情况,一般数组是连续的空间,我不清楚为啥不将之后的元素都设为 null,这个是很有意思的点
if (a.length > k)
a[k] = null;
return a;
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}
转换成字符串: public String toString()
略
置空队列: public void clear()
/**
* Atomically removes all of the elements from this queue.
* The queue will be empty after this call returns.
*/
public void clear() {
fullyLock();
try {
// 遍历节点,辅助 GC,这里面 p 负责清空节点里面元素,h 负责指针指向,二者相互协助辅助 GC
for (Node<E> p, h = head; (p = h.next) != null; h = p) {
h.next = h;
p.item = null;
}
// 置空后队头 = 队尾
head = last;
// assert head.item == null && head.next == null;
// 可能在置空之前,队列已满,所以要考虑释放入队信号量
if (count.getAndSet(0) == capacity)
notFull.signal();
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}
全部出队:public int drainTo(Collection c)
/**
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
*
* 这个没啥好说的
*/
public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c) {
return drainTo(c, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
批量出队,指定大小:public int drainTo(Collection c, int maxElements)
/**
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c, int maxElements) {
// c 不能为空
if (c == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// 不能为本身
if (c == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// 出队数量要合法
if (maxElements <= 0)
return 0;
// 判断是否需要释放入队的信号量
boolean signalNotFull = false;
// 获取 takeLock 对象
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
// 获取锁
takeLock.lock();
try {
// 获取实际能出队的数量
int n = Math.min(maxElements, count.get());
// count.get provides visibility to first n Nodes
// 获取头节点
Node<E> h = head;
// 记录位置
int i = 0;
try {
// 进行遍历。出队操作
while (i < n) {
// 从头节点下一个节点开始获取元素
Node<E> p = h.next;
// 添加到集合
c.add(p.item);
// 以下是辅助 GC
p.item = null;
h.next = h;
h = p;
// 计数加一
++i;
}
// 返回数量
return n;
} finally {
// Restore invariants even if c.add() threw
if (i > 0) {
// assert h.item == null;
head = h;
// 判断是否队满
signalNotFull = (count.getAndAdd(-i) == capacity);
}
}
} finally {
// 释放出队的锁
takeLock.unlock();
// 为啥在这个里面进行释放非队满信号?写在这是因为程序的严谨性,出队锁完成才算完整的出队操作结束,这样才能释放非满队列信号,唤醒生产者进行生产。
if (signalNotFull)
signalNotFull();
}
}
获取迭代子: public Iterator iterator()
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this queue in proper sequence.
* The elements will be returned in order from first (head) to last (tail).
*
* The returned iterator is
* weakly consistent.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this queue in proper sequence
* 直接声明一个 继承 Iterator 的内部类并返回
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
/*
* Basic weakly-consistent iterator. At all times hold the next
* item to hand out so that if hasNext() reports true, we will
* still have it to return even if lost race with a take etc.
*/
/**
* 当前节点
*/
private Node<E> current;
/**
* 记录指针移动前的节点
*/
private Node<E> lastRet;
/**
* 当前元素
*/
private E currentElement;
Itr() {
// 锁出出入队操作
fullyLock();
try {
// 获取第一个节点
current = head.next;
// 获取第一个节点元素
if (current != null)
currentElement = current.item;
} finally {
// 释放出入队锁
fullyUnlock();
}
}
public boolean hasNext() {
// 判断是否还有下一个节点.为啥不是 current.next!=null?联系下 remove就知道问题所在
return current != null;
}
/**
* Returns the next live successor of p, or null if no such.
*
* Unlike other traversal methods, iterators need to handle both:
* - dequeued nodes (p.next == p)
* - (possibly multiple) interior removed nodes (p.item == null)
*/
private Node<E> nextNode(Node<E> p) {
for (;;) {
Node<E> s = p.next;
// 若在迭代器中执行了 clear() 方法会出现这种情况
if (s == p)
return head.next;
// 若 p 为 队尾,next 指向 null ,若不是队尾,返回下一个元素
if (s == null || s.item != null)
return s;
p = s;
}
}
public E next() {
// 锁出出入队操作
fullyLock();
try {
// 节点为空
if (current == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// 当前的元素
E x = currentElement;
// 记录当前节点,用于删除操作
lastRet = current;
// 指针向后继节点移动
current = nextNode(current);
// 获取后继节点的元素
currentElement = (current == null) ? null : current.item;
// 返回结果
return x;
} finally {
// 释放出入队锁
fullyUnlock();
}
}
public void remove() {
// 因此在执行 remove 方法之前必须执行 next()
if (lastRet == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
// 锁住出入队操作
fullyLock();
try {
// 获取节点
Node<E> node = lastRet;
// 删除后置为空,保证不能重复删除
lastRet = null;
// 这个和 remove 方法类似,不多说了
for (Node<E> trail = head, p = trail.next;
p != null;
trail = p, p = p.next) {
if (p == node) {
unlink(p, trail);
break;
}
}
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}
}
分割迭代器:public Spliterator spliterator()
略
序列化队列:private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
略
反序列化队列:private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
略
解读 LinkedBlockingQueue 遇到的问题
- 入队的时候,需要注意队列从空队转换成非空队,出队的时候,需要注意从队满转换成非队满,这是为什么?
因为当调用 take 的时候,空队会阻塞等待,空队->非空队,需要释放非空信号量,通知消费者消费;同理调用 put 的时候,队满则阻塞等待,队满->非队满,需要释放非满信号量,通知生产者生产。
- 在 offer 方法的时候,之前已经判断达到阈值则返回 false 表示失败,为什么在入队之前还判断是否达到阈值?
这步操作是为了线程的安全,在竞争大的情况下,判断是否达到阈值到获取到 putLock 锁中间可能会有入队成功并达到队满的情况,所以必须在入队之前判断是否达到阈值。
- fullyLock 方法入队锁在前,出队锁在后,而 fullyUnlock 则是释放出队锁在前,释放入队锁在后,why?
因为这样能更好的利用系统资源,入队是在占用资源,出队是在释放资源。
- 在 contains 不涉及到出入队操作,为什么也需要限制出入队?
说到底还是保证原子性,防止在多线程的情况删除了某个值或者添加了某个值导致和预期不一致。
- toArray(T[] a) 方法中为什么只将紧跟其后的元素置为空,后续数组空间为啥不用处理?
注释上只是说了这样操作,但没有说这种情况,理论上我们也不会做这种傻事。这个原因阿导也在思考…
- 批量出队 drainTo(Collection c, int maxElements) 方法中,为什么释放非满信号量要放在释放出队锁之后
写在这是因为程序的严谨性,出队锁完成才算完整的出队操作结束,这样才能释放非满队列信号,唤醒生产者进行生产。
- 观察下面代码,这是迭代器 next 中调用的一个方法,目的是获取下一个节点,请问什么情况下会出现 s==p 的情况
private Node<E> nextNode(Node<E> p) {
for (;;) {
Node<E> s = p.next;
// ?
if (s == p)
return head.next;
if (s == null || s.item != null)
return s;
p = s;
}
}
显然,当 s!=null&& s.item == null&& p=p.next 才会发生,也就是空队的时候才会出现,但是在获取迭代子的时候然后进行判断是否有后续节点 hasNext 方法的时候为 false,执行 next 会报 NoSuchElementException 异常。
因此出现这种情况必然是 hasNext 为 true 的情况下然后调用了 clear() 方法将队列置空后再调用 next() 方法才会出现 s==p 的情况。