Android App 启动流程梳理(基于 Android 10)
1. 概述
当我们点击桌面的应用图标,直到应用的启动页出来,这期间的在源代码的流程中到底是什么样子的?之前追过 Android App 启动的相关源码,由于没有做相关记录,时间一久,已经忘得差不多了。现在有时间,也下载了 Android 10 的源码,就重新追一遍并且画一画相关的流程图。
2. 从点击桌面图标开始
Android 的桌面本身也是一个 APP,为 Launcher。由于 Android 是开源的,很多手机厂商都做了相关的修改,甚至重新做一个新的启动页。之前做公司做电视系统的定制化,就没有用系统的这个 Launcher。
当我们点击桌面的应用图标开始,就是 Launcher 中的一次点击事件:
Launcher.java (\packages\apps\launcher3\src\com\android\launcher3)
/**
* Creates a view representing a shortcut.
*
* @param info The data structure describing the shortcut.
*/
View createShortcut(WorkspaceItemInfo info) {
return createShortcut((ViewGroup) mWorkspace.getChildAt(mWorkspace.getCurrentPage()), info);
}
/**
* Creates a view representing a shortcut inflated from the specified resource.
*
* @param parent The group the shortcut belongs to.
* @param info The data structure describing the shortcut.
*
* @return A View inflated from layoutResId.
*/
public View createShortcut(ViewGroup parent, WorkspaceItemInfo info) {
BubbleTextView favorite = (BubbleTextView) LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext())
.inflate(R.layout.app_icon, parent, false);
favorite.applyFromWorkspaceItem(info);
favorite.setOnClickListener(ItemClickHandler.INSTANCE);
favorite.setOnFocusChangeListener(mFocusHandler);
return favorite;
}真正的点击事件位于 ItemClickHandler.java 中:
ItemClickHandler.java (\packages\apps\launcher3\src\com\android\launcher3\touch)
private static void onClick(View v, String sourceContainer) {
// Make sure that rogue clicks don't get through while allapps is launching, or after the
// view has detached (it's possible for this to happen if the view is removed mid touch).
if (v.getWindowToken() == null) return;
Launcher launcher = Launcher.getLauncher(v.getContext());
if (!launcher.getWorkspace().isFinishedSwitchingState()) return;
Object tag = v.getTag();
if (tag instanceof WorkspaceItemInfo) {
onClickAppShortcut(v, (WorkspaceItemInfo) tag, launcher, sourceContainer);
} else if (tag instanceof FolderInfo) {
if (v instanceof FolderIcon) {
onClickFolderIcon(v);
}
} else if (tag instanceof AppInfo) {
startAppShortcutOrInfoActivity(v, (AppInfo) tag, launcher,
sourceContainer == null ? CONTAINER_ALL_APPS: sourceContainer);
} else if (tag instanceof LauncherAppWidgetInfo) {
if (v instanceof PendingAppWidgetHostView) {
onClickPendingWidget((PendingAppWidgetHostView) v, launcher);
}
}
调用的是 startAppShortcutOrInfoActivity 方法:
private static void startAppShortcutOrInfoActivity(View v, ItemInfo item, Launcher launcher,
@Nullable String sourceContainer) {
...
...
launcher.startActivitySafely(v, intent, item, sourceContainer);
}主要代码是 startActivitySafely 方法:
public boolean startActivitySafely(View v, Intent intent, ItemInfo item,
@Nullable String sourceContainer) {
...
boolean success = super.startActivitySafely(v, intent, item, sourceContainer);
...
...
return success;
}这里调用的是父类的 startActivitySafely 方法:
Launcher 的父类为 BaseDraggingActivity,其中 startActivitySafely 方法如下:
public boolean startActivitySafely(View v, Intent intent, @Nullable ItemInfo item,
@Nullable String sourceContainer) {
...
// Prepare intent
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK); //1
if (v != null) {
intent.setSourceBounds(getViewBounds(v));
}
try {
boolean isShortcut = (item instanceof WorkspaceItemInfo)
&& (item.itemType == Favorites.ITEM_TYPE_SHORTCUT
|| item.itemType == Favorites.ITEM_TYPE_DEEP_SHORTCUT)
&& !((WorkspaceItemInfo) item).isPromise();
if (isShortcut) {
// Shortcuts need some special checks due to legacy reasons.
startShortcutIntentSafely(intent, optsBundle, item, sourceContainer);
} else if (user == null || user.equals(Process.myUserHandle())) {
// Could be launching some bookkeeping activity
startActivity(intent, optsBundle); //2
...
...
return false;
}注释1 中:要在一个新的 Task 中启动 Activity;
注释2 中:调用的是 Activity 的 startActivity 方法。
Launcher 的相关类继承关系如下:
3. Activity
Activity.java (framework\base\core\java\android\app)
在第 2 步中,从 Launcher 中的代码追溯到了 Activity ,调用了熟悉的 startActivity 方法:
@Override
public void startActivity(Intent intent) {
this.startActivity(intent, null);
}接着调用了两个参数的 startActivity 方法,这里第二个参数为 null:
@Override
public void startActivity(Intent intent, @Nullable Bundle options) {
if (options != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, -1, options);
} else {
// Note we want to go through this call for compatibility with
// applications that may have overridden the method.
startActivityForResult(intent, -1);
}
}
由于第2个参数为 null,所以 startActivityForResult(intent, -1, options),因为 Launcher 启动应用并不需要应用给予回复,所以 这里 requestCode 为 -1。startActivityForResult 的代码如下:
public void startActivityForResult(
String who, Intent intent, int requestCode, @Nullable Bundle options) {
Uri referrer = onProvideReferrer();
if (referrer != null) {
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_REFERRER, referrer);
}
options = transferSpringboardActivityOptions(options);
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(
this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, who,
intent, requestCode, options);
if (ar != null) {
mMainThread.sendActivityResult(
mToken, who, requestCode,
ar.getResultCode(), ar.getResultData());
}
cancelInputsAndStartExitTransition(options);
}这里的核心代码是调用了 Instrumentation 的 execStartActivity 方法。
4. Instrumentation
Instrumentation.java (framework\base\core\java\android\app)
Instrumentation 是 Android 系统中启动 Activity 的一个实际操作类,它用来监控应用程序和系统的交互。execStartActivity 方法如下:
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
...
...
try {
intent.migrateExtraStreamToClipData();
intent.prepareToLeaveProcess(who);
int result = ActivityTaskManager.getService() //3
.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, 0, null, options);
checkStartActivityResult(result, intent);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failure from system", e);
}
return null;
}这个方法的核心代码是注释3:ActivityTaskManager.getService().startActivity
5. ActivityTaskManager
ActivityTaskManager.java (framework\base\core\java\android\app)
ActivityTaskManager 的 getService 方法:
public class ActivityTaskManager {
...
...
public static IActivityTaskManager getService() {
return IActivityTaskManagerSingleton.get();
}
@UnsupportedAppUsage(trackingBug = 129726065)
private static final Singleton IActivityTaskManagerSingleton =
new Singleton() {
@Override
protected IActivityTaskManager create() {
final IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.ACTIVITY_TASK_SERVICE);
return IActivityTaskManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
}
};
...
} 从这里代码可以看出这是一个 AIDL 的调用,此处是 AIDL 的 client 端,那 Server 端在哪里呢?这里的 Server 端是 ActivityTaskManagerService。Instrumentation 中 execStartActivity 方法实际调用的是 ActivityTaskManagerService 中的 startActivity 方法。
6. ActivityTaskManagerService
ActivityTaskManagerService.java (framework\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\wm)
public class ActivityTaskManagerService extends IActivityTaskManager.Stub {
...
@Override
public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions) {
return startActivityAsUser(caller, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, resultTo,
resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profilerInfo, bOptions,
UserHandle.getCallingUserId());
}
@Override
public int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions, int userId) {
return startActivityAsUser(caller, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, resultTo,
resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profilerInfo, bOptions, userId,
true /*validateIncomingUser*/);
}
int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions, int userId,
boolean validateIncomingUser) {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivityAsUser");
userId = getActivityStartController().checkTargetUser(userId, validateIncomingUser,
Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(), "startActivityAsUser");
// TODO: Switch to user app stacks here.
return getActivityStartController().obtainStarter(intent, "startActivityAsUser")
.setCaller(caller)
.setCallingPackage(callingPackage)
.setResolvedType(resolvedType)
.setResultTo(resultTo)
.setResultWho(resultWho)
.setRequestCode(requestCode)
.setStartFlags(startFlags)
.setProfilerInfo(profilerInfo)
.setActivityOptions(bOptions)
.setMayWait(userId)
.execute();
}
...
}这边的核心代码是 startActivityAsUser 中的 return。
首先通过 getActivityStartController 方法获取 ActivityStartController 的实例,接着调用 ActivityStartController 的 obtainStarter 方法。
7. ActivityStartController
ActivityStartController.java (framework\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\wm)
obtainStarter 方法如下:
ActivityStarter obtainStarter(Intent intent, String reason) {
return mFactory.obtain().setIntent(intent).setReason(reason);
}这里返回的是 ActivityStarter 对象。看到了 “Factory”,自然而然的想到了工厂模式,这里梳理下该工厂模式的具体调用流程:
mFactory 是在 ActivityStartController 的构造方法中以参数的方式传递进来的:
@VisibleForTesting
ActivityStartController(ActivityTaskManagerService service, ActivityStackSupervisor supervisor,
Factory factory) {
mService = service;
mSupervisor = supervisor;
mHandler = new StartHandler(mService.mH.getLooper());
mFactory = factory;
mFactory.setController(this);
mPendingRemoteAnimationRegistry = new PendingRemoteAnimationRegistry(service,
service.mH);
}在 ActivityTaskManagerService 对于 ActivityStartController 的初始化:
public void initialize(IntentFirewall intentFirewall, PendingIntentController intentController,
Looper looper) {
mH = new H(looper);
mUiHandler = new UiHandler();
...
mActivityStartController = new ActivityStartController(this);
...
}这是一个参数的构造方法:
ActivityStartController(ActivityTaskManagerService service) {
this(service, service.mStackSupervisor,
new DefaultFactory(service, service.mStackSupervisor,
new ActivityStartInterceptor(service, service.mStackSupervisor)));
}所以刚才的 mFactory 就是这里的 DefaultFactory,从导包可以看出这里的 DefaultFactory 是 ActivityStarter 中的类:
import com.android.server.wm.ActivityStarter.DefaultFactory;
import com.android.server.wm.ActivityStarter.Factory;接着把关注对象转为 ActivityStarter。
8. ActivityStarter
ActivityStarter.java (framework\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\wm)
DefaultFactory 是 ActivityStarter 中的一个静态内部类,并且实现了接口 Factory
static class DefaultFactory implements Factory {
/**
* The maximum count of starters that should be active at one time:
* 1. last ran starter (for logging and post activity processing)
* 2. current running starter
* 3. starter from re-entry in (2)
*/
private final int MAX_STARTER_COUNT = 3;
private ActivityStartController mController;
private ActivityTaskManagerService mService;
private ActivityStackSupervisor mSupervisor;
private ActivityStartInterceptor mInterceptor;
private SynchronizedPool mStarterPool =
new SynchronizedPool<>(MAX_STARTER_COUNT);
DefaultFactory(ActivityTaskManagerService service,
ActivityStackSupervisor supervisor, ActivityStartInterceptor interceptor) {
mService = service;
mSupervisor = supervisor;
mInterceptor = interceptor;
}
@Override
public void setController(ActivityStartController controller) {
mController = controller;
}
@Override
public ActivityStarter obtain() {
ActivityStarter starter = mStarterPool.acquire();
if (starter == null) {
starter = new ActivityStarter(mController, mService, mSupervisor, mInterceptor);
}
return starter;
}
@Override
public void recycle(ActivityStarter starter) {
starter.reset(true /* clearRequest*/);
mStarterPool.release(starter);
}
}
interface Factory {
/**
* Sets the {@link ActivityStartController} to be passed to {@link ActivityStarter}.
*/
void setController(ActivityStartController controller);
/**
* Generates an {@link ActivityStarter} that is ready to handle a new start request.
* @param controller The {@link ActivityStartController} which the starter who will own
* this instance.
* @return an {@link ActivityStarter}
*/
ActivityStarter obtain();
/**
* Recycles a starter for reuse.
*/
void recycle(ActivityStarter starter);
} 工厂模式的好处就是外界不用管如何创造 ActivityStarter 对象,只要告诉 Factory 要获取 ActivityStarter 对象就能得到想要的 ActivityStarter 对象。关于工厂模式的相关介绍可以看另外的三篇文章:
Java设计模式:简单工厂模式
Java设计模式:工厂方法模式
Java设计模式:抽象工厂模式
切回流程主线,在 6 中 通过 obtainStarter 方法获取到了 ActivityStarter 对象:
return getActivityStartController().obtainStarter(intent, "startActivityAsUser")
.setCaller(caller)
.setCallingPackage(callingPackage)
.setResolvedType(resolvedType)
.setResultTo(resultTo)
.setResultWho(resultWho)
.setRequestCode(requestCode)
.setStartFlags(startFlags)
.setProfilerInfo(profilerInfo)
.setActivityOptions(bOptions)
.setMayWait(userId)
.execute(); public ActivityStarter obtain() {
ActivityStarter starter = mStarterPool.acquire();
if (starter == null) {
starter = new ActivityStarter(mController, mService, mSupervisor, mInterceptor);
}
return starter;
}在 obtain 方法中创建了 ActivityStarter 对象,随后通过多个 set 方法设置相关参数,最后调用 execute 方法:
/**
* Starts an activity based on the request parameters provided earlier.
* @return The starter result.
*/
int execute() {
try {
// TODO(b/64750076): Look into passing request directly to these methods to allow
// for transactional diffs and preprocessing.
if (mRequest.mayWait) {
return startActivityMayWait(mRequest.caller, mRequest.callingUid,
mRequest.callingPackage, mRequest.realCallingPid, mRequest.realCallingUid,
mRequest.intent, mRequest.resolvedType,
mRequest.voiceSession, mRequest.voiceInteractor, mRequest.resultTo,
mRequest.resultWho, mRequest.requestCode, mRequest.startFlags,
mRequest.profilerInfo, mRequest.waitResult, mRequest.globalConfig,
mRequest.activityOptions, mRequest.ignoreTargetSecurity, mRequest.userId,
mRequest.inTask, mRequest.reason,
mRequest.allowPendingRemoteAnimationRegistryLookup,
mRequest.originatingPendingIntent, mRequest.allowBackgroundActivityStart);
} else {
return startActivity(mRequest.caller, mRequest.intent, mRequest.ephemeralIntent,
mRequest.resolvedType, mRequest.activityInfo, mRequest.resolveInfo,
mRequest.voiceSession, mRequest.voiceInteractor, mRequest.resultTo,
mRequest.resultWho, mRequest.requestCode, mRequest.callingPid,
mRequest.callingUid, mRequest.callingPackage, mRequest.realCallingPid,
mRequest.realCallingUid, mRequest.startFlags, mRequest.activityOptions,
mRequest.ignoreTargetSecurity, mRequest.componentSpecified,
mRequest.outActivity, mRequest.inTask, mRequest.reason,
mRequest.allowPendingRemoteAnimationRegistryLookup,
mRequest.originatingPendingIntent, mRequest.allowBackgroundActivityStart);
}
} finally {
onExecutionComplete();
}
}这里该走的是哪条呢?由于上面执行多个set 方法中有 setMayWait 方法中 mayWait 设置了 true,所以执行的 if 中的语句:
ActivityStarter setMayWait(int userId) {
mRequest.mayWait = true;
mRequest.userId = userId;
return this;
}接着看看 startActivityMayWait 方法:
private int startActivityMayWait(IApplicationThread caller, int callingUid,
String callingPackage, int requestRealCallingPid, int requestRealCallingUid,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession,
IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, WaitResult outResult,
Configuration globalConfig, SafeActivityOptions options, boolean ignoreTargetSecurity,
int userId, TaskRecord inTask, String reason,
boolean allowPendingRemoteAnimationRegistryLookup,
PendingIntentRecord originatingPendingIntent, boolean allowBackgroundActivityStart) {
...
...
final ActivityRecord[] outRecord = new ActivityRecord[1];
int res = startActivity(caller, intent, ephemeralIntent, resolvedType, aInfo, rInfo,
voiceSession, voiceInteractor, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, callingPid,
callingUid, callingPackage, realCallingPid, realCallingUid, startFlags, options,
ignoreTargetSecurity, componentSpecified, outRecord, inTask, reason,
allowPendingRemoteAnimationRegistryLookup, originatingPendingIntent,
allowBackgroundActivityStart);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
...
...
return res;
}
}这里又调用了 startActivity 方法:
private int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, Intent intent, Intent ephemeralIntent,
String resolvedType, ActivityInfo aInfo, ResolveInfo rInfo,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int callingPid, int callingUid,
String callingPackage, int realCallingPid, int realCallingUid, int startFlags,
SafeActivityOptions options, boolean ignoreTargetSecurity, boolean componentSpecified,
ActivityRecord[] outActivity, TaskRecord inTask, String reason,
boolean allowPendingRemoteAnimationRegistryLookup,
PendingIntentRecord originatingPendingIntent, boolean allowBackgroundActivityStart) {
...
mLastStartActivityResult = startActivity(caller, intent, ephemeralIntent, resolvedType,
aInfo, rInfo, voiceSession, voiceInteractor, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode,
callingPid, callingUid, callingPackage, realCallingPid, realCallingUid, startFlags,
options, ignoreTargetSecurity, componentSpecified, mLastStartActivityRecord,
inTask, allowPendingRemoteAnimationRegistryLookup, originatingPendingIntent,
allowBackgroundActivityStart);
...
...
return getExternalResult(mLastStartActivityResult);
}再次调用不同参数的 startActivity 方法:
private int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, Intent intent, Intent ephemeralIntent,
String resolvedType, ActivityInfo aInfo, ResolveInfo rInfo,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int callingPid, int callingUid,
String callingPackage, int realCallingPid, int realCallingUid, int startFlags,
SafeActivityOptions options,
boolean ignoreTargetSecurity, boolean componentSpecified, ActivityRecord[] outActivity,
TaskRecord inTask, boolean allowPendingRemoteAnimationRegistryLookup,
PendingIntentRecord originatingPendingIntent, boolean allowBackgroundActivityStart) {
...
...
final int res = startActivity(r, sourceRecord, voiceSession, voiceInteractor, startFlags,
true /* doResume */, checkedOptions, inTask, outActivity, restrictedBgActivity);
mSupervisor.getActivityMetricsLogger().notifyActivityLaunched(res, outActivity[0]);
return res;
}再次调用 startActivity 方法:
private int startActivity(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int startFlags, boolean doResume, ActivityOptions options, TaskRecord inTask,
ActivityRecord[] outActivity, boolean restrictedBgActivity) {
int result = START_CANCELED;
final ActivityStack startedActivityStack;
try {
mService.mWindowManager.deferSurfaceLayout();
result = startActivityUnchecked(r, sourceRecord, voiceSession, voiceInteractor,
startFlags, doResume, options, inTask, outActivity, restrictedBgActivity);
} finally {
...
...
}
postStartActivityProcessing(r, result, startedActivityStack);
return result;
}这里的核心调用了 startActivityUnchecked 方法:
// Note: This method should only be called from {@link startActivity}.
private int startActivityUnchecked(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int startFlags, boolean doResume, ActivityOptions options, TaskRecord inTask,
ActivityRecord[] outActivity, boolean restrictedBgActivity) {
...
mTargetStack.startActivityLocked(mStartActivity, topFocused, newTask, mKeepCurTransition,
mOptions);
if (mDoResume) { // mDoResume 的值由上面参数传递过来,值为 true
final ActivityRecord topTaskActivity =
mStartActivity.getTaskRecord().topRunningActivityLocked();
if (!mTargetStack.isFocusable()
|| (topTaskActivity != null && topTaskActivity.mTaskOverlay
&& mStartActivity != topTaskActivity)) {
// If the activity is not focusable, we can't resume it, but still would like to
// make sure it becomes visible as it starts (this will also trigger entry
// animation). An example of this are PIP activities.
// Also, we don't want to resume activities in a task that currently has an overlay
// as the starting activity just needs to be in the visible paused state until the
// over is removed.
mTargetStack.ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(mStartActivity, 0, !PRESERVE_WINDOWS);
// Go ahead and tell window manager to execute app transition for this activity
// since the app transition will not be triggered through the resume channel.
mTargetStack.getDisplay().mDisplayContent.executeAppTransition();
} else {
// If the target stack was not previously focusable (previous top running activity
// on that stack was not visible) then any prior calls to move the stack to the
// will not update the focused stack. If starting the new activity now allows the
// task stack to be focusable, then ensure that we now update the focused stack
// accordingly.
if (mTargetStack.isFocusable()
&& !mRootActivityContainer.isTopDisplayFocusedStack(mTargetStack)) {
mTargetStack.moveToFront("startActivityUnchecked");
}
mRootActivityContainer.resumeFocusedStacksTopActivities(
mTargetStack, mStartActivity, mOptions);
}
} else if (mStartActivity != null) {
mSupervisor.mRecentTasks.add(mStartActivity.getTaskRecord());
}
mRootActivityContainer.updateUserStack(mStartActivity.mUserId, mTargetStack);
mSupervisor.handleNonResizableTaskIfNeeded(mStartActivity.getTaskRecord(),
preferredWindowingMode, mPreferredDisplayId, mTargetStack);
return START_SUCCESS;
}这里走的是 RootActivityContainer 的 resumeFocusedStacksTopActivities 方法。
9. RootActivityContainer
RootActivityContainer.java (framework\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\wm)
RootActivityContainer是10.0新引入的类,从类的注释可以看出这个类是暂时用来分担 ActivityStackSupervisor 的部分职责的。
/**
* Root node for activity containers.
* TODO: This class is mostly temporary to separate things out of ActivityStackSupervisor.java. The
* intention is to have this merged with RootWindowContainer.java as part of unifying the hierarchy.
*/
class RootActivityContainer extends ConfigurationContainer
implements DisplayManager.DisplayListener {
...
boolean resumeFocusedStacksTopActivities(
ActivityStack targetStack, ActivityRecord target, ActivityOptions targetOptions) {
if (!mStackSupervisor.readyToResume()) {
return false;
}
boolean result = false;
if (targetStack != null && (targetStack.isTopStackOnDisplay()
|| getTopDisplayFocusedStack() == targetStack)) {
result = targetStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(target, targetOptions);
}
...
return result;
}
...
}主要调用了 ActivityStack 的 resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked 方法。
10. ActivityStack
ActivityStack.java (framework\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\wm)
/**
* Ensure that the top activity in the stack is resumed.
*
* @param prev The previously resumed activity, for when in the process
* of pausing; can be null to call from elsewhere.
* @param options Activity options.
*
* @return Returns true if something is being resumed, or false if
* nothing happened.
*
* NOTE: It is not safe to call this method directly as it can cause an activity in a
* non-focused stack to be resumed.
* Use {@link RootActivityContainer#resumeFocusedStacksTopActivities} to resume the
* right activity for the current system state.
*/
@GuardedBy("mService")
boolean resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options) {
if (mInResumeTopActivity) {
// Don't even start recursing.
return false;
}
boolean result = false;
try {
// Protect against recursion.
mInResumeTopActivity = true;
result = resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(prev, options);
// When resuming the top activity, it may be necessary to pause the top activity (for
// example, returning to the lock screen. We suppress the normal pause logic in
// {@link #resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked}, since the top activity is resumed at the
// end. We call the {@link ActivityStackSupervisor#checkReadyForSleepLocked} again here
// to ensure any necessary pause logic occurs. In the case where the Activity will be
// shown regardless of the lock screen, the call to
// {@link ActivityStackSupervisor#checkReadyForSleepLocked} is skipped.
final ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivityLocked(true /* focusableOnly */);
if (next == null || !next.canTurnScreenOn()) {
checkReadyForSleep();
}
} finally {
mInResumeTopActivity = false;
}
return result;
}核心代码是调用了 resumeTopActivityInnerLocked 方法:
@GuardedBy("mService")
private boolean resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options) {
...
boolean pausing = getDisplay().pauseBackStacks(userLeaving, next, false);
if (mResumedActivity != null) { // 4
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Pausing " + mResumedActivity);
pausing |= startPausingLocked(userLeaving, false, next, false);
}
...
if (next.attachedToProcess()) {
...
mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, false); // 5-1
return true;
}
// From this point on, if something goes wrong there is no way
// to recover the activity.
try {
next.completeResumeLocked();
} catch (Exception e) {
// If any exception gets thrown, toss away this
// activity and try the next one.
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception thrown during resume of " + next, e);
requestFinishActivityLocked(next.appToken, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null,
"resume-exception", true);
return true;
}
} else {
// Whoops, need to restart this activity!
if (!next.hasBeenLaunched) {
next.hasBeenLaunched = true;
} else {
if (SHOW_APP_STARTING_PREVIEW) {
next.showStartingWindow(null /* prev */, false /* newTask */,
false /* taskSwich */);
}
if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH, "Restarting: " + next);
}
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES, "resumeTopActivityLocked: Restarting " + next);
mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, true); // 5-2
}
}注释 4:首先会去判断是否有 Activity 处于 Resume 状态,有的话会先调用 startPausingLocked 方法让 Activity 执行 Pausing 过程。接着才会调用 注释5-1 或者 5-2 中 ActivityStackSupervisor 中 的 startSpecificActivityLocked 方法。
这里先追 注释4 的 startPausingLocked 方法:
final boolean startPausingLocked(boolean userLeaving, boolean uiSleeping,
ActivityRecord resuming, boolean pauseImmediately) {
...
if (prev.attachedToProcess()) {
if (DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE, "Enqueueing pending pause: " + prev);
try {
EventLogTags.writeAmPauseActivity(prev.mUserId, System.identityHashCode(prev),
prev.shortComponentName, "userLeaving=" + userLeaving);
mService.getLifecycleManager().scheduleTransaction(prev.app.getThread(),
prev.appToken, PauseActivityItem.obtain(prev.finishing, userLeaving,
prev.configChangeFlags, pauseImmediately));
} catch (Exception e) {
// Ignore exception, if process died other code will cleanup.
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception thrown during pause", e);
mPausingActivity = null;
mLastPausedActivity = null;
mLastNoHistoryActivity = null;
}
} else {
mPausingActivity = null;
mLastPausedActivity = null;
mLastNoHistoryActivity = null;
}
...
}这里的核心是 mService.getLifecycleManager().scheduleTransaction,这里的 mService 是 ActivityTaskManagerService。而
getLifecycleManager 方法获取到的是 ClientLifecycleManager。
11. ClientLifecycleManager
ClientLifecycleManager.java (framework\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\wm)
在 ClientLifecycleManager 的中 scheduleTransaction 重载了四个方法:
void scheduleTransaction(ClientTransaction transaction) throws RemoteException {
final IApplicationThread client = transaction.getClient();
transaction.schedule();
if (!(client instanceof Binder)) {
// If client is not an instance of Binder - it's a remote call and at this point it is
// safe to recycle the object. All objects used for local calls will be recycled after
// the transaction is executed on client in ActivityThread.
transaction.recycle();
}
}
/**
* Schedule a single lifecycle request or callback to client activity.
* @param client Target client.
* @param activityToken Target activity token.
* @param stateRequest A request to move target activity to a desired lifecycle state.
* @throws RemoteException
*
* @see ClientTransactionItem
*/
void scheduleTransaction(@NonNull IApplicationThread client, @NonNull IBinder activityToken,
@NonNull ActivityLifecycleItem stateRequest) throws RemoteException {
final ClientTransaction clientTransaction = transactionWithState(client, activityToken,
stateRequest);
scheduleTransaction(clientTransaction);
}
/**
* Schedule a single callback delivery to client activity.
* @param client Target client.
* @param activityToken Target activity token.
* @param callback A request to deliver a callback.
* @throws RemoteException
*
* @see ClientTransactionItem
*/
void scheduleTransaction(@NonNull IApplicationThread client, @NonNull IBinder activityToken,
@NonNull ClientTransactionItem callback) throws RemoteException {
final ClientTransaction clientTransaction = transactionWithCallback(client, activityToken,
callback);
scheduleTransaction(clientTransaction);
}
/**
* Schedule a single callback delivery to client application.
* @param client Target client.
* @param callback A request to deliver a callback.
* @throws RemoteException
*
* @see ClientTransactionItem
*/
void scheduleTransaction(@NonNull IApplicationThread client,
@NonNull ClientTransactionItem callback) throws RemoteException {
final ClientTransaction clientTransaction = transactionWithCallback(client,
null /* activityToken */, callback);
scheduleTransaction(clientTransaction);
}最后都调用到了:
void scheduleTransaction(ClientTransaction transaction) throws RemoteException {
final IApplicationThread client = transaction.getClient();
transaction.schedule();
if (!(client instanceof Binder)) {
// If client is not an instance of Binder - it's a remote call and at this point it is
// safe to recycle the object. All objects used for local calls will be recycled after
// the transaction is executed on client in ActivityThread.
transaction.recycle();
}
}通过 ClientTransaction 的 getClient 方法获取到 client 对象,client 是 IApplicationThread 类型,在 ClientTransaction 的静态方法 obtain 中进行初始化:
public static ClientTransaction obtain(IApplicationThread client, IBinder activityToken) {
ClientTransaction instance = ObjectPool.obtain(ClientTransaction.class);
if (instance == null) {
instance = new ClientTransaction();
}
instance.mClient = client;
instance.mActivityToken = activityToken;
return instance;
}12. ActivityThread
ActivityThread.java (framework\base\core\java\android\app)
在 ActivityThread 中的内部类 ApplicationThread 继承了 IApplicationThread.Stub,这里又是一个 AIDL,这里是 AIDL 的 Server 端:
public final class ActivityThread extends ClientTransactionHandler {
...
private class ApplicationThread extends IApplicationThread.Stub {
...
@Override
public void scheduleTransaction(ClientTransaction transaction) throws RemoteException {
ActivityThread.this.scheduleTransaction(transaction);
}
...
}
...
}这里 ActivityThread.this.scheduleTransaction(transaction),但是在 ActivityThread 中并找不到 方法 scheduleTransaction,在父类 ClientTransactionHandler 中可以找到该方法。
13. ClientTransactionHandler
ClientTransactionHandler.java (framework\base\core\java\android\app)
public abstract class ClientTransactionHandler {
// Schedule phase related logic and handlers.
/** Prepare and schedule transaction for execution. */
void scheduleTransaction(ClientTransaction transaction) {
transaction.preExecute(this);
sendMessage(ActivityThread.H.EXECUTE_TRANSACTION, transaction);
}
...
}ClientTransactionHandler 为抽象类,这里调用了 sendMessage 方法,这里 sendMessage 为抽象方法:
abstract void sendMessage(int what, Object obj);回到子类 ActivityThread 中,sendMessage 方法:
void sendMessage(int what, Object obj) {
sendMessage(what, obj, 0, 0, false);
}
private void sendMessage(int what, Object obj, int arg1) {
sendMessage(what, obj, arg1, 0, false);
}
private void sendMessage(int what, Object obj, int arg1, int arg2) {
sendMessage(what, obj, arg1, arg2, false);
}
private void sendMessage(int what, Object obj, int arg1, int arg2, boolean async) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) {
Slog.v(TAG,
"SCHEDULE " + what + " " + mH.codeToString(what) + ": " + arg1 + " / " + obj);
}
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = what;
msg.obj = obj;
msg.arg1 = arg1;
msg.arg2 = arg2;
if (async) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
mH.sendMessage(msg);
}
private void sendMessage(int what, Object obj, int arg1, int arg2, int seq) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(
TAG, "SCHEDULE " + mH.codeToString(what) + " arg1=" + arg1 + " arg2=" + arg2 +
"seq= " + seq);
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = what;
SomeArgs args = SomeArgs.obtain();
args.arg1 = obj;
args.argi1 = arg1;
args.argi2 = arg2;
args.argi3 = seq;
msg.obj = args;
mH.sendMessage(msg);
}如果之前有去研究:主线程 Looper.loop() 死循环为何不会ANR 就会知道有个 H 类,H类就是负责生命周期的驱动,由于上面 传递了 ActivityThread.H.EXECUTE_TRANSACTION:
class H extends Handler {
...
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
...
case EXECUTE_TRANSACTION:
final ClientTransaction transaction = (ClientTransaction) msg.obj;
mTransactionExecutor.execute(transaction);
if (isSystem()) {
// Client transactions inside system process are recycled on the client side
// instead of ClientLifecycleManager to avoid being cleared before this
// message is handled.
transaction.recycle();
}
// TODO(lifecycler): Recycle locally scheduled transactions.
break;
...
}
}
}这里调用了 TransactionExecutor 的方法 execute(transaction)。
14. TransactionExecutor
TransactionExecutor.java (framework\base\core\java\android\app\servertransaction)
execute 方法如下:
public void execute(ClientTransaction transaction) {
...
executeLifecycleState(transaction);
...
}这里的核心就是方法 executeLifecycleState:
private void executeLifecycleState(ClientTransaction transaction) {
final ActivityLifecycleItem lifecycleItem = transaction.getLifecycleStateRequest();
...
// Execute the final transition with proper parameters.
lifecycleItem.execute(mTransactionHandler, token, mPendingActions);
lifecycleItem.postExecute(mTransactionHandler, token, mPendingActions);
}这里返回一个 ActivityLifecycleItem 类型的对象,而 ActivityLifecycleItem 是一个抽象类,必然要有实现类,通过全局搜索存在三个实现类:PauseActivityItem,ResumeActivityItem,StopActivityItem,由于这里是要让 Activity 进入 Pause 状态,所以这里是 PauseActivityItem。
15. PauseActivityItem
PauseActivityItem.java (framework\base\core\java\android\app\servertransaction)
public class PauseActivityItem extends ActivityLifecycleItem {
...
@Override
public void execute(ClientTransactionHandler client, IBinder token,
PendingTransactionActions pendingActions) {
Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityPause");
client.handlePauseActivity(token, mFinished, mUserLeaving, mConfigChanges, pendingActions,
"PAUSE_ACTIVITY_ITEM");
Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
}
...
}在 execute 中调用了 ActivityThread 中的 handlePauseActivity 方法:
@Override
public void handlePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished, boolean userLeaving,
int configChanges, PendingTransactionActions pendingActions, String reason) {
ActivityClientRecord r = mActivities.get(token);
if (r != null) {
if (userLeaving) {
performUserLeavingActivity(r);
}
r.activity.mConfigChangeFlags |= configChanges;
performPauseActivity(r, finished, reason, pendingActions);
// Make sure any pending writes are now committed.
if (r.isPreHoneycomb()) {
QueuedWork.waitToFinish();
}
mSomeActivitiesChanged = true;
}
}接着看 performPauseActivity 方法:
/**
* Pause the activity.
* @return Saved instance state for pre-Honeycomb apps if it was saved, {@code null} otherwise.
*/
private Bundle performPauseActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, boolean finished, String reason,
PendingTransactionActions pendingActions) {
if (r.paused) {
if (r.activity.mFinished) {
// If we are finishing, we won't call onResume() in certain cases.
// So here we likewise don't want to call onPause() if the activity
// isn't resumed.
return null;
}
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
"Performing pause of activity that is not resumed: "
+ r.intent.getComponent().toShortString());
Slog.e(TAG, e.getMessage(), e);
}
if (finished) {
r.activity.mFinished = true;
}
// Pre-Honeycomb apps always save their state before pausing
final boolean shouldSaveState = !r.activity.mFinished && r.isPreHoneycomb();
if (shouldSaveState) {
callActivityOnSaveInstanceState(r);
}
performPauseActivityIfNeeded(r, reason);
// Notify any outstanding on paused listeners
ArrayList listeners;
synchronized (mOnPauseListeners) {
listeners = mOnPauseListeners.remove(r.activity);
}
int size = (listeners != null ? listeners.size() : 0);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
listeners.get(i).onPaused(r.activity);
}
final Bundle oldState = pendingActions != null ? pendingActions.getOldState() : null;
if (oldState != null) {
// We need to keep around the original state, in case we need to be created again.
// But we only do this for pre-Honeycomb apps, which always save their state when
// pausing, so we can not have them save their state when restarting from a paused
// state. For HC and later, we want to (and can) let the state be saved as the
// normal part of stopping the activity.
if (r.isPreHoneycomb()) {
r.state = oldState;
}
}
return shouldSaveState ? r.state : null;
} 调用 performPauseActivityIfNeeded 方法:
private void performPauseActivityIfNeeded(ActivityClientRecord r, String reason) {
if (r.paused) {
// You are already paused silly...
return;
}
// Always reporting top resumed position loss when pausing an activity. If necessary, it
// will be restored in performResumeActivity().
reportTopResumedActivityChanged(r, false /* onTop */, "pausing");
try {
r.activity.mCalled = false;
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPause(r.activity);
if (!r.activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException("Activity " + safeToComponentShortString(r.intent)
+ " did not call through to super.onPause()");
}
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(r.activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to pause activity "
+ safeToComponentShortString(r.intent) + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
r.setState(ON_PAUSE);
}这里有回到了 Instrumentation 类中的 callActivityOnPause 方法:
public void callActivityOnPause(Activity activity) {
activity.performPause();
}接着回到 Activity 中的方法 performPause:
final void performPause() {
dispatchActivityPrePaused();
mDoReportFullyDrawn = false;
mFragments.dispatchPause();
mCalled = false;
onPause();
writeEventLog(LOG_AM_ON_PAUSE_CALLED, "performPause");
mResumed = false;
if (!mCalled && getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion
>= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.GINGERBREAD) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + mComponent.toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onPause()");
}
dispatchActivityPostPaused();
}在这里就看到了我们熟悉的 onPause 方法。
16. 小结
从第 10 开始存在着两条线,从 10 到 15 是其中将 Activity 切换为 onPause 状态的逻辑,相应的流程图如下所示:
17. ActivityStackSupervisor
ActivityStackSupervisor.java (framework\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\wm)
在第10 中的注释5-1 和 5-2 中 调用了ActivityStackSupervisor 中 的 startSpecificActivityLocked 方法:
void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {
// Is this activity's application already running?
final WindowProcessController wpc =
mService.getProcessController(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo.uid);
boolean knownToBeDead = false;
if (wpc != null && wpc.hasThread()) { // 6
try {
realStartActivityLocked(r, wpc, andResume, checkConfig); // 7
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting activity "
+ r.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
}
// If a dead object exception was thrown -- fall through to
// restart the application.
knownToBeDead = true;
}
// Suppress transition until the new activity becomes ready, otherwise the keyguard can
// appear for a short amount of time before the new process with the new activity had the
// ability to set its showWhenLocked flags.
if (getKeyguardController().isKeyguardLocked()) {
r.notifyUnknownVisibilityLaunched();
}
try {
if (Trace.isTagEnabled(TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER)) {
Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "dispatchingStartProcess:"
+ r.processName);
}
// Post message to start process to avoid possible deadlock of calling into AMS with the
// ATMS lock held.
final Message msg = PooledLambda.obtainMessage( // 8
ActivityManagerInternal::startProcess, mService.mAmInternal, r.processName,
r.info.applicationInfo, knownToBeDead, "activity", r.intent.getComponent());
mService.mH.sendMessage(msg);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
}
}注释 6 中:判断 App 进程是否存在,并且已经启动,如果存在而且已经启动,则调用方法 realStartActivityLocked。
注释 8 :如果 App 进程不存在,从注释可以看出通过 sendMessage 启动新的进程。因为这里追的是从 Launcher 启动 App,所以进程必然不存在,这里追如果创建进程。
这里的 mService 是 ActivityTaskManagerService,它的内部和 ActivityThread 一样也存在一个 H 类,只是它比 ActivityThread 简单很多:
final class H extends Handler {
static final int REPORT_TIME_TRACKER_MSG = 1;
static final int FIRST_ACTIVITY_STACK_MSG = 100;
static final int FIRST_SUPERVISOR_STACK_MSG = 200;
H(Looper looper) {
super(looper);
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case REPORT_TIME_TRACKER_MSG: {
AppTimeTracker tracker = (AppTimeTracker) msg.obj;
tracker.deliverResult(mContext);
} break;
}
}
}这里看起来不像是启动进程的地方,这时候回头看这段代码:
final Message msg = PooledLambda.obtainMessage( // 8
ActivityManagerInternal::startProcess, mService.mAmInternal, r.processName,
r.info.applicationInfo, knownToBeDead, "activity", r.intent.getComponent());猜测启动进程在 ActivityManagerInternal::startProcess,真的有 ActivityManagerInternal 类,而且在它的内部也有方法 startProcess,只不过此类为抽象类,方法也为抽象方法。在庞大的 ActivityManagerService 类中存在一个内部类 LocalService,它的父类就是 ActivityManagerInternal。
18. ActivityManagerService
ActivityManagerService.java (framework\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\am)
ActivityManagerService 类之前有 2w多行的代码,在 Android 10 中仍然还是 19000多行,说它庞大一点也不冤枉。看看它里面的 LocalService 的 startProcess 方法:
@Override
public void startProcess(String processName, ApplicationInfo info,
boolean knownToBeDead, String hostingType, ComponentName hostingName) {
try {
if (Trace.isTagEnabled(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER)) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "startProcess:"
+ processName);
}
synchronized (ActivityManagerService.this) {
startProcessLocked(processName, info, knownToBeDead, 0 /* intentFlags */,
new HostingRecord(hostingType, hostingName),
false /* allowWhileBooting */, false /* isolated */,
true /* keepIfLarge */);
}
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
}
}调用了方法 startProcessLocked 方法:
@GuardedBy("this")
final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName,
ApplicationInfo info, boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags,
HostingRecord hostingRecord, boolean allowWhileBooting,
boolean isolated, boolean keepIfLarge) {
return mProcessList.startProcessLocked(processName, info, knownToBeDead, intentFlags,
hostingRecord, allowWhileBooting, isolated, 0 /* isolatedUid */, keepIfLarge,
null /* ABI override */, null /* entryPoint */, null /* entryPointArgs */,
null /* crashHandler */);
}调用了 ProcessList 的 startProcessLocked 方法。
19. ProcessList
ProcessList.java (framework\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\am)
startProcessLocked 方法中调用了 startProcess 方法:
private Process.ProcessStartResult startProcess(HostingRecord hostingRecord, String entryPoint,
ProcessRecord app, int uid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal,
String seInfo, String requiredAbi, String instructionSet, String invokeWith,
long startTime) {
try {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "Start proc: " +
app.processName);
checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: asking zygote to start proc");
final Process.ProcessStartResult startResult;
if (hostingRecord.usesWebviewZygote()) {
startResult = startWebView(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, null, app.info.packageName,
new String[] {PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.startSeq});
} else if (hostingRecord.usesAppZygote()) {
final AppZygote appZygote = createAppZygoteForProcessIfNeeded(app);
startResult = appZygote.getProcess().start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, null, app.info.packageName,
/*useUsapPool=*/ false,
new String[] {PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.startSeq});
} else {
startResult = Process.start(entryPoint, // 9
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, invokeWith, app.info.packageName,
new String[] {PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.startSeq});
}
checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: returned from zygote!");
return startResult;
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
}
}最后调用了 注释 9 中的 Process 的 start 方法。
20. Process
Process.java (framework\base\core\java\android\os)
start 方法:
public static ProcessStartResult start(@NonNull final String processClass,
@Nullable final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, @Nullable int[] gids,
int runtimeFlags,
int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
@Nullable String seInfo,
@NonNull String abi,
@Nullable String instructionSet,
@Nullable String appDataDir,
@Nullable String invokeWith,
@Nullable String packageName,
@Nullable String[] zygoteArgs) {
return ZYGOTE_PROCESS.start(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
runtimeFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith, packageName,
/*useUsapPool=*/ true, zygoteArgs);
}调用了 ZygoteProcess 的 start 方法。
21. ZygoteProcess
ZygoteProcess.java (framework\base\core\java\android\os)
public final Process.ProcessStartResult start(@NonNull final String processClass,
final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, @Nullable int[] gids,
int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
@Nullable String seInfo,
@NonNull String abi,
@Nullable String instructionSet,
@Nullable String appDataDir,
@Nullable String invokeWith,
@Nullable String packageName,
boolean useUsapPool,
@Nullable String[] zygoteArgs) {
// TODO (chriswailes): Is there a better place to check this value?
if (fetchUsapPoolEnabledPropWithMinInterval()) {
informZygotesOfUsapPoolStatus();
}
try {
return startViaZygote(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
runtimeFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith, /*startChildZygote=*/ false,
packageName, useUsapPool, zygoteArgs);
} catch (ZygoteStartFailedEx ex) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG,
"Starting VM process through Zygote failed");
throw new RuntimeException(
"Starting VM process through Zygote failed", ex);
}
}继续调用 startViaZygote 方法:
private Process.ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(@NonNull final String processClass,
@Nullable final String niceName,
final int uid, final int gid,
@Nullable final int[] gids,
int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
@Nullable String seInfo,
@NonNull String abi,
@Nullable String instructionSet,
@Nullable String appDataDir,
@Nullable String invokeWith,
boolean startChildZygote,
@Nullable String packageName,
boolean useUsapPool,
@Nullable String[] extraArgs)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
...
synchronized(mLock) {
// The USAP pool can not be used if the application will not use the systems graphics
// driver. If that driver is requested use the Zygote application start path.
return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi),
useUsapPool,
argsForZygote);
}
}两个核心方法:openZygoteSocketIfNeeded 和 zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult。
openZygoteSocketIfNeeded :
@GuardedBy("mLock")
private ZygoteState openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(String abi) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
try {
attemptConnectionToPrimaryZygote();
if (primaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {
return primaryZygoteState;
}
if (mZygoteSecondarySocketAddress != null) {
// The primary zygote didn't match. Try the secondary.
attemptConnectionToSecondaryZygote();
if (secondaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {
return secondaryZygoteState;
}
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Error connecting to zygote", ioe);
}
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Unsupported zygote ABI: " + abi);
}通过 attemptConnectionToPrimaryZygote 方法向主 Zygote 发起连接请求。
zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult:
private Process.ProcessStartResult zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(
ZygoteState zygoteState, boolean useUsapPool, @NonNull ArrayList args)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
...
return attemptZygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(zygoteState, msgStr);
} 调用了方法 attemptZygoteSendArgsAndGetResult:
private Process.ProcessStartResult attemptZygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(
ZygoteState zygoteState, String msgStr) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
try {
final BufferedWriter zygoteWriter = zygoteState.mZygoteOutputWriter;
final DataInputStream zygoteInputStream = zygoteState.mZygoteInputStream;
zygoteWriter.write(msgStr);
zygoteWriter.flush();
// Always read the entire result from the input stream to avoid leaving
// bytes in the stream for future process starts to accidentally stumble
// upon.
Process.ProcessStartResult result = new Process.ProcessStartResult();
result.pid = zygoteInputStream.readInt();
result.usingWrapper = zygoteInputStream.readBoolean();
if (result.pid < 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("fork() failed");
}
...
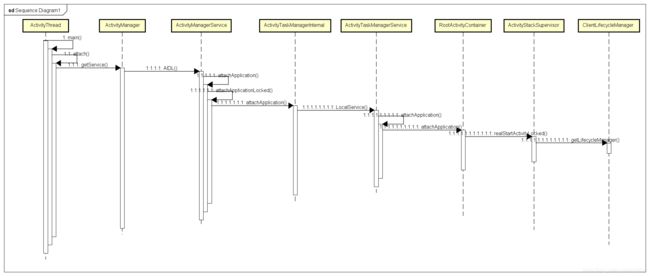
}这个方法中通过 socket 向 Zygote 进程发送参数列表,然后进入“阻塞等待”状态,直到 socket 服务端发送回来新创建的进程 pid。关于 Zygote 的创建请查看一位大神写的文章:【 Android 10 进程线程 】系列 -- 关于 "进程" -> "创建" 的原理。Zygote 进程源码的最后调用到了 ActivityThread.main() 方法。
附上以上流程的流程图:
22. 再次梳理 ActivityThread
ActivityThread.java (framework\base\core\java\android\app)
public final class ActivityThread extends ClientTransactionHandler {
...
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ActivityThreadMain");
// Install selective syscall interception
AndroidOs.install();
// CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We
// disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via
// StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs.
CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);
Environment.initForCurrentUser();
// Make sure TrustedCertificateStore looks in the right place for CA certificates
final File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId());
TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir);
Process.setArgV0("");
Looper.prepareMainLooper(); // 10
// Find the value for {@link #PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT} if provided on the command line.
// It will be in the format "seq=114"
long startSeq = 0;
if (args != null) {
for (int i = args.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if (args[i] != null && args[i].startsWith(PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT)) {
startSeq = Long.parseLong(
args[i].substring(PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT.length()));
}
}
}
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread(); // 11
thread.attach(false, startSeq);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
// End of event ActivityThreadMain.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
...
} 看到这个 main 方法,第一眼就是觉得这不就是 Java 的 main 方法吗?没错,这就是 Java 中的 main 方法。
注释 10:这里创建主线程的 Looper,主线程的 Handler 不需要创建 Looper。相关联的文章可以看下之前写过的:
Android Handler 消息机制,主线程 Looper.loop() 死循环为何不会ANR。
注释 11:初始化 ActivityThread,并且 attach 到系统进程。
attach 方法:
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private void attach(boolean system, long startSeq) {
sCurrentActivityThread = this;
mSystemThread = system;
if (!system) {
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("",
UserHandle.myUserId());
RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder());
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService(); // 12
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread, startSeq); // 13
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
...
} else {
...
}
...
ViewRootImpl.addConfigCallback(configChangedCallback);
} 注释 12:这里的 IActivityManager 类型对象是 ActivityManagerService;
注释 13:通过 ActivityManagerService 的 attachApplication 方法绑定一个 Application,这里的 mAppThread 是 ApplicationThread 对象。
23. 再次梳理 ActivityManagerService
ActivityManagerService.java (framework\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\am)
public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread, long startSeq) {
synchronized (this) {
int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid, callingUid, startSeq);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}这里调用了方法 attachApplicationLocked:
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid, int callingUid, long startSeq) {
...
boolean badApp = false;
boolean didSomething = false;
// See if the top visible activity is waiting to run in this process...
if (normalMode) { // 14
try {
didSomething = mAtmInternal.attachApplication(app.getWindowProcessController());
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown launching activities in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
...
// Find any services that should be running in this process...
if (!badApp) { // 15
try {
didSomething |= mServices.attachApplicationLocked(app, processName);
checkTime(startTime, "attachApplicationLocked: after mServices.attachApplicationLocked");
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown starting services in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
// Check if a next-broadcast receiver is in this process...
if (!badApp && isPendingBroadcastProcessLocked(pid)) { // 16
try {
didSomething |= sendPendingBroadcastsLocked(app);
checkTime(startTime, "attachApplicationLocked: after sendPendingBroadcastsLocked");
} catch (Exception e) {
// If the app died trying to launch the receiver we declare it 'bad'
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown dispatching broadcasts in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
...
}注释 14、15、16 是对于Activity、Service、BroadcastReceiver的处理逻辑。这里追的是 Activity 的启动流程,所以这里只追注释 14 。
注释 14 :调用了 ActivityTaskManagerInternal 的 attachApplication 方法。
ActivityTaskManagerInternal 在 ActivityManagerService 的构造方法中进行初始化:
mAtmInternal = LocalServices.getService(ActivityTaskManagerInternal.class);24. ActivityTaskManagerInternal
ActivityTaskManagerInternal.java (framework\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\wm)
ActivityTaskManagerInternal 是一个抽象类,attachApplication 也是一个抽象方法:
public abstract class ActivityTaskManagerInternal {
...
/** Called by AM when an application process attaches. */
public abstract boolean attachApplication(WindowProcessController wpc) throws RemoteException;
...
}而 ActivityTaskManagerInternal 的实现类是 ActivityTaskManagerService 中的内部类 LocalService 继承了此抽象方法:
final class LocalService extends ActivityTaskManagerInternal {
...
@HotPath(caller = HotPath.PROCESS_CHANGE)
@Override
public boolean attachApplication(WindowProcessController wpc) throws RemoteException {
synchronized (mGlobalLockWithoutBoost) {
return mRootActivityContainer.attachApplication(wpc);
}
}
...
}这里调用了 RootActivityContainer 的 attachApplication 方法。
25. 再次回到 RootActivityContainer
RootActivityContainer.java (framework\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\wm)
attachApplication 方法:
boolean attachApplication(WindowProcessController app) throws RemoteException {
...
if (stack != null) {
stack.getAllRunningVisibleActivitiesLocked(mTmpActivityList);
final ActivityRecord top = stack.topRunningActivityLocked();
final int size = mTmpActivityList.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
final ActivityRecord activity = mTmpActivityList.get(i);
if (activity.app == null && app.mUid == activity.info.applicationInfo.uid
&& processName.equals(activity.processName)) {
try {
if (mStackSupervisor.realStartActivityLocked(activity, app,
top == activity /* andResume */, true /* checkConfig */)) {
didSomething = true;
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception in new application when starting activity "
+ top.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
throw e;
}
}
}
}
}
return didSomething;
}核心代码是调用 ActivityStackSupervisor 的 realStartActivityLocked 方法。
26. 再次回到 ActivityStackSupervisor
ActivityStackSupervisor.java (framework\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\wm)
realStartActivityLocked 方法:
boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, WindowProcessController proc,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) throws RemoteException {
...
// Schedule transaction.
mService.getLifecycleManager().scheduleTransaction(clientTransaction);
...
}mService.getLifecycleManager().scheduleTransaction,这里的 mService 是 ActivityTaskManagerService。而
getLifecycleManager 方法获取到的是 ClientLifecycleManager。又再次回到了 ClientLifecycleManager 的 scheduleTransaction 方法了。接下来的流程在第11 已经分析过了,最终都会走到 Activity 的生命周期。
附上第 22 到 26 的流程图:
27. 总结
a. 当在桌面点击 App 图标后,会调用 startActivity 转而调用 startActivityForResult,接着调用 Instrumentation 的 execStartActivity 方法。
b. 接着通过 AIDL 调用到 ActivityTaskManagerService ,接着分两步:
第一步:调用 ClientLifecycleManager 去控制当前 Activity 的生命周期切换为 onPause 状态,而切换生命周期在 ActivityThread 的类中去完成。
第二步:调用 ActivityManagerService 通过 socket 去通知系统启动时候的 Zygote 进程 fork 一个新的 App 进程;
c. 当进程创建后,又会调用到 ActivityThread 的 main 方法,通过 AIDL 调用到 ActivityManagerService。
d. ActivityManagerService 经过一系列的调用,通过 ClientLifecycleManager 来执行新 Activity 的生命周期,最后生命周期的执行在 ActivityThread 中的 H 类中触发。